Skeletal system biol 305
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
How can we classify bones based on their shape?
Long, short, flat, and irregular
How can we classify bones based on location?
Axial and Appendiular
What do axial bones form and whats some examples
Form the central axis of the body. Skull, sternum, ribs, vertebral column
The main job of appendicular bones
Movement
Why are most appendicular bones long bones and what can we say about their function due to their shape
They are long bones, such as arm and leg bones, meaning they are responsible and assist with mobility, movement, and flexibility.
Cranial bones
Flat bones that enclose and protect the brain
Why are all skull bones flat bones?
Because their job is to protect the brain and support the structures.
What are the connective tissues that make up the skeletal system?
Bones, ligaments, and cartilage
Bones
The hardest elements of the skeleton. Give the body shape and allow us to move, sit, and stand.
Ligaments
Dense fibrous connective tissues that attach bones to other bones.
Cartilage
Specialized connective tissue, fibers of collagen and elastic in a gel-like ground substance. Reduces friction in joints and are categorized into 3 parts
Why do bones have a hard, rigid appearance?
Because of the nonliving extracellular crystals of calcium minerals.
Are bones living or nonliving tissues? explain.
Bones are living tissue containing several types of cells involved in bone formation and remodeling. Despite their hard appearance from mineral crystals
What are the 5 important functions of bones?
Support, protection, movement, blood cell formation, and mineral storage
How do bones contribute to movement?
Bones serve as attachment points for muscles and provide rigid levers that enable movement when muscles contract.
What is a compact bone and where is it located in long bones?
A compact bone forms the shaft (diaphysis) and ends (epiphyses) of long bones and contain marrow space
Diaphysis
The shaft (long middle portion) of a long bone, formed by the compact bone.
Epiphyses
The ends of long bones, formed by compact bones on the outside
What is yellow bone marrow, and where is it found?
Mostly fat and is found in the marrow space within compact bones.
What is spongy bone and where is it located?
Spongy bone consists of trabeculae that forms a lattice-like support in the ends (epiphyses) of long bones.
Trabecular
The lattice-like structures that make up spongy bone, proving support while keeping the bone lightweight.
What is red bone marrow and what does it produce?
Found in the spaces of spongy bone and contains stem cells that product red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets
The difference between red and yellow bone marrow
red bone marrow produces blood cells and platelets, while yellow bone marrow is mostly fat
periosteum
The connective tissue covering of bone
What are osteoblasts and what is their function?
Osteoblasts are bone-forming cells that generate new bone during growth and repair
Osteons (Harvesian systems)
The cellular arrangement found in compact bone, consisting of extracellular deposits of calcium phosphate enclosing living cells (osteocytes) arranged in rings.
Osetocytes
Living bone cells that are trapped in spaces called lacunae within the bone matrix. They are arranged in rings called osteons
What are lacunae
Small spaces in bone where osteocytes are trapped
Canaliculi
Thin canals that connect osteocytes to each other, allowing for communication and nutrient exchange,
What is found in the central canal of an osteon?
Blood vessels
What is the primary function of ligaments
To attach bones to bones
What type of tissue are ligaments made of?
Dense fibrous connective tissue
How do ligaments contribute to joint function?
By providing strength in joins yet enable movement.
What is the general function of cartilage?
providing support under pressure
What is fibrocartilage and where is it found?
A type of cartilage found in intervertebral disks between vertabrae and in menisci in knee joints. It provides strong support under compression
What is hyaline cartilage and what is it’s main 2 functions?
It forms embryonic structure, which later forms bone and covers and protects ends of long bones in joints, providing protection and reducing friction
What is elastic cartilage and where is it found?
A flexible cartilage found in the outer ear, nose and epiglottis.
Where would you find hyaline cartilage in an adult?
In adults, hyaline cartilage covers and protects the ends of long bones in joints
What forms the initial bone models in early fetal development?
Cartilage models form the initial bone structre
Chondroblasts
A cartilage forming cell that creates the cartilage models during early fetal development
What happens to cartilage during later fetal development?
During later fetal development, osteoblasts replace cartilage with bone
Osteoid
A mixture of proteins, including collagen, that is secreted by osteoblasts and forms the structural framework of bone
What 2 substances do osteoblasts secrete during bone formation?
Osteoid (protein mixture including collaged) and enzymes to crystallize calcium phosphate
What happens to osteoblasts as they mature?
They become osteocytes trapped in lacunae that maintain the bone matrix
Where does bone lengthening occur in long bones?
At the growth plate (epiphyseal plate)
Epiphyseal plate
The region where long bones continue to lengthen during childhood and adolescence
What do chondroblasts do at the growth plate?
Produce cartilage on the outer surface of the growth plate
How do long bones lengthen?
Chondroblasts produce cartilage on the outer surface of the growth plate. Osteoblasts replace this with bone on the inner surface, and the growth plate migrates further apart.
How do bones grow in diameter?
As osteoblasts deposit bone beneath the periosteum
What hormone is associated with bone growth?
Growth hormone (GH)
Bone remodeling
A change in the bone’s size, shape, and strength
What factors influence bone remodeling?
Diet, age, exercise and hormone activity
Weight-bearing exercise affect on bones
Increases overall bone mass and strength. The compression generates electrical currents that activate osteoblasts to form bones where stress is high, thus strengthening bones
Bone homeostasis
The balance of osteoblast and osteoclast activity
Osteoclasts
Cells that remove bone through a process called resorption
What is the relationship between osteoblasts and osteoclasts in healthy bone?
In healthy bone, there must be a balance between osteoblasts (which deposit new bone) and osteoclasts (which remove bone) to maintain bone homeostasis
What happens when a bone is compressed?
Compression generates electrical currents in bone
What do electrical currents in bone activate?
Activate osteoblasts
Where do bones form/remove in response to stress?
Bones form where stress is high and are removed where stress is low
Osteoporosis
Bone loss that results from a long-term cell imbalance between osteoblasts and osteoclasts. Bone removal exceeds bone formation
Parathyroid hormone
secreted from
target tissue(s)
function
effect
Secreted from the parathyroid
Targets osteoclasts
Regulates bone cells and calcium levels in the blood
Stimulates osteoclasts to secrete more bone-dissolving enzymes, which break bone down and release calcium into the blood
Pneumonic: Parathyroid↝ parent↝parents RAISE their kids↝para RAISES calcium levels in the blood
Calcitonin
Secreted from
target tissue(s)
function
effect
Secreted from thyroid gland
Targets osteoblasts
Regulates bone cells and calcium levels in the blood
Stimulates osteoblasts to deposit calcium and phosphate in bone, removing calcium from the blood
Hematoma in bone repair
A clotted blood that forms at the site of a bone fracture
Initial signs of a bone fracture
Inflammation, swelling, and pain appear at the fracture site
What cells migrate to start bone repair?
Fibroblasts migrate to start bone repair. Some fibroblasts become chondroblasts during bone repair
Fibrocartilage callus
Temporary structure that forms at the fracture site during bone repair
Osteoclasts role in bone repair
Osteoclasts remove dead bone and hematoma remnants during bone repair
What is the sequence of bone repair?
Hematoma forms
inflammation occurs
Fibroblasts
Some become chondroblasts
Fibrocartilage callus forms
Osteoclasts remove dead tissue
osteoblasts deposit new bone
callus converts to hard bone
What gives bones their structural framework?
From a protein mixture (including collagen) produced by osteoblasts
How many bones make up the human skeleton?
206
What are the 2 main groupings of the skeleton?
The axial and appendicular skeleton
Axial skeleton
Forms the central axis of the body
What are the components of the axial skeleton?
The skull, sternum, ribs, and vertebral column
what are the components of the appendicular skeleton?
The pectoral girdle, arms, pelvic girdle, and legs
Appendicular skeleton
consists of bones of the appendages and their attachment structures
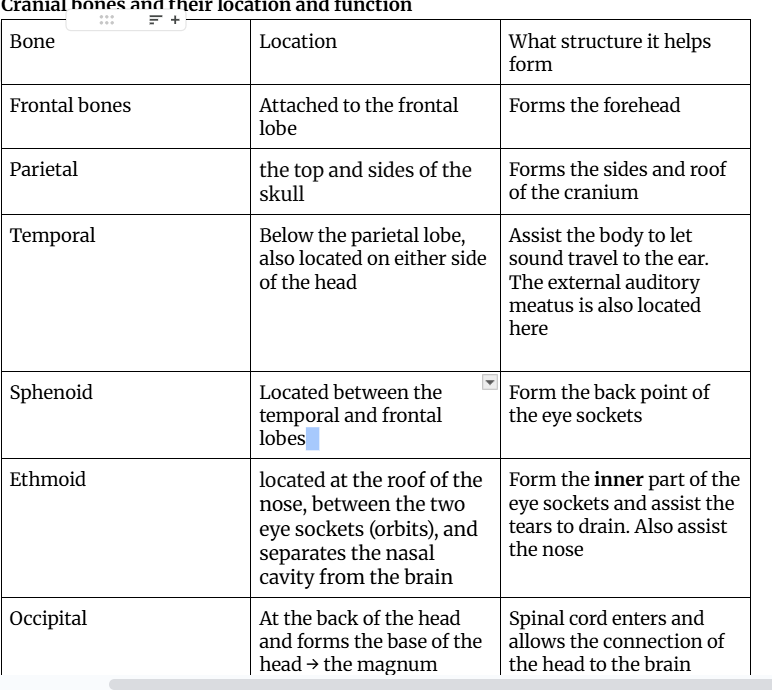
What are the six cranial bones?
Frontal bone, parietal bones, temporal bones, sphenoid bones, ethmoid bone, and occipital bone
Foramen magnum
A large opening near the base of the occipital bone
Where is each cranial bone located, what is it’s function and/or what does it form (facial structure)