psych personality disorders
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
how poeple think of severly mentally ill
adam lanza and omar mateen
there is a ____ _____ and ___ in language that can effect how we percieve mental illness, for example
generational divide shift
ex: someone is strugglingw ith their mental health, more associated with normalized mental illnesses
a lot of young people have been through the pandemic and if you’re coming of age, one thing that happens during that time is _______ _____ and ______ bc of the stressful experiences, a lot going on and things uncertain
significant anxiety, depression
in terms of anxiety and depression, are the rates higher or lower now after covid? Has it gone down or up after the peak
higher bit'/got down from the peak.
true or false, mental disorders are smth that we don’t have an attitude towards
false
explain the interaction study
what were they trying to measure
what percentage of indivs were willing to interact with someone that has been hospitalized with panic disoder/control
what 2 mental illnesses did it drop for and what percentage were people iwlling to itneract with the lease one
there’s this interaction study that asks if you’ve been hospitalized or nont either no, yes panic disorder, yes depression, yes schizophrenia
measured: your willingness to interact with someone who has or has not been in the hospital
they found in control condition, 9o percent of hte indivs are willing to interact with someone that has been hospitalized with panic disoder /control
drop with someoen that has been hospitalized for depression, drop again for those who have been hospitalized for schizophrenia, less than 5o percent
the more those with mental illnesses believe that others will have a negative reaction with those with mental disorders, the…….
the less likely they will report that they need help
what is psychopathology
a disorder of the mind
the overrachring category
why does cultural context shape the way we consider what is abdnormal
there is some _____ _____
what is Taijin Kyofusho
what can there be across different cultures regarding mental disorders, but what remains true to each culture and mental disorders
what sets the norm, waht do cultural norms set the norm for
psychological disorders exist globally but there is some cultural bariation
ex: taijin kyofusho-japan mental disorder: people are afriad to interact with others bc they feel like parts of their body don’t smell good
there are similarities between mental disorders but it can be specific on the culture
it has to be abnormal and our cultural norms set the ocntext for us of what is considered normal vs deviant
about how many americans will suffer from a psychological disorder at some point in their lives
how many will be severely effected
about half of americans will suffer from a psychological disorder at some point in their lives
however only 7 percent iwll be severly effected
what is abnormal vs atypical
a lot of ppl in our society are atypical, aren’t normal like beyonce, steve jobs, etc
just bc you’re atypical does not mean you have a psychological disorder
abnormal: behaviors that deviate from typical functioning
what are the 3 criteria for abnormal,
3 d’s
which one does cultural context effect
deviant” behavior that violates the norms of what’s expected, one of the ways that cultural context matters bc what is deviant here might not be deviant somewhere else, have ot think of where you are before consideering if it’s deviant
maladaptive/dysfunctional : interferes with functioning, danger to yourself or danger to others, losing touch between reality and your experiences
personal distress: behavior must lead to personal distress, pretty standard
what are the three deviants
deviant, dysfunctional, and distressing
if you meet all 3 it’s abnormal, but you don’t always have to meet all 3
emphasize maladaptive the most, but you need all of them to have a mental disorder
behaviors can vary from being ____ to ____, it’s a _____ ____
however behavior can be _____ vs _____ depending on the ____ _______
functional, dysfunctional, sliding scale
functional, dysfunctional, social context
what is the diagnostic criteria
what does it give us
what kind fo assesment is done
what is included in the assessments
true or false, you can observe behavior on certain tasks
what is a way to label dimensia and who must it be done by
DSM5TR
a set of criteria that a person is required to meet to be diagnosed with a specific disorder
a standardized assesment
there are also guidelines to assessments
true
labeling numbers on clock is good for labeling dimensia, must be done by a professional
how does the DSM sort disorders
what do the distinguising features result in
cany ou have more than 1 diagnosis, how common is this
waht does comorbidity mean
what are the 3 psoitives about the DSM-5-TR
in categories
diff diagnostic labels
yes, v common
when ppl ahve 2 or more diagnoses, we call that comorbidity=multiple disorders at the same time
standard evlauation criteria
common basis for communication - diff scientists have hte same definition for a mental disorder
enables research and treatment
soem disorders that go together
depression and anxiety occur together-comorbid
diagnostic and statistic anual of disorders -text reviison, not enough to make a new edition
what are the cons of the DSM
entirely categorical, you have this disorder or you don’t, doesn’t deal with spectrum
focuses on problems, disorder-focused
labels open risk of stigma, continues the cycle of stigma
what is the biological approach what kind of model is this
the root of psychological disorder is essentialy biological
we see them as physical illnesses that need to be treated via medication
doesn’t acount for everything realted to mental disorders
medical model
what is the psychlogical model
focuses on our internal psych epxeirences like emotions, trauma, our personality, our childhood experiences can inform our disorders,
abnormal behaviors are learned
ex like cognitive behavioral therapists
what is the sociocultural model
approaches psych disorders as a mitch match between
interactions between people and their behaviors and their contexts
perfered model/ biopsychosocial model
the best model is all of them smooshed together
bio+ psych+sociocultural model
consider influences of all these groups + how they interact
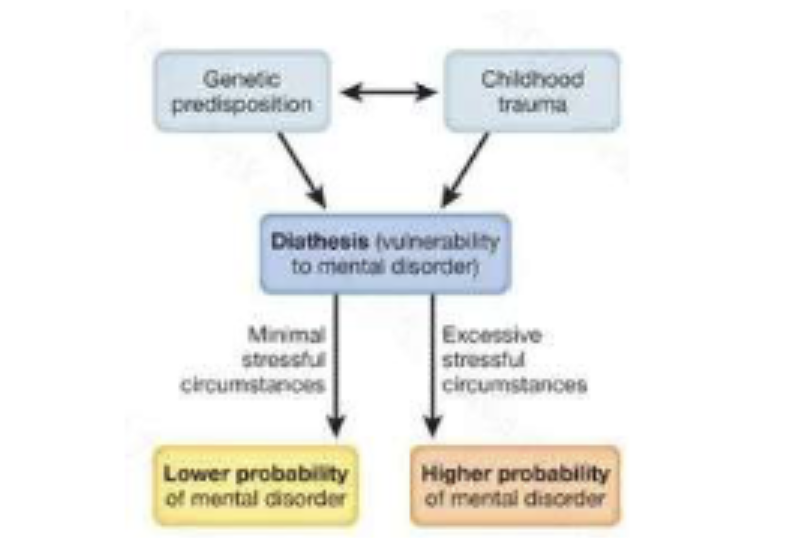
what is the vulnerability stress model, also called the diathysis stress model
childhood trauma can influence genetic pedisposition OR vice versa
biological factors interacting with personal experiences
can cause diathesis: vulnerability to mental disorders
minimal stress= lower porability of mental disorder
excessive stress= increased probability of developing a mental disorder
psychological disroders…
tend to be _____ common than people think, take ____ forms, are diagnosed using the _____ _____, arise from an interaction of ____, ____ and _____ factors
more, many, DSM-5-TR, biolgoical, social, and environmental factors
anxiety disorders
is a ___, _____ ___ stae, and _____ ____
anxiety does prepare us for _____, to ___ ____
let’s us respond in _____ ways
it can also be seen as ____ _____ and anxiety over situations that aren’t ____
what does it interfere with
how common is it, how many audlts experience it
what percentage of people have it in a year
tense, negative emotional, high arousal
action, to pay attention
adaptive
excessive fear, dangerous
interferes with our functioining
most common type of mental disorder, 1/3 of adults experience anxiety disorder
19 to 2o percent of people have it in a year
what are commons symptoms
what is apprehension are people with anxiety more or less likekly to think a bad thing happening is worse than usual and what is this called
muscle tension, restlessness-can lead to chronic fatigue
hyperactivity-excessive arousal like dizziness and racing heart
apprehension-tend to focus on potential danger and threats remembering a threatening vs non threatening event
more, a magnification to a threat
generalized anxiety disorder : GAD
how long does the persisten anxiety need to last and what must it not have
what are they in a constant state of
what do they have a pattern of ?
what is the etiology of GAD and why
does harsh self standards increase or decrease the risk of this disorder and why
what percentage of people does this effect and which gender does it effect more
atelast six months without a speciifc cause
constant state of worrying
pattern of hypervigilance, people are constantly on the lookout, very easily distracted, irritable and fatigued
etiology-GABA deficiency-the brains off switch, without enough GABA you’re not able to shut down some of that activity which can lead to constant activation of anxiety
increase risk bc of a tendency towards negative thoughts
under six percent of pop, women
panic disorder
what is the definition
what do they also worry about
what is the duration that they ocur
what are some symptoms
what are the 3 risk factors
what percentage of people are effected, who are more likely to get it
Recurring sudden episodes of intense terror
worry about future attacks, happen for 2o minutes or less
-chest pain/trembling, shortness of breath, hyperventilation, dizziness, heart palpatations, numbness or tingling and feeling helpless
risk factors: ppl with this tend to have higher levels of lactate, also causal to an extent,
condiitoned response to CO2, overgeneralization or fear learning
affects abt three percent of ppl, women
specific phobia
what is the definition
what do people do to avoid it
what are the 3 factors for etiology
persistent excessive fear of an object or situation
treies to avoid exposure of the trigger
etiology-through learning
biological factors
family history of mental illness
what are common phobias
snakes, spider, heights, flying
ushe end in obia
social anxiety disorder
what is the definition
how do they relieve it
at what age can it develop
the more social fear you have, the more likely you’ll ____ ____ ___ becuase it’s a _____
what are the 2 reasons regarding etiology
intense fear of being humilliated or embarassed in social situations
they avoid situations that could cause negative social situations
can develop early age of 13+
devleop other things, comorbidity
etiology-biology and oxytocin.
Oxytocin deficiency/imbalance is what turns our fear response off and helps us feel safer and bonded to other people, also learning,
biology: due to difference in amygdala activation you can be more likely to develop social anxiety
obsessive complusive disorders
is it an anxiety disorder
what are ob
no, but it’s considered related to anxiety
obsessions-frequent intrusive thoughts
compulsions-behaviors or rituals that one feels compelled to perform
these thoughts become reactivated
cleaning, checking and counting are the most frequent compulsions
worrying that you didn’t do something
etiology-
glutamat plays a role, ovveractivity of impulse constantly hitting your thalamus
avoidance learning
if we learn tht performing tha copulduion helps us to avoid that outcome, were’ more liekly to do that ocmpulsion
PTSD
what is the definition
what is it related to
intrusive thouoghts that are recurring, unwanted and invasive
related to a traumatic event
what is truama defined as
is it single or repeated
is it an even you experienced or an event that someone else experienced
ny event that overwhelms are ability to cope could be traumatic
both
DSM-5 says both
prevalance for PTSD
what is the lifetime and yearly pirevalence
what population is it high in
what is the prevalance for those that are in the military
which other group is ___ times more liekly to be diagnosed with PTSD
lifetime prevalence is 7 percent and 4 percent in a given year, high in populations like the military
6-35 percent ofr in the military
sexual assault survivors, 6
what are some common experiences for those with PTSD
what can it be triggered by
flashbacks, it’s like you’re reliving that trauma
nightmares
distressing memories, intrusive thoughts that people don’t want to have
physiological reactions
impulsive outbursts
issues with memory concentration or anxiety
emotional numbness
triggered by external cues or internal thoughts
where does etiology come from, the more extreme the ….
explain the experience in nnorthern illinois university
Genetics, in northern illlinois university, there was a ____ ____ and they tracked ____ and their responses and sort them into groups over time of students that developed symptoms that would qualify themf or PTSD or not, there were diff between them as genetic marker realted to _____ ____ , dysregulation in ____ _____ that _____ risk for developing PTSD
those with PTSD have two things, ___, which means that they have a ____ volume in their _____
and _____ meaning that
experiences- from trauma, the higher the stress level
school shooting, students, serotonin function, serotonin sysstem, increases
Memory system dysfunction-have a smaller volume in their hippocampus
failure of extinction learning-they have trouble getting rid of the stimulus/strong physical reaction even when a negative experience doens’t happen with it again
dissociative disorders
what is the definition
what is it related to
disruptions of identity, memory or concscious awareness
related to experiences of extreme stress
what is disociative amnesia
what can it happen with or without
dissociative amnesia-you forget aspects of who you are and or loose autobiographical info of an event, or period of time
can happen with or without dissociative fugue, which is when there is sudden travel and you forget who/wher you are and where you came from
what is didsociative identity disorder/sometimes DID
what is the def
is it the least or more severe of these disorder
what gender is it seen the most in, to what level is their abuse usually
1 person has 2 or more distinct identities, multiple personality disorder
most sever
women, extreme abuse
expressed one at a time and each personality has it’s own set of memories, traits and characterists, behaiors adn relationships
controversial bc maybe it’s a leanred response to extreme stress and segmenting parts of who they are and a therapist treating you like you have diff personalities is encouraignng it , we should similar responses of this for people that have experience the same level of trauma
it’s not entirely a social construction which is why it’s controversial
the fact hat we still see it in palces that is not socialized means that there is osmething there
depressive disorders
what is the prime symptom
what are the two factors that make depressive disorder
it’s the ____ cause and risk factor of ____ worldwide and ___
why are depressive disorders seen as pernicious/harmful
prime symptom is depression-an unreleenting lack of pleasure in life
the presence of a negative mood + physical symptoms
leading, disabilities, suicide
bc sometimes you don’t see the signs outwardly but they’re there
how long does major depression have to be minimum
what does one of the symptoms have to be
what are some of the symptoms
all of the symptoms have to be severe enough that your ___ ___ is ____
what is the prevalence for adults
what percentage of people does it affect at any given time
at least 2 weeks
one of the symptoms MUST be depressed mood or loss of interest in pleasurable activities
-extra: sleep and appetite disturbances
-fatigue
-issues with concentrating and making decisions
-feeling worthless, thoughts of death or suicide
daily funcitoning, iimpaired
-last on average abt six months
prevalence: 16--2o perent for adults
affects 8 percent of americans at any given time
what is persistent depressive disorder
how long must it last atleast for adults
what is the difference between persistent depressive disorder and major depressive disorder/just the def
you can’t go more than ____ months without symptoms to have this
what percentage of the population does this effect
how many years must it last for children
which kind of depression does acute go with
which kind of depression does not acute go with
two years
similar symptoms that are less severe and for longer durations
2
about two percent
must last one year minimum for children
acute=major depression
not acute=persistent depressive disorder
rates of depression_____ by 5o percent, but there is a particular rise among ____ ____ and even when ___ ___aren’t saying they have it, they’re saying they see it in other ppl their age
depression is _____ common in_____, ___ times more likely to have it
increased, 5o percent, young people, young people, more, women, 2
gender differences
women are more likely too __ ____, so it’s easier to diagnose women
disorders can be ____ vs ____
where ___ is, and ___ is
which is more common in women and which is more common in men
women are more likely to seek help so it’s easier to diagnose it more in women
disorders can be internalizing vs externalixing
internalizing=negative emotions, anxiety, depression, panic disorder, more common in women
externalizing: characterizzed by outward behaviors and disinhibition
ex: alcoholism/ addictions , conduct disorders,a cting out against disorders, antisocial behavior
mroe common in men
depression is ____ in young people, more common in ______ and , more common among people from____ bc of ___ and _____
which causes negative mental health outcomes, this is called the ____ ____ ____
the way we talk about depression ____ across ____
increasing, girls/women, marginalized groups and those living in poverty
pejudice+ discrimination causes negative mental health outcomes: minoritisy stress model
we can see depression globally ind eveloopoing countries
thew ay that we talk about depression varies across cultures. Ex: you can’t say thing slike i can’t say things like i think i might be depressed
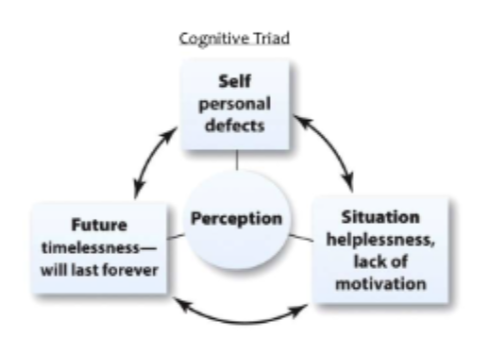
explain the cognitive triad
what two things fuel the cognitive triad
what does this cause
more specifically what two things keep this wheel going
are people with this more or less liekly to ruminate or replay negative experiences over and over/experiences that make you feel bad
what does it mean when they say that those with this have pessimistic attributions(internal and external attributions)
rumination and pessimistic attributions
their way of thinking causes risk factors that maintain and sustain this way of thinking
they feel helpless in a situation with lack of motivation + future timelessness will last forever
causes self personal defects(negative perosnlaity traits or behaviors that hinder perosnal growth, relationships, and goals
ppl witht his are more liekly to ruminate
AND: pessimisitc attrivutions: ppl with depression tend to think that bad things hapen bc of who they are, internal attributions for negative events and external attributions for positive events
what is the etiology with depression
END OF PT 1
what 4 factors play a role in depression
what percentage does hte biggest one have in effecting depression
genetics-genes explain forty percent of the rates of depressoin
less strong for bipolar or schizophrenia
neurotransmitters: fever transmitters for things like norepinephrine, serotonine, and dopamine
stress and negative life events
lack of social support-when ppl feel like they have other sin their life to talk abt negative events with they’re less likely to end up in these cycle
what psychological disorder is a failure of fear extinction learning
PTSD
definition of bipolar disorder-maniic episode ,
how many cycles per year
how many months between cycles
manic episode: abnormally elevated mood, feel great, tend to have higher self esteem, can do anything, increases risk taking, decreased need for sleep, very talkative/racing thoughts
1-2 cycles per year
6-12 months
describe bipolar 1
____ + ______
how often in a day will you experience mania for atleast how long
can it or can it not be disrupted in daily life
by extreme mania+ depression
, a full onset of a manic episode-meaning you’re experiencing mania for most of the day for atleast a week
both the mania ande depresson can be disreputed in daily life, both sides
describe bipolar 2
what is the main difference between BP1 and BP2
what two things does BP 2 have
how long does the mania last
which one is more harmful, the mania or the depression
is bipolar more or less common than depression
which gender is it more common in?
reduced form of mania
hypomania=isn’t a full on episode of mania but still have elevtated mood, reduced need for sleep, etc AND depression
mania only lasts for 4 days
depressive swings are more harmful than the hypomanic phases, diff patterns of interruption of dialy functioning
bipolar is less common than depression and is equally common in men and owmen
what are the 3 risk factors for bipolar
genetics-the numbe rone risk facotr is a family history,
changes in brain activity-higher levels in glutamate, higher levels of brain activity
oversensitivty to reward in manic phase (less activie in depressive phases(
what are depression and bipolar commonly linked to
how many more suicides are there in comparison to homicides
for people in the age of ___ to ____, suicide is the __ leading cause after an accident
depression and bipolar are commonly linked to suicide
there are 2.5 more suicides as homicides
for people in the age of 1o-24, suicide is the 2nd leading cause after an accident
risk factors of suicide
always
specific plans
history of injury or self harm
other:
when ppl don’t feel like they belong, feel like. a burden tend to lead to a desire to this circumstance
factor 2: history or ability or capability of desensization-those things desensitize us to pain and tends to us to be more liekly to continue to trya nd harm ourselves
schitzophrenia
what is it also called
what are common symptoms
what is psychosis
when is it often diagnosed
does it exist mostly in the US or everywhere
what is the prevalance
are the rates more common in men or in women
it’s much more severe-called splitting of the mind
abnormal behavior, thoughts, perceptions, and consciousness
psychosis: ppl with schitzo loose touch with reality, psychosis=dissosociation from relatiy
it’s debilititating, often diagnosed in early adulthood
it exists everywehre, similar across culture
not very common, prevalance is abt 1 percent, still increadibly disruptive
similar rates in men and in women
schitzophrenia can be divided into two categories
____ symptoms and _____ symptoms
explain them both + give examples of both
what is anhedonia and the flat effect
divide symptoms into two categories
positive symptoms: addition of things that wouldn’t normally take place
-hallucinations, most common auditory(hearing voices), delusions, false beliefs based on incorrect things of society, delusions of persecutions
patterns of disorganized thoughts/ speech, disorganized movements
negative sympotms: removing things
flat affect-don’t have any emotional displays, dont make faces, voice modulations, etc anhedonia-inability to feel pleasure, tjihings that make you happy don’t anymore, lack of interest in socializing/asocial
what are the risk factors of schizophrenia
what is the strongest risk factor
what are the other 5 risk factors
what is referential thinking
genetics is the strongerst one, if someone in your family had it
differecnes inb rain structure: enlarged verticals, smaller prefrontal cortex
overpruning synaptic connections in adolescenc
increased dopamine and glutamate
pre natal enviro, babies were born in late winter or early spring, bc their mothers may have gotten a viral infeciton which increases the risk
Genes adn enviro interaction: int with genes and stressful family home
referential thinking: when we think that things are about us, but it’snot
how is social support related to schitzophrenai
give examples of these outcomes
it helps improve the outocmes with those that have schitzophrenia
tend to end up with less frequent hospital admissions, shorter durations of hospital vistis, less ever symptoms
descrbie the outocme paradox
why is this the case
if you look at outcomes with those with schitzo they are better for folks in developing countries than in western industrialized countries
bc generally folks family members and friends are most accepting in developing countries so they are able to experience more support which helps ot improve their outcomes
makes ppl more likely to stick with their treatment plans
why is early intervention with schitzophrenia important
we keep the ____ in _____ ____ if we treat the psychosis earllier
bc the longer they have psychosis without treamtnet the worse their prognosis becomes
psychosis in check
generla info about personality disorder
what two aspects are usually present in this mental illness and what do they both mean
which one do people ususally tend to ahve
ppl tend to interact with the world in maladaptive ways
inflexible and enduring behavioral patterns that impair funcitoning
when those tendencies are oth maladaptive and inflexible, they tend ot interfere with our ability to function
what are symtpoms for those with borderline personality disorder
what is schizophrenia independent
Auto eccentric relationship, have issues forming relationships with others , displaying strange ad erratic patterns of behavior
those with schizophronia that are able ot live by themselves
EXAM: know the discription for schitoz independent , figure 6 MUST know figure 6
anitsocial personality disorder
what do they lack
when they pursue gratification what do they not do
where is their level of arousal
what feelings are htey low in
how does their brain react to seeing others show their emotions
what are other symptoms of their behavior and what does it make it easier to do
who is it more common in
what is the prevalance
lack empathy and remorse-big symptom
pursue gratification without considering others, don’t care if it hurts others
lower arousal, meaning lower fear, anxiety , etc
when they look at ppl that are showing these emotions, they have lower brain reactivity to it
lots of lying and dcriminal behavior, easier to manipulate ppl like therapists and lie detectors
more common in men than women
prevelance is between 1 and 4 percent
general info about borderline personality disorder
what is the definition
what do they have a poor amount of
what is their two top fears
are they stable or unstable
describe their mood swings
describe their sense of self
how do they view the world
what is a common characteristic in their relationship
waht are they prone to
what is the prevalance rate
who si it more common in gender wise
long-term patterns of unstable emotions, impulsive actions, and turbulent relationships
poor self-control
fear of abandonment and being alone
unstable:
affect: emotionally unstable. can go from happy to angry to sad, heavy mood swings
sense of self: display lot’s of change in understanding of who they are, their goals, etc
relationships:
-can be manipulative others in terms of their relationship
viewing hte world as black or white: splitting-you’re either with me or against me type thinnking
prone to self harm
1-2 percent, more comon in women
what is the etiology of BPD
genetics
reduced frontal lobe functioning
enviro-malnutrition in childhood can increase it
extreme childhood trauama and abuse can predict it
what are early signs that are looked for after being age 15 that could hint at having this
f they have patterns of theft, destruction of property, high levels of aggression/harming others
hurting animals
deception
trying to reshift this can help with preventing this
what are neurodevelopment disorders
disorders that we look for and diagnose in childhood
what is autism sepctrum disorder
what are symptoms
is it categorical or spectrum in terms of severity and sysmtpoms
what are the two common symptoms
what is another one
previously asperger’s syndrome
ppl can fall anywhere on the spectrum of severity, variation in symptoms
defecits in communicaiton and interactions
repetitive behaviors, circumscriped interests-means that people hav eone area or topic that they are particularly interested in, become experts in
can go from not being able to be by yourself to being one of the smartest people in the room
which gender is it more common in and by how many times
what is key for this disorder
1 percent estimates are increasing rapidly
4 times more common in boys
early intervention is key
what is the etiology of autism spectrum disorder
what is the illusory correlation
what are the two big reasons for autism spectrum disorder
it’s not parenting or vaccines
illusory correlation-people predict that there is a relationship between two varaiables when there isn’t or it’s very small
diffs in language processing area of the brain called broca’s area
diffs in mera neurons, we see diff patterns of activation in mera neurons, affects imitation and theory of mind, diff pattenrs of reward of the brain
variety of risk factors
what is ADHD
what are the 3 variables that are apart of ADHD and what do they mean
what are the 3 ways that you can have ADHD
what is it called when you have all 3 variables
how long do you have to look back from when looking at the criteria
inattention
hyperactivity-like fidgeting or running around wheny ou hsould b e still
impulsivity-acting without planning or thinking things through
predominately inattentive, predominatly hyperactive/ impulsive, or alll 3,
combined presentaiton: you have both inattention and hyperactivity or impulsivity
lookn at the last 6 moths there are seperate criteria for both
whatistheprevalance
do they have better or worse academic outcomes
how is their relationship
are they more or less likely to end up in the criminal system and become deliquents
prevelance is 6 percent globally but higher in the US
are we over diagnosing?
does it pathologize what is actually normal behavior
tend to show worse academic outcomes
wose peer relationships
more likely to end up in the criminal justice systema nd be deliquents
general info about eating disorders
anorexia nervosa
anorexia bullimia
what are the two factors of it?
why do they underrate?
what is binge eating disorder
who is it more common in
anorexia nervose: chronically undereating due to fear of gaining wieght
-distorted body image
bulllimia nervose-bing eating and purging
impulsive relationship with food, eat a lot and feel bad about it so then thrwo it all up, show preoccupation with food and high stress levels/anxiety with food
fear of being overweight which leads to udnerating , association with shame and guilt which is bad
bing eating disorder: binge eating without purging
more common in girls than women
etiology
what is anorexia nervosas etiology
what is anorexia bullimias etiology
what it the most direct etiology
perfectionism, if you have this tendency of wanting to be perfect
Bulimia: predicted by high levels of perfecitonism with low self-efficacy
most direclt linked to physica health, can lead to organ damage
what are examples of treatment
medication, other biological treamtnets, therapy-BIGGEST one
-types
context: family, group, couple , indiv
cognitive behavioral therapy/CBT:
what does negative explanatory style continue
negative explanatory style continues this depressed cycle, so they make changes to cognitive ad behavioral changes
what is the ABC model
explains why we thnk and feel and do the things that we do
Activating event-anything that actually happens to us, any situation
Belief: what we think about the sitch
Consequence: the result and our belief abt the sitch, how we feel or what we do after the sitch
try and avoid the stich if you can, if not then try and change the belief
you can also change the consequence, by doing debriefing after the consequence