Psych Final Exam
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 5:25 PM on 5/3/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
1
New cards
Schizophrenia
A class of psychological disorders characterized by grossly impaired social, emotional, cognitive, and perceptual functioning.
Has Sensory perception issues, cognitive symptoms, social emotional issues, and motor symptoms.
Has Sensory perception issues, cognitive symptoms, social emotional issues, and motor symptoms.
2
New cards
What do we use to classify psychological disorders?
DSM 5(edition) 2013
3
New cards
Prosopagnosia
Face blindness
4
New cards
Guilty knowledge test
a method that assess lying by comparing \n physiological arousal in response to information that is relevant to a transgression.
5
New cards
Arousal motive (Curve in particular)
The motive to maintain an optimal level of physiological activation.
\
Yerkes-Dodson law – the principle that the relationship between arousal and performance is best represented by an inverted U-shaped curve.
\
Yerkes-Dodson law – the principle that the relationship between arousal and performance is best represented by an inverted U-shaped curve.
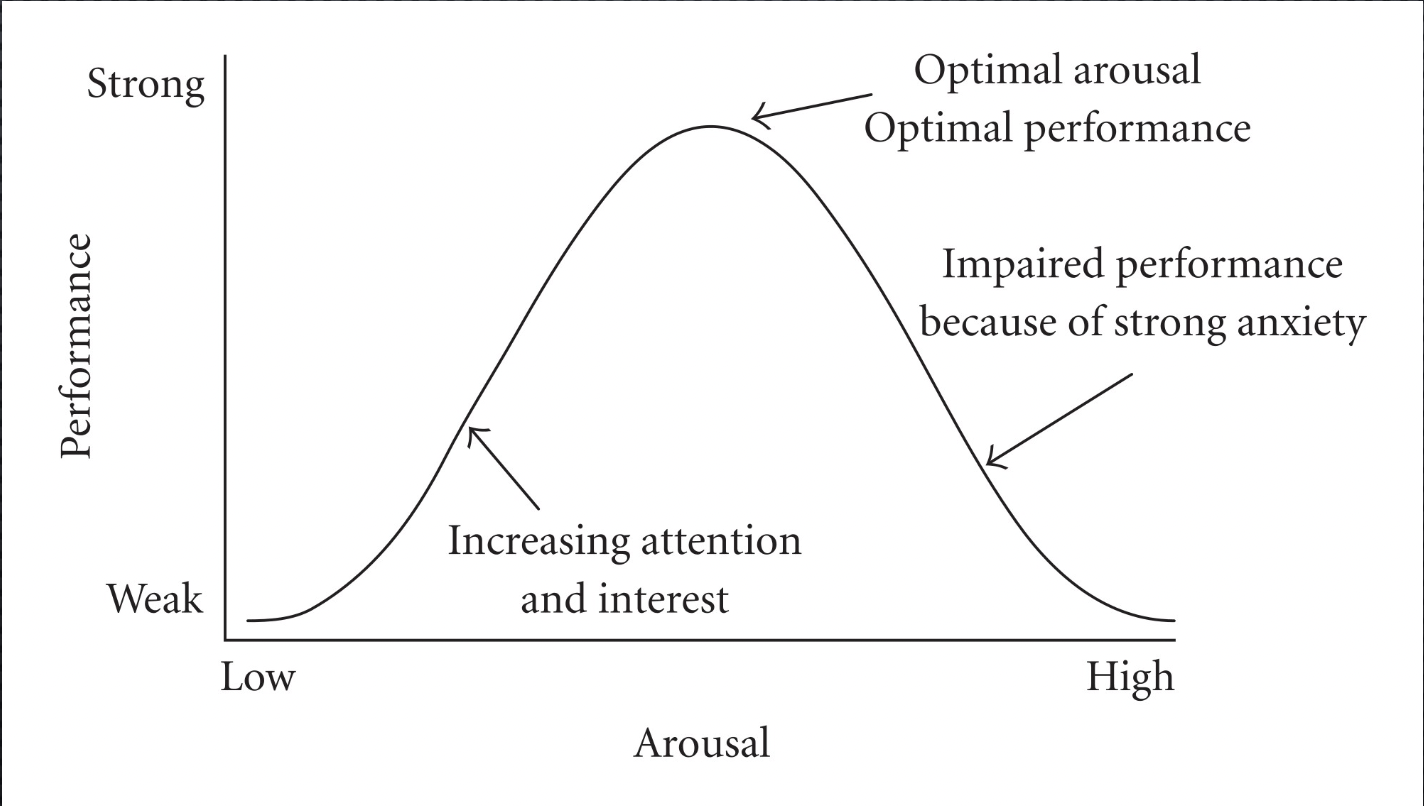
6
New cards
Sensation
the process that detects stimuli from the body or \n surroundings
7
New cards
Perception
the process that organizes sensations into meaningful \n patterns
8
New cards
Anorexia Nervosa
an eating disorder marked by self-starvation.
9
New cards
Bulimia Nervosa
an eating disorder marked by binging and purging. \n Both are dangerous
10
New cards
Crystallized intelligence
the form of intelligence that reflects knowledge \n acquired through schooling and in everyday life (__**Grows with age)**__
11
New cards
Fluid intelligence
the form of intelligence that reflects reasoning ability, \n memory capacity, and speed of information processing. (largely inherited) __**(slows with age)**__
12
New cards
Hallucinogens
__**psychoactive drugs**__ that induce extreme alterations in \n consciousness, including visual hallucinations, a sense of timelessness, and feelings of depersonalization
13
New cards
Manifest content
Sigmund Freud’s term for the verbally reported dream
14
New cards
Latent content
Sigmund Freud’s term for the true, though disguised, \n meaning of a dream
15
New cards
Attention
the process by which the individual focuses awareness on \n certain contents of consciousness while ignoring others.
16
New cards
Unconditioned Stimulis
in classical conditioning, a stimulus that \n automatically elicits a particular unconditioned response.
17
New cards
unconditioned response
in classical conditioning, an unlearned, \n automatic response to a particular unconditioned stimulus.
18
New cards
Condition Stimulus
in classical conditioning, a neutral stimulus \n that comes to elicit a particular conditioned response after being paired with a particular unconditioned stimulus that already elicits that response
19
New cards
Conditioned Response
in classical conditioning, that learned \n response given to a particular conditioned stimulus
20
New cards
Classical Conditioning
a form of learning in which a neutral stimulus \n comes to elicit a response after being associated with a stimulus that already elicits that response
21
New cards
Sensory Memory
the stage of memory that briefly (for at most a few \n seconds) stores exact replicas of sensations.
22
New cards
Short term memory
the stage of memory that can store a few items of \n unrehearsed information for up to about 20 seconds.
23
New cards
Long term memory
the stage of memory that can store a virtually \n unlimited amount of information relatively permanently.
24
New cards
Major Depressive Disorder (MDD)
A disorder marked by depression so intense and prolonged that the person may be __**unable to function in everyday life.**__
25
New cards
Black Swan
an event that is unexpected, has a \n major effect, and is often inappropriately \n rationalized after the event. (hindsight bias)
26
New cards
Phi Phenomenon
The mind responds to stimuli, you edit what you see, the mind fills in the blanks
\
this is from my notes couldnt find it in the slides
\
this is from my notes couldnt find it in the slides
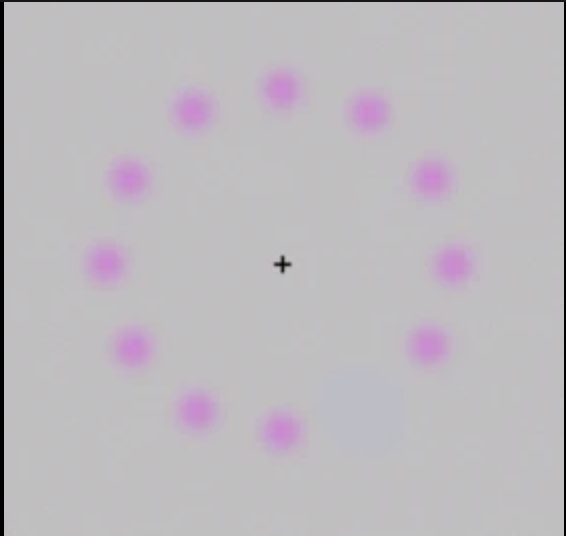
27
New cards
Gamblers Phallacy
the misperception that a \n number must occur because it is due. They ignore \n the independence of events.
28
New cards
Theory
an integrated set of statements that summarizes and explains research findings and from which research hypotheses can be derived.
29
New cards
Wernicke’s
the region of the temporal lobe that controls the \n meaningfulness of speech.
30
New cards
Bronchas
The region of the frontal lobe responsible for speech production.
31
New cards
Iconic Memory
visual sensory memory, which lasts about a second.
Think Icon=image
Think Icon=image
32
New cards
Echoic Memory
auditory sensory memory, which lasts up to 4 or more \n seconds.
Echoic=echo(sound)
Echoic=echo(sound)
33
New cards
Flashbulb Memory
A vivid, long-lasting memory of a surprising, important, emotionally arousing event.
9/11/01 everyone remembers 9/11
9/11/01 everyone remembers 9/11
34
New cards
Instinctive drift
the reversion of animals to behaviors characteristic of \n their species even when being reinforced for performing other behaviors.
35
New cards
Representative Heuristic
In decision making, the assumption that a small sample is representative of its population
\
Not everyone from Texas wears a cowboy hat and boots
\
Not everyone from Texas wears a cowboy hat and boots
36
New cards
Availability Heuristic
In decision making, the tendency to estimate the probability of an event by how easily relevant instances come to mind
\
When you get on a plane and all you can think of is plane crashes
\
When you get on a plane and all you can think of is plane crashes
37
New cards
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
an anxiety disorder marked by a \n persistent state of worry that exists independently of any particular stressful situation and often interferes with daily functioning.
\
THE DSM DEFINITION FOR ANXIETY NOT (GAD)- A psychological disorder marked by persistent and unrealistic worry that disrupts everyday functioning.
\
THE DSM DEFINITION FOR ANXIETY NOT (GAD)- A psychological disorder marked by persistent and unrealistic worry that disrupts everyday functioning.
38
New cards
Post Traumatic Stress {disorder} (PTSD)
A psychological injury with physical symptoms that appears as a delayed \n response after exposure to an extremely emotionally disturbing event. \n A continuation of response to traumatic stimuli for an extended period \n after the removal of the stressor.
\
\
__**This is different from anxiety because its after a traumatic event, caused by trauma (Post Trauma)**__
\
\
__**This is different from anxiety because its after a traumatic event, caused by trauma (Post Trauma)**__
39
New cards
Functional fixedness
the inability to realize that a problem can be solved by using a familiar object in an unusual way
\
fork to hang pic
\
fork to hang pic

40
New cards
Intrinsic Motivation
the desire to perform a behavior for its own sake.
41
New cards
Extrinsic Motivation
the desire to perform a behavior in order to obtain \n an external reward, such as praise, grades, or money
42
New cards
Heuristic
A decision-making shortcut or habit. Are usually functional, but not optimal. Derived from experience
43
New cards
Availability Heuristic
In decision making, the tendency to estimate the probability of an event by how easily relevant instances come to mind
44
New cards
2 Systems of thinking: System 1
fast, effortless, more likely to engage in \n parallel processing
45
New cards
2 Systems of thinking: System 2
slow, effortful, more likely to engage in \n serial processing
46
New cards
IQ 130 or greater
Above intellectual superiority
47
New cards
IQ 70 and below
would have problems doing every day tasks
48
New cards
Base Rate Neglect
Ignoring the likelihood of something happening
49
New cards
Hot hand fallacy
the notion that a hit raises \n the probability of hitting again.
50
New cards
Cerebral hemisphere
the right and left halves of the brain
51
New cards
is bias good or bad
can be both?
52
New cards
Illusion of majority
constructing the \n appearance that a particular position or notion is \n supported by a majority, when it is not true.
53
New cards
Glittering Generalities
broad, vague, sweeping \n statements with very little detail. The language use cues \n deeply held beliefs (freedom, liberty, equality, fairness, \n etc. etc. etc. etc. ad nauseam)
54
New cards
Assertion
no debate, just forceful statements
55
New cards
Pinpointing the enemy
Us v. Them; propaganda is more effective if an enemy can be identified and vilified
56
New cards
Repetition
repeated message or slogans
“Si Se Puede” (Hispanic United Farm Workers movement), or “Make America Great Again”
“Si Se Puede” (Hispanic United Farm Workers movement), or “Make America Great Again”
57
New cards
Selection of facts
propaganda is not delivered in a \n balanced manner, tends towards one sided-arguments \n and audience inoculation
58
New cards
Fear then relief
focuses attention on the source of relief.
59
New cards
Sensorimotor stage
from birth through the second year, during which the \n infant learns to coordinate sensory experiences and motor behaviors.
60
New cards
Pre-operational stage
extends from two years to seven years of age, \n during which the child’s use of language becomes more sophisticated but \n the child has difficulty with the logical mental manipulation of information.
61
New cards
Concrete operational stage
extends from seven to eleven years of age, \n during which the child learns to reason logically about objects that are \n physically present.
62
New cards
pre-conventional
the level of moral reasoning characterized by concern \n with the consequences that behavior has for oneself. Relate to egocentrism
63
New cards
conventional
the level of moral reasoning characterized by concern with \n upholding laws and conventional values and by favoring obedience to authority. (this is as far as many people go)
64
New cards
post-conventional
the level of moral reasoning characterized by concern \n with obeying mutually agreed-upon laws and by the need to uphold human dignity.
65
New cards
Radical behavioralism and the skinner box
Radical behavioralism and the skinner box, led to the blank slate belief, issues with that are instinctive drift or behavioral preparedness.
66
New cards
Formal Operation
4th stage
67
New cards
Status quo bias
people have a tendency to want \n things to remain as they are, as long as their basic \n needs are met. (Allostatic avoidance)
68
New cards
Confirmation bias
a search strategy in which we seek information that \n confirms what we already belief to be true, and discounts or ignores contrary information.
69
New cards
Nativism
the philosophical position that \n heredity provides individuals with inborn knowledge and abilities.
70
New cards
Rationalism
the philosophical position that \n true knowledge comes through correct \n reasoning.
71
New cards
Empiricism
the philosophical position that true knowledge comes through the senses.
72
New cards
Existential Perspective
A branch of humanistic psychology that studies how individuals respond to the basic philosophical issues of life, such as death, meaning, freedom and isolation.