Topic 1- Cell Biology
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Compare the structure of a red blood cell to a plant cell.
(6 marks)
Differences:
red blood cell has no nucleus, plant cell has a nucleus
red blood cell has no cell wall, plant cell has a cell wall
red blood cell is a biconcave disc
plant cells do not contain haemoglobin
red blood cells do not contain chlorophyll or
similarities:
both have cytoplasm
both have cell membrane
both have pigments.
When placed into a beaker of water, explain why a red blood cell bursts and a plant cell doesn’t.
(2 marks)
water enters cell via osmosis
plant cell has a cell wall which prevents that
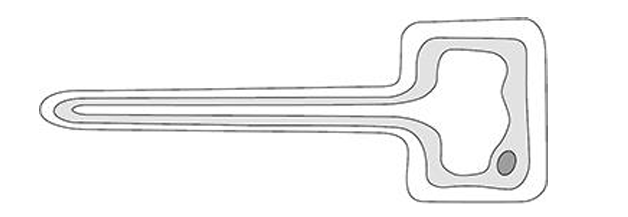
Name of this specialised cell:
Root hair cell
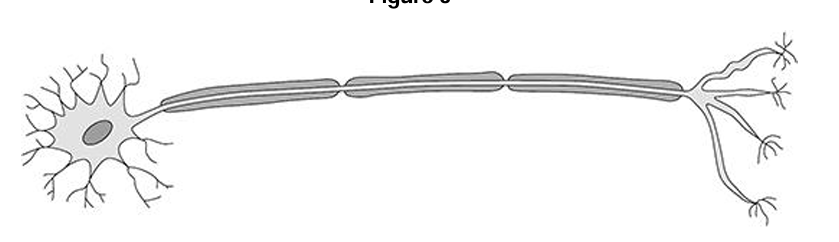
Name of this specialised cell:
Nerve cell
Explain why root hair cells contain mitochondria.
(4 marks)
aerobic respiration occurs in mitochondria
mitochondria releases energy
energy used for active transport
to transport ions from low to high conc
Compare the structure and function of xylem tissue and phloem tissue.
(6 marks)
Structure:
xylem is made of dead cells, whilst phloem is made of living cells
phloem cells have pores in their end walls, whilst xylem cells don’t
xylem is hollow, whilst phloem contains cytoplasm
both are: .tubular .made of cells
Function:
xylem transports water/mineral ions whilst phloem transports dissolved sugars
xylem= transpiration, phloem= translocation
xylem transports unidirectionally, phloem transports directionally
both transport substances through plant
Describe what happens during each stage of the cell cycle.
(4 marks)
dna duplicate and subcellular structures increase in number
dna condense into chromosomes in middle of cell and one set is pulled to either side of cell
cell membrane and cytoplasm divide, creatin 2 new daughter cells
Explain how a transplant of bone marrow cells can help to treat medical conditions.
(2 marks)
the cells can differentiate into many types of cells
so they can cure diseases caused by damaged cells, by replacing them
Define the term double circulatory system.
(1 mark)
blood is pumped into lungs by right side of heart
blood is pumped to body by left side of heart
Explain why an axolotl may die in water with a low concentration of oxygen.
(4 mark)
conc gradient of oxygen is less steep
(therefore) less oxygen diffuses into blood
less aerobic respiration occurs so less energy is available
so less metabolism
What is a stem cell?
(2 marks)
an undifferentiated cell
that can differentiate into many other cells
Suggest how a stent in the trachea helps to keep the patient alive.
(2 marks)
stent opens up the trachea
allowing air to flow through.
Evaluate the use of stem cells from a patient’s own bone marrow instead of stem cells from an embryo.
(6 marks)
Embryo Advantage:
can create many embryos in a lab
painless technique
can treat many diseases, whereas bone marrow can treat a limited number
Disadvantages-
. harm to embryo
. ethical issues
. may not work
Bone Marrow Advantages:
no ethical issues
can treat some diseases
procedure is relatively safe
reliable
Disadvantages:
. risk of infection
. can only treat a few diseases
Both Advantages:
can treat the disease
Disadvantages:
. risk of transfer or viral infection
. stem cells become cancerous
Explain how the human lungs are adapted for efficient exchange of gases by diffusion.
(6 marks)
many alveoli
. for large surface area
. for higher diffusion rate
capillaries are thin
. which provides a short diffusion pathway for oxygen and co2
. this allows for quicker diffusion
lungs are ventilated
. to bring fresh oxygen and remove co2
. helps maintain a good conc gradient
good blood supply
. removes oxygenated blood quickly
. maintains conc gradient.
Give two reasons why a kidney transplant is a better method for treating kidney disease than dialysis.
(2 marks)
less chance of infection/blood clots
no restrictions on diet
cheaper