4.1 Transverse and Longitudinal Waves
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Define a Wave
A repeated vibration that transfers energy but not matter
Progressive Wave
A wave where energy is transferred without transferring matter
Stationary Wave
A wave with no net energy transfer
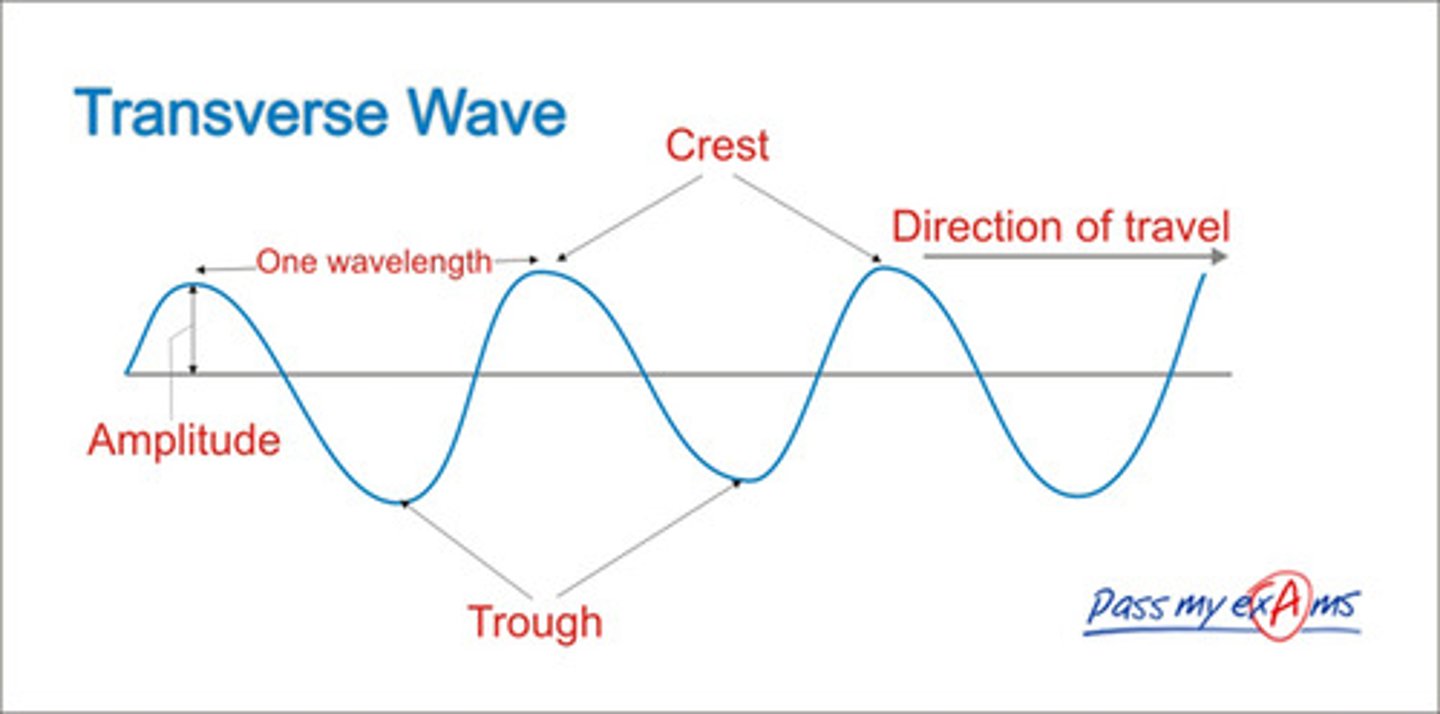
What is a transverse wave?
A wave that oscillates perpendicular to the direction of the wave.
What are examples of transverse waves?
Electromagnetic waves, water waves, waves on strings, earthquake waves.
Displacement
How far a wave has travelled from equilibrium position
Amplitude
Maximum displacement from equilibrium position
Wavelength
The length of one complete wave. Distance from peak to peak.
Longitudinal Waves
A wave that oscillates parallel to the direction of the wave made of compressions and rarefactions
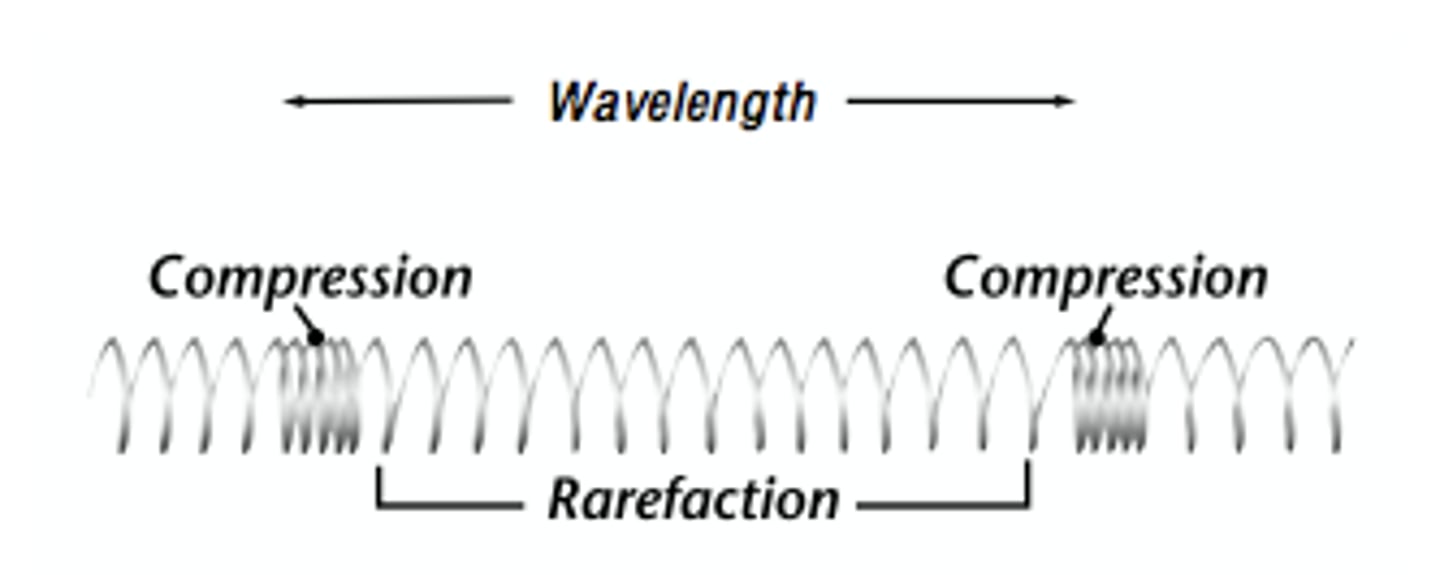
Compressions
Region where particles are closest together
Rarefaction
Region where the particles are furthest apart
Define Time Period (T)
The time taken for one complete wave, measured in seconds.
Define the frequency of a wave
The number of complete waves per second measured in Hertz (Hz)
Frequency Equation
f = 1/T (frequency = 1/period)
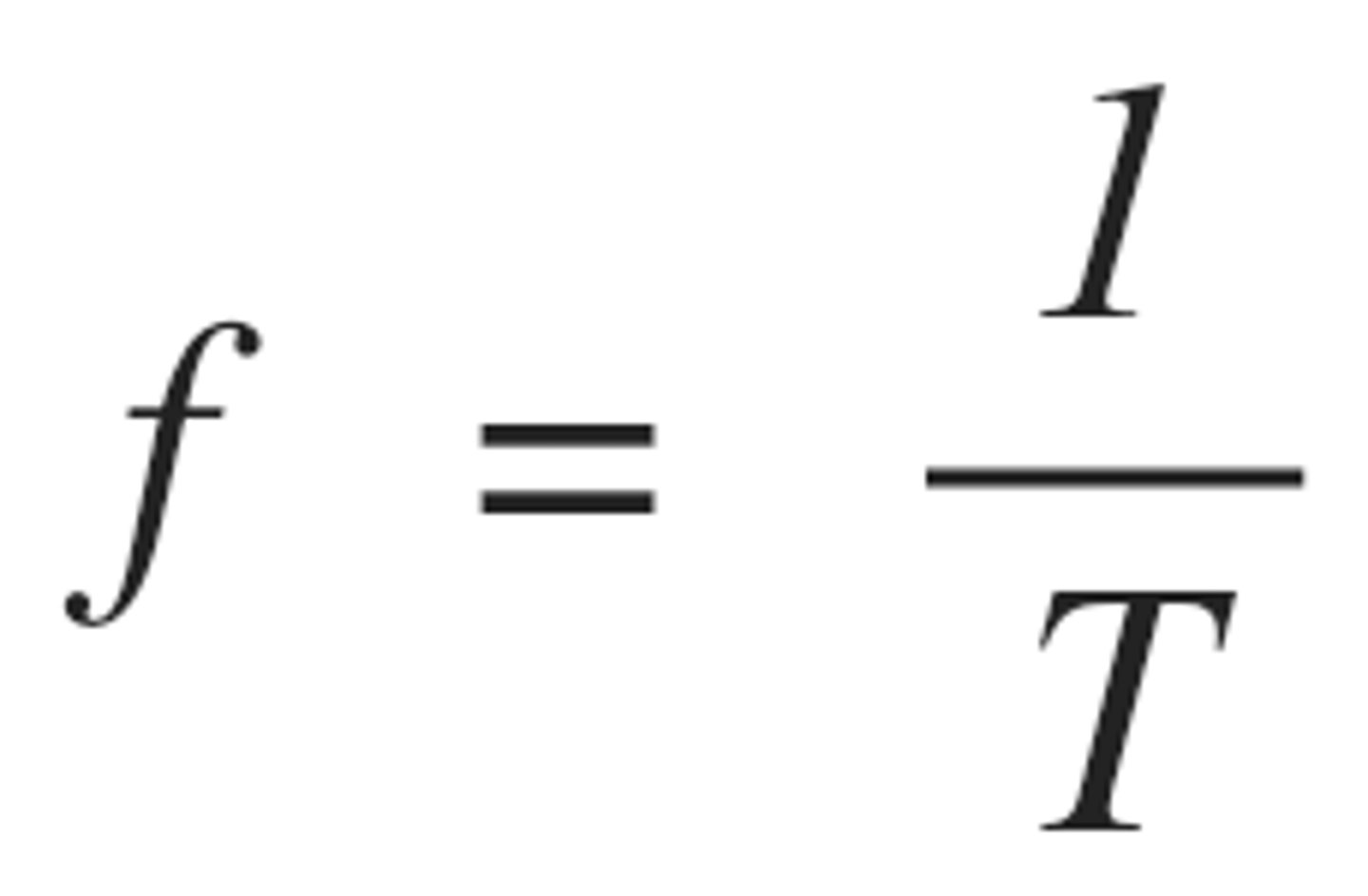
Wave Speed Equation
v = f x λ