Wharton Earth Systems Final Exam Review Vocabulary
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards for Wharton Earth Systems Final Exam Review
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Big Bang Theory
Theory explaining the origin of the universe.
Star Properties
Characteristics of stars, such as brightness, temperature, and size.
Star Color
Indicates the star's surface temperature.
How is the universe changing?
The universe is expanding.
Low/Average Mass Star Life Cycle
Nebula, protostar, main sequence, red giant, planetary nebula, white dwarf.
High Mass Star Life Cycle
Nebula, protostar, main sequence, red supergiant, supernova, neutron star or black hole.
Star Spectrum
Tells us about a star's chemical composition, temperature, and density.
Sun's Age
Approximately 4.6 billion years old.
Sun's Surface Features
Sunspots, prominences, flares, etc.
Light Year
The distance light travels in one year.
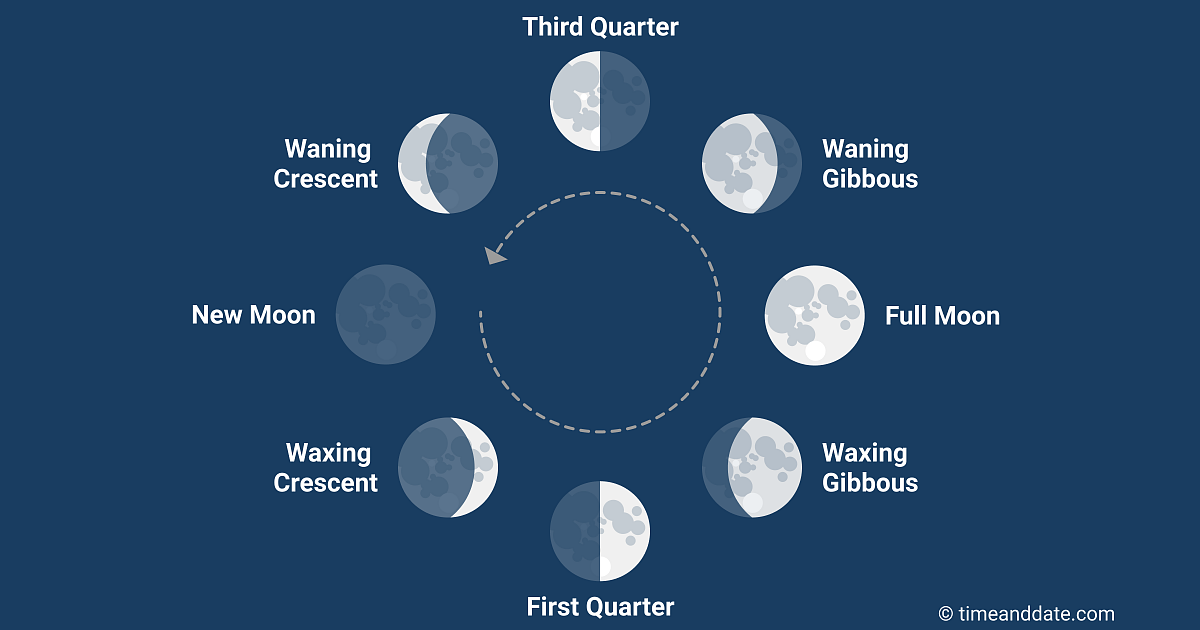
Lunar Phases
New moon, waxing crescent, first quarter, waxing gibbous, full moon, waning gibbous, third quarter, waning crescent
What are the major parts of the electromagnetic spectrum?
Radio
Microwave
Infrared
Visible
Ultraviolet
X-ray
Gamma rays
“Remember My Incredible Visual Ultra X-ray Guide”
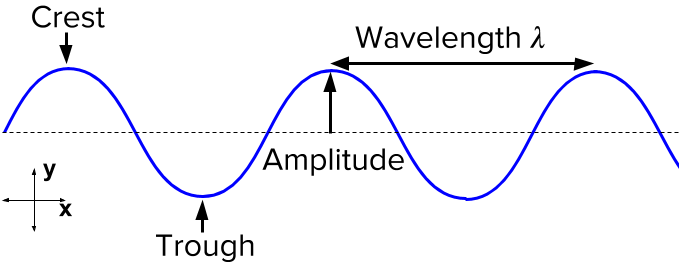
Transverse Wave Parts
Crest, trough, wavelength, amplitude.
Red Shift
Object moves away
Blue Shift
Object moves closer
Lunar Features
Maria, highlands, craters.
HR Diagram
Hertzsprung-Russell diagram; a scatter plot of stars showing the relationship between the stars' absolute magnitudes or luminosities versus their stellar classifications or effective temperatures.
Lunar Eclipse
Earth blocks sunlight from reaching the Moon.
Solar Eclipse
Moon blocks sunlight from reaching Earth.
Planetesimals
Small celestial bodies that collided to form planets.
Umbra
The darkest part of a shadow.
Penumbra
The lighter part of a shadow where light is partially blocked.
Coriolis Effect
The apparent deflection of moving objects when they are viewed from a rotating reference frame.
Air Masses
Large bodies of air with uniform temperature and humidity characteristics.
Orographic effect
Changes in atmospheric conditions caused by a change in elevation of terrain.
Climate
The average weather conditions in an area over a long period.
Weather
The state of the atmosphere at a particular place and time.
Fossils
Preserved remains or traces of ancient organisms.
Alfred Wegener
Proposed the Theory of Continental Drift.
Lithosphere
The rigid outer part of the earth, consisting of the crust and upper mantle.
Asthenosphere
The plastic-like, mechanically weak and ductile region of the upper mantle.
Law of Superposition
The principle that in undisturbed rock layers, the oldest layers are at the bottom and the youngest are at the top.
Salinity
The measure of dissolved salts in water.
Polarity
A molecule with an uneven distribution of electrical charge.
Adhesion
The attraction between molecules of different substances.
Cohesion
The attraction between molecules of the same substance.
Ecology
The study of the interactions between organisms and their environment.
Autotrophs
Organisms that produce their own food.
Heterotrophs
Organisms that consume other organisms for food.
Carrying Capacity
The maximum number of individuals an environment can support.