BMS123 Heme Metabolism
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
iron (Fe2+) + porphyrin ring
Heme
indispensable partner for hemoglobin, myoglobin, peroxidase, cytochromes (electron transport chain) and cytochrome p450 enzymes
What is heme important for?
liver and RBC precursors are most active due to their demand for heme-containing p450 enzymes (detox pathways for liver) and hemoglobin (red cell precursors)
what cells are most active during heme synthesis? why?
- iron is at center
- iron held by four bonds to N's of porphyrin ring
- heme iron can form two more bonds, one on each side of the planar porphyrin ring
describe heme structure
in myoglobin or hemoglobin, one of these positions is coordinated to the side chain of a histidine residue of the global molecule, whereas the other positions Is available to bind oxygen
what is structurally different about myoglobin and hemoglobin?
polypeptide + cofactor (heme)
hemoglobin and myoglobin is made up of
exclusively in RBCs, where its main function is to transport oxygen from the lungs to the tissues
Hemoglobin is found in... and functions as...
hemeprotein in skeletal and heart muscle; function as a reservoir for oxygen and an oxygen carrier that increases the rate of transport of oxygen within the muscle cell
Myoglobin is found in... and functions as...
2 alpha chains and 2 beta chains;
4 hemes
Hemoglobin A (Hb) # globin and # cofactor
1 polypeptide and 1 heme
Myoglobin (Mb) # globin and # cofactor
deoxy form of hemoglobin
T form of hemoglobin
taut or tense because there's a stronger interaction between alpha and beta chain when there is no oxygen binding to the polypeptides
what does T in T-form of hemoglobin mean?
when Hb binds to oxygens
R form of hemoglobin
relax because the interaction between alpha and beta chain is less when there is oxygen binding to the polypeptides
what does R mean in R-form of hemoglobin?
no oxygen bound, so strong hydrophobic bond between alpha and beta chains to form stable alpha-beta dimers - also weak ionic and hydrogen bonds occur between dimers
describe the T structure of hemoglobin (what kind of bonds...)
hemoglobin is oxygenated, so ionic and hydrogen bonds between alpha-beta dimers are broken
what bonds are broken in hemoglobin R-form?
autosomal recessive disease (heterozygotes are fine, homozygotes are not) -- polypeptide gene of hemoglobin is mutated, so does not form normal structure
what is sickle cell anemia?
2 normal alpha-globing + 2 mutant beta-globins
Sickle-Cell Hemoglobin (HbS) structure
valine (nonpolar AA) instead of glutamic acid (polar)
what is the mutant beta chain of HbS
when Hb doesn't have oxygen, it will aggregate to form long fibrous polymers = sickle cell shape
How is the shape of an RBC altered in sickle-cell anemia?
sickle shape RBC is easy to break down and clog small blood vessels - if RBC breaks down, this is anemia
How is anemia caused by the sickle-cell shape?
hereditary disorder characterized by impaired synthesis of polypeptide chain of hemoglobin - either alpha or beta chain mutation (alpha-thalassemia and beta-thalassemia)
Thalassemia
oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve
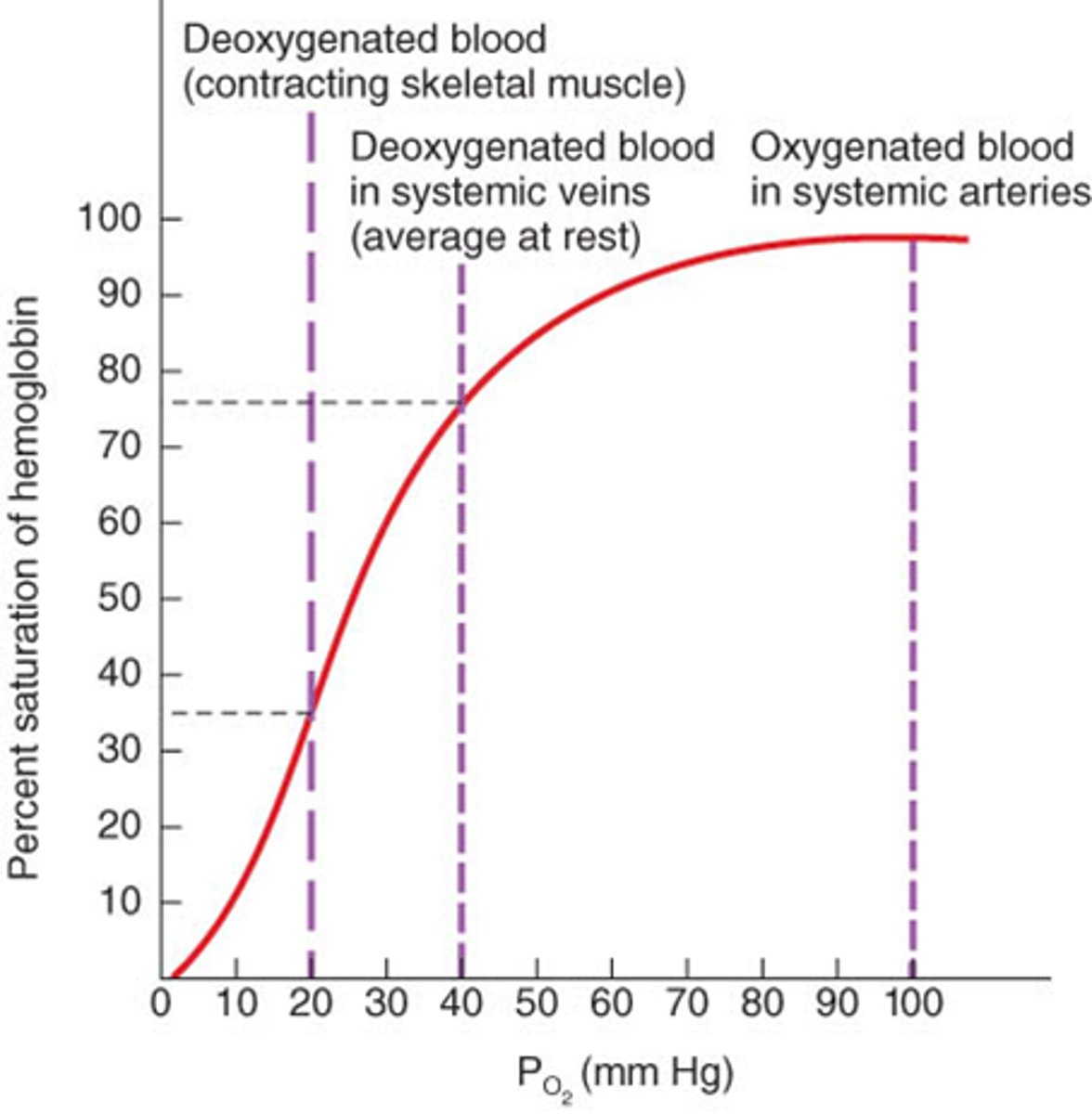
oxygen partial pressure (pO2) in units of mmHg (tells us the oxygen level)
what is the x-axis of the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve?
hemoglobin saturation (%)
what is the y-axis of the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve?
25% saturation because hemoglobin can maximally bind to 4 oxygen molecules
when Hb binds to one oxygen, it is called...
curve of hemoglobin-oxygen dissociation curve is sigmoidal, which means that Hb has an increasing affinity for O2 as the number of bound O2 increases
what is positive cooperatively of hemoglobin?
partial pressure of oxygen in blood when hemoglobin is 50% saturated
P50
p50 decrease, affinity increases
when the oxygen hemoglobin dissociation curve shifts left, what does it mean?
p50 increases, affinity decreases
when oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve shifts right, what does it mean?
decreasing the pH or increasing pCO2 results in a decreased oxygen affinity of Hb, a shift to right in the oxygen-dissociation curve, and stabilizes the T-state
what is the Bohr effect?
metabolism (lactic acid or H2CO3)
in the Bohr effect, where does H+ and CO2 come from?
lungs have a higher pH, tissues a lower pH
differential pH gradient
favors the unloading of oxygen in the peripheral tissues, and the loading of oxygen in the lungs
what does the differential pH gradient favor?
CO2, pH, 2,3-DPG and temperature
what factors can change oxygen hemoglobin dissociation curve?
because it affects Hb's binding ability to oxygen
why is it important to know that CO2, H+, and 2-3-DPG bind to Hb?
increase CO2, temp, 2-3 DPG;
decrease pH
what happens to levels of CO2, temperature, 2-3-DPG, and pH when we exercise?
we need Hb to unload more oxygen to the tissue --> Hb affinity to oxygen decreases (increase p50, shift right)
what happens to Hb during exercise? how does this affect p50? how does this affect the oxygen hemoglobin dissociation curve?
binds to Hb with greater affinity than oxygen, results in impaired oxygen transport and utilization
why is CO toxic?
carboxyhemoglobin (COHb)
what does CO and Hb form?
shifts the curve to the left, Hb is unable to release oxygen to the tissue
how does CO affect the oxygen dissociation curve?
not enough oxygen in the tissue
tissue hypoxia
100% oxygen at high pressure (hyperbaric oxygen therapy)
how to treat CO poisoning?
- 2 alpha chains and 2 gamma chains
- higher affinity for oxygen than HbA
Fetal hemoglobin (HbF) characteristics
the transfer of oxygen from the maternal circulation across the placenta to the RBCs of the fetus
what does the higher oxygen affinity of HbF facilitate?
a covalently glycated form of Hb that results from a non-enzymatic reaction with glucose
what is A1C?
over 6.5%
diabetes diagnosis if HbA1C levels
the A1C
the higher the blood glucose, the higher
measures glucose levels over 2-3 months and provides a snapshot of average blood glucose levels - used to monitor pre-diabetes and diabetes
what is the HbA1C test?
hormone produced by kidneys, in response to cellular hypoxia
Erythropoietin
production of mature RBCs in bone marrow
what does erythropoietin promote?
HIF is no hydroxylated in hypoxia and promotes expression of erythropoietin, which travels through blood and promotes production of mature RBC in bone marrow, so that more oxygen can be carried to tissue
how does our kidney sense hypoxia?
hypoxia-inducible factor
HIF
hydroxylate and degraded by proteasome
normal condition HIF
inject EPO which increases RBC number and ability to carry oxygen
why would an athlete blood dope?
livers, erythrocyte-producing cells of the bone marrow
where are the major sites of heme biosynthesis?
glycine (AA) and succinyl-CoA --> form porphyrin rings and add iron at the end
what are the initial molecules of heme synthesis?
the first reaction and last 2 steps in the formation of porphyrins occur in mitochondria; intermediate steps in the cytosol
where do the steps of heme synthesis occur in the cell?
mitochondria and are unable to synthesize heme
what do mature RBCs lack?
pyridoxal phosphate (vitamin B6) because it is a cofactor of ALA
what is the rate limiting step in heme synthesis?
heme and hemming (heme containing iron)
what is ALA synthesis inhibited by?
results in no heme, no hemoglobin, and therefore anemia
what does vitamin B6 deficiency cause?
drugs which require hepatic cytochrome P450 monooxygenase system for metabolism
what is ALA synthase activity induced by?
at the 2nd and at the last steps
where does lead inhibit the heme synthesis pathway?
when heme synthesis is inhibited because iron is not being consumed by the heme/hemoglobin synthesis pathway
when does iron accumulate?
blue-purplish line on the gums seen in lead poisoning caused by a reaction between circulating lead with sulphur ions released by oral bacterial activity
Burton's line
most is in RBC hemoglobin; 10% in muscle fibers (myoglobin); other tissues (enzymes and cytochromes); liver, macrophages, bone marrow
where is iron located in the body?
iron absorption from the digestive tract
how is iron hemostasis regulated?
1. Ferrus form of iron as part of heme (ani al products like steak, muscle and blood)
2. non-heme iron (Fe3+ form) (plant-based food)
what are the two forms of food iron?
not directly; reduced to ferrous (Fe2+) by ferrireductase; DMT1 mediates proton-dependent Fe2+ import; dietary heme is transported by HCP1
how does our intestine intake iron?
divalent metal transporter
DMT1
heme carrier protein
HCP1
releases iron, allowing it to enter the same pool as non-heme iron
what does heme oxygenate do once inside the cell?
disorder resulting from buildup of certain chemicals related to RBC proteins
porphyria
defects in heme synthesis, resulting in the accumulation and increased excretion of porphyrins or porphyrin precursors
what is porphyria caused by?
autosomal dominant (except congenital erythropoietin porphyria is autosomal recessive)
what kind of disease is porphyria
decreased heme synthesis leads to increased ALA synthase activity (due to loss of negative feedback) and super accumulation of intermediates
what exacerbates the presentation of porphyria?
shows reddish brown discoloration of teeth
symptoms of congenital erythropoeitc porphyria
1. in macrophage, heme oxygenate releases irons from heme and produce green pigment biliverdin
2. biliverdin reductase changes biliverdin to bilirubin, a red-orange pigment
(both reactions use NADPH)
3. Bilirubin is not water dissolvable and binds to albumin in blood, then transported to liver
4. in liver, 2 glucuronic acids are added to bilirubin to increase water solubility
5. conjugated bilirubin is excreted into the bile, later feces and urine
explain heme degradation (5 main steps)
after 120 days
when does heme degradation occur?
reflect the varying pattern of intermediates that occur during heme degradation (green pigment biliverdin and then red-orange pigment bilirubin)
what explains bruise changing colors?
conjugated bilirubin is actively transported into bile canaliculi and bile
secretion of bilirubin into bile
yellow color of skin, nail beds and sclera caused by deposition of bilirubin, secondary to increased bilirubin levels in the blood
jaundice
symptom of an underlying disorder
jaundice is not a disease, but a
1. hemolytic jaundice
2. obstructive jaundice
3. hepatocellular jaundice
4. neonatal jaundice
what are the four types of jaundice?
massive lysis of RBC over the processing ability of liver (ex: sickle cell anemia)
what is hemolytic jaundice?
physically block the excretion to bile (ex: gallstone)
what is obstructive jaundice?
damage of liver cell (ex: cirrhosis or hepatitis)
what is hepatocellular jaundice?
bilirubin UDP is low at birth (ex: preterm baby; treat with blue fluorescent light)
what is neonatal jaundice