CH 22 & 23: atypical vascular disorders & alternative tests and therapeutic interventions
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
The majority of blood flow reducing lesions are related to ____________ changes.
Atherosclerotic
Although a majority of blood flow reducing lesions are related to atherosclerotic changes, there are still some nonatherosclerotic related pathologies.
List 3 nonatherosclerotic changes.
Subclavian steal
Takayasu’s Arteritis
Temporal arteritis
Name the pathology:
“A condition in which blood going to the brain is shunted away from the cerebral circulation because the subclavian or innominate artery has a high-grade stenosis or occlusion proximal to the takeoff of the vertebral artery.”
Subclavian steal
Subclavian steal syndrome is when…
The blood going to the brain is shunted away from the cerebral circulation because the _________ or ________ artery…
Has a high-grade _________ or _________ proximal to the takeoff of the…
________ artery
Subclavian or Innominate
Stenosis or occlusion
Vertebral
Subclavian steal syndrome can result in (1)_________ flow in the ipsilateral (2)________ artery to provide blood flow to the arm.
Retrograde
Vertebral
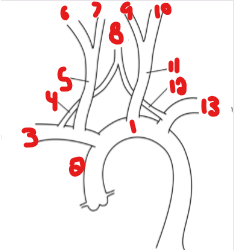
List the crossed-out parts on this structure.
Aortic Arch
Innominate
Right Subclavian
Vertebral
Right CCA
Right ICA
Right ECA
Basilar
Left ECA
Left ICA
Left CCA
Vertebral
Left Subclavian
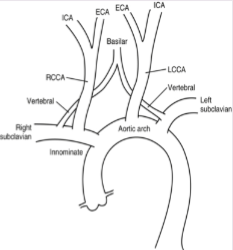
Where will a stenosis or occlusion be found with subclavian steal syndrome? (2)
Subclavian artery
Innominate artery
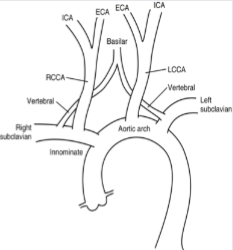
Where will retrograde flow be seen with subclavian steal syndrome?
Vertebral artery
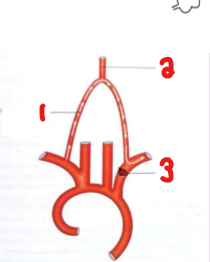
Label the crossed-out structures on this image.
Vertebral artery
Basilar artery
Blocked subclavian artery
The vertebral artery normally takes blood __________ brain.
To the
The abnormal vertebral artery will take blood __________ brain.
Away from
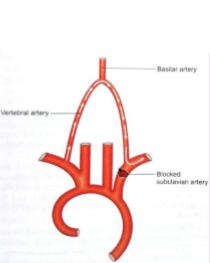
What pathology is occurring here?
Explain why you think that.
Subclavian Steal
The blockage in the subclavian steal syndrome has caused retrograde flow in the ipsilateral vertebral artery.
Patients with subclavian steal syndrome typically present with what symptoms?
Asymptomatic
Subclavian steal syndrome is more common on which side of the neck?
Left
Which side of the neck will present with a lower brachial blood pressure if a patient is suffering from subclavian steal syndrome on the right?
Right
Which side of the neck will present with a lower brachial blood pressure if a patient is suffering from subclavian steal syndrome on the left?
Left
Which side of the arm will present with a decrease in pulses if a patient is suffering from subclavian steal syndrome on the right?
Right
Which side of the arm will present with a decrease in pulses if a patient is suffering from subclavian steal syndrome on the left?
Left
Pulses in the affected arm of subclavian steal syndrome are…
Decreased
How does flow resistance appear in the vertebral artery with subclavian steal syndrome?
Explain why.
Increased
Due to feeding a higher resistance bed of the upper extremity
Why would flow resistance increase in the vertebral artery with subclavian steal syndrome?
Because it is feeding a higher resistance bed of the upper extremity
List the 4 treatment options available for subclavian steal syndrome.
Bypass graft
Endarterectomy
Balloon angioplasty
Stenting
Flow resistance in subclavian steal syndrome goes from (1)____ to (2)____ when it is feeding a higher resistance bed of the upper extremity.
Low
High
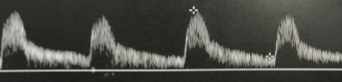
This waveform was dopplered at the vertebral artery.
Does this waveform appear normal or abnormal?
If abnormal, explain why.
Normal

This waveform was dopplered at the vertebral artery.
Does this waveform appear normal or abnormal?
If abnormal, explain why.
Abnormal
Retrograde
High resistive
Pick the best option: Blood flow in the ipsilateral vertebral artery may have an early systolic deceleration
Subclavian stenosis
Complete occlusion
Subclavian stenosis
Describe the ‘bunny in profile.’
When a waveform has an early systolic deceleration
What is the name of the waveform finding when there is an early systolic deceleration?
Bunny in profile
A progression of subclavian steal syndrome will show flow in the ipsilateral vertebral artery as…
Bidirectional
What is another term for ‘bidirectional flow’?
To-Fro
List the 2 ways the waveform can change with progressive subclavian steal syndrome.
Bidirectional (To-Fro)
Complete flow reversal
Subclavian Steal Syndrome that has progressed pass the bidirectional flow stage can then show what?
Complete flow reversal
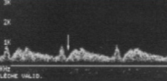
What is seen here?
What pathology can be associated with this finding?
Early systolic deceleration (bunny in profile)
Subclavian steal syndrome
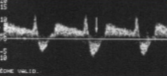
What is seen here?
What pathology can be associated with this finding?
Bidirectional flow (To-Fro)
Incomplete steal (Subclavian steal syndrome)
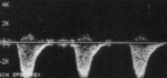
What is seen here?
What pathology can be associated with this finding?
Complete flow reversal
Complete steal (Subclavian steal syndrome)
List the sonographic characteristic of an incomplete steal?
Bidirectional flow (To-Fro)
List the sonographic characteristic of a complete steal?
Complete flow reversal
Takayasu’s Arteritis is thought to be an ____________ disorder.
Autoimmune
Name the pathology:
“A fairly rare disease involving inflammation in the walls of the largest arteries (aorta and its main branches)”
Takayasu’s Arteritis
Describe what ‘Takayasu’s Arteritis’ is.
Inflammation in the walls of the largest arteries in the body
Takayasu’s Arteritis involves what structures? (2)
Aorta
Aortic branches
Inflammation of the arterial walls will cause it to do what? (2)
Thicken
Narrow
The ‘Pulseless Disease’ is another name for which pathology?
Takayasu’s Arteritis
How will the resulting arterial stenosis or occlusion from Takayasu’s Arteritis affect the rest of the body?
Causes a weak pulse or loss of pulse in the arms or legs
Which pathology in this lecture can lead to a weak pulse or loss of pulses in the arms or legs?
Takayasu’s Arteritis
Takayasu’s Arteritis can also be referred to as the ____________ disease.
Pulseless
Why is Takayasu’s Arteritis referred to as the ‘Pulseless Disease’?
Due to the stenosis or occlusion causing a weak pulse or loss of pulse in the arms or legs
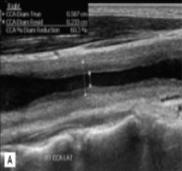
This was seen at the patient’s aorta.
How does it appear sonographically?
What pathology can be assumed here?
Inflamed arterial walls (thickened and narrow)
Takayasu’s Arteritis
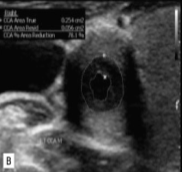
This was seen at the patient’s aorta.
How does it appear sonographically?
What pathology can be assumed here?
Inflamed arterial walls (thickened and narrow)
Takayasu’s Arteritis
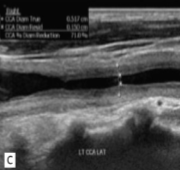
This was seen at the patient’s aorta.
How does it appear sonographically?
What pathology can be assumed here?
Inflamed arterial walls (thickened and narrow)
Takayasu’s Arteritis
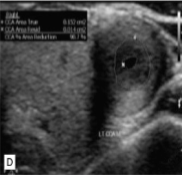
This was seen at the patient’s aorta.
How does it appear sonographically?
What pathology can be assumed here?
Inflamed arterial walls (thickened and narrow)
Takayasu’s Arteritis
List the 9 possible symptoms a patient with Takayasu’s Arteritis can have.
Dizziness
Headaches
Fainting
Weakness
Fatigue
Chest pain
Hypertension
Heart attack
Stroke
Takayasu’s Arteritis is more common in which gender?
Females
Takayasu’s Arteritis is more common in women.
Which specific demographic women in more prone? (2)
Young women
Teenage girls
What is the best imaging modality to use for Takayasu’s Arteritis?
Angiography
On an angiogram, how will Takayasu’s Arteritis appear?
Tubular narrowing of the large arteries
What is the main treatment option for Takayasu’s Arteritis?
Steroid administration (Prednisone)
Prednisone is used to treat what pathology?
Takayasu’s Arteritis
Prednisone is used to treat Takayasu’s Arteritis.
What does it help with?
Reducing inflammation
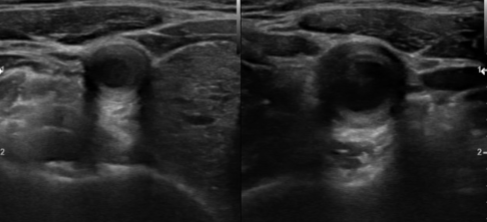
A 33-year-old women comes in complaining of worsening headaches that can even lead to fainting episodes. She has a history of high blood pressure.
What can be seen sonographically?
What pathology can be assumed here?
Inflamed arterial walls (Thickened and narrow)
Takayasu’s Arteritis
Name the pathology:
“The inflammation of the superficial temporal artery and/or its branches.”
Temporal arteritis
What is Temporal Arteritis?
Inflammation of the superficial temporal artery and/or its branches
List the 5 symptoms associated with Temporal Arteritis.
Headaches
Tenderness on palpation of the distal superficial temporal artery
Ipsilateral visual changes
Blindness
Double vision
What is the key sonographic feature of Temporal Arteritis?
Anechoic halo around the vessel lumen
List the 2 sonographic findings of Temporal Arteritis.
Narrowed segment of the vessel
Anechoic halo around the vessel lumen secondary to edema
The anechoic halo seen on Temporal Arteritis is secondary to what other pathology?
Edema
What treatment option is available for Temporal Arteritis?
Steroid therapy
What is needed for a definitive diagnosis of Temporal Arteritis?
Biopsy
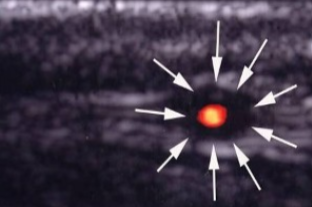
What pathology is seen here?
Temporal Arteritis
How should normal anatomy appear on the films of an arteriogram?
Contrast completely filling the vessel
If a filling defect was seen on an arteriogram, is that normal or abnormal?
Abnormal
If a filling defect was seen on an arteriogram, what can that be an indication of?
Arterial abnormality
What can be used to calculate the percentage of stenosis on the basis of vessel diameter? (2)
Percentage stenosis calculation
Diameter reduction
The percentage stenosis calculation or diameter reduction can be used to calculate the percentage of (1)________ on the basis of vessel (2)___________.
Stenosis
Diameter
What is the formula for diameter reduction?
1 - (d/D) x 100
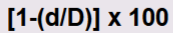
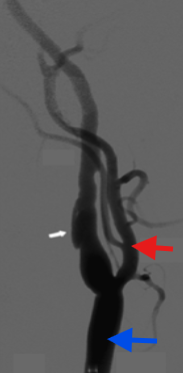
What exam is seen here?
If this was imaged at the neck, what vessel is the white arrow?
Red arrow?
Blue arrow?
Arteriogram
ICA
ECA
CCA
Which imaging modality is very sensitive to the presence of stenosis, leading to an overestimation of the severity of disease process?
MRI
How does an MRI affect the imaging of a stenosis?
Sensitive to stenosis, therefore can overestimate the severity of the disease process
Why would an MRI be done instead, if a carotid ultrasound couldn’t be done? (2)
Limited
Equivocal
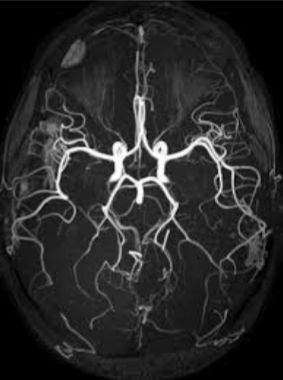
What imaging is seen here of the cranial vessels?
MRI
CT can be done to evaluate for cerebrovascular disease, specifically, to evaluate for the presence or absence of what 5 pathologies?
Cerebral infarctions
Hemorrhage
Tumors
Masses
Anatomic variations
Which imaging modality is used with cerebrovascular disease and to evaluate the status of the extracranial and intracranial vessels?
CT/CTA
What can CTA be used for if not to look for a certain pathology?
Evaluate the status of the extracranial and intracranial vessels
What can CTA be used to look for? (6)
Patency
Stenosis
Occlusion
Hemorrhage
AV malformations
Intracranial aneurysms
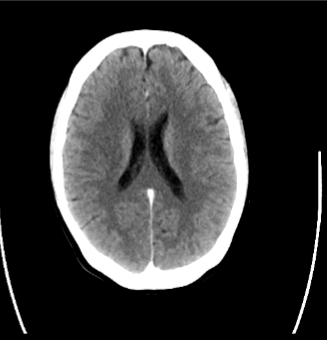
What imaging modality is seen here?
CT/CTA
List the 4 risk factors to control for arterial disease.
Blood pressure medication
Weight control
Stop smoking
Management of diabetes
List the 3 pharmacological therapies done to treat arterial disease.
Aspirin
Antiplatelet/Antithrombotic medication
Statin therapy (Lower cholesterol)
Why is statin therapy used for patients managing arterial disease?
Lowers cholesterol
Name the procedure:
“Surgical removal of intraluminal atherosclerotic material”
Endarterectomy
An Endarterectomy is the surgical removal of what kind of material?
Intraluminal atherosclerotic
What can change about the vessel after a carotid endarterectomy?
Geometry of the vessel
What is used after a carotid endarterectomy has been performed?
Patch closure
How will a patch closure affect the geometry of the vessel after a carotid endarterectomy has been done? (2)
Diameter decreases
Increased velocities
The atherosclerotic process following an endarterectomy can result in what?
Restenosis
The narrowing of the vessel wall within 6 months to 2 years following an endarterectomy is usually attributable to what pathology?
Neointimal hyperplasia
The narrowing of the vessel wall within what time span following an endarterectomy is usually attributable to neointimal hyperplasia?
6 months to 2 years
A stent acts as a…
Scaffold
A stent is designed to do what? (2)
Maintain intraluminal structure
Patency of an artery
Why does post operative surveillance of stented arteries with carotid duplex not rely on the same interpretive guidelines used for diagnosis of a stenosis?
Because some flow acceleration is a normal finding in a stented vessel
Is it normal to see flow acceleration when dopplering inside a stented artery?
Yes