Nitrogen Chemistry and Kc
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What is the haber process and is it ^H+ve or ^H-ve
N2 + 3H2 <=> 2NH3
^H-ve
Why is Nitrogen gas very unreactive
Contains triple bond which is very difficult to break
What is the name, appearance and source of N2O
N2O
Dinitrogen (I) Oxide
Colourless gas
Bacteria in soil
What is the name, appearance and source of NO
Nitrogen (II) Oxide, Colourless gas, Car exhaust/Lightning
What is the name, appearance and source of NO2
Nitrogen (IV) dioxide, Brown gas (toxic), Oxidation of NO in air
What is NO3- and NO2-
NO3- = Nitrate (V)
NO2- = Nitrate (III), contains a lone pair
Draw a dot and cross diagram of NH3 and state its shape
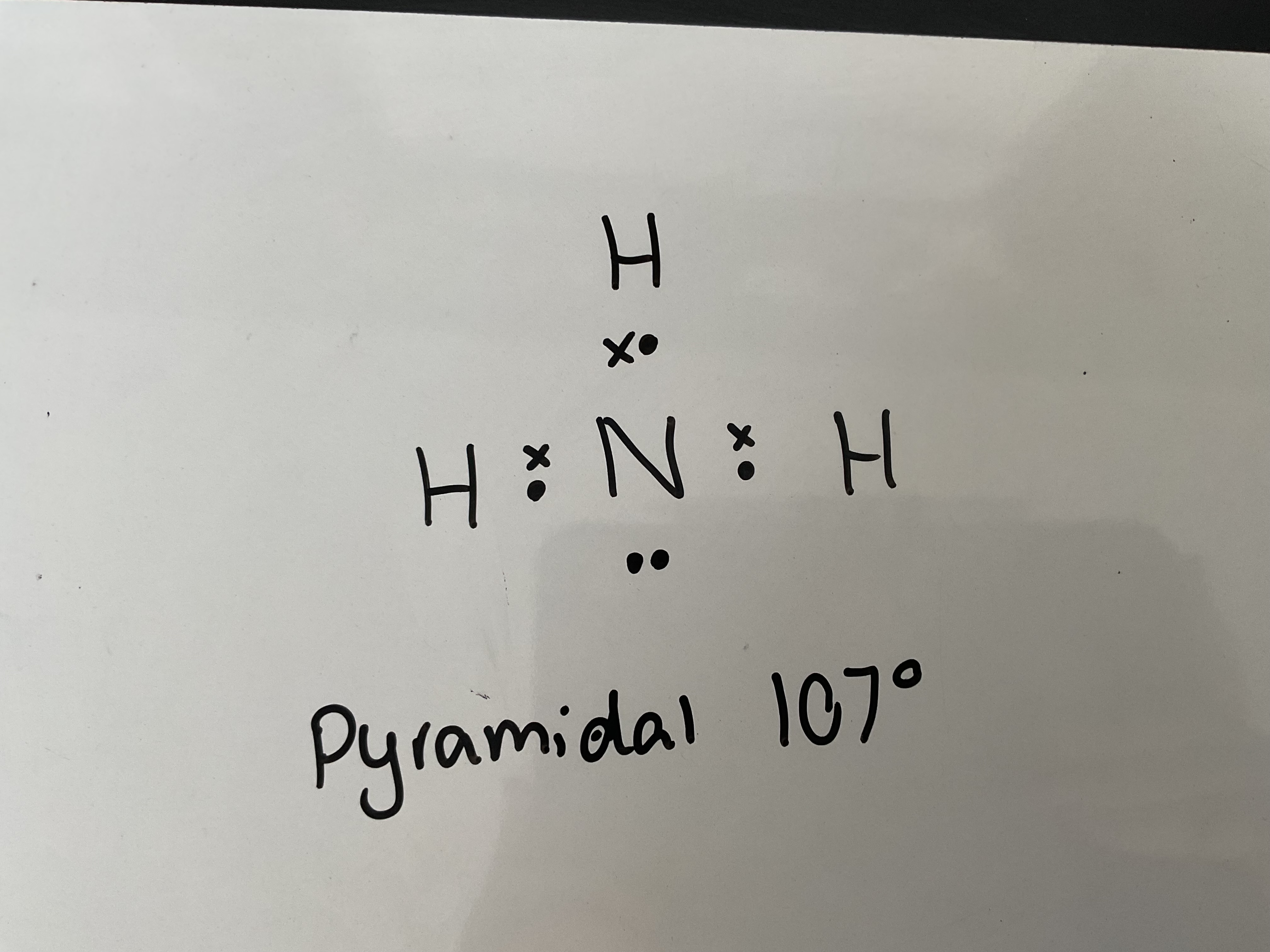
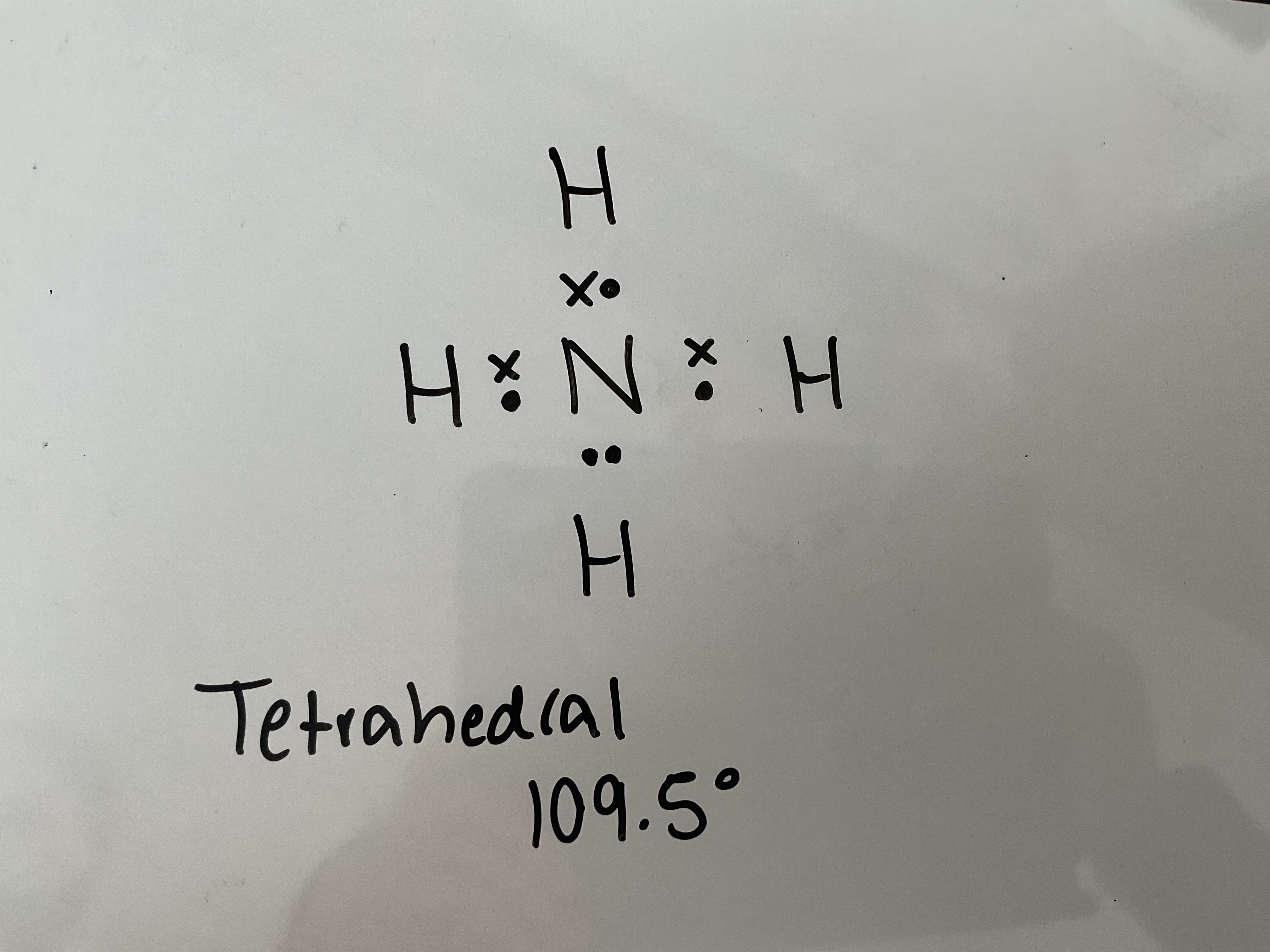
Draw a dot and cross diagram of NH4+ and state its shape
Draw a dot and cross diagram for nitrate (V) and state the shape

Draw a dot and cross diagram for Nitrate (|||) and state its shaped
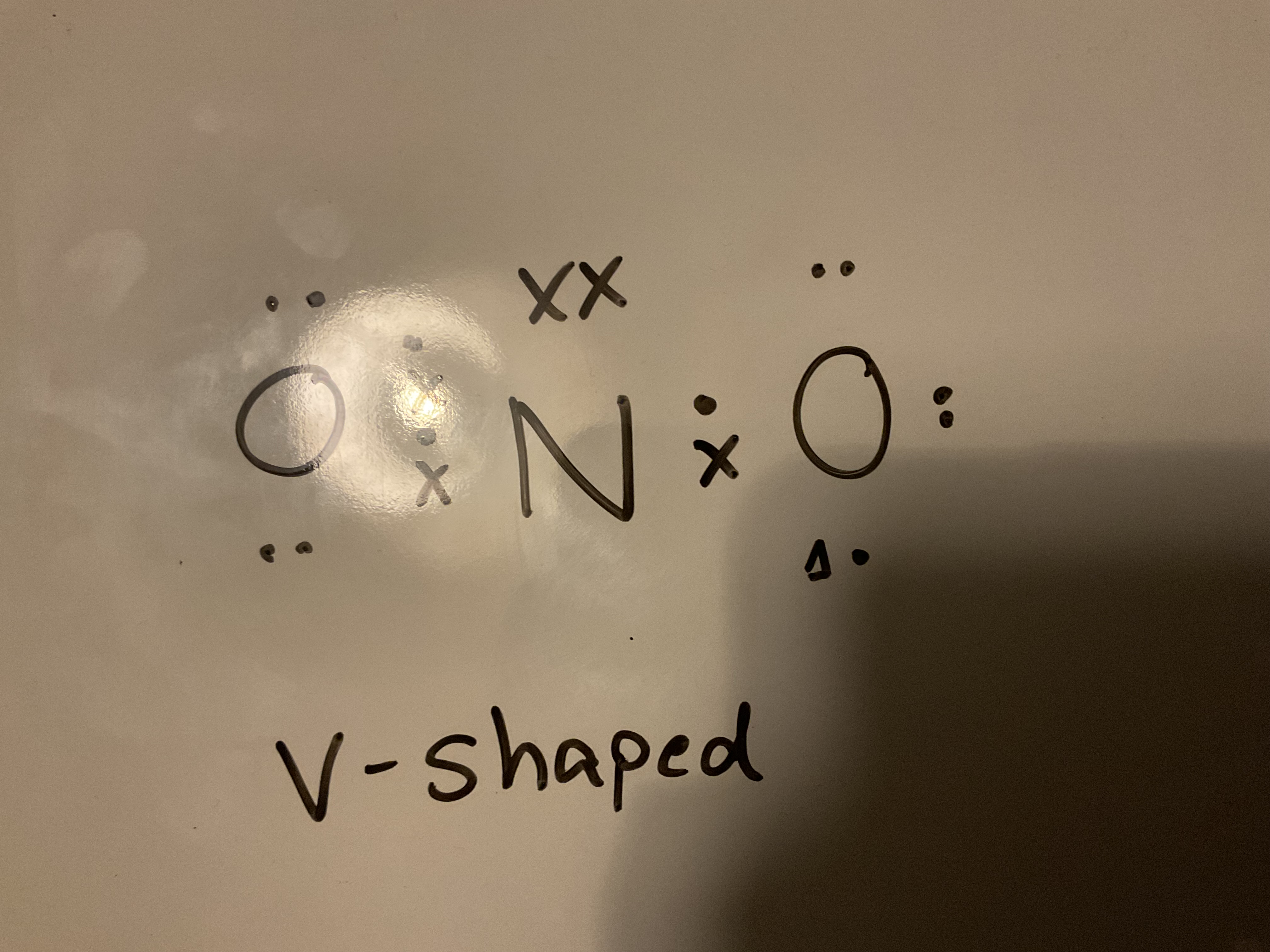
What is the chemical test for nitrate (V) ions (NO3-)
Add NaOH(aq)
Add Devarda’s Alloy
Warm gently
Test gases with damp red litmus paper
Gas evolved (NH3) turns blue
3NO3- + 8Al + 18H2O + 5OH- —> 3NH3 + 8[Al(OH)4]
What is the chemical test for ammonium ions
Add NaOH(aq)
Warm gently
Test gases with damp red litmus paper
Paper turns blue if NH3 is formed
NH4+ + OH- —> NH3 + H2O
If Kc is large, the position of the equilibrium to to the ___, so there are more _______, and a _______ yeild
If Kc is large, the position of the equilibrium to to the RHS, so there are more Products, and a High yeild
If Kc is small, the position of the equilibrium to to the ___, so there are more _______, and a _______ yeild
If Kc is small, the position of the equilibrium to to the LHS, so there are more reactants, and a low yeild
How can Kc be determined experimentally
Measure starting quantities accurately.
Allow the reaction to reach equilibrium (use a catalyst if needed).
Control and measure the temperature (e.g., with a water bath).
After a set period (e.g., 1 week), take a sample.
Determine the concentration of one component (e.g., by titration, pH measurement, or colorimetry).
Calculate moles and concentrations of all species.
Calculate Kc using the equilibrium concentrations.
Repeat sampling at intervals until the Kc value remains constant, confirming equilibrium is reached
How does temperature affect Kc and Equilibrium
Exothermic reactions: Increasing temperature shifts equilibrium to the left, so Kc decreases.
Endothermic reactions: Increasing temperature shifts equilibrium to the right, so Kc increases.
How does pressure affect Kc and Equilibrium
Kc stays the same when pressure changes.
Changing pressure only affects the concentrations of reactants and products temporarily.
If you increase the total pressure, the equilibrium shifts toward the side with fewer moles of gas to reduce the pressure.
To keep Kc unchanged, the ratio of concentrations adjusts (top increases, bottom decreases proportionally).
Decreasing pressure does the opposite—shifts equilibrium to the side with more gas molecules (in this case, to the LHS).
How do catalysts affect Kc
Catalysts do not change Kc.
They speed up the rate at which equilibrium is reached but do not affect the position of equilibrium.