sleep disorders and treamtent
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What is a sleep disorder
this is any medical condition which has a negative effect on sleep patterns, this means an individuals can get too much or too less sleep, have difficult staying or getting to sleep and having abnormal behaviours during sleep.
Investigations of sleep disorders
Detailed patient history
medications
Day time symptoms
Sleep hygiene
Evening symptoms
Does the patient have difficulty falling or staying asleep
Quality of sleep
Sleep diary and sleep questionnaires
Sleep studies
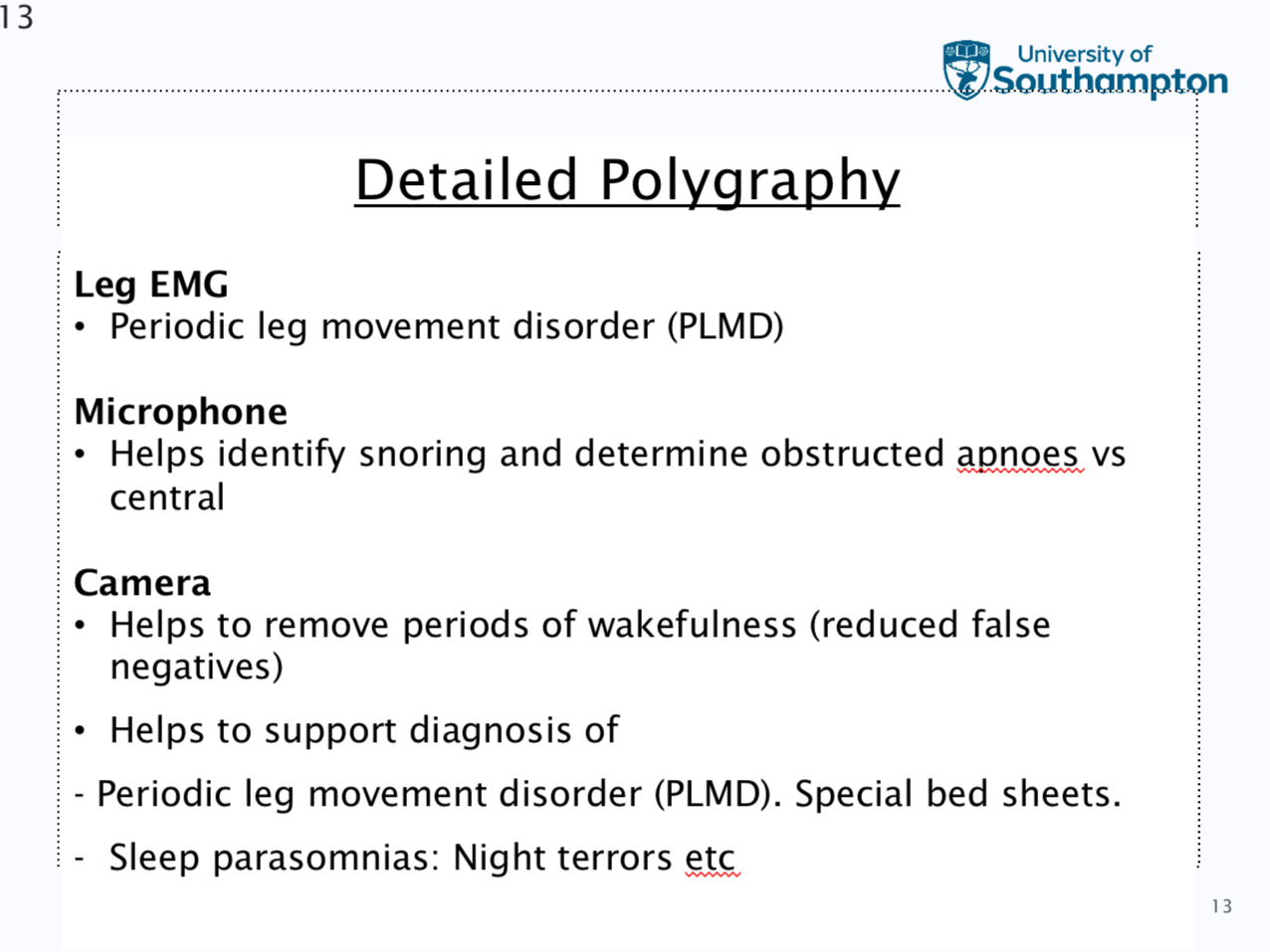
large spectrum of different sleep studies can include: actigraphy, overnight pulse oximetry, polygraphs, detailed polygraphs and polysomography
Actigraphy
This is worn on the wrist or ankle, this contains an accelerometer to record movement. This can be work for days or weeks to build up a patients’s sleep patterns and it is more accurate than a sleep diary
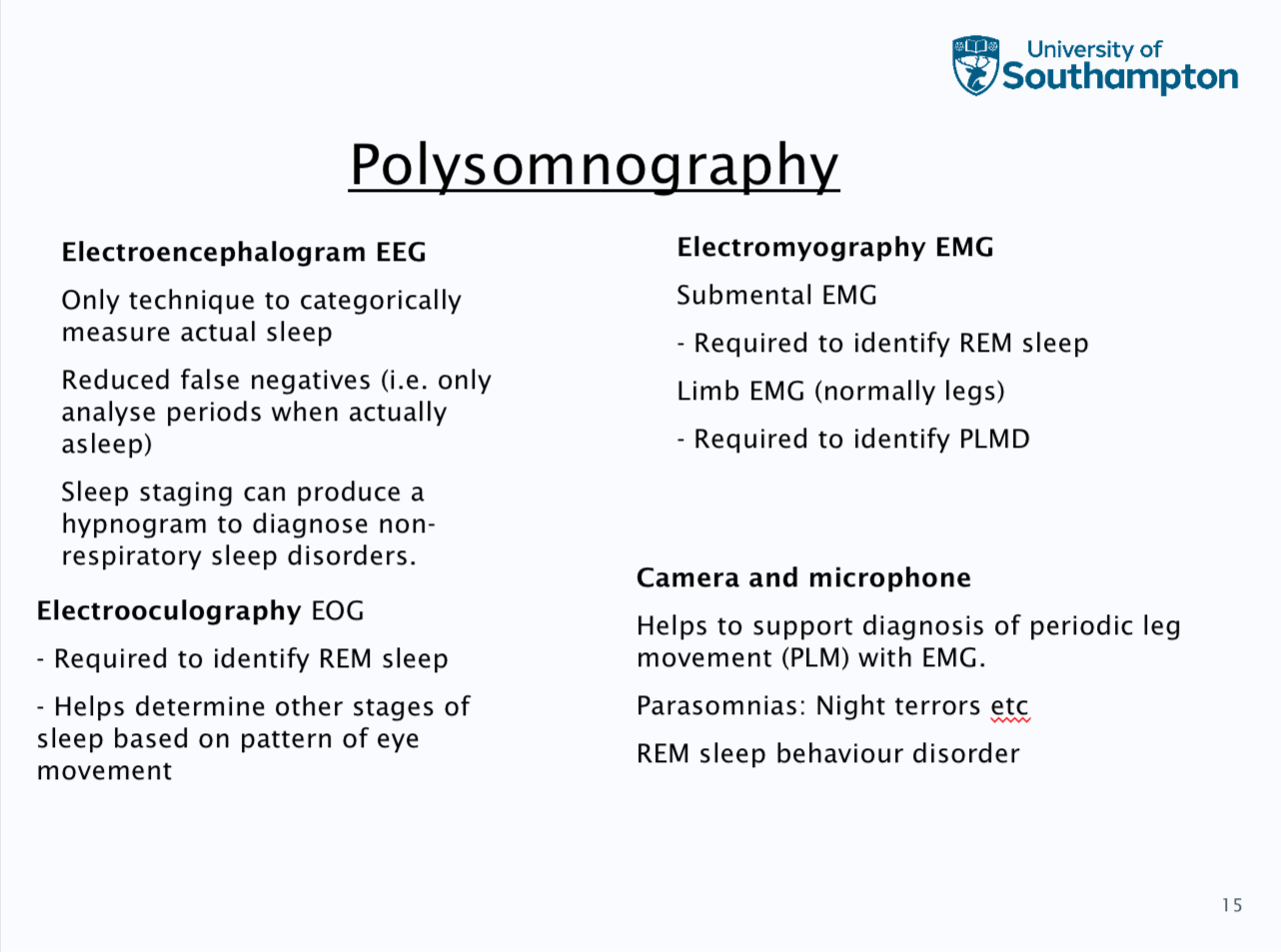
Polygraphy
Nasal flow- this can identify apnoeas that do not cause a significant destruction, this identifies artefact.
Chest and abdomen bands- this helps differentiate between central and obstructive events and mixed events, if flow fails then it can act as a back up and often is of diagnostic quality
Types of sleep disorders
insomnias, circadian rhythm sleep disorders, parasomnias, sleep related movements disorders, excessive sleepiness, narcolepsy and sleep related breathing disorders
Parasomnias
This is abnormal or inappropriate behaviour, an / or movement and / or emotion or perception of demeans which takes place at any time during sleep
This often occurs during transitions between sleep stages, hypnogogic can occur wake to sleep and hypnopmpic can happen from sleep to wake


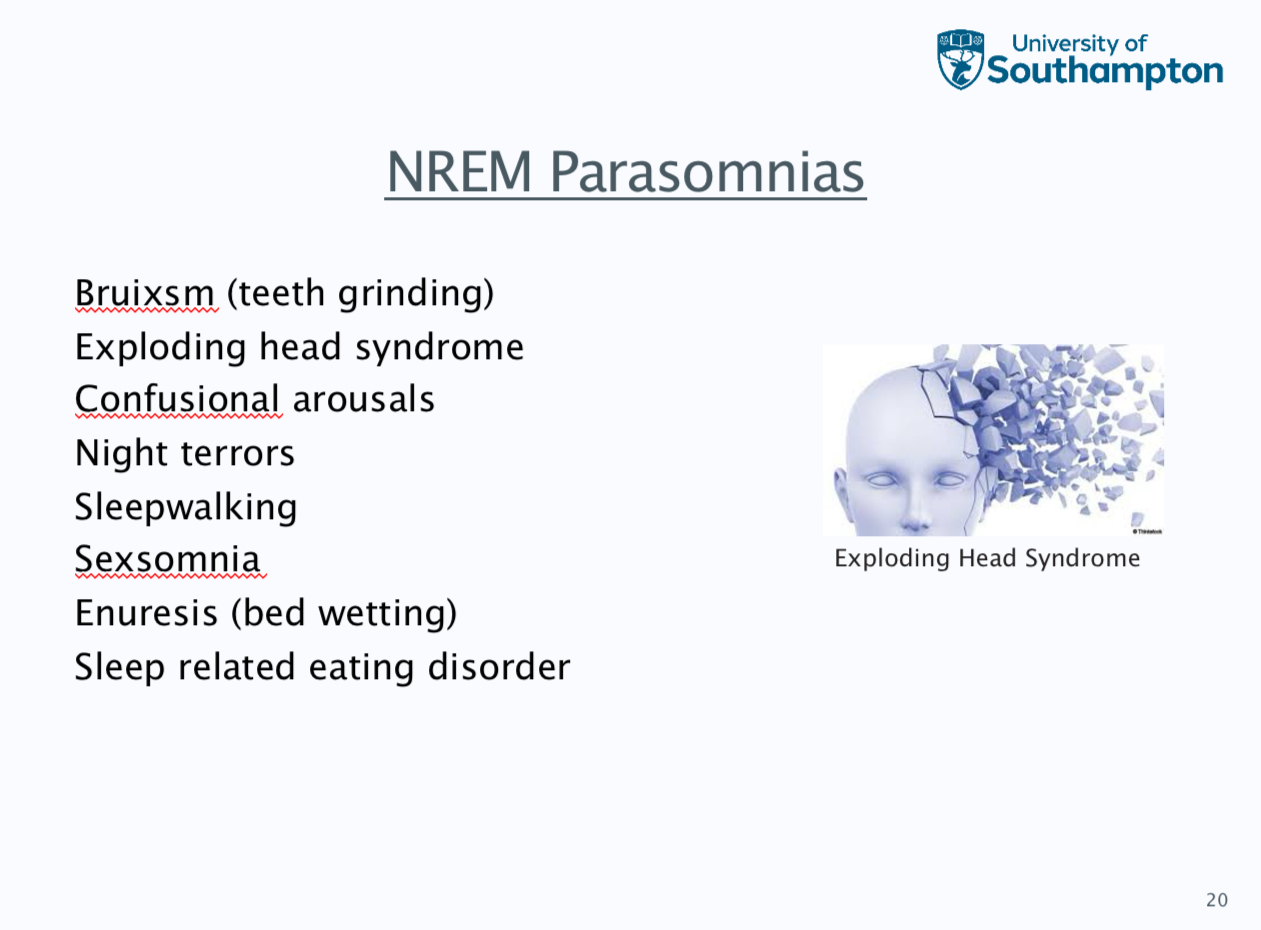
A1: confusional arousals and A2 sleep walking


A3 night terrors and A4 bruxium

Diagnosis and treatment of NREM parasomnias
This is significant delay to diagnosis, clinical history and PSG often necessary but tricky.
Good sleep hygiene and limit anything that causes sleep fragmentation, avoid sleep deprivation, safety assessment sleep environment, drug therapy, treatment for entries (limit food intake, alarm and medication) and education / reassurance

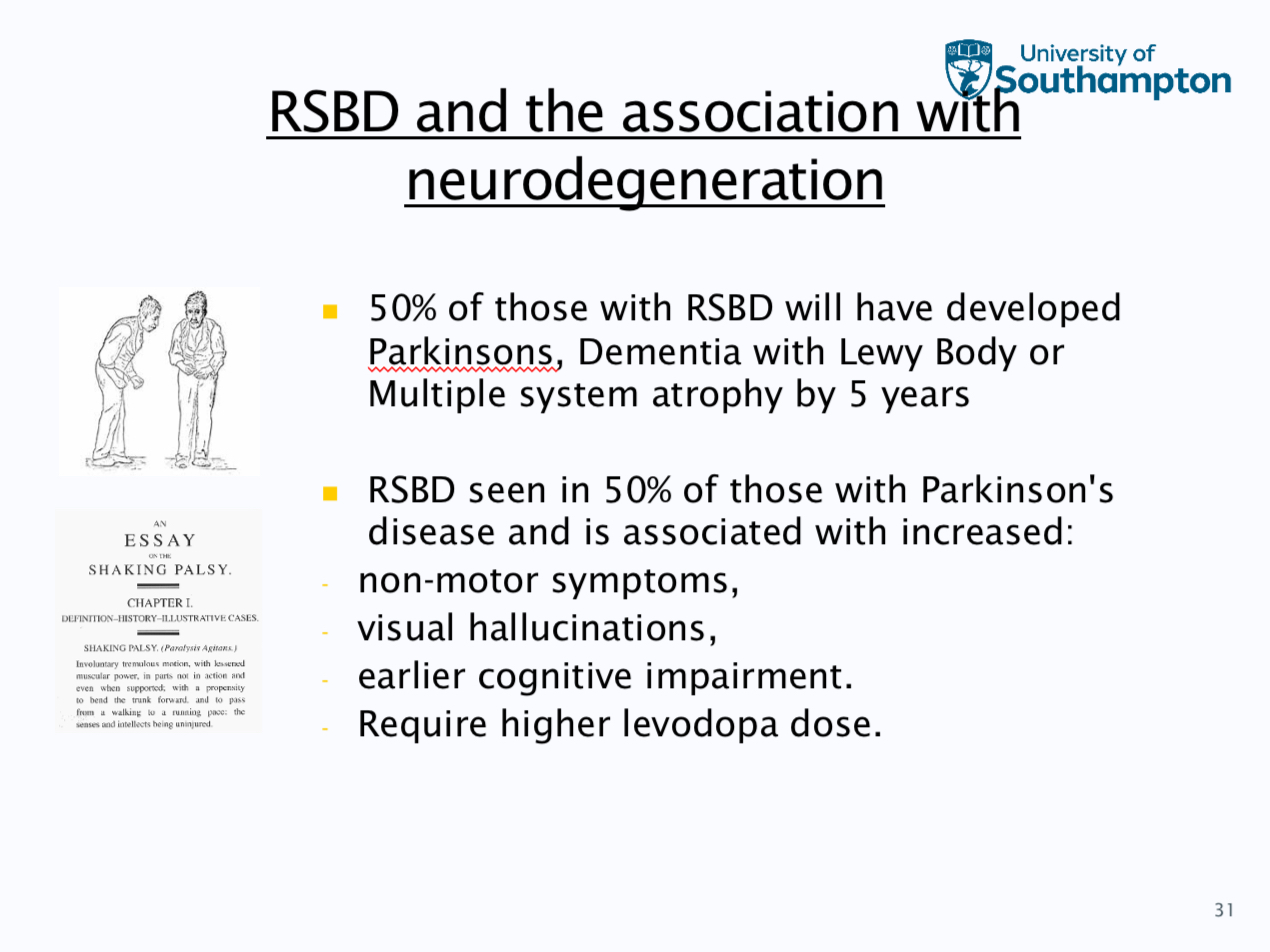
REM sleep parasomnias
REM sleep behaviour disorder, sleep paralysis and nightmares
Treatment can involve- limit sleep deprivation to prevent excessive REM rebound, safety assessment sleep environment can have barrier bed partner, the most common would be drug therapy
anti depressant
Clonazepam
Melatonin

Nightmares
This is the most common REM associated sleep parasomnia, this is frightening dreams which causes awakenings, subjects can usually recall the nightmare, it usually involves fear and anxiety but can also have sadness and anger, there can be an increased autonomic nervous system and usually takes place in the later stages of rem
Restless legs syndrome
Subject experiences an uncomfortable feeling in their legs while at rest, irresistible urge to move legs and symtoms are only relieved by movement, this has a circadian rhythm which is late evening and night only
5-10% of population, often familial and progressive over the years


Periodic limb movement in sleep
Level 1- patients presents with Hx of distributed sleep and daytime sleepiness and other causes ruled out
Level 2 - additions of bed partner witnessed movements
Level 3 actigraphy and watchPAT
Level 4 - PG study with limb EMG and camera
Level 5 - PSG that has additional EEG shown in aroulasa

Excessive sleepiness including narcolepsy
Increased effort t stay awake in low stimulus or inactive situations, increased tendency to fall asleep, sleep onset can occur during active situations such as during a conversation or eating a meal
Subjects experience problems with memory and concentration and are often irritable
Treatment can be good sleep hygiene, avoid sleep deprivation, treatment of underlying medical condition, behavioural strategies, medication like modafinil which increased dopamine levels and amphetamines which increase noradrenaline and dopamine levels
Narcolepsy
Rare neurological condition, this is unable to regulate sleep wake switch
This means that there is excessive daytime sleepiness which can be chronic and persistent, irresistible urge to sleep which it’s recurring throughout the day, sleep attacks a occur during low stimulus situations


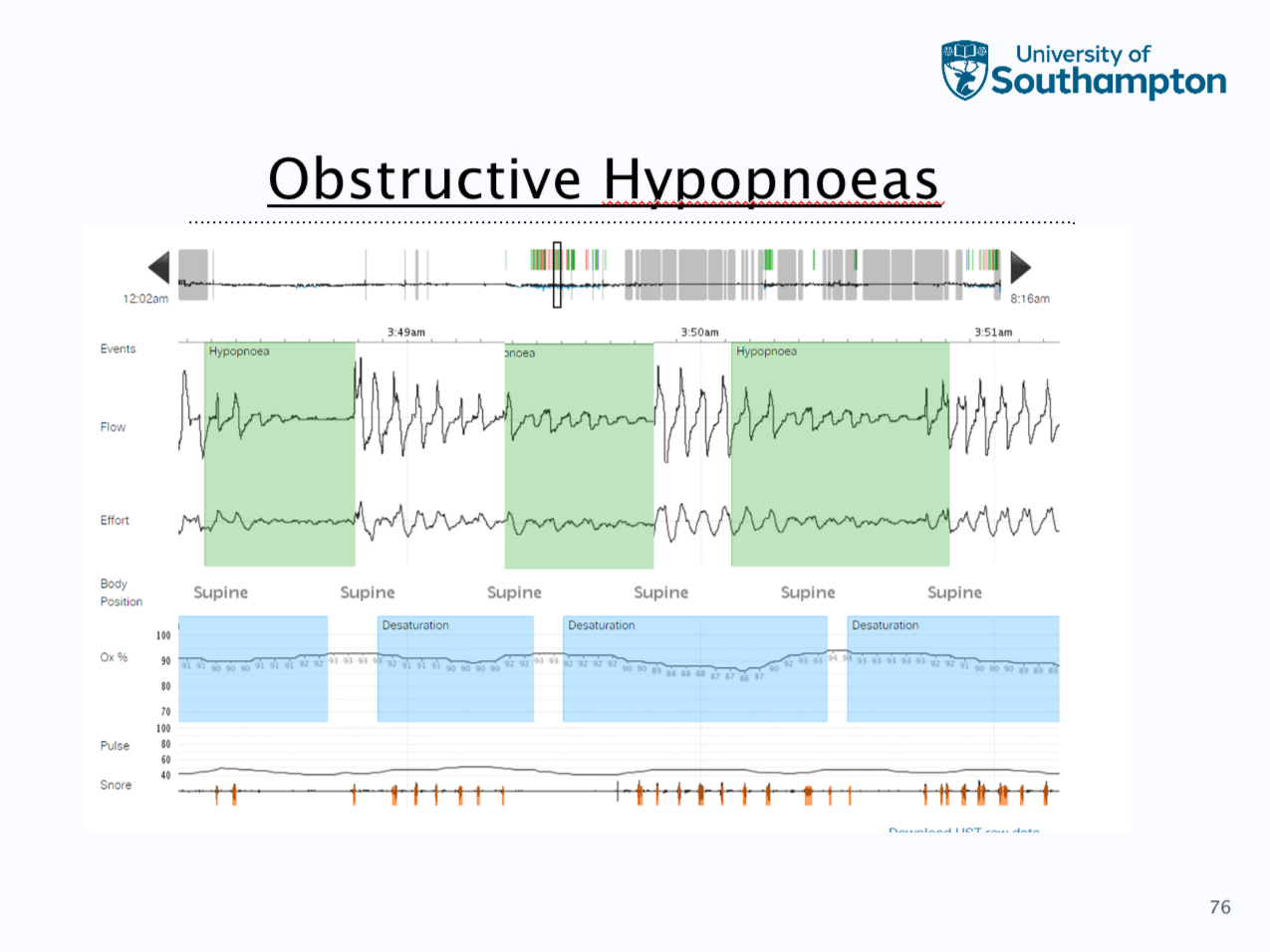
Hypopnoea, obstructive apnoea and respiratory effort related arousal
defined as a 30% reduction in flow lasting and 10 seconds that is associated with a 3% reduction in spo2 from the pre event baseline
Obstructive as a 90% reduction in flow for 10 seconds, these do not need an associated desaturation to be scored, chest band signal maintained i.e. continued effort
Respiratory effort related arousals - this is an aurosal from sleep following a sequence of breaths lasting 10 seconds, this is characterised by increasing a respiratory effort or flattening of the inspirapty flow but does not meet the criteria for a hypopnea
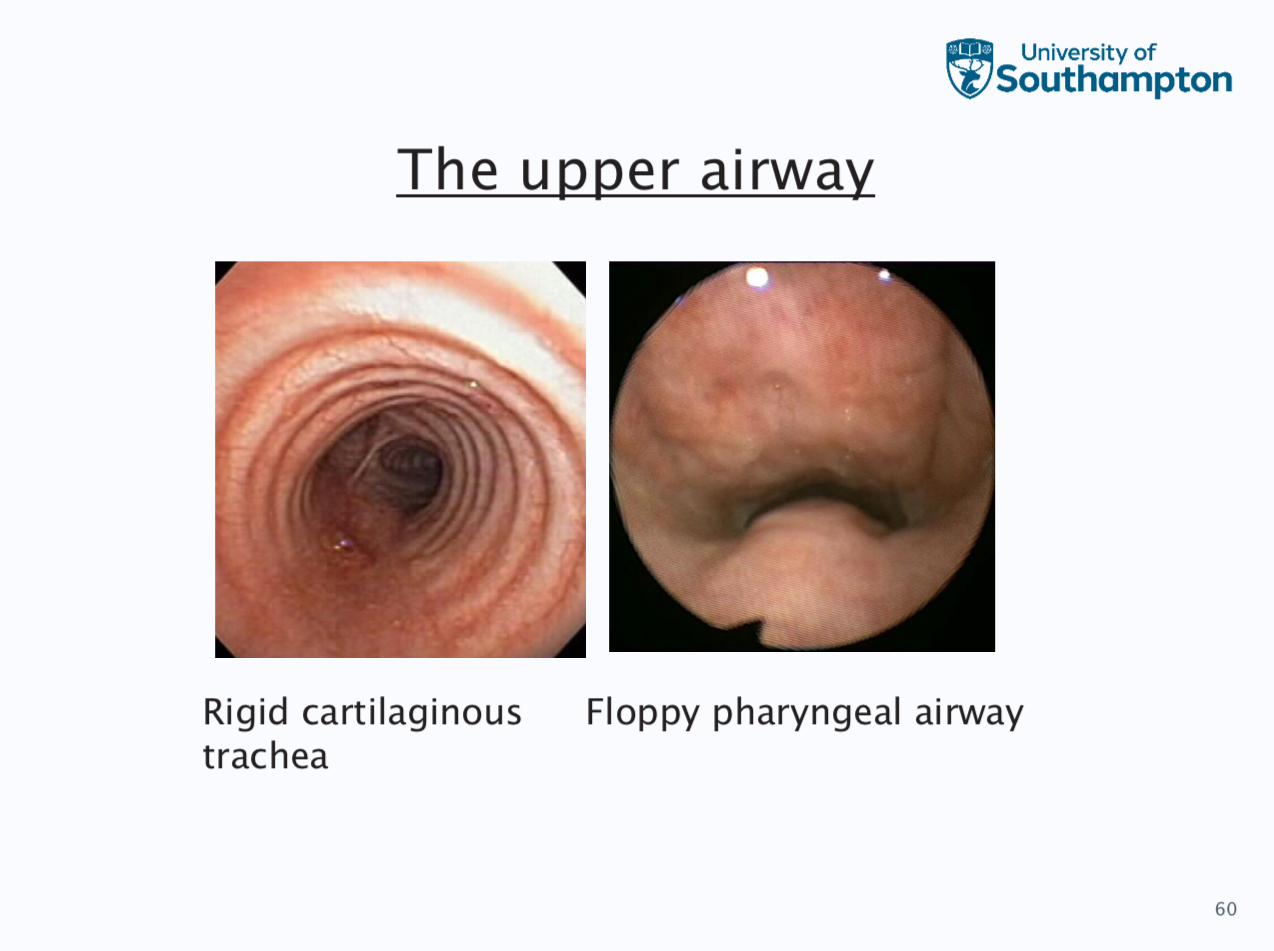
Obstructive sleep apnoea
This does not happen when awake because upper airway dilator muscle sleep the airway open

Risk factors for the upper airway collapse
excess fatty deposits within the bony structure which surrounds the upper airway, this has increased extraluminal pressure
Excess fat tissues in the upper airway
Any physical deformintiy
Muscle weakness of the upper airway
Some risk factors are male, increasing age, obesity, neck circumference, smoking, alcohol, pregnancy
Loud snoring, witnessed apnoeas,, waking up chocking, distracted sleep or insomnia, nocturnal, sweating
Daytime sleepiness, morning headache, dry mouth on waking, problems with memory or concentration, mood or personality changes
Diagnosis - most are undiagnosed, patient history epworth sleepiness scale, bed partner questionnaire, PSG is gold stranded, overnight oximetry and polygraphy
(Look at images)
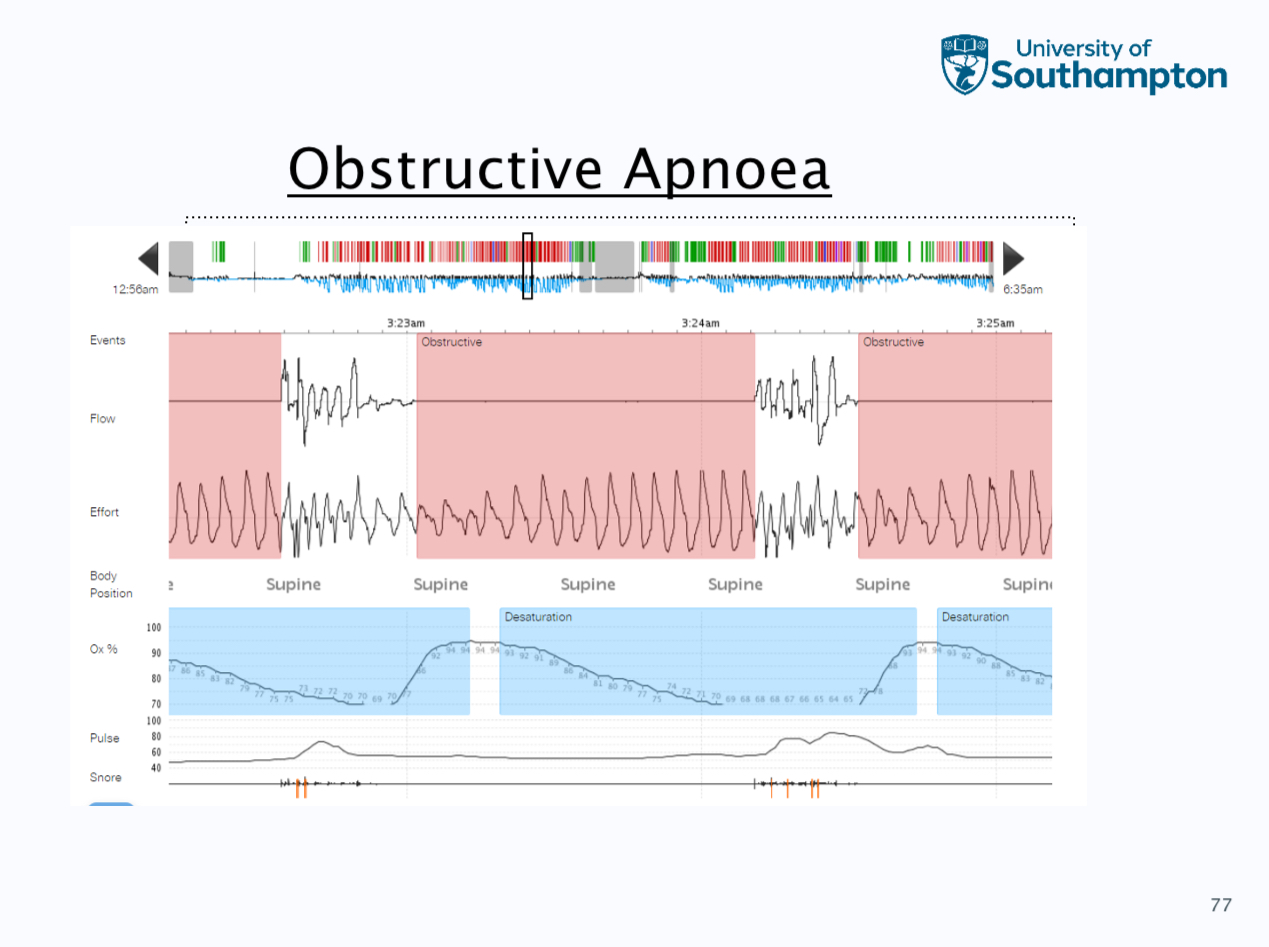
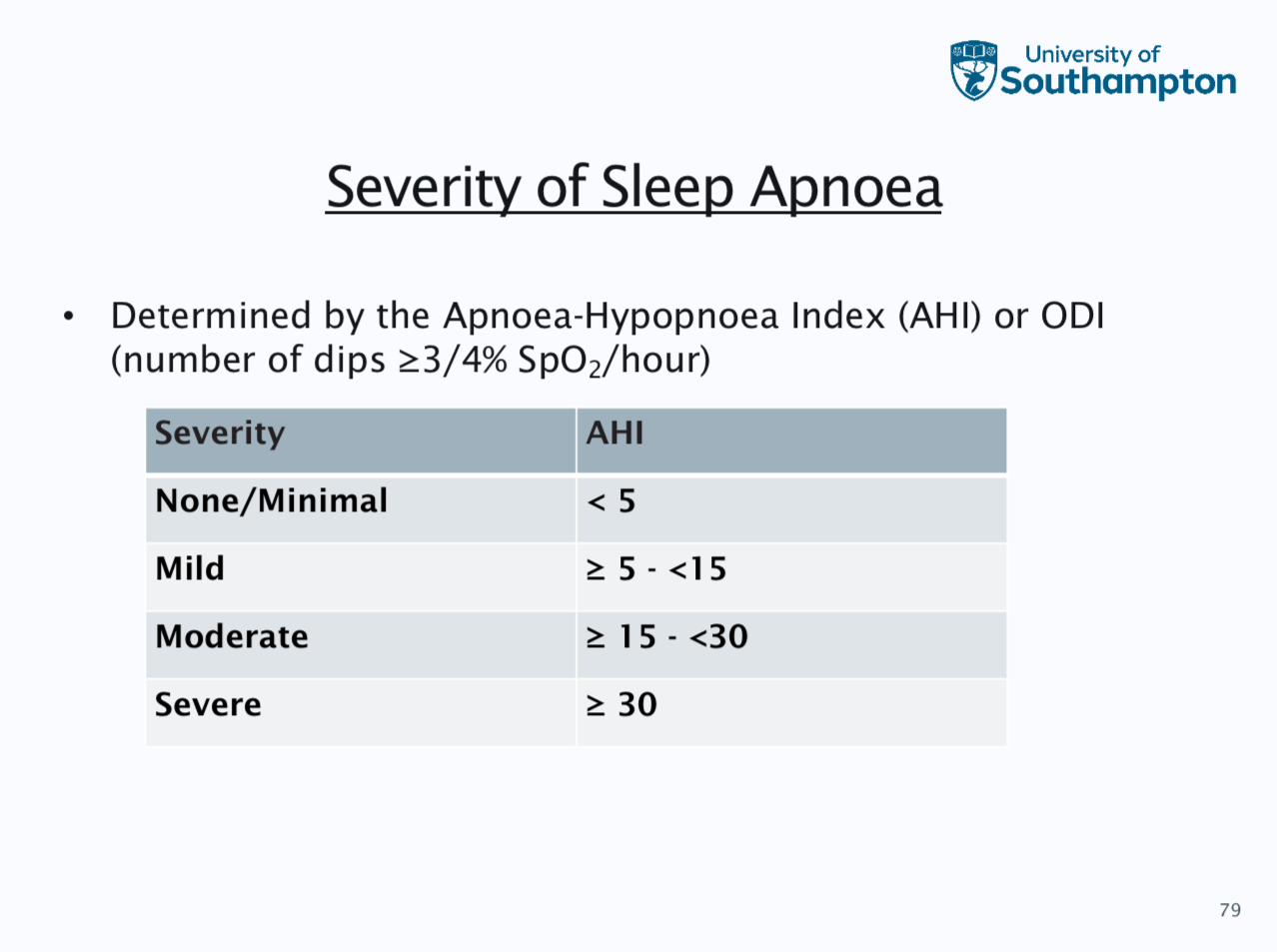
More info on OSA
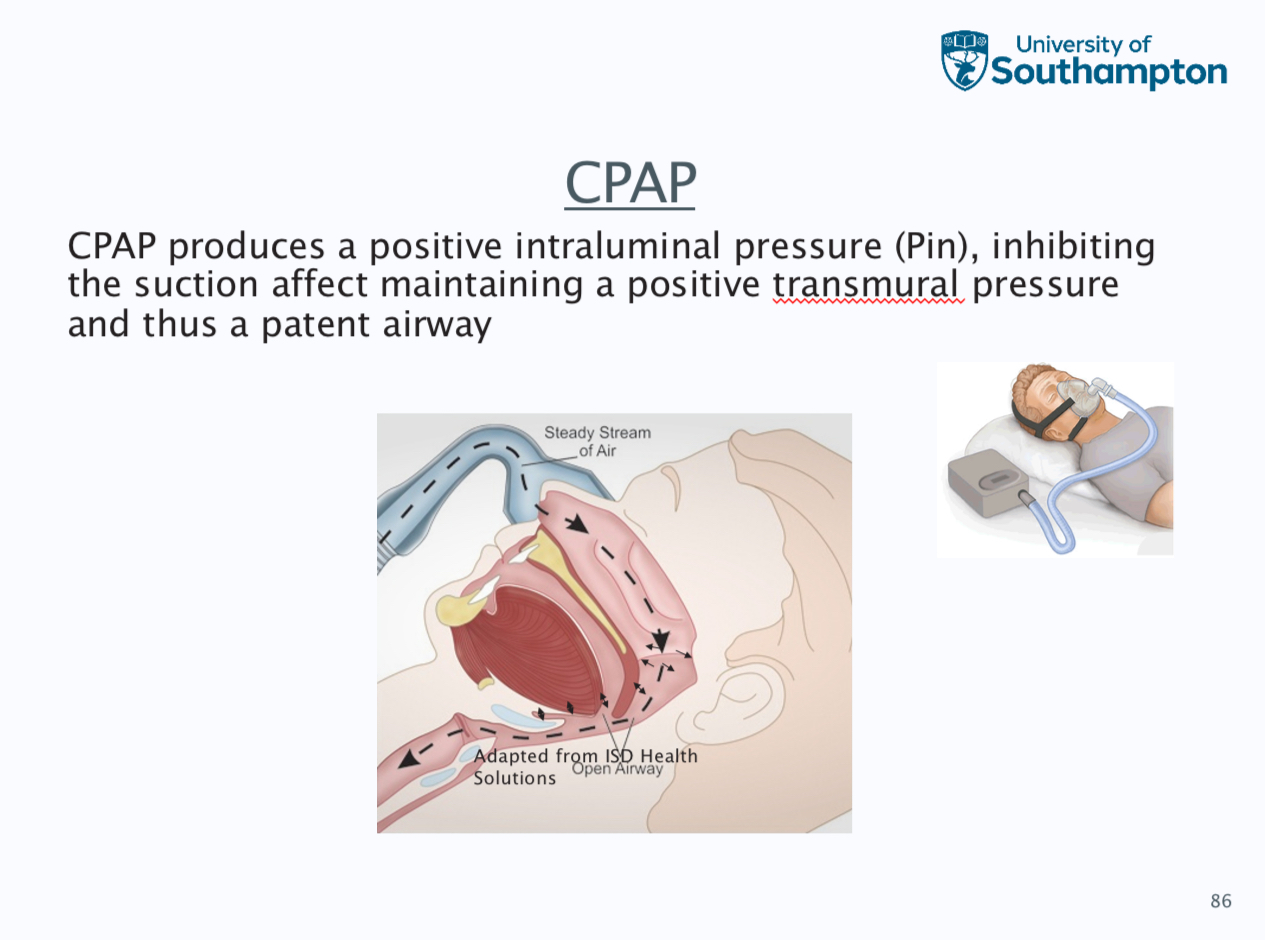
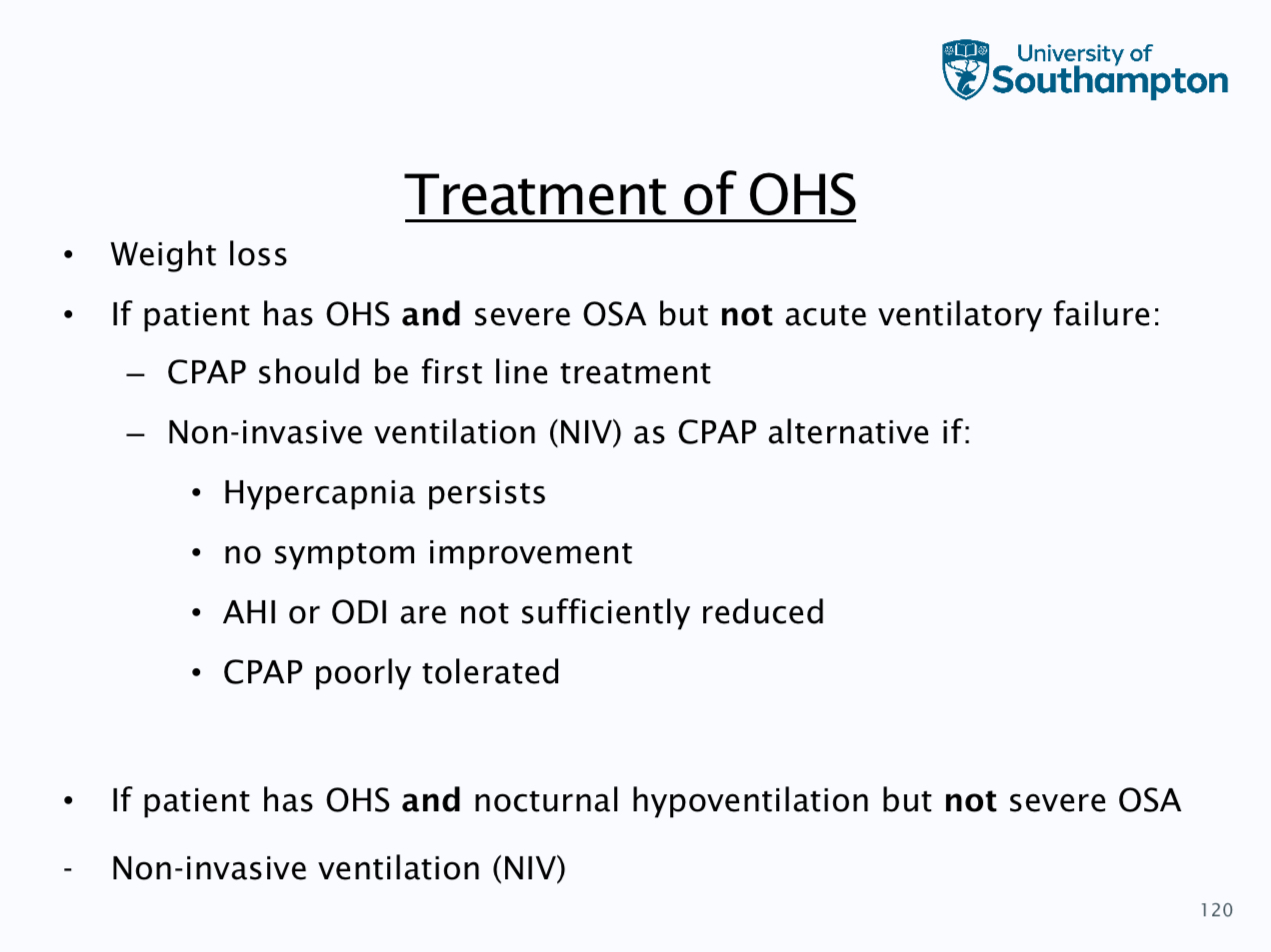
Treatment- weight loss, continuous positive airway pressure, positional therapy, mandibular advancement splints, surgery and hyperglossal nerve stimulation


Extra info
CRAP masks- nasal mask, full face, nasal pillow, total face and hybrid
CRAP pressures should be tirades for each patient to ensure pressure is sufficient to prevent apnoeas
. Pressure are usually in the range of 4-20 cm, auto tirating CRAP, fixed pressure manually chosen from auto - tirating study or algorithm, higher pressures difficult to tolerate and machine can ramp up pressures gently during first hour of use in order that patients can get used to the flow rate
Need to wear for at least 4 hours every night, machines can be noisy and instructive, patient do not like sensation of airflow on face, aversion to wearing headgear, patients may feel claustrophobic etc
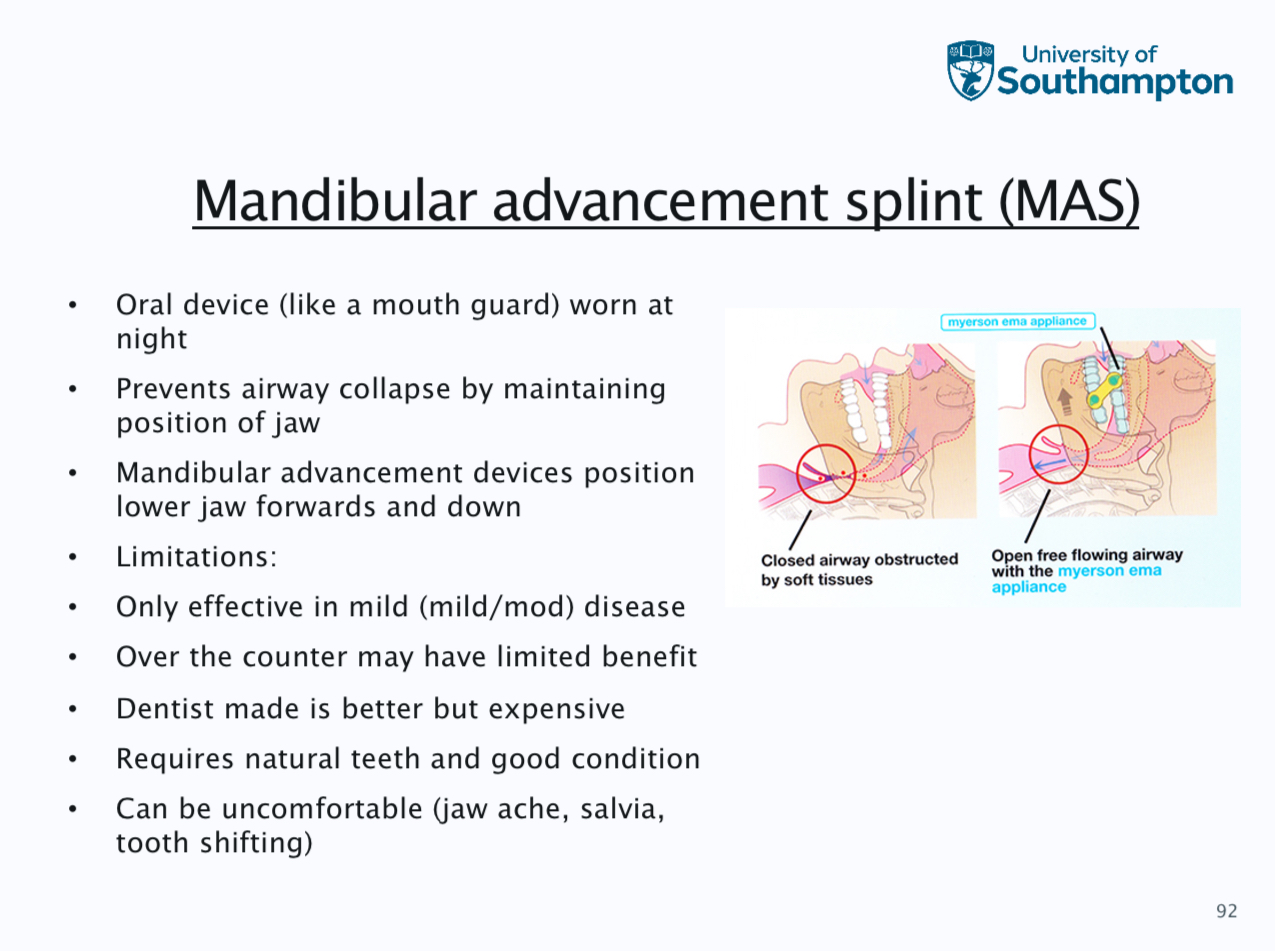
Mandibular advancement slip
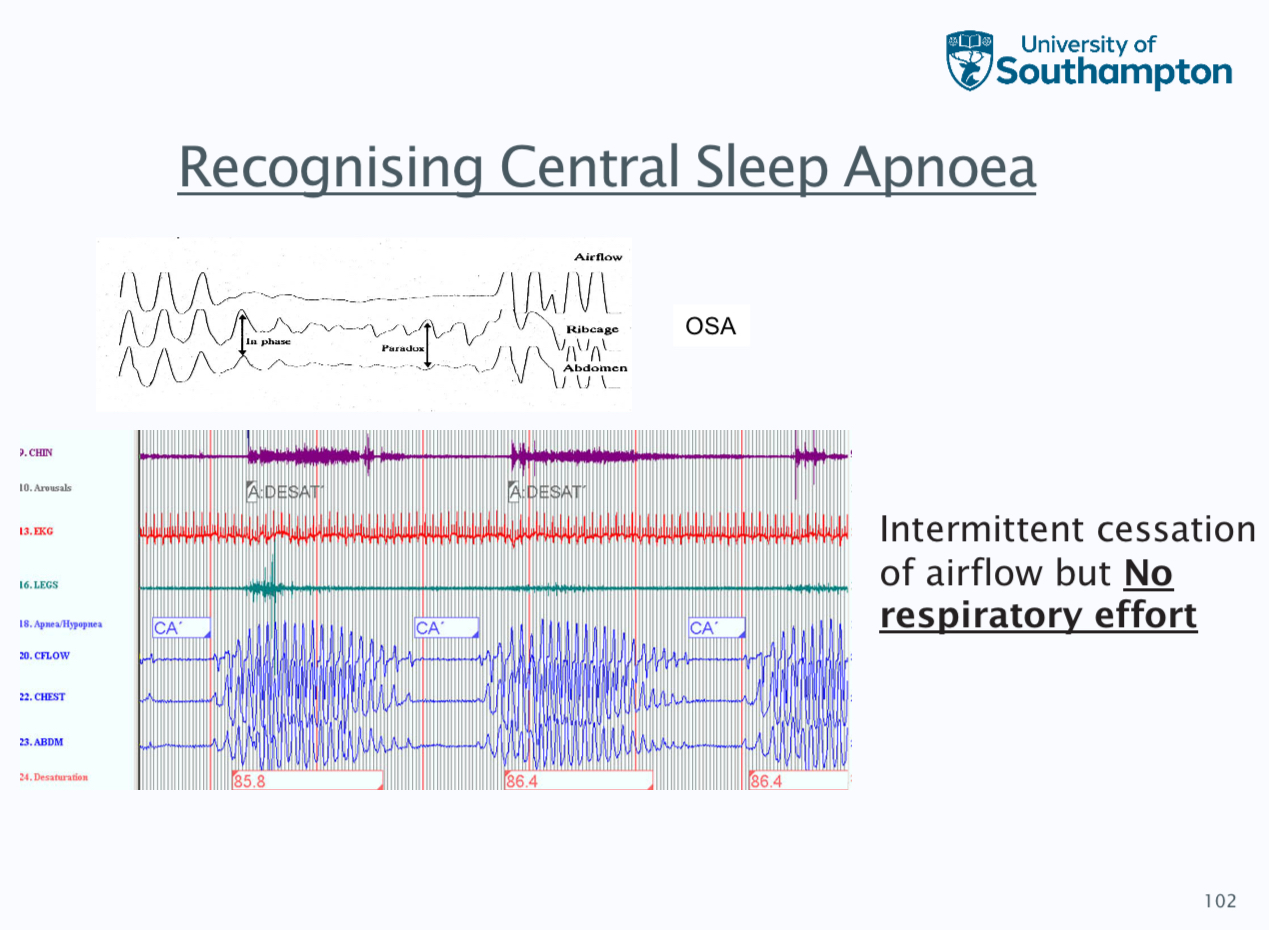
Central breathing disturbance during sleep
central apnoeas and hypopnoeas, nocturnal hypo ventilation, obesity hypoventialtion, much less common than OSA and due to insufficient respiratory effort (neural drive, muscle weakness or mechanical restriction)
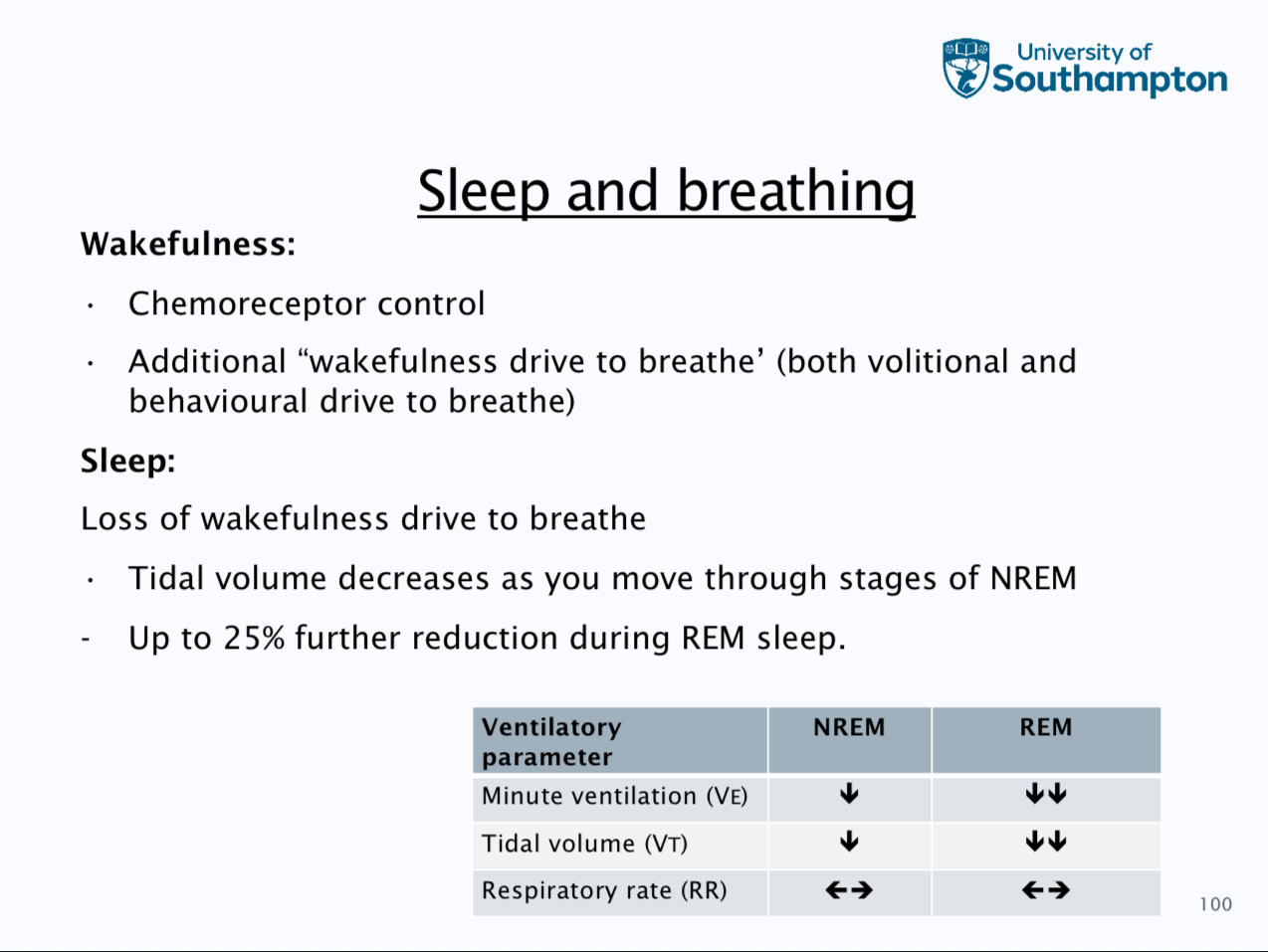
Sleep onset is respiratory control more dependant on chemorecpetors
Apnoea threshold is the lowest level of co2 at which apnoea occurs
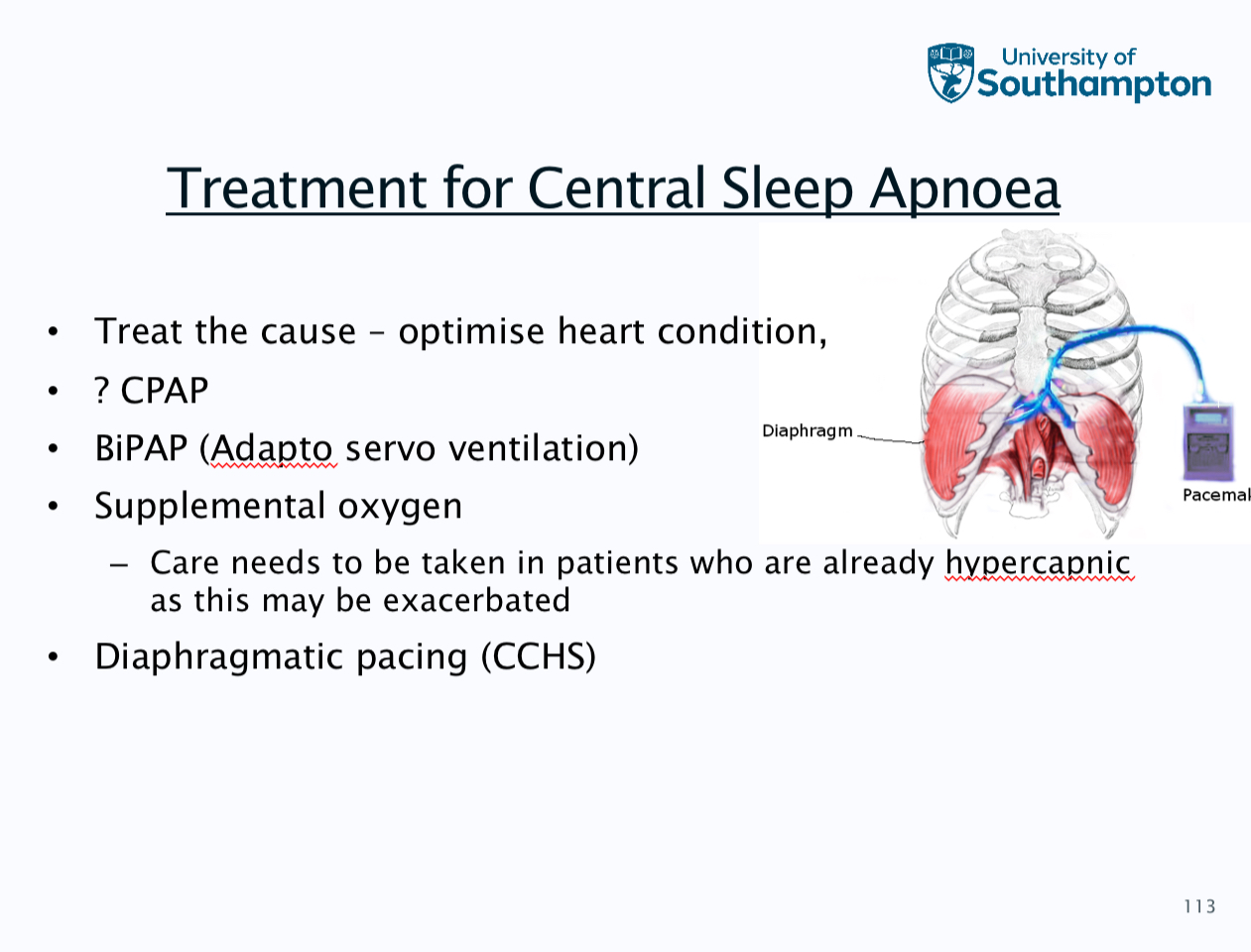
Causes of central sleep apnoea
Diagnosis is polygraphy and five central apnoeas
Nighttime symptoms - waking up gasping for air, witnessed apnoeas, restless sleep or insomnia and absent or mild snoring
Daytime symptoms - daytime sleepiness or fatigue, morning headache, problems with memory or concentration and mood or personality changes

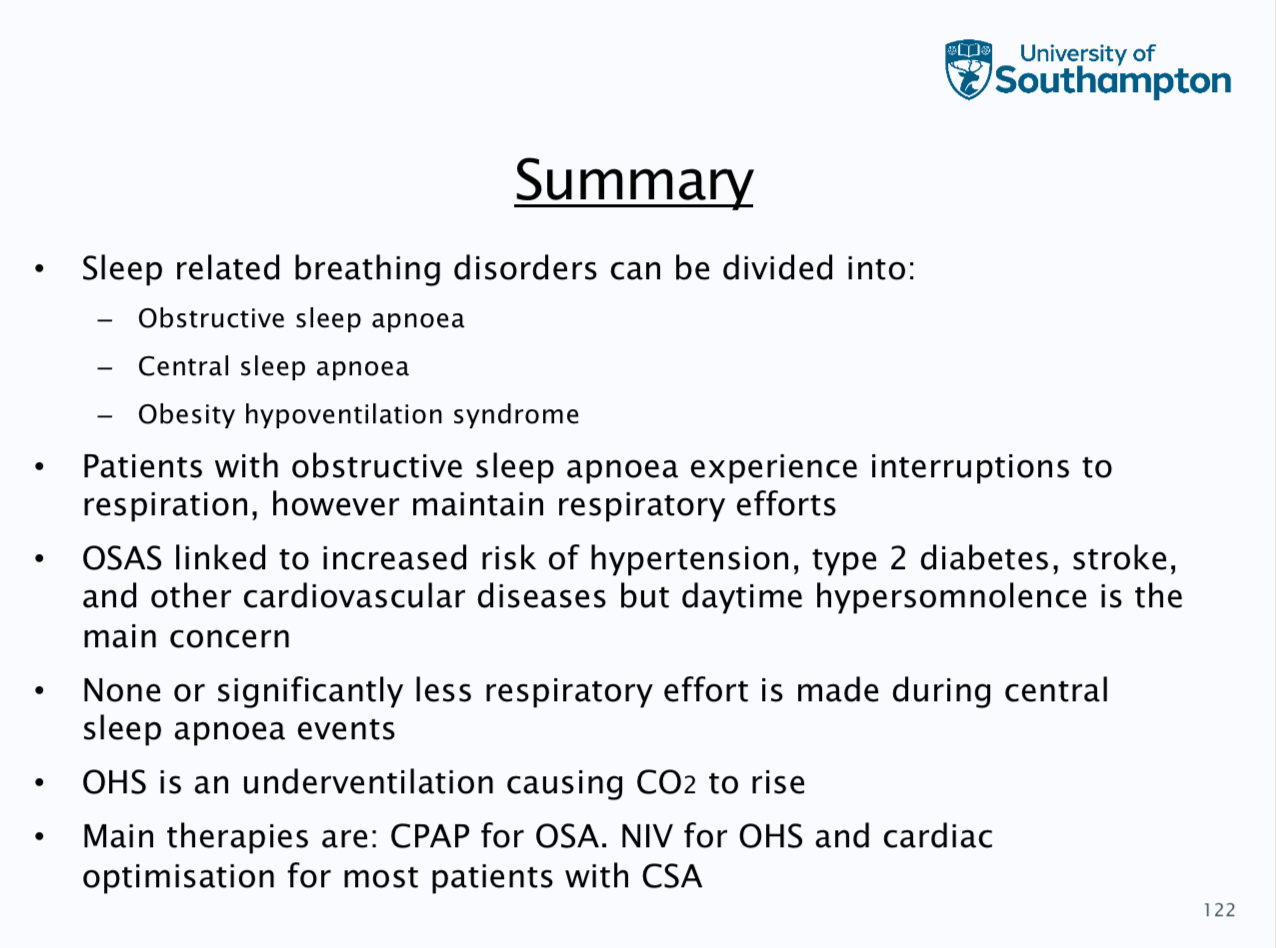
Summary
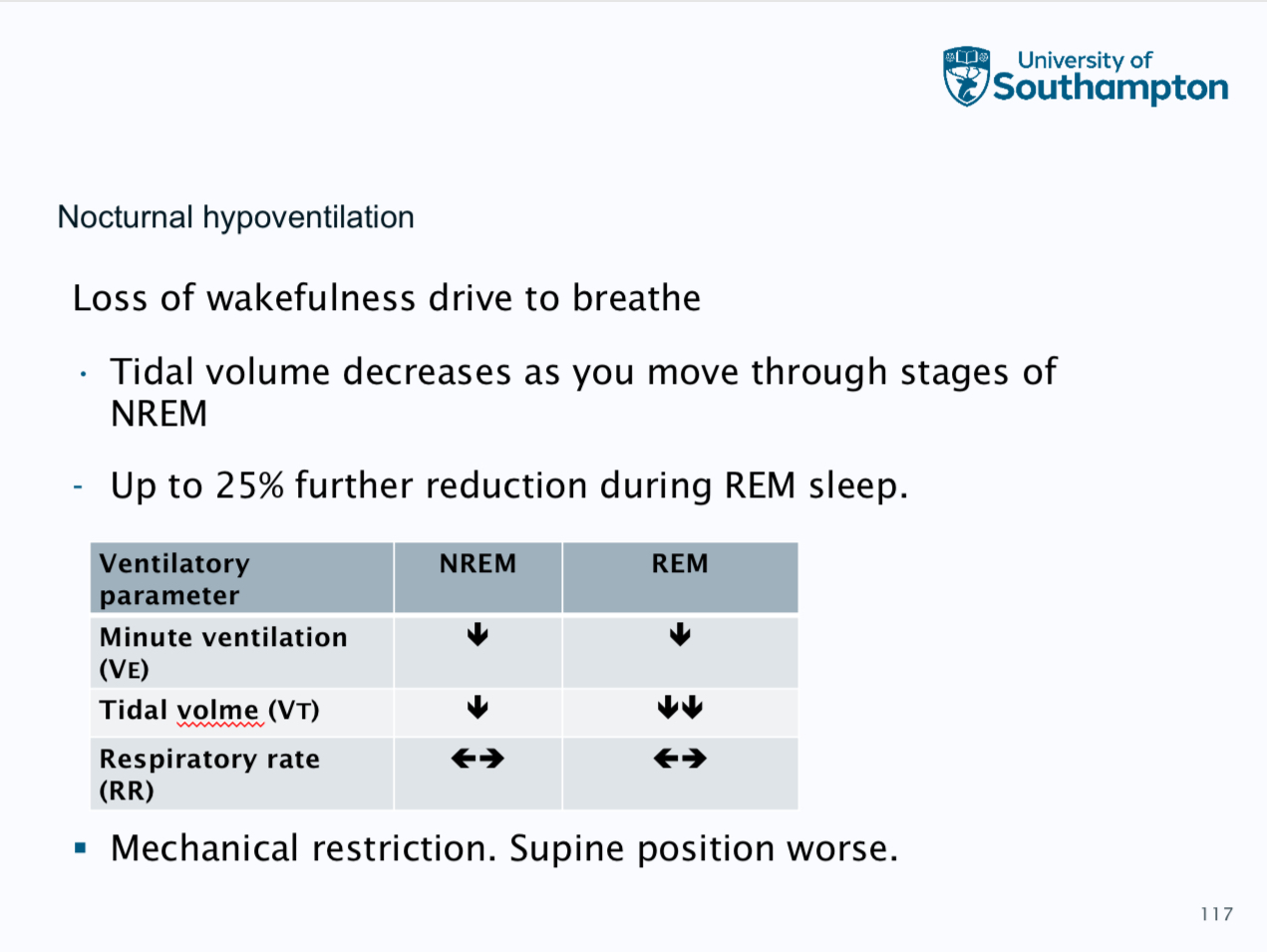
Features of nocturnal hypoventialtion- raised nocturnal paCO2, low SpO2 during sleep, waking headaches, peripheral oedema and unexplained polycythaemia
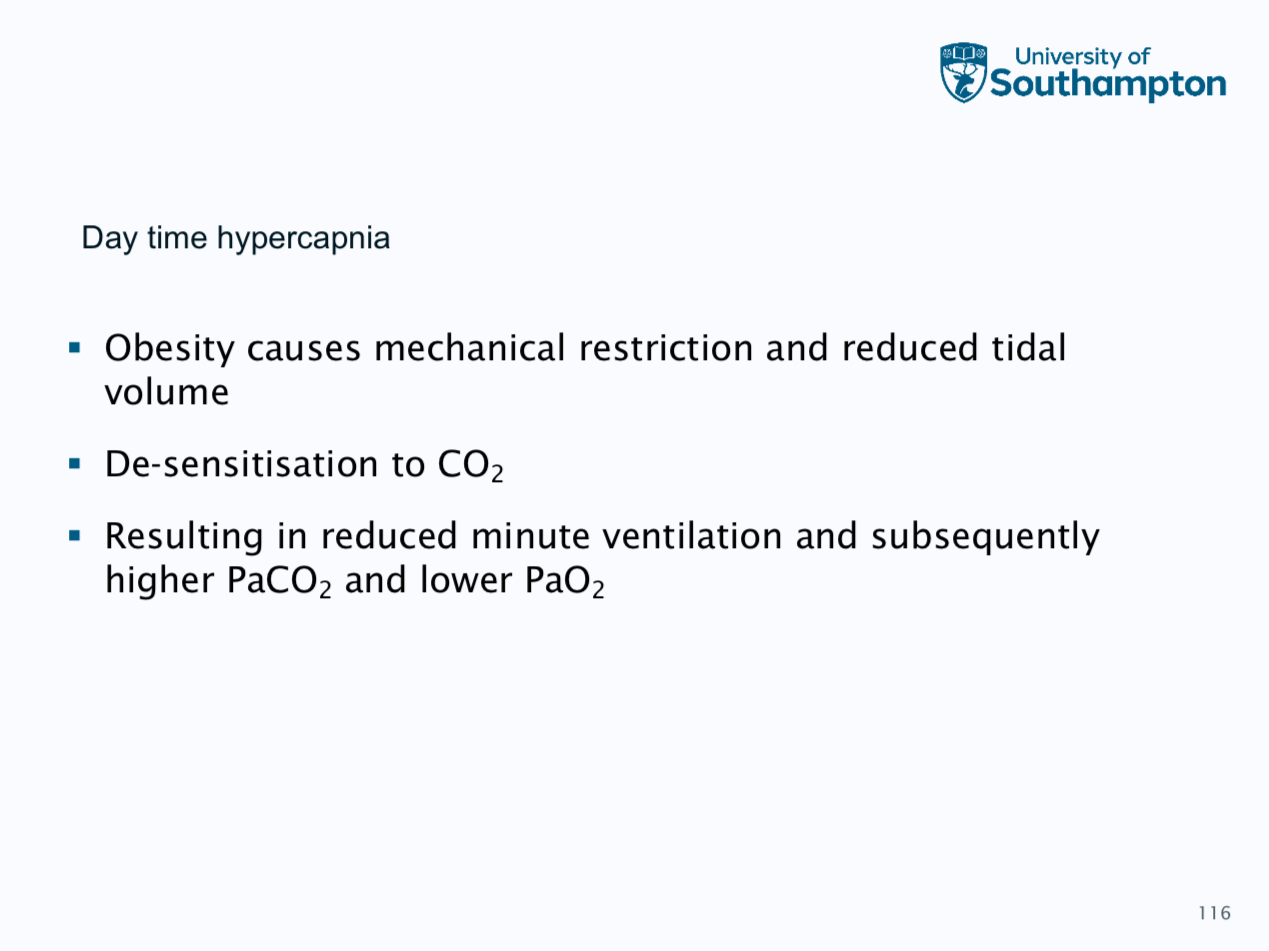
Obesity hypoventialtion syndrome
Form of chronic ventilatory failure with a combination of
obesity
Daytime hypercapnia
Nocturnal hypoventialtion