10 bio - sleep D - NO PICS ⚠️
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Recuperation theory
important physiological function
Adaptation theory
Predator avoidance
Energy conservation
what are the theories that explained why do human sleep in general?
Circadian and homeostatic influences.
What “influences” help regulate sleep and wakefulness over a 24-hour period?
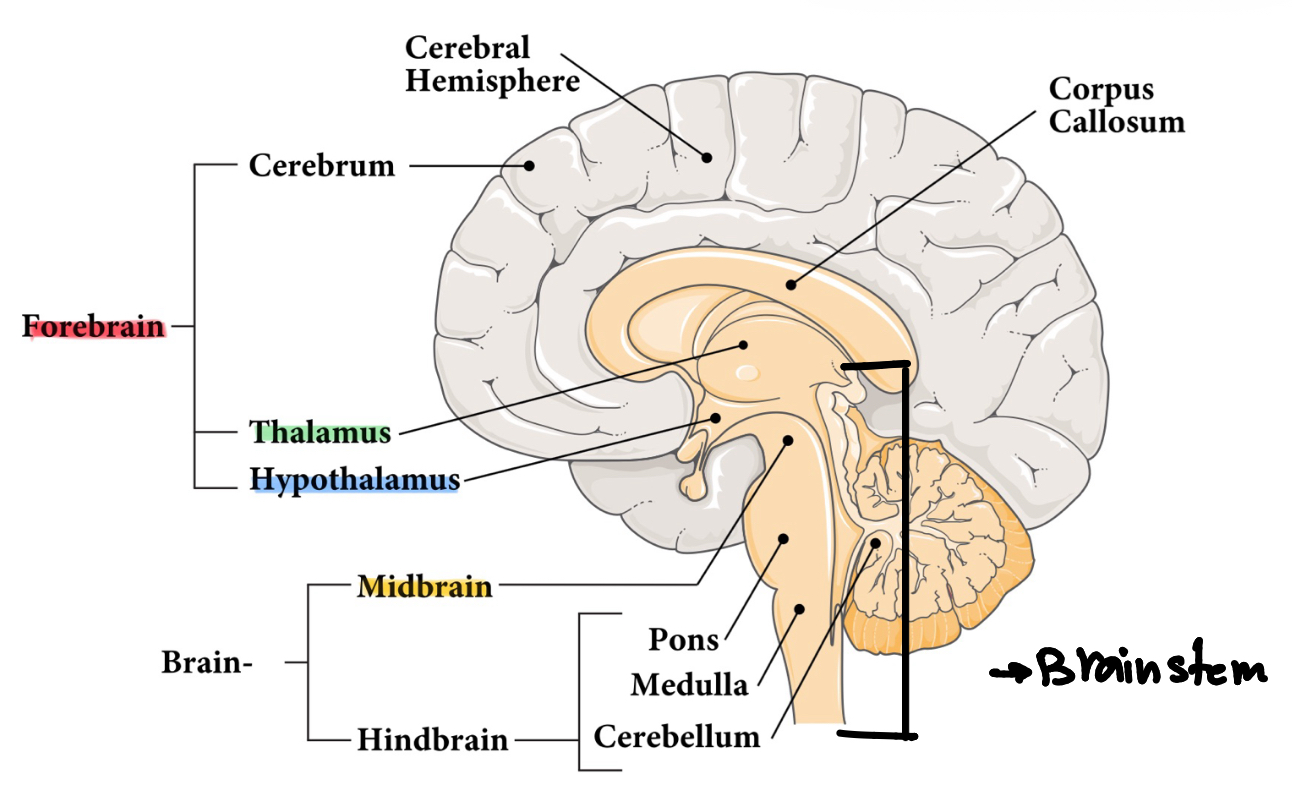
Which brain regions produce sleep and wake states?
A wake-promoting group
a sleep-producing group.
What are the two mutually inhibitory groups involved in sleep-wake regulation?
A mutually inhibitory system
that provides sleep-wake control.
What is the flip-flop circuit?
Activity in brain stem and hypothalamic arousal centers (ARAS). = The ascending reticular activating system.
What produces wakefulness?
Limbic system
Cortex
Where do ARAS neurons project?

What are the two ARAS pathways to the cortex & limbic system?
active ✅→ during wakefulness
inactive ❌→ during sleep, especially during rapid eye movement (REM) sleep.
When is the Ascending Reticular Activating System (ARAS) active and inactive?
ARAS activity produces excitatory effects and increases neuronal activity in the cortex and other regions.
What is the effect of ARAS activity on the cortex and other brain regions?
Acetylcholine
Which neurotransmitter is involved in thalamocortical transmission during wakefulness?
They inhibit all wake-promoting brain regions,
ensuring all arousal systems are inhibited in a coordinated fashion.
How do GABAergic neurons in the hypothalamus produce sleep?
VLPO: ventrolateral preoptic area → helping to shut down the activity of wake-promoting systems.
فكر فيها كـ زر إيقاف (switch) لأنظمة اليقظة في الدماغ.
VLPO تظل نشطة أثناء نوم NREM، وهذا النشاط يساعد على إبقاء الشخص نائمًا عن طريق إيقاف تنشيط ARAS وأنظمة اليقظة الأخرى
Which neurons remain active during NREM sleep and what is their role?
responsible for wakefulness.
What is the function of the Tuberomammillary Nucleus (TMN)?
responsible for sleepfulness
What is the function of the Ventrolateral Preoptic Area (VLPO)?
Fall asleep
Histamine is one of the neurotransmitters that’s responsible for arousal, so when a patient takes anti-histamine it makes him…?
السؤال هذا للمعرفة فقط
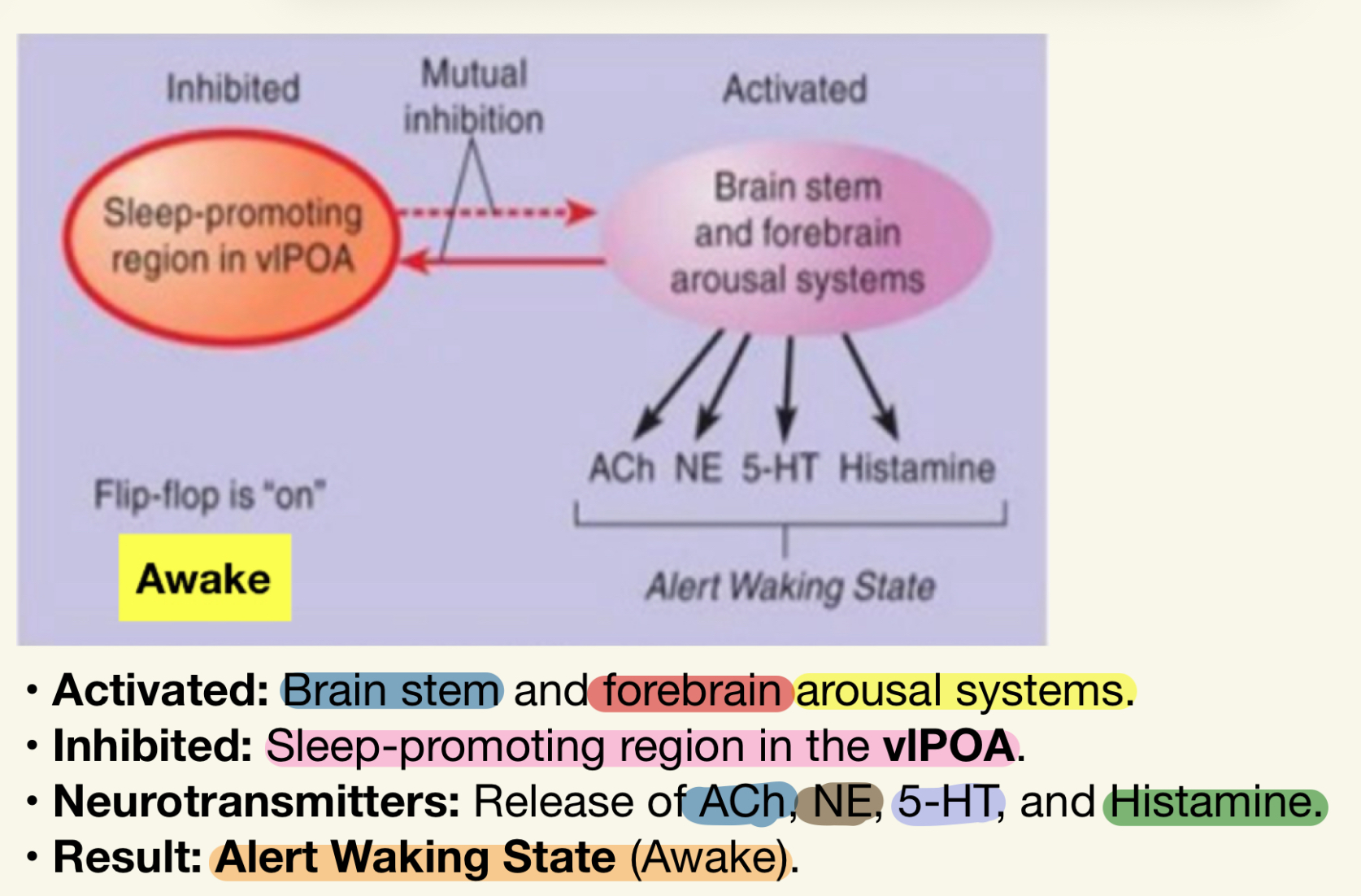
What happens when the sleep/wake flip-flop is in the "ON" position?
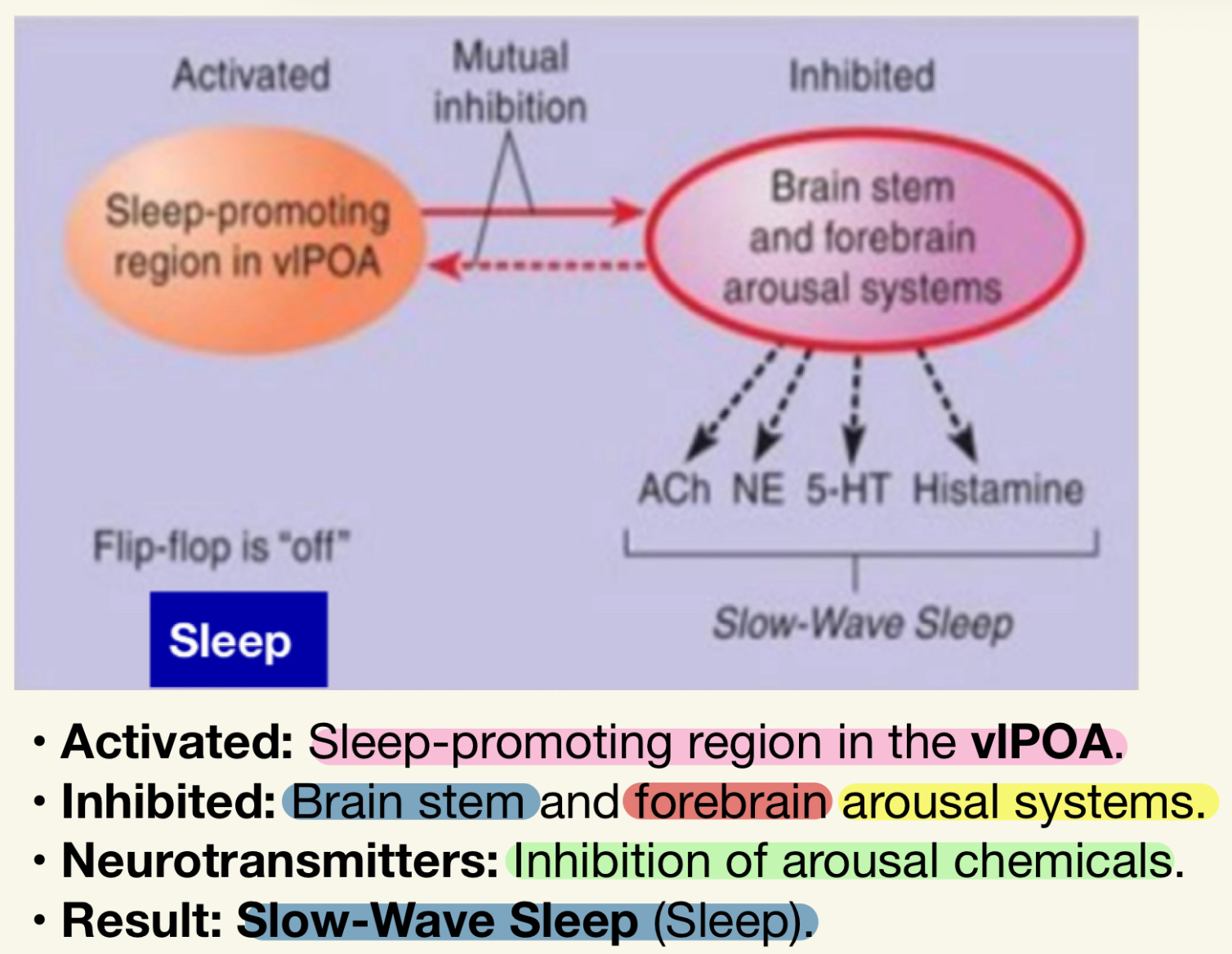
What happens when the sleep/wake flip-flop is in the "OFF" position?
In the ventrolateral preoptic nucleus (VLPO) of the hypothalamus.
Where is the sleep-promoting “off” setting localized?
tuberomammillary nucleus (TMN) of the hypothalamus
Where is the wake-promoting “on” setting localized?
Histamine from TMS
GABA from VLPO
Which two neurotransmitters regulate the sleep/wake switch?
histamine is released
wake-promoter is ON
sleep-promoter is INHIBITED
What happens when the TMN is active ?
GABA is released
wake-promoter is INHIBITED
sleep-promoter is ON
What happens when the VLPO is active?
does not regulate sleep directly,
but regulates the circadian (day/night) rhythm
and times sleep like a real clock (it times sleeping)
What’s suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) relationship with sleep?
Environmental cues that control the timing of the circadian rhythm, such as
light
drugs
temperature
exercise
eating and drinking patterns.
What are Zeitgebers?
It causes release of melatonin which is responsible for making a person sleepy
How does the body respond to environmental cues in regulating the sleep/wake cycle?
on average two hours before normal bedtime.
What is the timing of melatonin release?
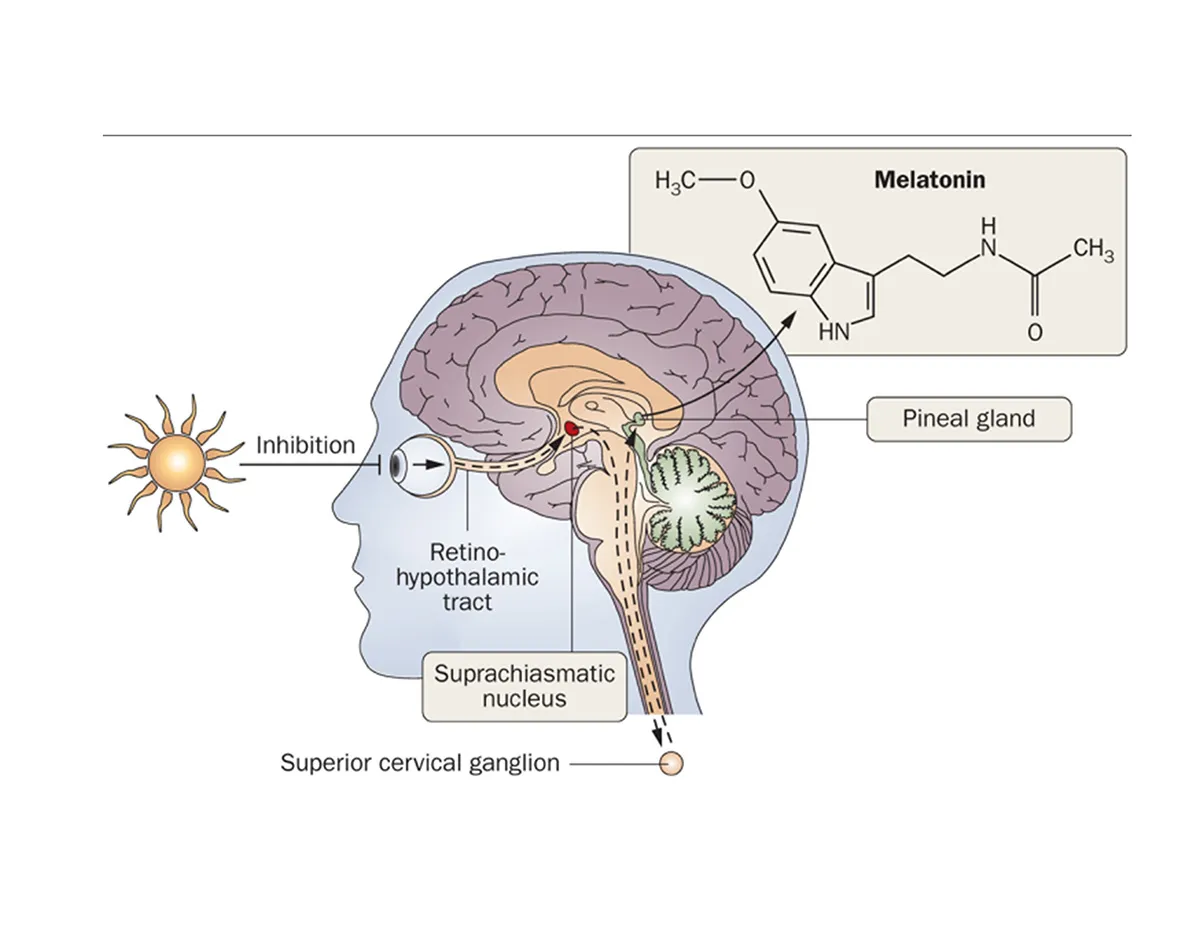
1⃣ Light affects the retina,
2⃣ the signal travels to the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN),
3⃣SCN is connected to the pineal gland
How does light affect melatonin secretion?
Melatonin secretion is inhibited by the light–retina–SCN–pineal gland system.
What happens to melatonin secretion during daytime?
At night, the absence of light stimulation to the SCN allows melatonin secretion.
What happens to melatonin secretion during nighttime?
Even small amounts of sleep loss Can cause Negative effect on mood.
what sleep deprivation can cause?
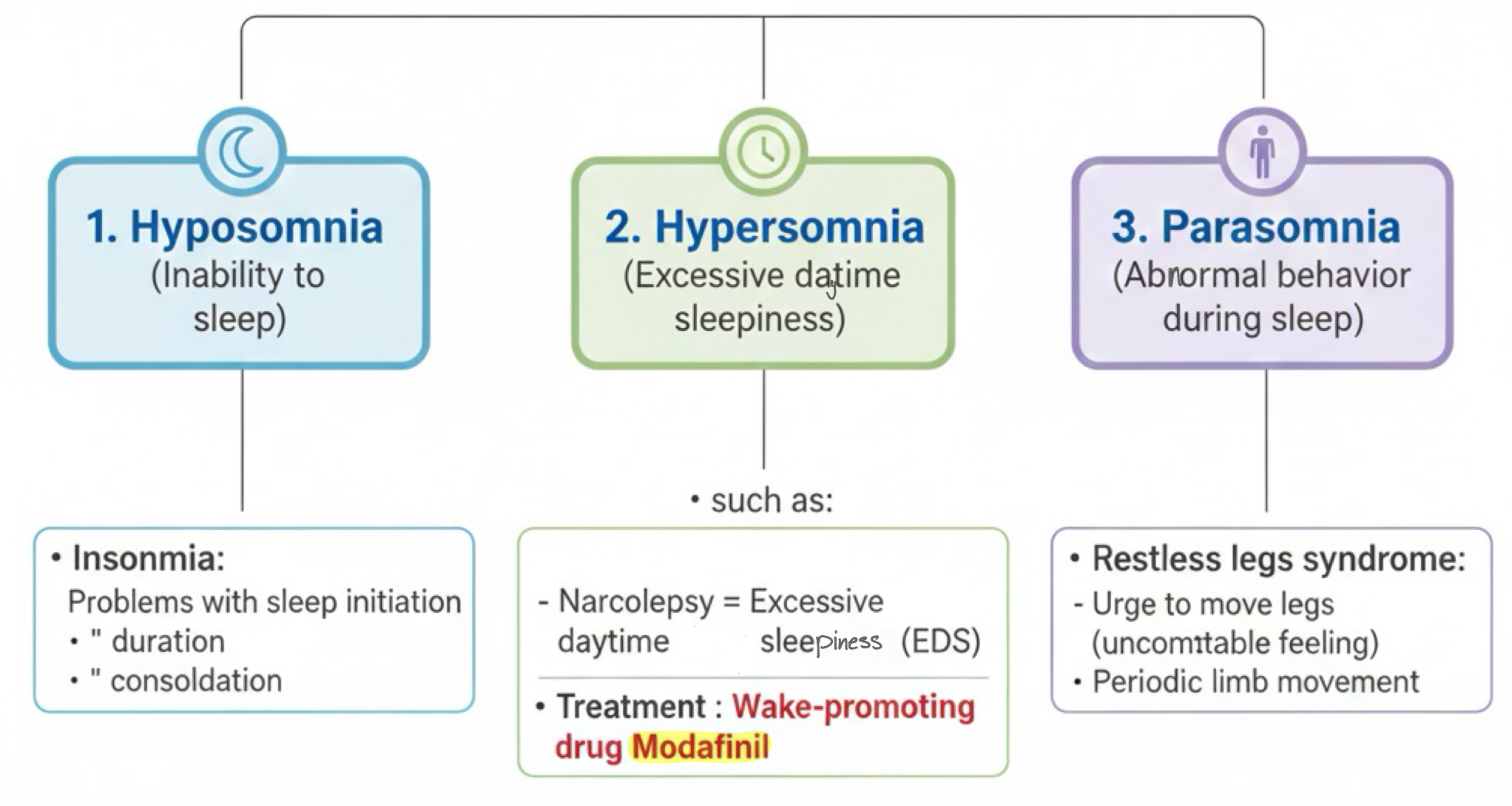
What are the types of sleeping disorders with examples?
▶ Orexin promotes wakefulness
▶ melatonin promotes sleep.
Which two main chemicals regulate the sleep/wake switch?