Dental acrylics 2 - Room temperature cured PMMA
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Compare heat cured vs room temperature cured (basic)
HC - require heat to cure - polymerise
RT cured acrylics cure at room temperature - no heat required
What can RT cured acrylics also be referred to as? (3)
self cured
autopolymerised
cold cured
What are some uses of RT cured PMMA/MMA? (5)
relining denture bases at the chair side as hard reliners
repairing a denture
additions to denture
special trays
temporary crown and bridge material
in repairing dentures bases, how is the PMMA different?
consists of finer particle size, lower molecular weight

What special addition in the PMMA powder and MMA liquid?
PMMA powder - benzoyl peroxide
MMA liquid - tertiary amine
What form does the RT cured acrylics come in and how is it mixed?
powder and liquid
RT PMMA polymer powder and RT MMA monomer liquid
both mixed using the ‘dough technique’
other name for RT PMMA?
RT acrylic
Again, how is the PMMA formed?
pre-polymerised MMA monomer using suspension polymerisation - also contains benzoyl peroxide
Again, what does the monomer liquid contain?, and what is the reactive part of the polymerisation reaction of the RT acrylic?
MMA monomer liquid contains tertiary amine
MMA is the reactive part - polymerise, it is the active part of the dough, it polymerises at RT
The PMMA powder is added to the MMA monomer liquid and then mixed carefully to form what?
what does it set as?
how long does this take?
a dough which then cures/polymerises and sets at Room temperature into a rigid glassy polymer
10 minutes
Why is the dough technique used? (3)
Reduces polymerisation shrinkage of the material on setting
enhances mechanical properties
reduces the exotherm on setting
PMMA powder replaces how much of the monomer and what is its role and purpose?
2/3 parts
filler
improves set materials mechanical properties compared to the monomer polymerising alone
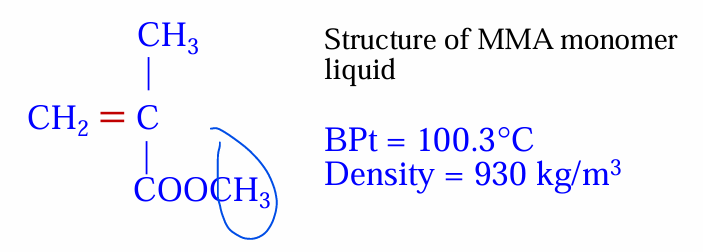
again what is the boiling point temperature and density of MMA?
Dispensing of RT cured PMMA

What is the powder (4) and liquid (3) constituent of the RT cured PMMA?
powder:
PMMA - beads finer particle sizes than heat cured powder
Benzoyl peroxide - initiator
colour pigments
opacifiers
Liquid:
MMA
HQ
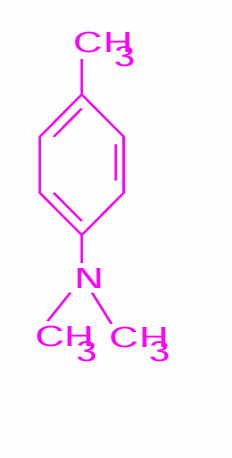
DMPT activator - not found in heat cured
(N,N-dimethyl-p-toluidine)
Why can the polymerisation reaction take place at room temperature?
polymerisation can commence at room temperature if benzoyl peroxide is activated with a tertiary amine - DMPT
in order for the RT polymerisation reaction to take place what must you do?
mix the powder and liquid
What is the ratio?
the polymer powder is added to the liquid monomer in 2.5:1 ratio - as soon as this happens the polymerisation reaction begins
What happens to the polymer beads?
they dissolve in the monomer
What does the DMPT do? (what is this stage called?)
the DMPT reacts with the peroxide, it breakdown the BP at RT providing free radicals - activations
What does the free radical do?
it attacks the double bond of the monomer molecules
the reaction then follows the same steps as for the heat cure reactions - initiation, propagation and termination
how long does it take to cure, can be affected by two things?
10 minutes
cure depending on the coolness of the monomer
room temperature
What are the changes to viscosity during the polymerisation reaction?
the monomer is initially a mobile fluid
its viscosity increases as polymerisation proceeds
the polymer chains begin to grow
eventually sets into a hard glassy rigid polymer
the RT polymerisation reaction speed? and another property?
rapid
exothermic
what can cause a higher exotherm?
the more monomer present the higher the exotherm
What does the finer polymer powder allow?
More rapid diffusion of monomer into the polymer beads and hence it rapidly gelates to a hard mass at RT
RT vs HC PMMA molecular weights and what does this mean (property)?
RT PMMA has a lower MW C to HC PMMA
results in the RT polymers having inferior physico-mechanical properties compared to HC PMMA
What are 2 advantages of RT cured to HC acrylics?
Cheaper to produce - little /no technician time needed - with HC the technician has to prepare the denture from the impression taken by dentist
can be used at chair side (denture is repaired at the chairside and the patient does not have to wait for weeks)
Disadvantages of RT cured to HC polymers? (5 main)
Physical weaker than HC:
The cured material contains lower molecular Weight (MWt) polymer chains, which in turn affects the materials overall mechanical properties
The reaction is rapid therefore not all of the monomer is able to polymerise before the material sets
Greater residual monomer contact (3-5% cf with 1% in HC)
Residual monomers leaches into the patients mouth causing hypersensitivity - mucosal irritation
poor colour stability - amine causes yellowing
Lower Tg (75-80 cf 105 in HC for PMMA)
porosity due to:
more rapid gelation - cures within 10 minutes (depending on the amount of initiator/activator present)
hand mixing of powder and liquid which results in incorporation of air
More prone to water uptake due to:
Low MWt
loss of residual monomer
porosity
What are the effects of water absorption (2)? (2 possible monomers)
Water can extract potentially toxic materials
residual monomers - MMA - mucosal irritation in the mouth, contact dermatitis and hypersensitivity, hypotensive
if the materials contains a plasticisers, this will also leach into the patients mouth (e.g phthalate based are classed as carcinogens)
pores fill with water and these can grow as well
How does water extract potentially toxic materials?
The water diffuses into the polymer causing minimal swell of the matrix (not seen visibly)
and the un-polymerised/unreacted materials diffuses out of the polymer and into the surrounding environment
compare the water absorption of the HC PMMA and RT PMMA?
if it is temporary not a problem
more of a problem with the more permanent

The higher the water uptake of the material affects what?
Mechanical properties
RT PMMA/MMA are only used for which purposes?
only used for temporary purposes
the autopolymerising resins have inferior mechanical properties with some ductility and a lower transition temperature comparted to HC acrylic bases
what are some temporary uses of RT PMMA/MMA?
