Anatomy Final Exam
1/207
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
208 Terms
Endocrine System
secretes hormones directly into the bloodstream to maintain homeostasis.
Hormones
chemical messengers that act upon effectors to regulate bodily functions
a specific hormone must bind to a specific receptor in order to create a response
Main Endocrine Glands/Organs
pituitary gland - brain
hypothalamus - brain
thyroid gland - inferior neck just in front of trachea
adrenal gland - on top of kidneys; pyramidal shape
pineal gland - brain
parathyroid glands - neck; posterior surface of thyroid gland
pancreas - abdomen; sits posterior to the stomach
Organs with Secondary Endocrine Functions
heart, thymus, adipose tissue, digestive tract, kidneys, gonads (testes & ovaries)
Hypothalamus Hormones
antidiuretic hormone (ADH), oxytocin (OXT), regulatory hormones
ADH & OXT travel through hypothalamic neurons (their axons) & eventually released by posterior part of pituitary galnd
Pituitary Gland Hormones
anterior lobe - adrenohypophysis
dont need to know
posterior lobe - neurohypophysis
release of oxytocine OXT and antidiuretic hormone ADH
Thyroid Gland Hormones
thyroxine (T4), triiodothyronine (T3) - influence metabolism
calcitonin (CT) - lowers blood calcium levels
Adrenal Gland Hormones
Adrenal Medulla (inner portion)
epinephrine (E)
norepinephrine (NE)
Adrenal Cortex (outer portion)
cortisol - increases blood sugar so we have energy to respond to internal & external stresses
corticosterone
aldosterone - promotes water retention to increase blood volume and pressure
androgens - sex hormones; estrogen & testosterone
Pancreatic Islets Hormones
insulin - decreases blood sugar levels
glucagon - increases blood sugar levels
Pineal Gland Hormone
melatonin
Parathyroid Glands Hormones
parathyroid hormones (PTH) - increase blood calcium levels
Heart Hormones
atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)
brain natriuretic peptide (BNP)
release water from body - lower bp and blood volume
Thymus Hormones
thymosins
Adipose Tissue Hormones
leptin & resistin
Digestive Tract Hormones
numerous hormones
Kidney Hormones
erythropoietin (EPO) - stimulates creation of more red blood cells so we can carry more oxygen in body - released when needed to increase blood oxygen levels
calcitriol
renin - stimulates series of steps that lead to production/release of aldosterone by adrenal cortex - renin works to increase sodium & water retention
Gonad Hormones
male - testes
androgens (testosterone mainly)
inhibin
female - ovaries
estrogens
progesterone
inhibin
Hypothalamus
key endocrine organ that serves as link between neural and endocrine systems
connections between hypothalamus & pituitary gland
preganglionic neurons start in hypothalamus synapse on adrenal medulla
ADH
antidiuretic hormone
targets kidneys
works to reabsorb water (water retention)
by reabsorbing water, we can increase blood volume & pressure
OXT
oxytocin
targets mammary glands and uterus in females
mammary glands - causes milk ejection
uterus - wall contraction
acts on prostate gland and ductus deferens in males (leads to contractions of both structures)
Adrenal Gland
adrenal cortex (outer portion)
adrenal medulla (inner portion)
Pancreas
functions as both exocrine & endocrine gland
endocrine - relies on bloodstream to move hormones made by the pancreas
exocrine - relies on ducts within pancreas to move its products, mainly digestive enzymes
head of pancreas is tucked into the U shaped curve of the duodenum of small intestine
Kidney Role - low blood calcium ion levels
sunlight converts a hormone into vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) (inactive), which travels to kidneys
parathyroid hormone targets kidneys
kidney cells concert vit D3 to calcitriol (vit D) (active)
calcitriol released and causes small intestine to absorb calcium ions into bloodstream
raises calcium ion levels back to homeostatic conditions
Primary Functions of Urinary System
maintaining electrolyte and fluid balance
eliminating wastes from the body
regulating blood volume and blood pressure
maintaining acid/base balance in the body
Kidney Location
retroperitoneal space in abdominal cavity - behind digestive tract
PARTIALLY covered by ribs, not fully encased (ribs 11&12)
Large Structures that Comprise Urinary Tract (superior to inferior)
kidney - produces urine
ureter - transports urine toward urinary bladder
urinary bladder - temporarily stores urine prior to elimination
urethra - conducts urine to exterior; in males it also transports semen
Kidney Protective Layers
renal capsule
fascia
substantial amount of fat
Structures that Supply & Drain Kidneys
renal artery - supply
renal vein - drain
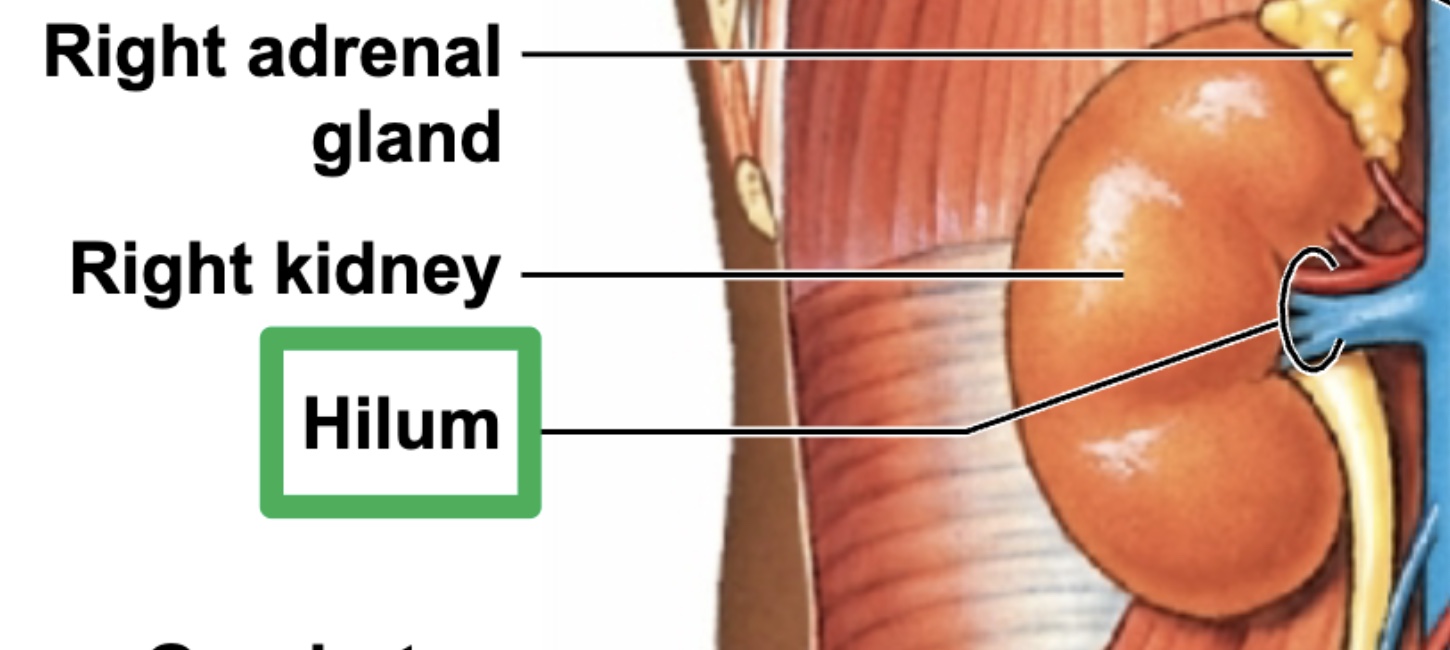
Renal Hilum
threshold at which renal artery, renal vein, and ureter enter/exit the kidney
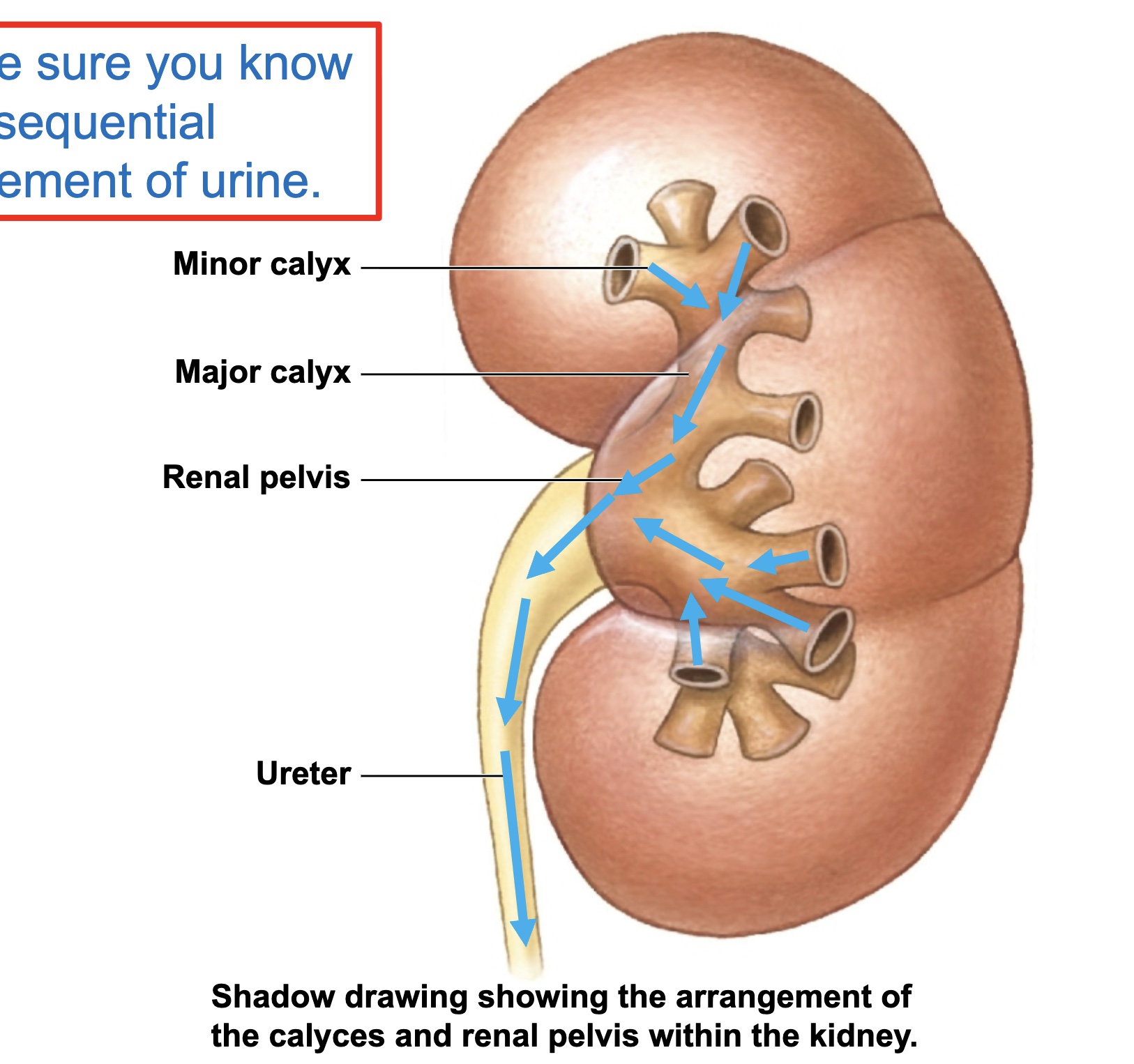
Relative positioning of calyces and renal pelvis relative to ureter
calyces and renal pelvis within kidney (superior to inferior = minor calyx, major calyx, renal pelvis)
ureter outside of kidney
Sequential Pathway of Urine Through Kidney
minor calyces —> major calyces —> renal pelvis —> ureter
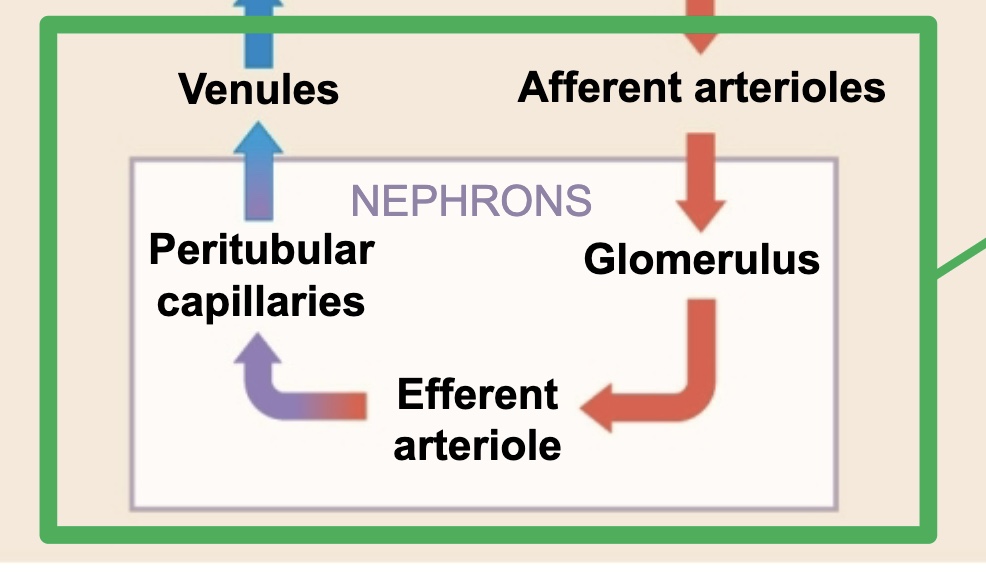
Kidney Blood Flow
enters through renal arteries (and then to others, but not included in test)
ultimately leads to afferent arterioles
glomerulus - filtration
efferent arterioles
peritubular capillaries
venules
other things then to renal veins
Glomerulus
small capillary bed in close proximity to Bowman’s capsule of nephron
Nephron General Structure
fundamental filtering unit of a kidney
bowman’s capsule
proximal convoluted tubule
descending/ascending limbs of nephron loop
distal convoluted tubule
DCT + PCT + nephron loop = main parts of nephron
What does Nephron lead to
into collecting duct
nephron and collecting system are distinct structures in kidney
multiple collecting ducts eventually channel urine toward a major calyx
Pyelogram
diagnostic medical image showing main urinary structures
helps to visualize blockages and narrowing along parts of urinary tract
Detrusor Muscle
the smooth muscle in the wall of urinary bladder
Bladder Positioning
posterior to pubic symphysis
Urethra in Male vs Female
males have longer urethras
Internal Urethral Sphincter
smooth muscle
involuntary
External Urethral Sphincter
skeletal muscle
voluntary
Urinary System as we age
urethral sphincters lose muscle tone as we age - Incontinence (involuntary leakage of urine)
risk of infection goes up due to urine retention
reduced sensitivity to ADH
Axial Skeleton
bones of skull, sternum, ribs, vertebrae, sacrum & coccyx, and other associated bones of this part of human skeleton
Axial Musculature
must attach to features of axial skeleton
include those that can position the head
include those that can move and position spinal column
includes those that move ribcage
4 Axial Muscle Categories
head & neck muscles
vertebral column muscles
rib cage & body wall muscles (thoracic and wall muscles)
pelvic floor muscles
Muscles of Facial Expression
occipitofrontalis
orbicularis oculi
orbicularis oris
zygomaticus major/minor
platysma
Sternocleidomastoid
neck muscle
Uni- ipsilateral lat flexion; contralateral lat rotation
Bi- flexion/extension of neck (depends on position/context); forced breathing
Buccinator
cheeks - walls of mouth
helps circulate food around mouth as we chew
help generate suction as we drink through straw
keeps cheeks tight so we do not bite down on the inside of our cheeks
distends out when you see someone play trumpet
Extra-ocular muscles
Superior Rectus - draws gaze superiorly
Lateral Rectus - draws gaze laterally
Medial Rectus - draws gaze medially
Inferior Rectus - draws gaze inferiorly
Inferior Oblique - draws gaze laterally & superiorly
Superior Oblique - draws gaze laterally & inferiorly
Chewing Muscles
mastication
masseter, temporalis, pterygoids
for the most part, muscles of mastciation work to elevate mandible so that biting surfaces of teeth are brought closer together to crush food
Muscles of Tongue
will have “-glossus” in their names
help with mechanical breakdown of food along with swallowing
Muscles of Throat Wall
usualy have “-pharyngeus” in their names
work to move food from mouth into esophagus
Ipsilateral
same side
Controlateral
opposite side
Unilateral Contraction
one side contracts to a greater degree than the other
Bilateral Contraction
both sides pull equally
Suprahyoid Muscles
anterior/posterior digastric
mylohyoid
stylohyoid
elevate and fixate hyoid bone and larynx in neck
Infrahyoid Muscles
sternohyoid
sternothyroid
omohyoid
thyrohyoid
depress and fixate hyoid bone and larynx in neck
Erector Spinae Muscles
3 vertical columns of muscle running up and down the length of the spine
I Love Spine
iliocostalis, longissimus, spinalis
iliocostalis column has segments attaching to portions of ribcage
bilateral - extension of vertrebral column; in practice, these muscles are actually working to reduce the movement of the spinal column
unilateral - lat flexion & ipsilateral rotation of vertebral column
Splenius Muscles
splenius capitis & cervicis
bilateral - extension of cervical spine
unilateral - ipsilateral rotation & lateral flexion of cervical spine
Scalene Muscles
deep aspect of anterior & lateral neck
3 segments - anterior, middle, posterior
can assist with forced inspirtion
help stabilize cervical spine or laterally flex it
roots of brachial plexus emerge between anterior and middle scalene muscles
Intercostal Muscles
thin layers of muscles found in-between adjacent ribs
main examples = external/internal intercostal
externals = forced inspiration
internals = forced expiration
Abdominal Wall Muscles
external oblique - controlateral rot, lat flex, flex of lumbar spine
internal oblique - ipsilateral rot, lat flex, flex of lumbar spine
transversus abdominis - compression of abdominal cavity - sucking in gut to tighten abdominal wall
rectus abdominis - flexion of lumbar spine, lat flex
Diaphragm
inspiration - contraction; descends to allow for lung expansion
expiration - relaxation; ascends to allow for lung contraction
Weakness of Pelvic Floor Muscles
can lead to urinary incontinence (urinary leakage)
Stability & Mobility
inverse relationship
more mobile = decreased stability or higher potential for instability
more secure = restrictive in terms of mobility
Main Purpose of Upper LImb
position and manipulate the hand
Phalanges
14 in each hand
3 phalanges in digits 2-5
2 in pollex/hallux
Metacarpals/Metatarsals
5 in each hand/foot
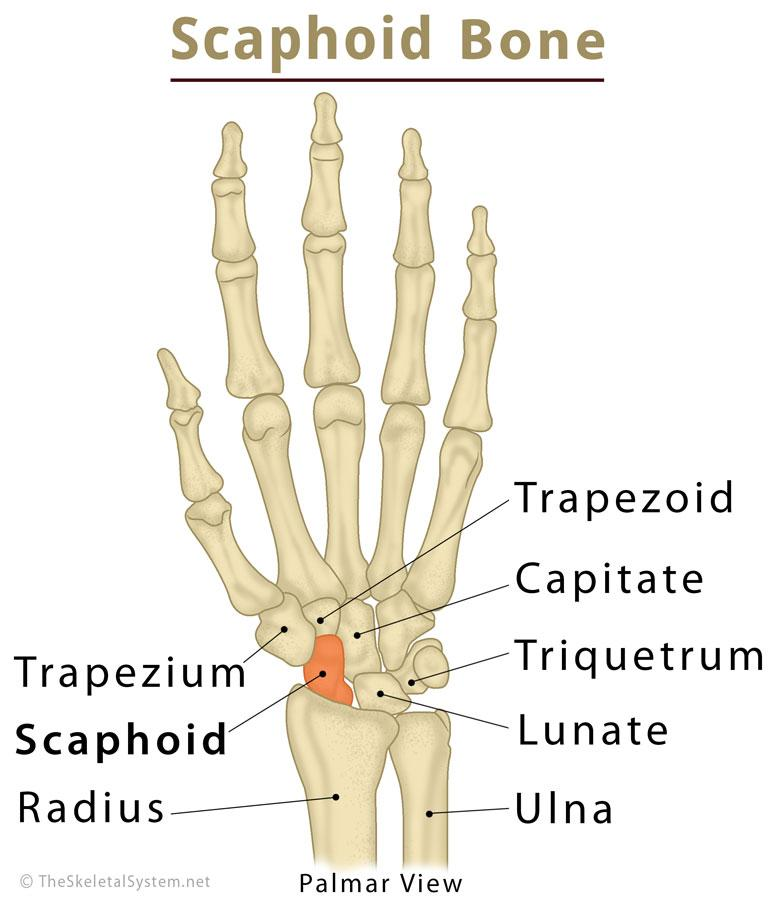
Carpal Bones
8 in each wrist
form base of carpal tunnel (passageway at wrist which tendons and median. nerve travel through)
arranged in 2 rows of 4 bones each
proximal & distal rows
scaphoid is most lateral in proximal row
Tarsal Bones
7 in each ankle/proximal foot
talus is superior to calcaneus (heel bone)
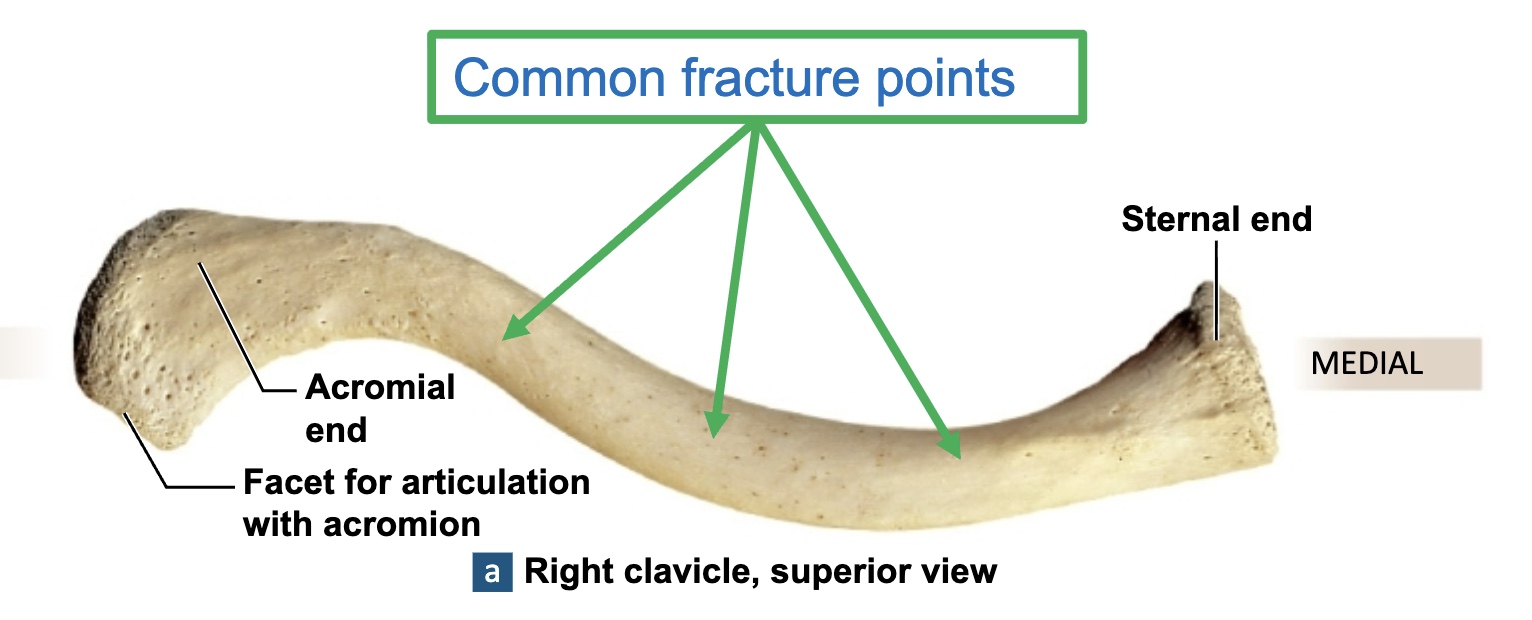
Clavicle
acts as a strut to hold upper limb in proper position and to space it away from trunk of body
usually injured because of fall onto an outstretched hand
Sternal end: medial end
Acromial end: lateral end
Conoid tubercle: near the acromial end
Costal tuberosity: near the sternal end
Sternoclavicular Joint
joint that unites the axial and appendicular skeletal structures
Scapula
sits in upper back (shoulder blade)
forms bony structure of shoulder
acromion process, spine, glenoid fossa
depression/elevation, retraction/protraction, superior/inferior rotation
Distinction of Arm, Forearm, Hand
Arm - humerus
Forearm - ulna & radius
Hand - carpals, metacarpals (I-V), phalanges
Humerus
only bone of arm
head of humerus faces medially
olecranon fossa faces posteriorly
lateral epicondyle & medial epicondyle (funny bone)
surgical neck
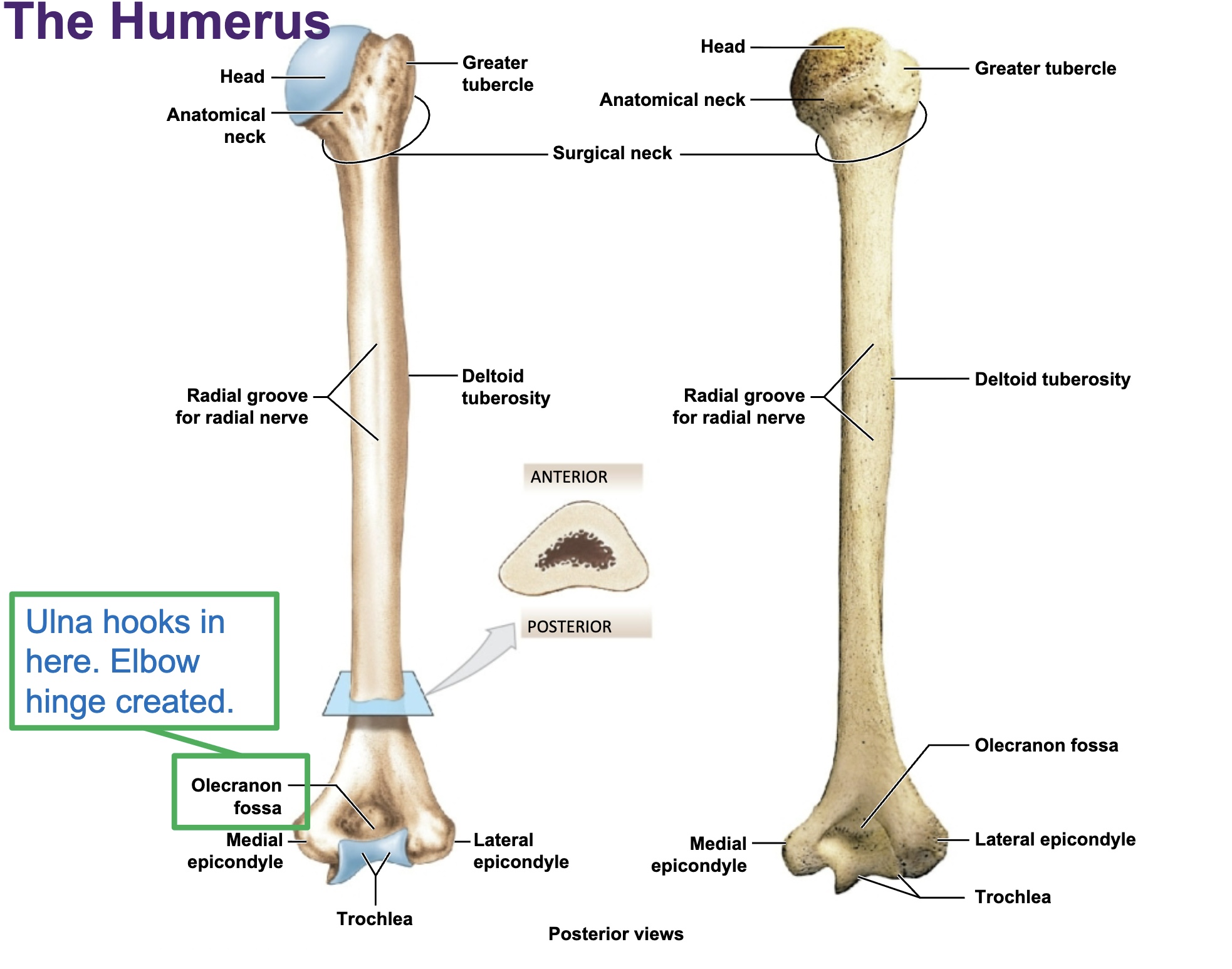
Olecranon Process of Ulna
hooks into humerus creating elbow hinge
Radius
thumb side
can rotate around ulna to create supination/pronation in wrist area
Ulna
pinky side
fixed at elbow
Numbering of Digits
thumb = 1
pinky = 5
General Properties of Appendicular Muscles
help with mvmt of upper & lower limbs
work to maintain posture and balance in body
work as shock absorbers which distribute these external forces
reinforce structure of joints
Muscles that Position the Pectoral Girdle
originate on axial skeleton
insert on clavicle and scapula
trapezius - elevate/retract/depress/superior rotation
rhomboid - retraction/inferior rotation
levator scapulae
pectoralis minor
serratus anterior - protraction/superior rotation
subclavius
Muscles That Move the Arm
originate on pectoral girdle and thoracic cage
insert on humerus
deltoid - flex/abd/ext of arm
supraspinatous - initiates abd of arm; rot cuff
infraspinatous - lat rot of arm; rot cuff
subscapularis - medial rot of arm; rot cuff
teres major - ext/add & medial rot of arm
teres minor - lat rot of arm; rot cuff
coracobrachialis - flex/add of arm
pectoralis major - add/horiz add/flex/medial rot of arm
latissimus dorsi - ext/add/medial rot of arm
Muscles that move the Forearm and Hand
primarily originate on pectoral girdle and humerus
insert on radius, ulna, and/or carpals
Extrinsic Muscles of Hands & Fingers
primarily originate on humerus, radius, and ulna
insert on metacarpals and phalanges
Intrinsic Muscles of the Hand
originate primary on carpal & metacarpal bones
insert on phalanges
Supination & Pronation Actions
occur at proximal and distal radioulnar joints (primarily the distal radioulnar joint)
pronator muscles found in anterior forearm
biceps brachii = powerful supinator
supinator muscle wraps behind elbow
Line of Action
muscles move along these lines
directionality of muscle fibers indicates direction along which muscle pulls
Deltoid Actions
abduction of arm at shoulder
posterior/scapular delt = extension & external rotation
anterior/clavicular delt = flexion & internal rotation
Spurt Muscles
insert close to joint of action
Shunt Muscles
insert far away from joint of action
Agonist
main muscle responsible for creating a movement
Antagonist
main muscles that do opposite of desired action
Stabilizer
fixate some part of body so that agonist can work efficiently/properly
Synergist
assist agonist in performing movement
Pectoral Girdle
bony connection of scapula with its adjacent collarbone
think about shoulder blade and its connection to neighboring collarbone
Rotator Cuff Muscles
SITS
supraspinatous
infraspinatous
teres minor
subscapularis
Pectoralis Major
adduction of arm
flexion of arm
internal rotation of arm
Flexor Muscles
anterior compartments of upper limb
Extensor Muscle of Upper Limb
posterior compartments of upper limb