chemistry topic 8
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
When dissolving ionic compounds in water, what bonds are broken and made
Ionic bonds in the solid and hydrogen bonds between water molecules are BROKEN
Ion dipole bonds between ions and water molecules are MADE
What is required for a substance to be soluble
The substance will be soluble if the bonds made are similar in strength to or stronger than the bonds broken
What is lattice enthalpy
The enthalpy change when 1 mole of a solid ionic compound is formed from separate gaseous ions
Eg Na+ (g) + Cl-(g) → NaCl(s)
Is lattice enthalpy exo or endo
Always exothermic as ionic bonds are being made (BMX)
What factor affect size of lattice enthalpy
The stronger the ionic bonding, the more negative the lattice enthalpy
charge on the ions → ions with higher charge attract more strongly
size of ions → the smaller the ionic radius the closer it can get to the opposite ion so stronger attractions
What is enthalpy of hydration
The enthalpy change when 1 mole of gaseous ions are added to water to give 1 mole of aqueous ions
Na+(g) + (aq) → Na+ (aq)
Is enthalpy oh hydration endo or exo
Exo as ion dipole bonds are made so ions in solution are hydrated
What factors affect size of hydration enthalpy
higher charge
Smaller ionic radius
As these ions have higher charge density
What is enthalpy change of solution
The enthalpy change when 1 mole of ionic solid dissolves in enough water to make an infinitely dilute solution
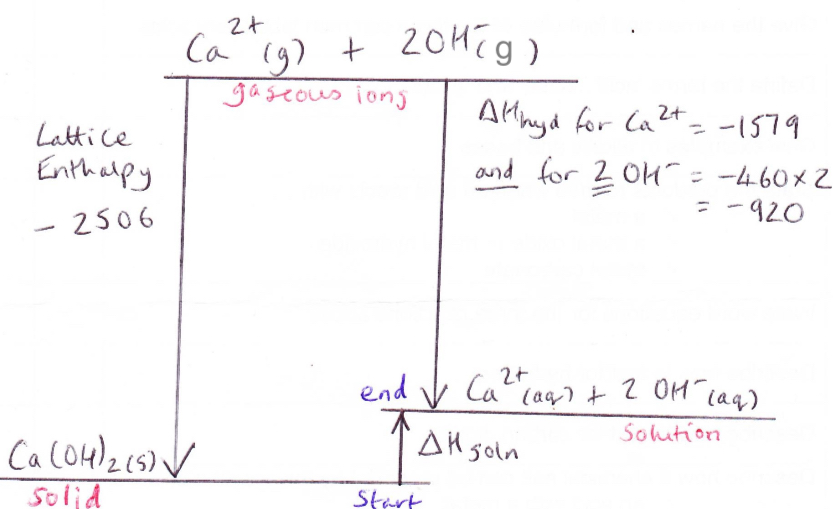
How do you draw an enthalpy diagram
start near bottom of space with solid on horizontal line
Draw a higher line for the gaseous ions (state symbols)
Join 2 lines with a downward arrow for lattice enthalpy
Draw a horizontal line on the right slightly above aqueous ions here
Include arrow from gaseous to aqueous ions labelled with all the enthalpies of hydration
Join solid to aqueous ions line with an arrow labelled triangle SolnH
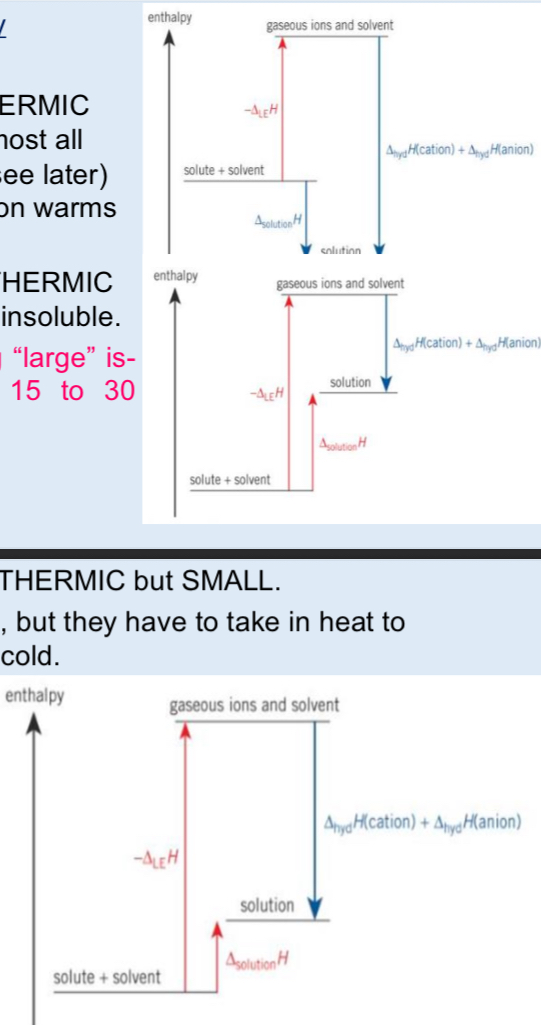
What are the 3 possibilities for enthalpy of solution and solubility diagrams
Enthalpy of solution if exothermic overall so substances are almost all soluble and when they dissolve the solution warms up
Enthalpy of solution is endothermic and large so these solids are insoluble
Enthalpy of solution is endothermic but small so solids usually soluble but they have to take in heat to dissolve so the solution will feel cold
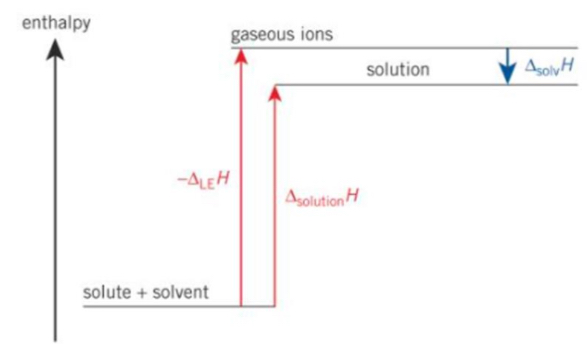
What’s the diagram for non polar solvents
Ionic substances do not dissolve so ions cannot form strong attractions with non polar solvent molecules so the down step is called enthalpy of solvated which is very s,all so enthalpy of solution is large and positive
What radiation does the sun give out
UV and visible
What radiation does the earth give out
Infrared
What do green house molecules do
Molecules in the atmosphere absorb some of the infrared radiation emitted from the earths surface and stop it from being re-radiated into space. Do not absorb uv or visible from the sun only ir which is vital for life or earth would be too cold to support life
How do green house molecules have an effect of warming the earth
some of the IR is re emitted by molecules in all directions so some of the ir that was going out into space gets radiated back towards earth
When molecules absorb certain frequencies of ir radiation their vibrational energy increases. When they collide with other molecules this extra energy is transferred increasing the kinetic energy of air molecules hence raising temperature
Which gases are green house gases
CO2 and H2O are very abundant, CH4, N2O, CFCs, O3 less abundant
What is the IR window
The IR spectrum which water doesn’t absorb as it’s very abundant but only absorbs certain frequencies. Those not absorb are the window which escape and gases put into troposphere like CO2 and CH4 can absorb
What’s used to predict earths climate
Complex computer modelling
What’s an alkali
A soluble base
What’s an acid
A proton donor
What’s a base
A proton acceptor
What’s a conjugate base/acid
When an acid has donated protons, what’s left is its conjugate base
When a base has accepted protons, what’s left is its conjugate acid
What’s special about water
It can act as both an acid and a base → amphoteric
Why is water neutral in pH
Because a tiny % of water molecules dissociate into ions, so equal quantities of [H+] and [OH-] ie a neutral solution
What’s a strong acid
fully dissociates in water into ions so very good proton donor eg HCl → H+ and Cl- (fully arrow used)
What’s a weak acid
Partially dissociates in water into ions. Once ions form they start joining back together so the reaction is an equilibrium ( therefore use double headed arrow)
How do indicators work
Indicators themselves are weak acids, but ones where HA is a different colour to A-. HA <=> H+ + A-
If acid is added, H+ conc increases so equilibrium shifts to the left to use up some of the extra H+. Most of the indicator is present as HA so we see that colour
If alkali is added, it reacts with hence removes H+ so the equilibrium shifts right to replace H+. Most of the indicator is now in the form A- so we see that colour
what is the ionic product of water
Kw=[H+][OH-] which is constant unless temperatyre changes
if water can still conduct a small current even when pure, what does this prove?
that water partially split into ions. conductivity of pure water is very low, showing equilibrium position is far on the left
H2O <=> H+ + OH-
whats the ionic product of pure water/any aqueous solution
1×10-14 mold2dm-6
[H+]=[OH-]=1×10-7
whats pH
the measure of concentration of H+
pH=-log[H+]


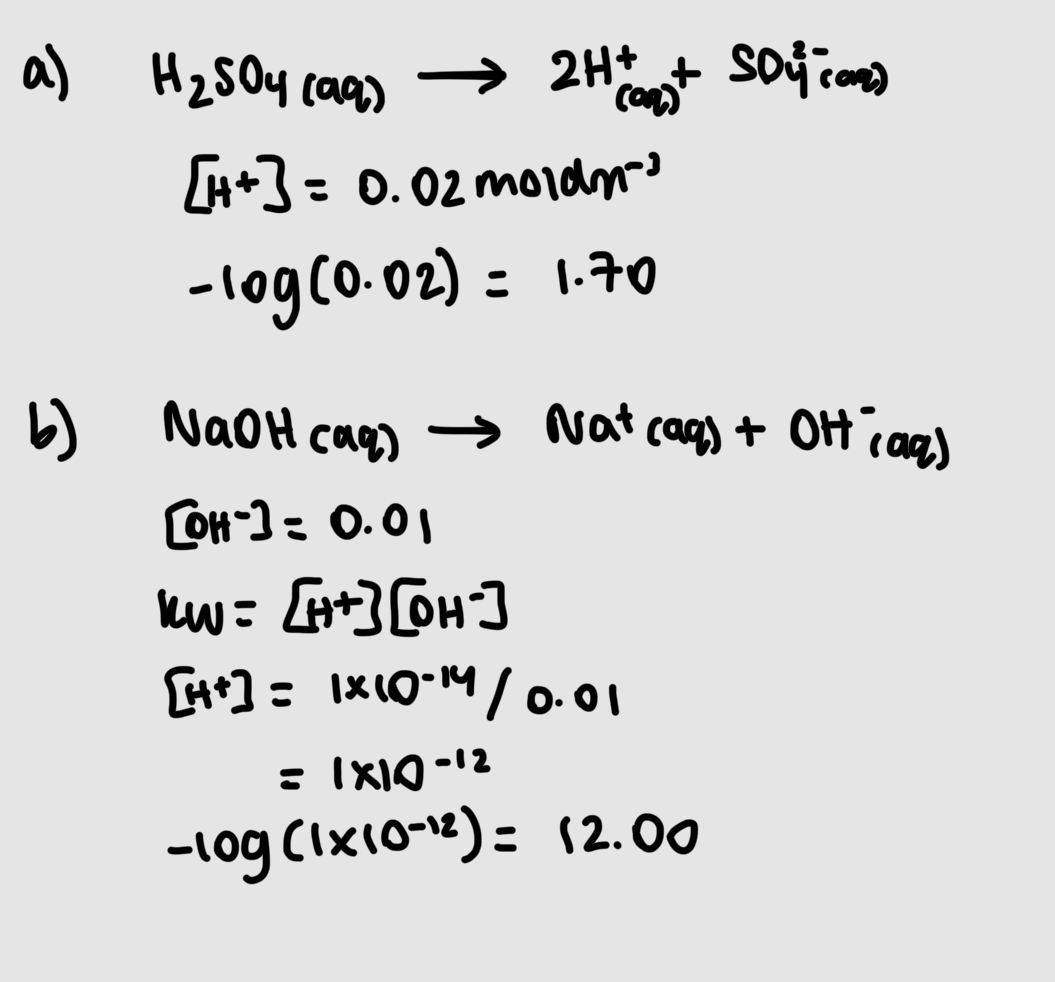
what type of reaction is Kw and how does temp effect this
H2O <=> H+ + OH-
must be endothermic as bonds being broken, so if temperature increases, equilibrium will shift to the right so Kw will increase
what is Ka
the acid dissociation constant
its a constant for a given acid which only changes if the temperature changes
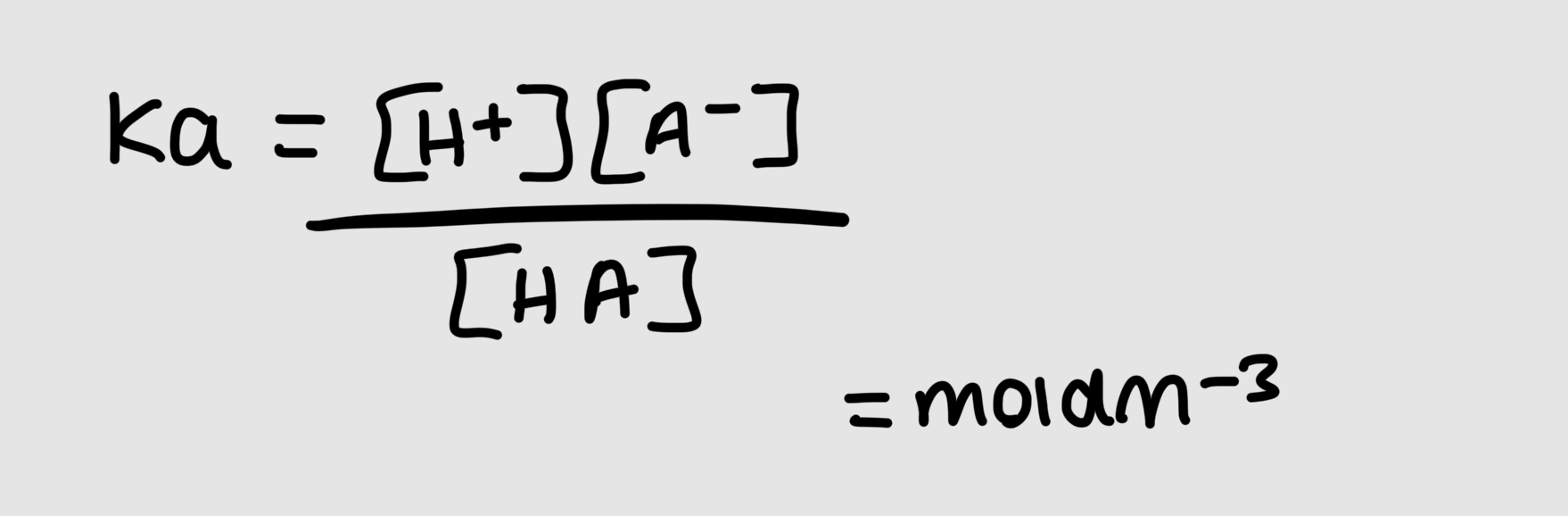
how is Ka and pKa affected
the stronger the acid, the bigger the Ka value, lower the pKa value
what is pKa
pKa = -logKa or Ka = 10-pKa
used as Ka are usually awkward numbers
how do pH and pKa differ
pH varies for a given acid with its concentration
pKa is a constant for given acid whatever its concentration
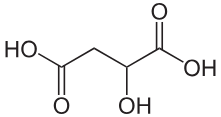
why would 2 pKa values be given for this acid
it has 2 carboxylic groups
how do you use Ka to calculate pH of a weak acid solution
make 2 approximations
that [H+] = [A-], so the top line of Ka is written as [H+]2
conc of [HA-] at equilib = conc of HA put in to the solution (ie [HA] = conc of the solution) → assumes no HA ionises
so Ka = [H+]2 / conc of solution then can do -log to find pH of acid
how do oceans remove CO2
partly by marine life photosynthesising
partly by CO2 dissolving
as concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere rises, what will happen to the concentration of H+ in the sea
as the concentration of CO2 in the air rises, the position of equilibrium (a) shifts right
so [CO2(aq)] rises and hence equilibrium (b) shifts right minimising the change
so [HCO3-] rises and hence equilibrium c shifts right minimising the change
so concentration of H+ in the ocean rises
![<ol><li><p>as the concentration of CO2 in the air rises, the position of equilibrium (a) shifts right</p></li><li><p>so [CO2(aq)] rises and hence equilibrium (b) shifts right minimising the change</p></li><li><p>so [HCO3-] rises and hence equilibrium c shifts right minimising the change</p></li><li><p>so concentration of H+ in the ocean rises</p></li></ol><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/78263f2a-691a-42f3-84ec-f77374f5c2c1.png)
what is a buffer solution
a buffer solution is a solution which minimises change in pH
when acid or alkali is added to it
in small quantities (or when diluted)
what are buffers made of?
theyre solutions containing
a weak acid and one of its salts (eg CH3COOH and CH3COONa)
a weak base and one of its salts (eg NH3 and NH4Cl)
how can you make eg CH3COOH/CH3COONa buffer?
adding both CH3COOH and CH3COONa to a solution or
adding NaOH to a solution of CH3COOH, making sure the acid is in excess to produce the left, so as long as some of the acid is left you will have a buffer
how does a buffer solution work? eg CH3COOH/CH3COONa
start by writing the weak acid equilibrium equation for the weak acid in the buffer, then keep referring to which way it shifts
when asked how it works, always start writing the equation of the weak acid equilibrium.
if acid is added, the equilibrium shifts to the left to minimise the change by using up most of the extra H+ (plenty CH3COO- to do this , but wouldn’t be plenty if we just had a weak acid) so pH hardly changes as all the extra H+ is removed
if alkali is added, the added OH- reacts with hence removes H+ making water, but equilibrium shift to the right to minimise the change so more CH3COOH dissociates replacing almost all he H+ hence pH hardly changes (plenty CH3COOH to do this)
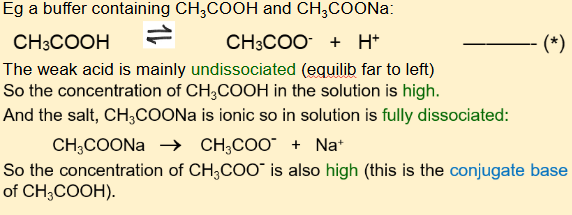
how do you do calculations involving buffer solutions
[HA] = conc of the weak acid in the buffer mixture
[A-] = conc of the salt in the buffer mixture
so Ka of weak acid in it = [H+][salt]/[acid]
so [H+] = Ka x [acid]/[salt] then do -log to find pH
what does the Ka expression of a buffer show?
[H+] = Ka x [acid]/[salt]
why pH is unaffected as the fraction [acid]/[salt] stays unaltered as both concs decrease
how to prepare buffer solutions of different pHs by picking a weak acid with pKa close to the pH you want the bugger to be, then fine tune the pH by altering acid and salt
for a buffer which the conc of the acid and the salt are equal, they cancel out in the expression so [H+]=ka so pH=pKa
What happens when ionic substances dissolve in water
They completely separate from each other, becoming surrounded by water molecules as water molecules are polar and form ion-dipole bonds with ions → hydrated ions
What is solubility
The maximum amount of solid which will dissolve in a certain solvent
What’s the units for solubility
Often gdm-3 and changes with temp, to convert to moldm-3 just divide by molar mass.
What does sparingly soluble mean
It only dissolves a little bit (some ionic solids are insoluble, but do in fact dissolve a tiny bit)
What happens when a sparingly soluble solid is dissolved in water to give a saturated solution
An equilibrium is established between the undissolved solid and dissolved ions
Eg AgCl(s) <=> Ag+ (aq) + Cl- (aq)
What is the solubility product
Ksp = [Ag+(aq)] [Cl-(aq)]
Which always has the same value for a given solution at a given temp
State symbols are required for the mark
What does Ksp give
The maximum concentration of ions that be in solution before a ppt forms
How do you work out with Ksp if a ppt will form
If the value of [A][B] in the mixture is more than the Ksp value given, a ppt will be given.
If it is smaller, no ppt will form
How do you calculate Ksp when mixing solutions
Work out the new concentration of each ion by working out the moles then diving by the new volume
How do you calculate solubility product from solubility
Write the equilibrium then Ksp equation, then plug in the concentration
What if there are 2 moles of an ion
[2x]²
What is common ion effect
Ksp is a constant even if there is another source of one of the other ions. If there is then the solubility of the solid will be lowered
What are practical considerations to make as the idea is to make a saturated solution of the solid and carry a suitable titration to find the conc of one of the ions
ensure the solution is saturated→ excess solid is added to water and stirred thoroughly
Should be filtered to remove any remaining solid
Accurately measure a volume of the solution using a pipette and put in conical flask
Conc of standard solution used in titration should be adjusted to ensure a big enough titre is given to avoid large % errors
Repeat to get concocrsnt results, go drop wise near end point
How do you calculate entropy change of the system
Units are JK-1mol-1 (J K moling)

what is entropy
The measure of the number of ways that particles can be arranged (or measure of disorder)
What effects entropy
Physical states - solids < liquids < gases as solids are in a more ordered arrangement in fixed positions, where as gases are more disordered as the particles are more spread out
the amount of energy a substance has - the more energy quanta a substance has, the more ways they can be arranged → heating a substance increases the number of energy quanta so increases entropy or bigger/heavier molecules have higher entropies as their energy levels are closer together so more energy quanta
number of particles - the more particles you got, the more ways they and their energy can be arranged so increase in number of moles increases entropy
what decides if a process will or wont happen?
for a process to happen (be spontaneous/feasible), the overall entropy change, ΔtotalS must be positive
how do you calculate ΔtotalS?
ΔtotalS = ΔsystemS + ΔsurroundingsS units are JK-1mol-1
where ΔsurroundingsS= -ΔH/T
have to convert ΔH from kJmol-1 to Jmol-1
how can you use entropy calculations to find the melting point
the temperature when ΔtotalS is zero, so when rearranging calculation
T= ΔH/ΔsysS
whats entropy at equilibrium
ΔtotalS = 0 with neither direction favoured, so Kc=1
Give examples of processes which have increasing disorder and are exothermic, giving the temperatures they will occur at
Ice melting, NaOH dissolving.
All temperatures because ΔtotalS is positive at all temperatures
Give examples of processes which have decreasing disorder and are endothermic, giving the temperatures they will occur at
No temperature because ΔtotalS is negative at all temperatures
Give examples of processes which have increasing disorder and are endothermic, giving the temperatures they will occur at
NaCl dissolving, thermal decomposition
Eg melting, boiling, dissolving ionic solutions occurs when ΔtotalS is positive which is when ΔH/T<ΔsysS which is more likely at higher temperatures ie will work better at a certain higher temp
Give examples of processes which have decreasing disorder and are exothermic, giving the temperatures they will occur at
Water freezing, 2Cl* - Cl2
eg freezing, dissolving gases
works when the magnitude of ΔH/T>ΔsysS so more likely at lower temperature ie will work below a certain temperature and work better
Many salts with a positive enthalpy change of solution are readily soluble in water. Explain this in terms of ΔtotS, ΔsysS and ΔsurrS for the dissolving process
ΔsysS for the dissolving must be positive
ΔsysS = ΔsysS + ΔsysS
ΔsysS is -ve here as ΔsysS is the +ve and temperature is always +ve
so for the ΔsysS to be +ve, ΔsysS must be +ve ( and > ΔsysS)
often the case for dissolving as the ions more disordered when in solution : more ways of arranging
do feasible reactions always happen?
no because ΔtotS tells us nothing about Ea. If Ea is very high the reaction may not happen spontaneously. It may need igniting in some way eg using a use to overcome the high Ea