Ch17: Gonadal (Testes)
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Testes
Paired, ovoid organ
production of sperm and reproductive steroid hormones
Secretes testosterone
embryonic stage
Aids in development and differentiation of the primordial gonads
after puberty
stage where testes Helps with sperm production and maintains 2° sexual characteristics
Week 6
Primordial germ cells migrate to gonadal ridges
Surrounded by sex cords to form primitive, bipotential gonads (in both XX and XY)
Sex-determining Region Y Gene
Gene on short arm of Y chromosome is the designated Testis determined factor (TDF) acts as a switch turning to male development pathway
Testis determined factor
Produces a DNA-binding protein that initiates male development
true
true or false: If no Y chromosome (46, XX), female development (ovaries) is followed automatically
SEMINIFEROUS TUBULES
Contains germ cells that develop into sperm (spermatogonia) & Sertoli cells
Tubuli recti>Ductuli efferentes testes>Epididymis>Vas deferens
Week 7
Medullary tissues are formed by how many weeks of gestation?
Vitamin C, fructose
Secretory products sperm mixes with as it travels through tubules
leydig cell
Cells that synthesize testosterone
Its activity is regulated by Luteinizing Hormone from pituitary gland
Luteinizing hormone
ANTI-MULLERIAN HORMONE
Causes mullerian ducts to disappear
Spermatogenesis
Sperm are from spermatogonia
Spermatogonia/Spermatogenesis
undergo mitosis and meiosis to form mature sperm
Spermatogonia>Mitosis>1st spermatocyte>Meiosis 1> 2nd Spermatocyte> Meiosis II>Spermatid
sequence of spermatogenesis
Acrosome, sperm head, nucleus, centriole, neck, mitochondri, midpriece, axoneme, principal piece, tail
identify major parts of sperm
Follicle stimulating hormone, Luteinizing hormone
2 pituitary hormone supporting male fertility
Follicle Stimulating Hormone
1st pituitary hormone acting on sertoli cells to support spermatogenesis
Acts on germ cells
Spermatogenesis
Luteinizing Hormone
2nd pituitary hormone acting on testes
Acts on leydig cells to stimulate testosterone synthesis
Testosterone
Principal androgen hormone (male) secreted in response to LH
➢ 2-3% Free
➢ 50% albumin bound
➢ 45% SHBG bound
➢ Provide (negative) feedback control to the hypothalamus and pituitary
8 AM
Peak of testosterone according to PPT
6 AM
Peak of testosterone according to Book bishop cc2
12 AM
Nadir of testosterone according to Book bishop cc2
8 PM
Nadir of testosterone according to PPT
4-10 mg
How much testosterone is secreted daily after puberty?
t
t/f: Testosterone is produced in small amounts by the ovaries and adrenal glands
Estradiol, Dihydrotestosterone
Testosterone is converted to two active metabolites called
Scrotal skin
it is rich in 5α-reductase which converts testosterone to DHT
no virilization
identify this stage
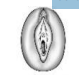
stage 1
identify this stage

stage 2
identify this stage
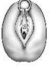
stage 3
identify stage
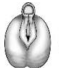
stage 4
identify stage

stage 5
identify which stage
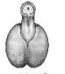
Hypothalamic-hypophyseal vascular connections
○ Responsible for LH release by GnRH
○ Becomes functional by weeks 11–12 or 3 weeks after Leydig cells start producing testosterone
postnatal development
a. Development of secondary sex hair (face, chest, axilla
and pubis)
b. Enhanced linear skeletal growth
c. Increase upper body musculature
d. Development of larynx and vocal cords
e. Deepening of the voice
Hypogonadism
leads to imprecise closure of growth plates leading to:
Excessive height
Long limbs
Disproportionate upper and lower body segment
Sertoli Cell
produce mullerian regression factor that aids in regression of female primordial genital tract
Scrotal skin
Rich in is 5α-reductase which converts testosterone to dihydrotestosterone
5α-reductase
converts testosterone to dihydrotestosterone
Tanner staging
Used to diagnose premature or delayed sexual development
Prepubertal, Enlargement of scrotum, increased length of penis, enlargement of testes with growth of glands, mature genitalia
Enumerate stages of genital development
Hypergonadotropic hypogonadism

Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism

Klinefelter’s syndrome
HYPERGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM
Trisomy (47, XXY)
Small testicles, gynecomastia,
azoospermia/sterile/infertility
↑ aromatase, ↑ estrogen;
Reduced bone density and breast
cancer
*high risk of osteoporosis
increased breast cancer risk
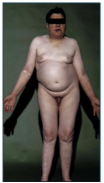
TESTICULAR FEMINIZATION SYNDROME
Complete Androgen Inensitivity Syndrome (CAIS)
Lack of testosterone action
Female phenotype
May appear to have fully developed breast, female-like distribution off fat & hair

Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome
most severe form of androgen resistance
mutation in androgen receptor gene
may be complete (CAIS) or partial (PAIS)
Quigley scale
Phenoypic grading from “fully masulinized” & “fully feminized” genitalia
5a-Reductase Deficiency
HYPERGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM
● ↓ Testosterone
○ Reduced conversion of testosterone → DHT
● Female phenotype until puberty
● Late action of testosterone
● Mutation in encoding type 2 isoenzyme, maps to chromosome 2p23
MYOTONIC DYSTROPHY
HYPERGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM
● Autosomal dominant
● Genetic disorder that causes progressive muscle loss
and weakness
● Testicular failure (in the 4th decade of life)
Type 1
Myotonic dystrophy with DMPK gene mutation
Type 2
Myotonic dystrophy with CNBP gene mutation
true
true or false: testicular failure usually occurs when px is 20-30s
TESTICULAR INJURY & INFECTION
HYPERGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM
Postpubertal mumps can result in mumps orchitis and permanent testicular injury
SERTOLI CELL ONLY SYNDROME
Also known as germ cell aplasia and arises from Y chromosome microdeletion on Yq11 locus
HYPERGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM
● Normal testosterone action
● Lack of germ cells
● Azoospermia
KALLMANN’S SYNDROME
●X-linked congenital disorder
● Affects the development of the hypothalamus (↓ GnRH)
and olfactory nerves.
● Anosomia
● Hypogonadism during puberty
hypogonadotropic hypogonadism
Anosomia
inability to smell and midline defects (cleft palate) color blindness and deafness
● Mutation in KAL1 gene
HYPERPROLACTINEMIA
● Can be drug-induced or caused by tumors
● Pituitary tumors
● Primary Hypothyroidism
decreased LH & testosterone
110 ng/dL
Average testosterone decline after 30 yrs old is (?) per decade
Also experience muscle loss and lesser bone density
type 2 diabetes
Pituitary disease that makes
○ ↓ Testosterone (Free or total serum); ↓ LH
○ Stem from insulin resistance, low SHBG
levels, inflammation, and ↑ estradiol levels
Opioid use
○ Caused by μ-opioid receptor–mediated suppression of pulsatile GnRH production
○ Reduced male fertility
○ Decreased sperm motility
○ Lower sperm counts
○ Abnormal sperm morphology
parenteral
replacement therapy that is injectable testosterone in muscle every few days
transdermal
daily skin patches that provide steady hormone levels w/ possible skin mild irritation
Buccal
tablets applied to gum/cheeck for slow absorption
subcutaneous
implanted under skin, long lasting pellets
Cutaneous/Testosterone gel
require stable levels and caution due to transfer through skin contact