Biology 1A03 Theme 5
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
DNA polymorphisms
one of two or more alternative forms(alleles) of a gene at a chromosomal region that differs in either a single nucleotide base or have variable numbers of tandem nucleotide repeats
Tandem repeats
are patterns of one or more nucleotides that are repeated (these repetitions are directly adjacent to each other and can
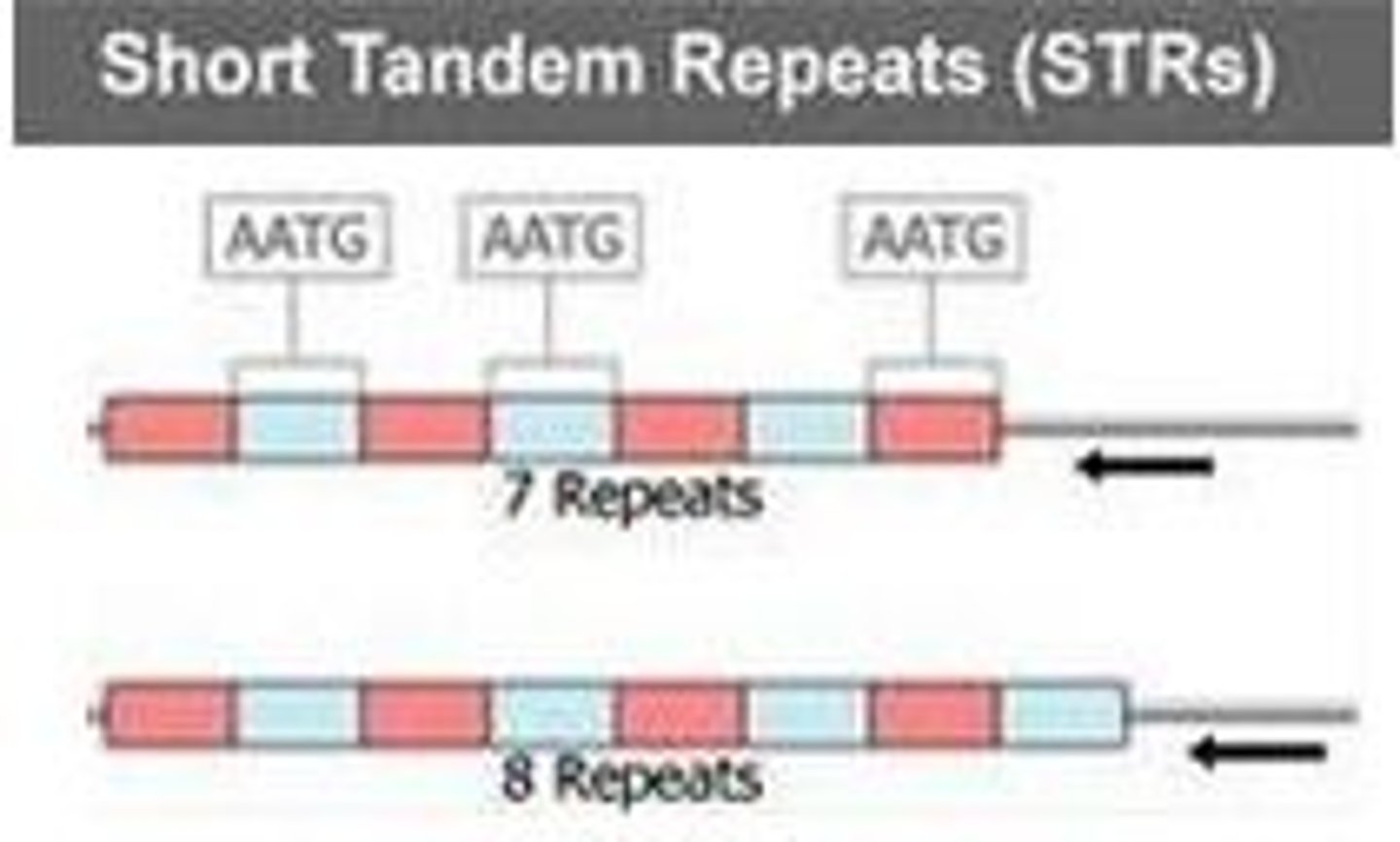
How are alleles detected?
microarray analysis, PCR, southern blot, and even dna sequencing
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs)
most common type of genetic variation and come from single nucleotie base changes or substitutions that can occur in a significant portion of a population and are usually found in non coding and coding region
How often are SNPs?
about once every 350bp
DNA markers
if an SNP if found close to a particular gene, they can be used as DNA markers for that specific gene (if the SNP is close enough of linked to a gene of interest, then every time that gene is passed on from a parent to a child, then the SNP is also passed on)
Silent variations
variations that happen in non coding regions of DNA and has no effect
Genotype
representation of the pair of alleles the person has
phenotype
the cell or bodily physical representation of the genotype (blue eyes, sickle cell shaped blood)
Beta Globin gene in sickle cell anemia
it is found in chromosome 11 and every person has two copies, one from each parent
HbA
the homozygous genotype and will express normal blood cells
HbS
the sickle allele brought about by SNPs
Homozygous HbS
leads to sickle cell anemia with blood that cant take oxygen properly
HbA/HbS
heterozygous allele will produce normal and sickle blood cells but they will make more normal blood cells and thus there is no sickle cell effect that will occur
Variation in populations
sickle cell anemia is found in many populations with different alleles or haploytypes emerging independently across many poplulations
Among nations with the highest prevalence of sickle-cell anemia, it has been found that there are a possible 5 distinct beta-globin haplotypes found across different patients that correlates with regional distribution of distinct sickle cell anemia single nucleotide polymorphism
Variation in gene copy number
gene copy number can contribute to genetic difference between individuals and result in a region that many be normally present in one copy per chromosome but may be duplicated or deleted (Ex. AMY1 gene for amylase)
Inheritence of chromosomes
done through mieosis
Gamete
cells in the body that are not produced through mitosis (sperm and egg)
Male gamete
4 haploid sperm cells
Female gamete
one large egg
Meiosis
similar to mitosis is the division of gamete cells
Interphase
allows for duplication of chromosomes by two consecutive cell divisions wich results in the production of four haploid daughter cells by the end which contain half the amount of chromosomes of the parent cell
Prophase 1
it is the first meiotic division wher ethe chromosomes condense and the nuclear envelope begins to degrad ealong side with the chromosomes undergoing synapsis
Synapsis
pairing of and physical connection of homologous chomosomes along their length
Synaptonemal complex
forms between homologous chromosomes which hold them together during synapsis
Chiasmata
the cross over and exhchange of corresponding segments of DNA molecules between homologous chromosome pairs
Recombiant Chromatids
all homologous chromosomes will pair with eachother during synapsis which allows for the formation of a bivalent unit which consists of a pair of synapsed chromosomes to form a a four stranded sturcutre
non sister chromatids
replicas of different chromosomes which are genetically similar but not identical
metaphase I
homologous chromosomes line up at metaphase plate
Anaphase I
synaptonemal complex breaks down and allows simple fibers to pull each homologous pair on opposite poles
Telophase I
allows the division of the cell into two haploid cells
the parent diploid of 46 chromosomes will now split into two haploid cells with 23 chromosomes each
Prophase II
23 different duplicated sister chromatids and nuclear envelope breaks down and chromosomes condense
Metaphase II
chromosomes positioned at center and since crossing over occured in Meiosis I, the two sister chromatids are not identical
Anaphase II
proteins holding the sister chromatids toether at the centromere broken down and allows chromatids to seperate and move to opposite poles of the cell as individual chromosomes
Telophhase II
reforming of nuclear envelope and chromosomal decondesing which is followed by cytokinesis
Nondisjunction
When gametes have an extra chromosomes or other have a missing chromosomes due to failures in meiosis
Gregor Mendel
Identified and documented two laws that would explain principles of inheritence
What did mendel do?
he bred true breeding plants and bred the first generations and saw what would happen
Law of Segregation
states that two alleles of a gene separate into two different gametes during gamete formation in both parents
Monohybrid
cross between two traits
heterozygous
Aa or Bb, when there is a dominant and recessive trait the dominant trait takes over
Heterozygous dominant
when there are two alleles and the dominant takes over
Homozygous Dominant
AA when both alleles are dominatn
Homozygous recessive
when both alleles are recessive (aa) they take over
Monohybrid Phenotype ratio
3:1
Monohybrid genotype ratio
1:2:1
Law of independent assortment
Applies to genes that are located different chromosomes stating that allele pairs seperate independant during the formation of gametes, thus traits are transmitted to offsprint independently of eachotehr
Dihybrid cross
cross between two parents of a two genes taht are linked
Mendel -from gene to protein
B gene in SBE1 gene (starch branding enzyme)
without this enzyme, sucrose contest was higher and caused swelling of the seed, and when the seed matured it lost its water and went wrinkled --> physical wrinkled seeds
Pedigrees
family trees that allow for a visual representation of the segregartion of s specific trait
Sex chromosomes
the X and Y chromosomes
Male sex chromosome
XY
female sex chromosome
XX
how do the sex chromosomes pair and segregate like homologous ones during meisis
they have small regions at the tips that are similar to allow pairing
Sex linked gene
gene that is on the sex chromosomes even if it has nothing to do with the sex of the organism because the expression depends on the sex of the individual
p arm
short arm of chromosome
q arm
long arm of chromosome
Colourblindness
an ishihara colour test is the most common way to test for red/green colour blindness, and it is a hemizygous state, the rule of dominance and recessiveness no longer apply
Linked genes on the X chromosome
genes positioned close together on the same chromosome are referred to as linked because they usually inherit together and do not segregate
Recombination of Alleles
- If two genes are far apart, during crossing over, there is a high chance that alleles can be switched from each chromosomes creating recombinant chromosomes
- But if the genes are close to each other, we see very little chance to switch alleles during crossing over
- Recombination frequency is higher with alleles that are farther apart than closer together
- Recombination frequency can be used to determine the distance between genes along the same chromosome
Linkage maps
shows you the distance between chromosomes but also the order the genes along the chromosome
What is recombination frequency used for?
to determine the distance between genes along the same chromosome
genes closer together
do not segregate
genes farther apart
segregate
The ABO blood system
variation in genetics contributes to the system. red blood cells all have the same function but different types exist and the blood type depends on the presence or absence of specific inherited cell surface proteins
glycosyltransferase enzyme
catalyzes the formation of speicific A or B agglutinogens that are expressed on the cell surfaceIn addition, the AB blood type has several SNP polymorphisms that leads to the formation of slightly different transferases
HIV resistance mutation
some mutations such as those by some people in the mid-14th century