DNA -> mRNA = Transcription
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
The RNA molecule
RNA nt. structure
A, G, C and Uracil (U)
Ribose, deoxyribose
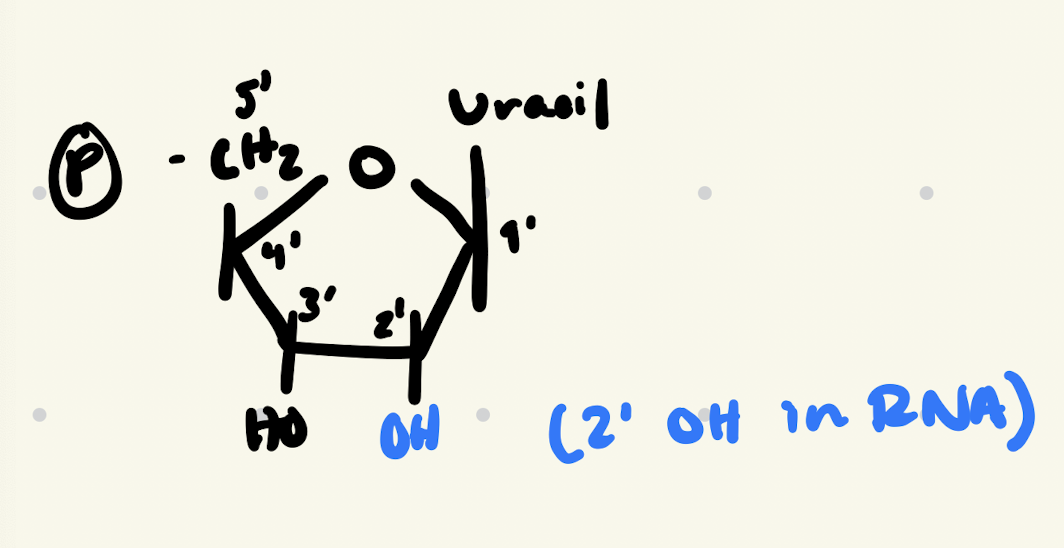
Phosphodiester
holds RNA nts. in 5’-3’ direction
normally single stranded
can fold (bp) internally
Nucleus
transcription location for Euk. cells
after synthesis, travels to cytosol
mRNA
messenger RNA = intermediate for protein synthesis
functional RNA
final RNA product has function and is not translated (tRNA, rRNA, snRNA, miRNA…)
Initiation of transcription
overview of gene coding region (2-3%) genome
Gene
genetic information/recipe to make protein
Humans have 20,000 to 30,000 diff genes
Each gene has a specific location in genome
-2-3% of genome codes for protein
Remaining DNA codes for functional RNA (low %) + involved in regulating gene expression
Locus
a specific location in genome
Gene structure
100s-1000s of base pairs
only one strand of DNA serves as template for transcription
Coding Strand
non-template
upstream transcription
negative numbers
downstream transcription
positive numbers
transcription start site
starts at +1 start site, 1st nt. to be transcribed
Promoter
Required for Ts but it is NOT transcribed
Directly upstream +1, on 5’ side of gene on coding strand
Promoter = binding side (DNA seq.) where RNA pol. binds
Prok. Promoter
DNA Sequence consensus sites =
-35 site 5’ TTGACAT 3’
-10 side (pribnow box) 5’ TATAAT 3’
RNA pol. Holoenzyme
binds to promote
sigma subunit recon. + binds to RNA pol. holoenzyme
beta subunit recog.
Eukaryotic Promoter
DNA sequence = TATA box (-25)
Basal Transcription factors (TF) = proteins that bind to the promoter (TATA) and recruit the polymerase
Synthesis/Elongation of RNA Transcript
RNA pol. opens the strands/unzips the DNA helix
begins (w/out primer) adding RNA nts. complimentary to the DNA. template (starting @ +1)
Strand is elongated by RNA pol. adding nts. to 3’ end of growing strand
As RNA transcript grows, it dissociates from DNA and DNA helix forms
Coding strand
always the same as mRNA (T’s rather than U’s)
identical to mRNA transcript
Prok. Termination of Transcription
Transcription ends w/ formation of stem-loop/hairpin loop in transcript
followed by a stretch of A nts. → causes mRNA to dissociate
Euk. Termination of Transcription
near end of RNA transcript. seq. AAUAAA= term. seq.
RNA Transcript cut +25 nts. downstream
Prok. product of transcription
mRNA → translation
Euk. product of transcription
pre-mRNA (primary transcript) must be modified before translatiopre-mRNAn
Nucleus
Location of pre-mRNA processing
pre-mRNA processing
5’ cap modified guanine (G) added to 5’ end
Poly-A Tail - 50-250 A. nts. are added to 3’ end
RNA Splicing
Reason for pre-mRNA processing
modifications are required to protect ends from being chopped up and to export mRNA from nucleus to cytosol
RNA Splicing (intron removal)
Exons = sequence to be translated
Introns = sequence removal (spliced out) before
SNRPS
form a complex called a splicosome complex → cut @ junctions. Introns removed, exons spliced together