Enolate reactions
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
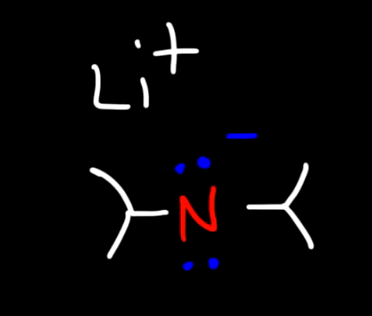
What is LDA?
Lithium Diisopropylamide it is a strong bulky base
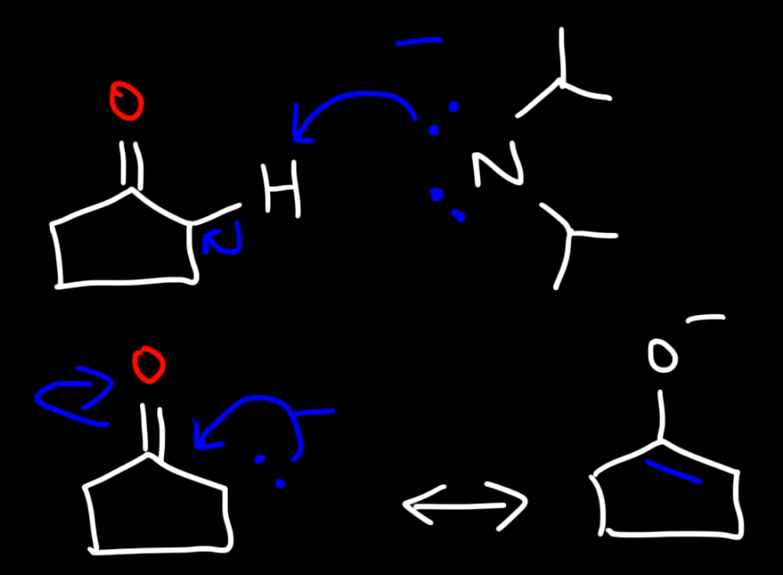
The mechanism of a ketone reacting with LDA and methyl bromine 1
The mechanism of a ketone reacting with LDA and methyl bromine 2
The mechanism of a ketone reacting with LDA and methyl bromine 1
What is different about unsymmetrical ketones?
That either hydrogen on either side can be attacked but depends on the reactants used
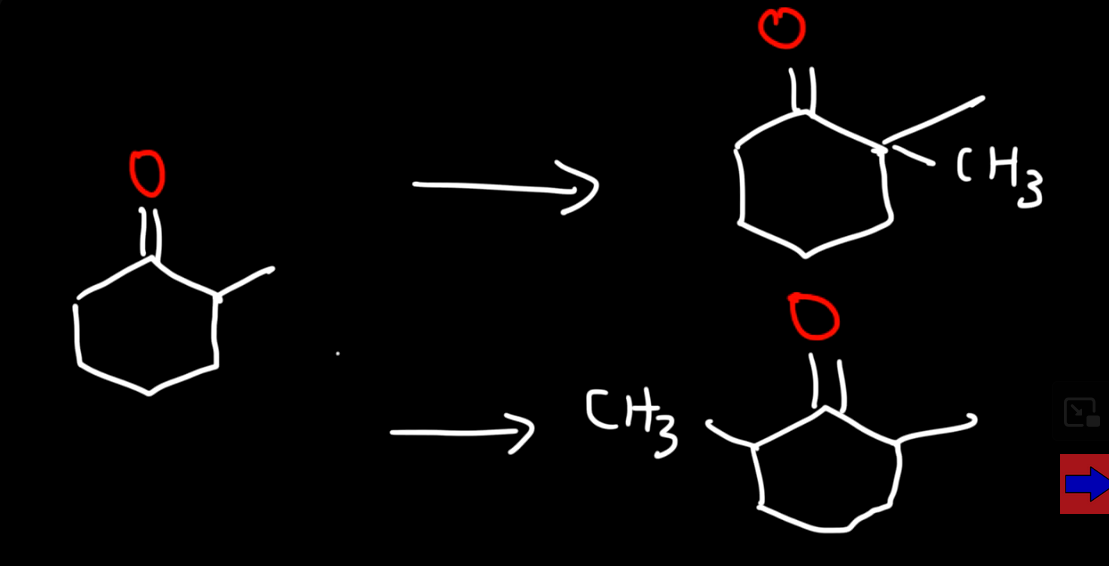
To have our hydrogen on the left side to be attacked what are the reagents/conditions? (kinetic product)
LDA at low temp e.g -78 and methyl bromine
To have our hydrogen on the right side to be attacked what are the reagents/conditions? (thermodynamic product)
Strong base which is not steriacally hindered e.g NaH at room temp and methyl bromine
A small base is able to..
…Attack from either side
Example of small base attacking from either side forming two products
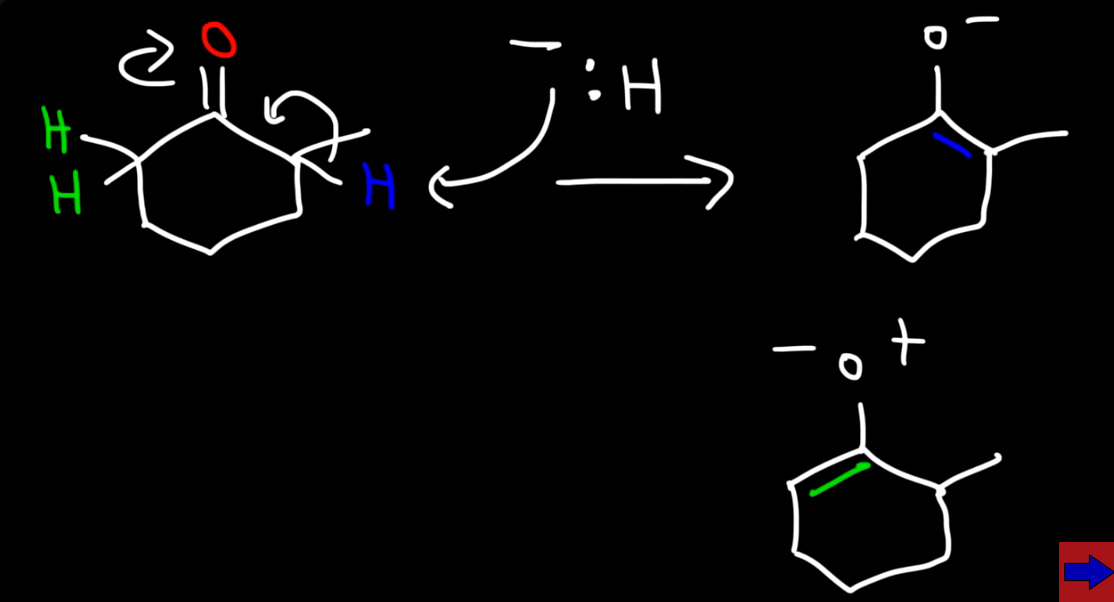
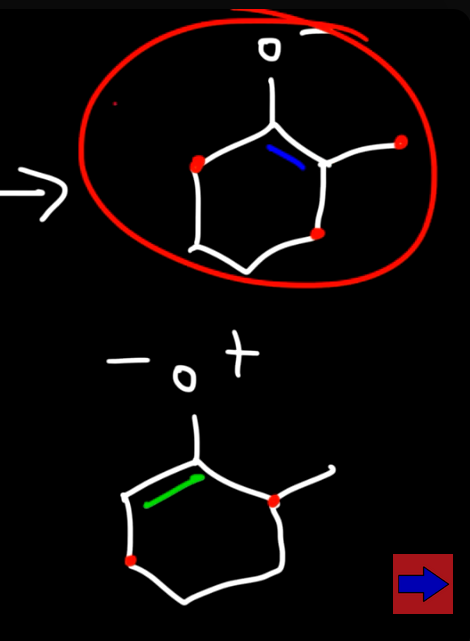
Because two products are formed which one is more stable? (usually at a higher temp)
The one with more R groups which is used as the major product when reacting with methyl bromine
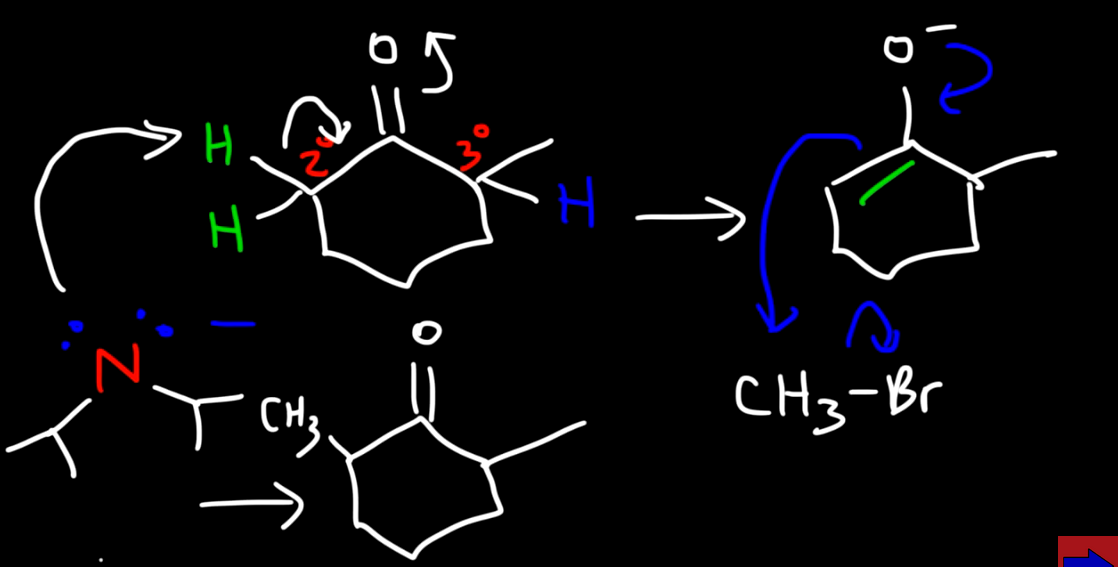
Reaction with LDA and an unsymmetical ketone
Bulky base so it prefers the secondary hydrogens as they are more accessiable favouring the kinetic product
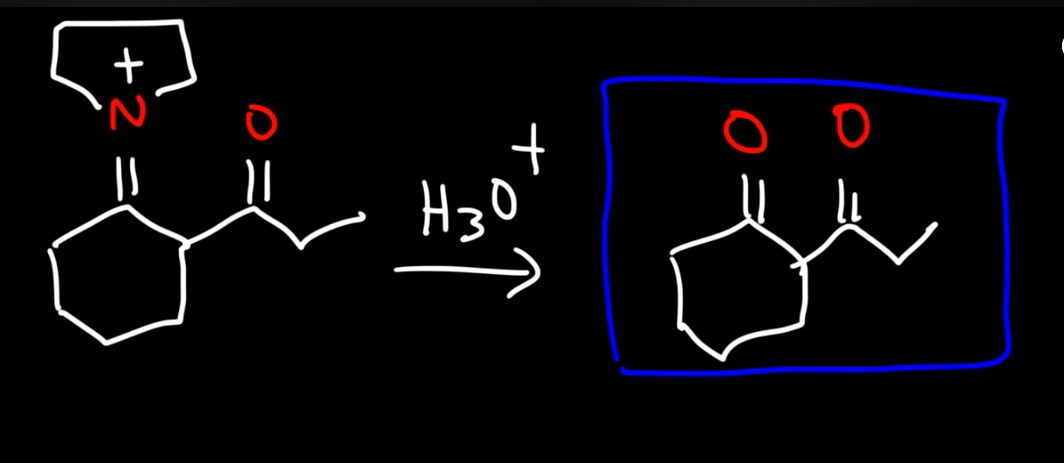
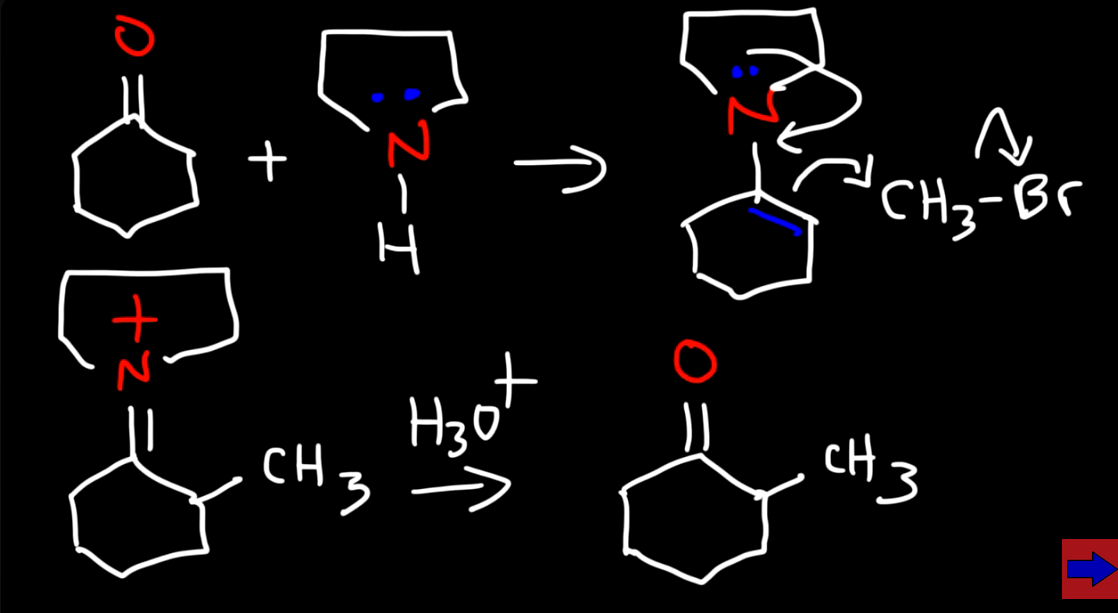
Alkylating a ketone with an enamine intermediate
No strong base is used
Enamine intermediate reacting with other electrohpile like alpha beta unsaturated aldehyde 1
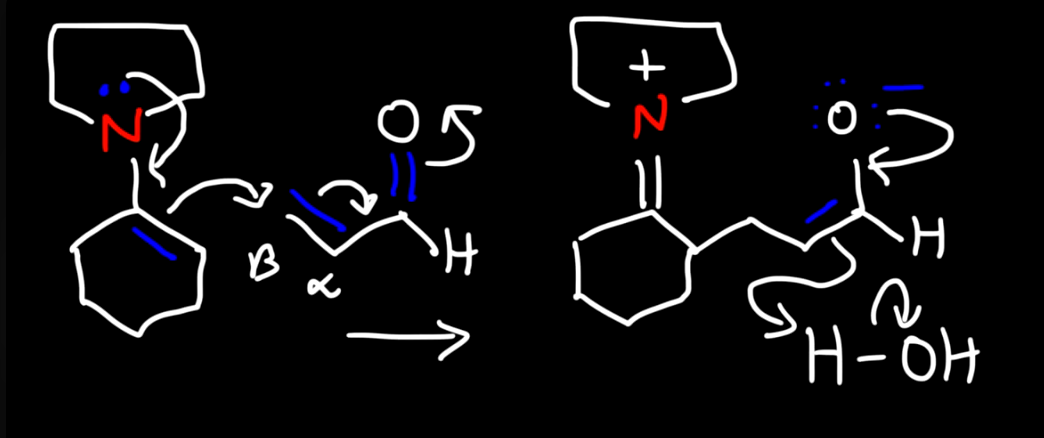
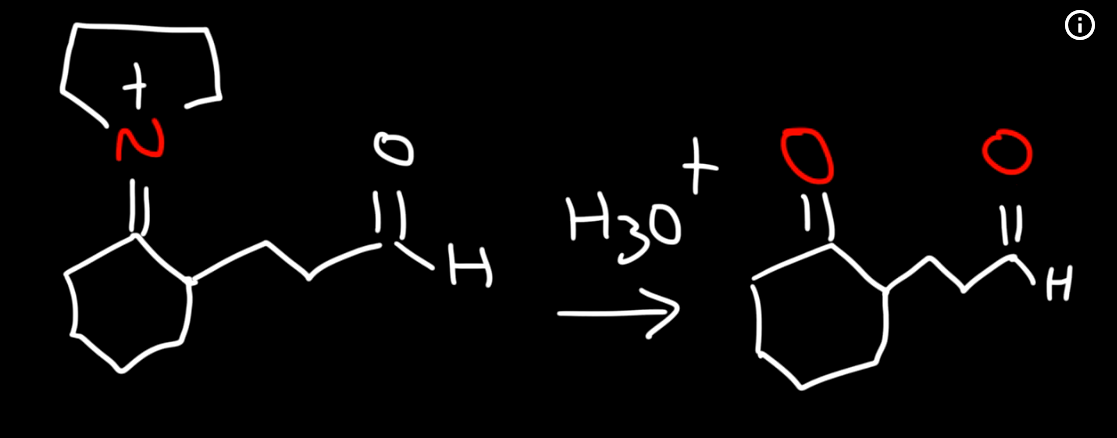
Enamine intermediate reacting with other electrohpile like alpha beta unsaturated aldehyde 2
Enamine intermediate reacting with acid chloride 1
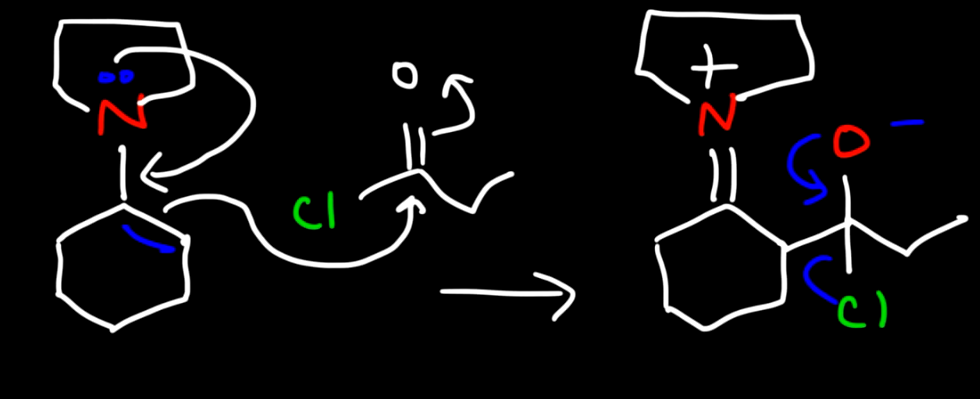
Enamine intermediate reacting with acid chloride 2