Unit 4: Cell Membrane
1/43
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
plasma (cell) membrane
the semipermeable membrane surrounding the cytoplasm of a cell
defines the boundary of a cell and determines what gets in/out of the cell
contains integral and peripheral proteins (determine membrane function)
cholesterol
can also help regulate spacing, & stabilize the membrane during high temperature exposure
osmosis
diffusion of water
movement of water through a selectively permeable membrane
active transport
requires energy, low → high concentration
Counteracts diffusion
Uses energy (ATP) and a protein channel to pump proteins from low to high concentration
ATP
is a molecule our cells use to provide energy.
Special type of nucleotide that’s an energy molecule
—-: Adenine + ribose sugar + triphosphate = energy released for cell + loss of a phosphate
—-: adenine + ribose sugar + diphosphate = energy absorbed from food + addition of a phosphate
hypotonic
the extracellular fluid has a lower concentration of solutes than the fluid inside the cell and water will enter the cell
The extracellular fluid has a higher concentration of water than the cell
Water will follow its concentration gradient and enter the cell which could cause it to burst (lyse)
isotonic
extracellular fluid has the same osmolarity of the cell
If the concentration of solutes in the cells matches the extracellular fluid then there will be no net movement of water
hypertonic
the extracellular fluid contains less water than the cell does with a lower concentration of solutes and water will exit the cell
The solute is drawing water out of the cell
May cause a cell to shrivel (crenate)
concentration gradient
the movement of molecules from where they are more concentrated to where they are less concentrated, which continues on and on until there is an equal number of molecules on either side
exocytosis
process by which bulky molecules are transported (such as polysaccharides)
In the cell this process involves:
The transport vesicle leaves the golgi apparatus
Vesicle moves to the plasma membrane
Fuses with the plasma membrane
Contents the vesicle was carrying are spilled in/become one with the plasma membrane
endocytosis
the process by which a cell takes in large molecules (opposite of exocytosis)
In the cell this process involves:
the plasma membrane depressions pinch in to form a material that will close in around the vesicle of a cell
phospholipid bilayer
Phospholipids made in the smooth ER
Phospholipids self-assemble into a bilayer
Hydrophobic tails inward
Hydrophilic heads outward
Exposed tails bend until all hydrophobic portions are protected, creating a sphere
Phospholipids help keep the membrane fluid which is essential for
it to work properly in different environments
channel proteins
a protein that allows the transport of specific substances across the cell membrane
provide a hydrophilic bridge across a hydrophobic core
glycoproteins
proteins that have a carbohydrate groups attached to the polypeptide chain
receptors
has a binding site that allows communication between the environment outside the cell (hormones) and inside the cell
diffusion
when particles spread out evenly in a space creating an equilibrium (a result of thermal energy from molecules vibrating and randomly moving)
solute
a substance that dissolves in a solvent
solvent
a liquid a solute dissolves in
substance
a mixture of a solute and solvent (transparent)
simple diffusion
diffusion without a helper protein
facilitated diffusion
diffusion using a helper protein
passive transport
does not require energy, high → low concentration
diffusion
osmosis
equilibrium
when things are balanced (opposing balances are balanced)
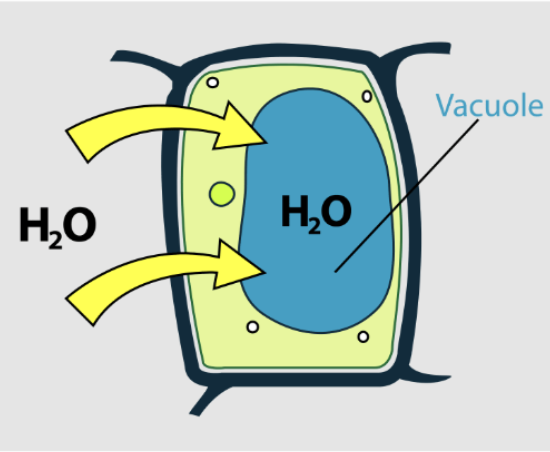
turgid
swollen (hypotonic)
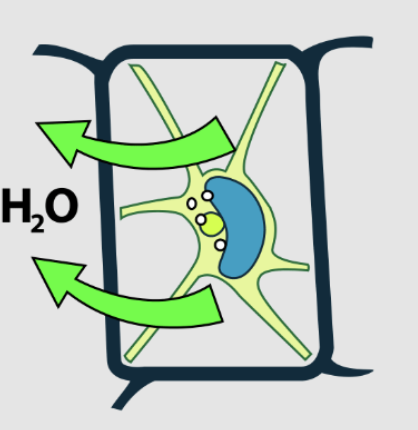
flaccid
drooping from lack of water (isotonic)
aquaporin
integral membrane proteins (reside within the bilayer membranes that surround cells and organelles) that serve as channels in the transfer of water and sometimes in small solutes across the membrane
semipermeable
allowing certain substances to pass through it but not others, especially allowing the passage of a solvent but not of certain solutes
vesicle
bubble-like membrane structures that stores and transports cellular products and digest metabolic wastes within the cell
cytosol
the component (usually containing water typically as a solvent) of the cytoplasm of a cell, within which various organelles and particles are suspended
fluid mosaic
part of the membrane is a thicker sort of liquid (compared to oil) that holds components that can float around, kinks are produced by some phospholipids
when the double bond in unsaturated fatty acid tails of the phospholipids prevents them from packing too tight together
Steroid cholesterol, found in animal membrane cells, has the ability to keep the membrane warm but the “fluid” cooler
“mosaic” aspect comes from the diverse types of proteins that different types of cells have or the diverse range of jobs that proteins can have
a “mosaic” is the protein diversity coming together to help complex organisms such as ourselves function.
concentration
the quantity of solute that is dissolved in a certain quantity of solvent in a solution
concentration solution = has a large mass of solute in a certain quality of solvent
dilution
the process of adding a solvent to a solution to reduce the concentration of the solute
dilute solution = has a small mass of solute in a certain quantity of solvent
paramecium
freshwater protist
Solution inside has a higher concentration of solutes (hypotonic)
Exocytosis (release water so it doesn’t explode, requires energy)
Contractile vacuole + radiating canals
cytolysis/lysis
the bursting or rupturing of cell membrane when the cell can no longer contain the excessive inflow of water (or extracellular fluid)
proton pump
a special kind of transporter that pushes hydrogen ions from areas of low concentration to areas with high concentration
ions moving down release energy and vice versa
bulk transport
exocytosis and endocytosis
plasmolysis
contraction/shrinkage due to water loss (hypertonic)
osmoregulation
the process in which cells and simple organisms maintain fluid and electrolyte balance with their surroundings
soluable
a substance that is able to dissolve in a certain solovent
insoluable
a material that is unable to dissolve in a certain solvent
selectively permeable
is that only substances can pass through while others struggle to get through the membrane
Ex. would be essential ions and molecules that need proteins to transport them to allow them to enter or exit the cell
permeable
it must allow liquids or gasses to pass through it
more specifically refers to a passage of molecules through a membrane or any other barrier molecules may encounter in a cell
concentration gradient
is the movement of molecules from where they are more concentrated to where they are less concentrated, which continues on and on until there is an equal number of molecules on either side
when a molecule moves “down” it is referring to the molecules moving to a place with fewer molecules (less concentration) from a place with more concentration
tonic
amount of solute in a solution