Kines: HW: Movement Arms/Levers
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
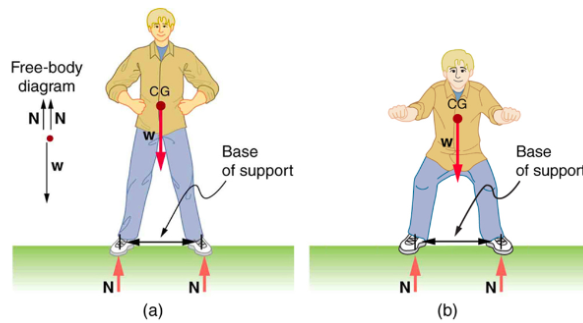
Stability is increased by:
a. Increasing the BOS and lowering the COM
✅ Why?
A wider base of support (BOS) provides more stability.
A lower center of mass (COM) reduces the risk of tipping over.
Think of a squat position vs. standing on tiptoes—lower and wider is more stable!
What is the effect of moving the line of gravity to the edge of the base of support?
Decreases stability
The base of support (like the feet or a surface) needs to be wider or more centered under the body to maintain balance.
When the line of gravity moves to the edge, the body is closer to tipping over.
When resistance is between the axis and the force, which class of lever is created
Second
A second-class lever happens when the resistance is in the middle, with the fulcrum on one side and the force on the other.
Example: Standing on tiptoes (heel = fulcrum, body weight = resistance, calf muscles = force).
Explain why using a wheelbarrow vs. using a shovel are two different types of levers.
Wheelbarrow = Second-Class Lever (A – R – F)
Axis/Fulcrum: Wheel
Resistance/Load: Inside the wheelbarrow
Force/Effort: Hands lifting handles
✅ Less effort is needed to lift heavy loads
Shovel = Third-Class Lever (A – F – R)
Axis/Fulcrum: Top hand
Force/Effort: Bottom hand pushing
Resistance/Load: Dirt on the blade
✅ More effort is needed, but allows faster movement
Key Difference:
Wheelbarrow = Easier lifting
Shovel = More control, but harder work
Explain, referencing mechanical advantage/leverage and joint reaction force, how using an adaptive jar opener increases the mechanical advantage to facilitate occupational performance.
An adaptive jar opener increases the force arm by providing a larger grip or added leverage.
This reduces the effort needed to generate enough torque to twist the lid.
More leverage = Less force required to achieve the same movement.
Reducing Joint Reaction Force
Joint reaction force occurs when the hand applies force to grip and twist.
A larger grip reduces the moment arm of finger joints, minimizing stress on small joints.
The adaptive opener distributes force more evenly, reducing strain on the wrist and fingers.
Which exercise is better for the quads
Squats:
Longer knee moment arm → Quads work harder.
Shorter hip moment arm → Glutes and hamstrings work less.
Deadlifts:
Shorter knee moment arm → Quads work less.
Longer hip moment arm → Glutes and hamstrings work harder.