Chapter 3 PSY220 Psychobiology (neural anatomy)
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
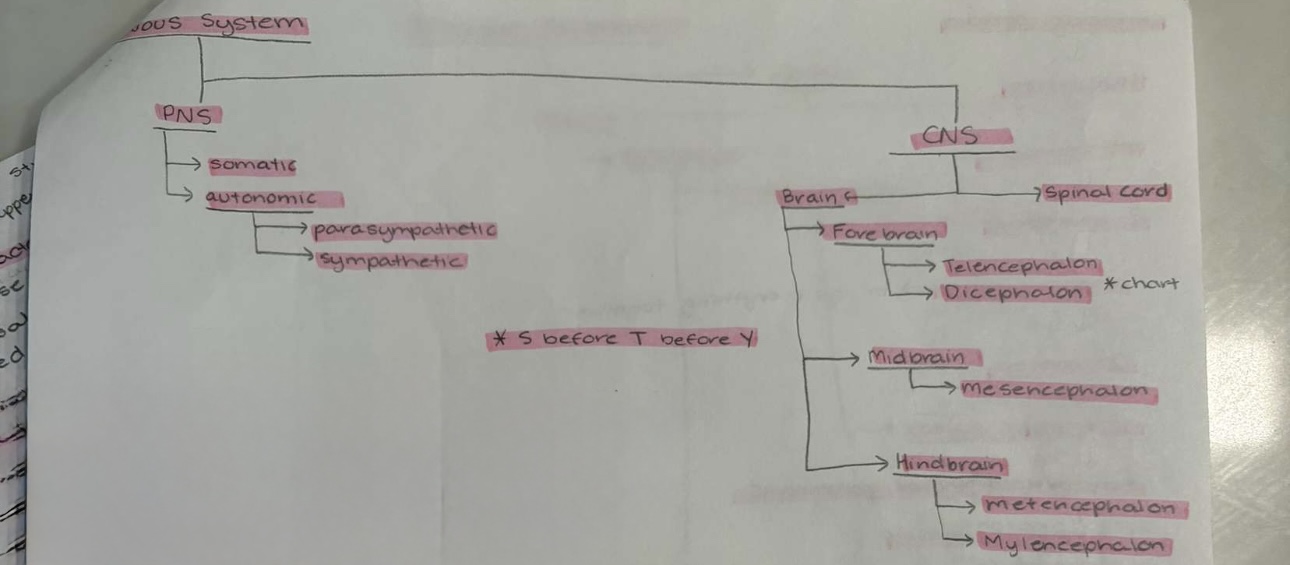
Somatic
—> compare voluntary movements (skeletal, muscle) —> Sensory input (eyes) —> integration (CNS) —> motor output (PNS)
Automatic
—> involuntary (organs)
executes commands
Sympathetic: (fight/flight)
Ex: accelerates heart, rigorous activity norepinephrine
Organs can function on their own but are influenced by the brain
Parasympathetic (rest/digest)
Ex: contracts bladder, inner calm acetylcholine
Neuraxis
Line down CNS as a refrence point
Ventral
Toward the stomach
Dorsal
Toward the back
Antenor
Toward the front end
Posterior
Toward the back (caudal)
Lateral
Toward the side/ far from the midline ← →
Medial
Toward the midline → ←
Frontal plane
separates the front (anterior) and back (posterior) of the body.
Saggital Plane
separates the left and right sides of the body.
Horizonatal plane
divides the body into superior and inferior sections.
Proximal
Close to origin (head, shoulder)
Distal
Distant from origin (head,hand)
Ipsilateral
same side
Contralateral
Opposite side
Function
EEG
Dots on your head, brain wave
PET
Inject isotope, areas of brain active during a task)
Laughter → cocaine
FMRI (used wehn preforming complex taks: talking )
Shows change in blood flow
Multitasking → shifting attention, causes neural conflcit
Structure
CT Scan (xray abstract by bone, shows white, brain matter white)
MRI
(Uses magnetic filed to arrange hydrogen atoms, more tissue → more hydrogen)
Nervous System Diagram
Alzheimers
→ Deficits in intellect & memory
Degeneration of cortical cells that use acetyclone
Beta amyloid deficits
Longitudinal Fissure
Large space
Sulcus
Small spaces
Gyrus
Band of tissue
Frontal lobe
Movement
Central sulcus
allows the brain to process sensory information and coordinate motor commands
Parietal Lobe
Tactile
Occipital lobe
Vision
Temporal lobe
Auditory
Lateral Sulcus
Separate temporal lobe from frontal and parietal lobe
Each lobe has a…
primary (awareness) & secondary (comprehend) associational cortex
Angular Gyrus
→ Combines sensory information / deeper reasoning
Flow of Movement
Sensory Organs
Thalamus
Primary somatosensory cortex
Secondary somatosensory cortex
Angular gyrus
2nd major association cortex “forms plans”
Primary motor cortex “performs the acts”
Subcontrol motor pathways
Skeletal muscle
Brocas Aphasia
Speech production deficit
Wenike’s Apahsia
Comprehension Defecit
Nervous System Diagram
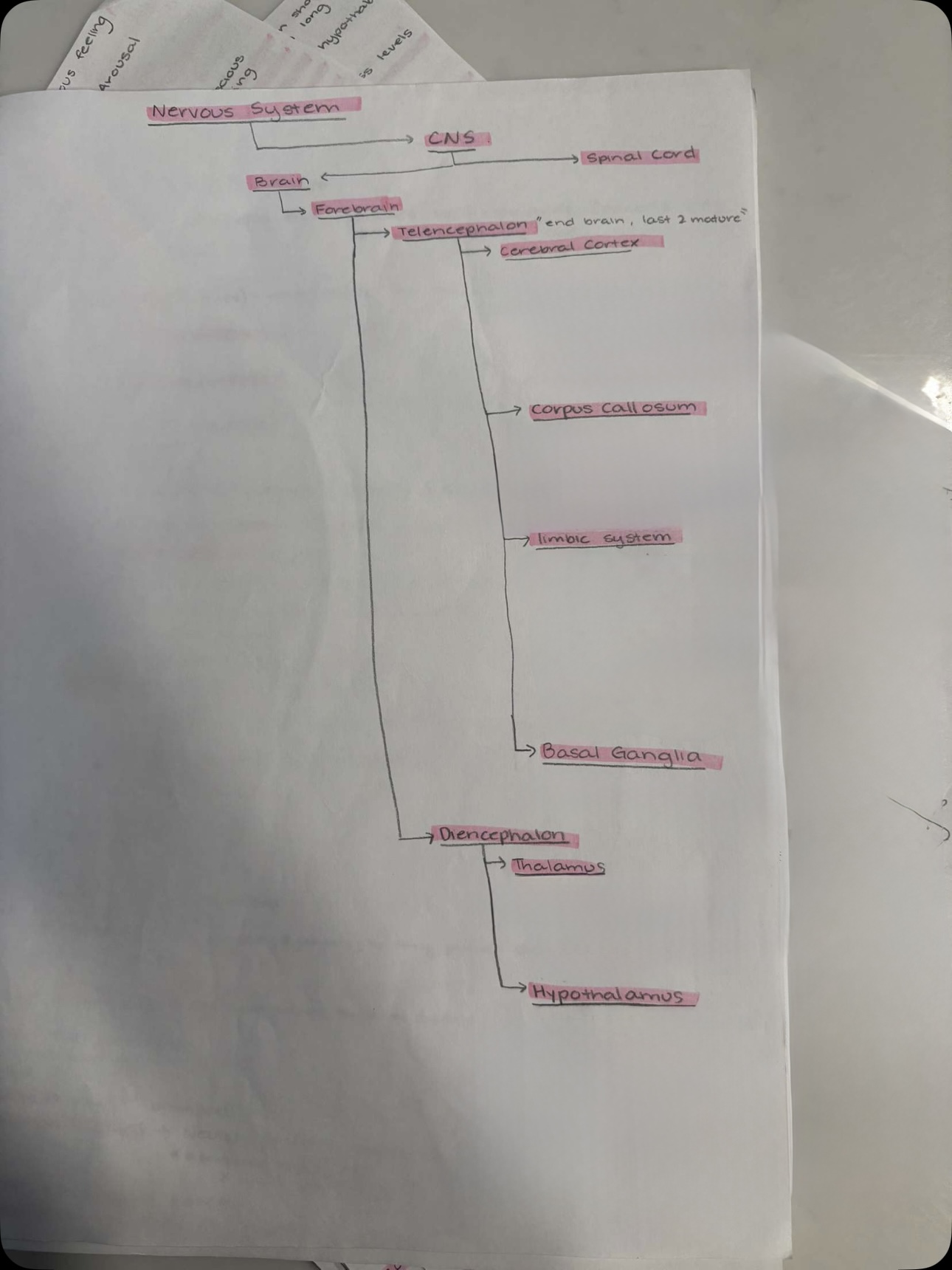
Telencephalon “end brain, last two mature”
Cerebral Cortex
Left and right hemispheres
Separated by longitudinal fissure (large space)
Sulcus (small space)
Gyrus (band of tissue)
Contralateral
Corpus Collosum
Largest track of myelinated axons in brain
Homotopic callosal pathways connects hemispheres
Interhemisphere communication
Limbic system
interlinked structures border around brain stem
Mediates emotion, aggression, motivation, learning & memory
Includes olfactory bulb, hypothalamus, hippocampus, amygdala, Cingulate gyrus
Basal Ganglia
Planning of movement, memory, & emotional expression
Diencephalon
Thalamus
relay station
Recieves info from sensory organs, forwards to cortex, and output/motor, forwards 2 muscles
Hypothalamus
Eating, drinking, sex
Below thalamus, smaller
Conveys messages to pituitary gland to release hormones influencing endocrine system