Science - Organic Chemistry🦋🦋🦋
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This is a summary and lot of key concepts covered in the organic chemistry topic.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
What is Ionic Bonding?
Electrons are swapped between metals and non-metals to create neutral ionic compounds.
What are covalent compounds?
Electrons are shared between non-metals to create covalent compounds.
What is a combustion reaction?
A reaction where a substance reacts with oxygen gas, releasing energy, water and carbon dioxide or carbon monoxide.
What order should you balance equations in?
Carbon, Hydrogens, Oxygens
What is a redox reaction?
The transfer of electrons between chemical species.
Examples of organic compounds?
DNA, fruits and vegetables, humans.
What is an organic compound?
A chemical compound that contains a hydrogen-carbon bond.
What is organic chemistry?
The study of carbon compounds.
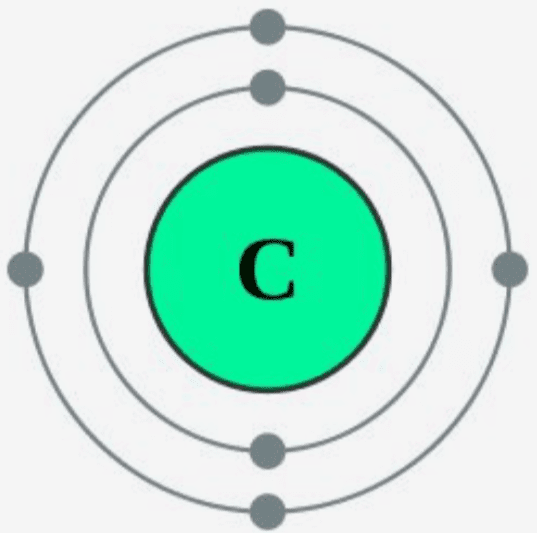
How many valence electrons does carbon have?
4, meaning it can form 4 bonds, making it very strong.
What is a hydrocarbon?
A hysdrocarbon is a compound that only contains carbon and hydrogen.
What is an alkane, it’s molecular formula, and saturation level?
Alkanes are hydrocarbons that contain single bonds between carbon atoms. It is a saturated compound, and has the molecular formula CnH2n+2
What is structural formula?
The formula that shows every bond and atom.
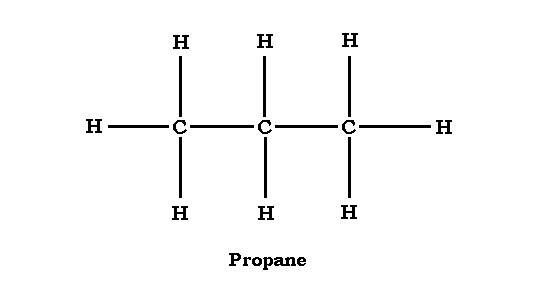
What are the first 10 alkanes?
Methane, Ethane, Propane, Butane, Pentane, Hexane, Heptane, Octane, Nonane, Decane.
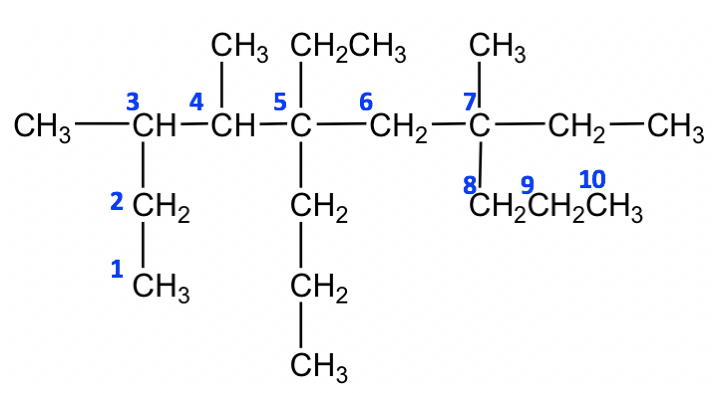
Name this alkane.
5,7-diethyl-3,4,7-trimethyl-5-propyldecane
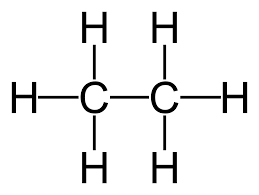
Name this alkane.
Ethane
What is an alkene, it’s molecular formula, and saturation level?
Alkened are hydrocarbons that contain one double bond between 2 carbon atoms. It is unsaturated, and has the molecular formula CnH2n.
What is a homologous series?
A series of compounds with similar chemical properties in which each member differs from the previous one.
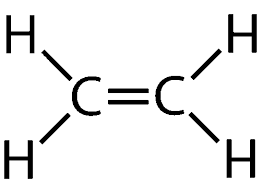
name this Alkene.
Ethene.
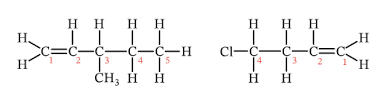
Name these alkenes.
3-Methylpent-1-ene and 4-chlorobut-1-ene.
What is a structural isomer?
Structural isomers are molecules with the same molecular formula but with different arrangements of their atoms.
An example fo a structural isomer is:
Butane and 2-methylpropane
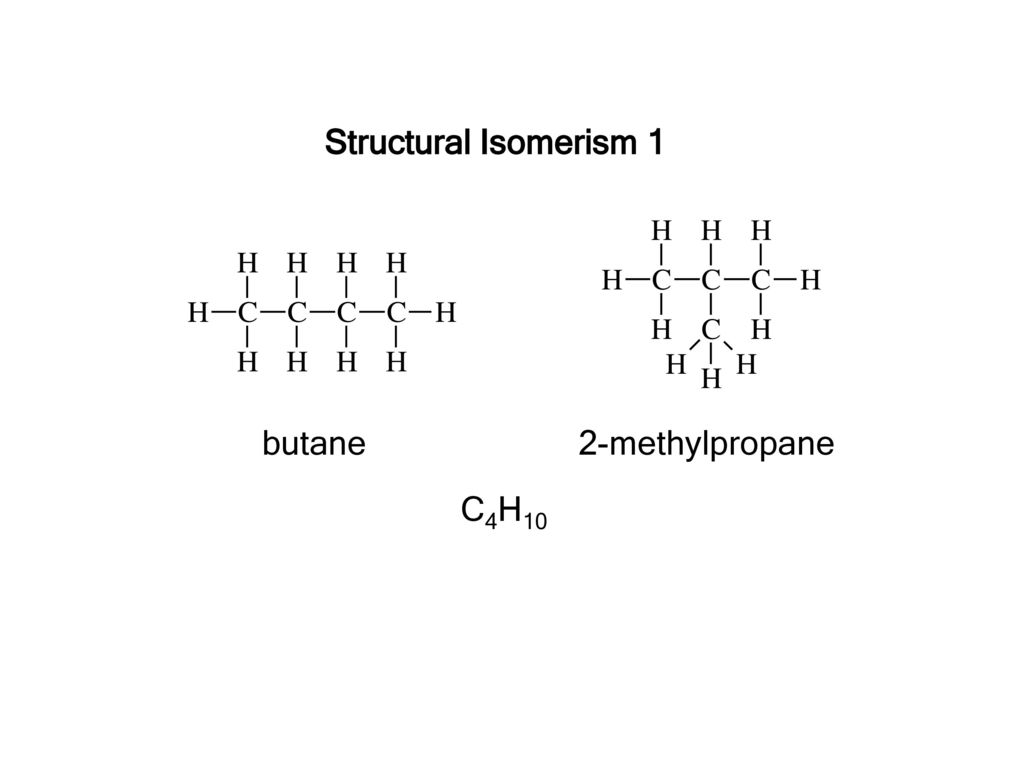
What is the same and different about structural isomers?
Structural isomers have similar chemical properties, but differ in some physical properties such as melting temperature and boiling point.
What is saturation?
The degree to which something is dissolved or absorbed.
Are alkanes saturated?
Yes, becasue there are only single bonds.
Are alkenes & Alkynes saturated?
No, they are unsaturated because they contain double or triple bonds, meaning they have less hydrogens.
What is an alkyne, it’s molecular formula, and saturation level?
An alkyne is a hydrocarbon that contains one triple bond between 2 carbon atoms. They are unsaturated compounds, and have the molecular formula CnH2n-2.
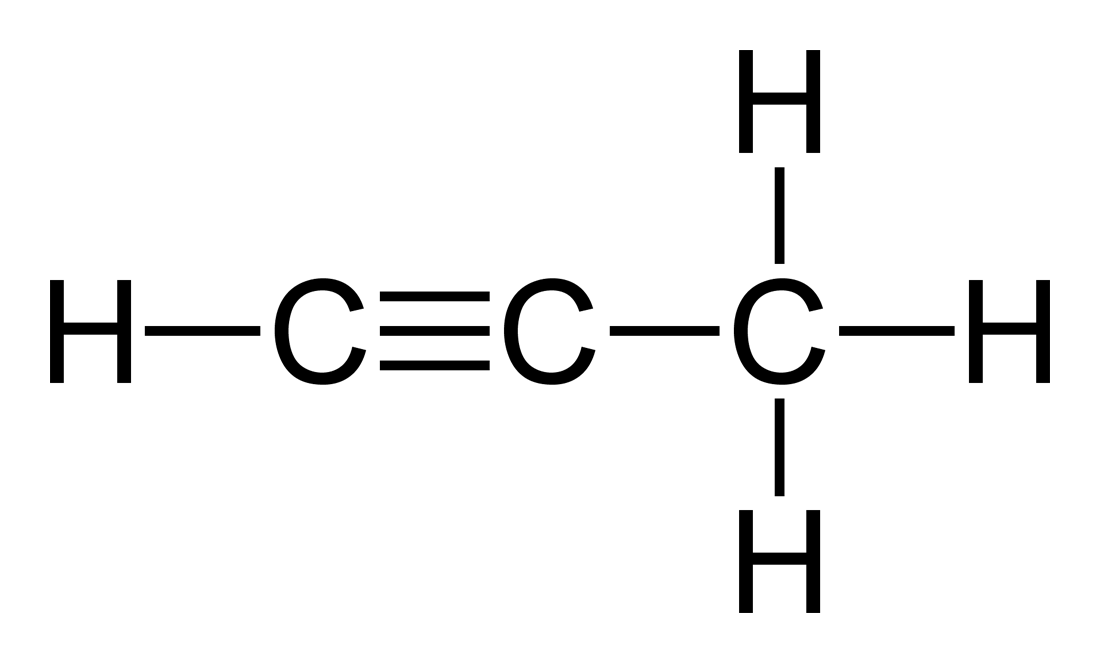
Name this alkyne.
Propyne.
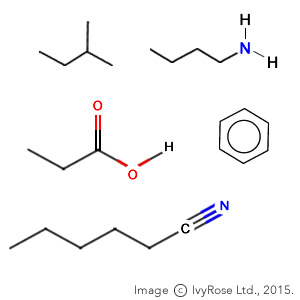
What is semi-structural formula?
Semi structural formula is a condensed structural formula, written from the lowest to highest carbon on a hydrocarbon.
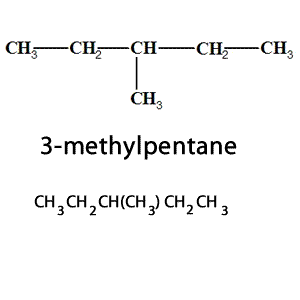
What is skeletal formula?
A representation of molecular formula where bonds are shown as lines, and letters are not present.
What is molecular formula?
A chemical formula that displays the total number of atoms of each element present in a molecule.

What is a cyclic molecule?
A compound where atleast some of it’s atoms are connected in a ring.
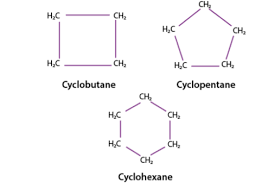
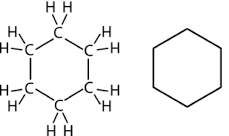
Name this cyclic Hydrocarbon.
Cyclohexane.
What is the difference between a molecule and a compound?
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together with chemical bonds. A compound is a group of two or more different elements united.
Molecules and compounds saying.
All molecules are not compounds. All compounds are molecules.
What is an alkyl?
An alkyl group is an alkane missing a hydrogen atom, and are side chains.

Name this alkane.
3-methylheptane
What is a functional group?
A functional group is an atom or group of atoms that gives a characteristic set of chemical properties to a molecule containing that group.
What are the functional groups?
Hydroxyl, Carboxyl, haloalkane.
What is an alkanol?
This is under functional group hydroxyls, which have hydrogen bonds that increase boiling point. They are polar and dissolve in water.
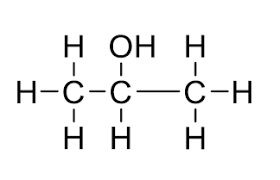
What functional group is this?
Alkanol
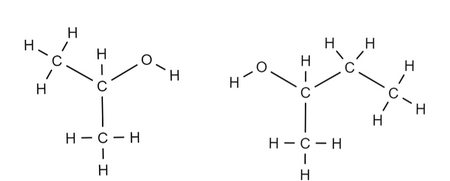
Name these alkanols.
2-propanol and 2-butanol.
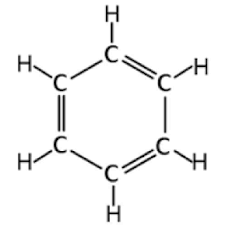
What cyclic molecule is this?
Benzene.
What are carboxylic acids?
They are under the functional group carboxyl, and contain a double bond with oxygen, and an OH. They are polar.
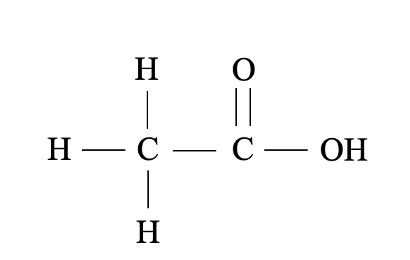
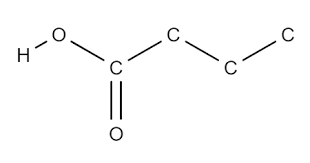
What functional group is this?
Carboxyl.
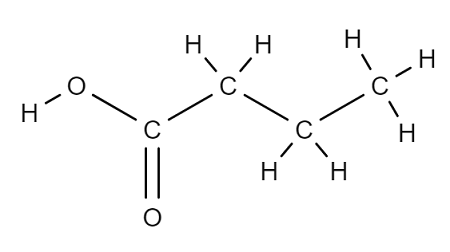
Name this carboxylic acid.
Butanoic acid.
What is a haloalkane?
A homologous series in which one hydrogen atom is replaced with a halogen atom.
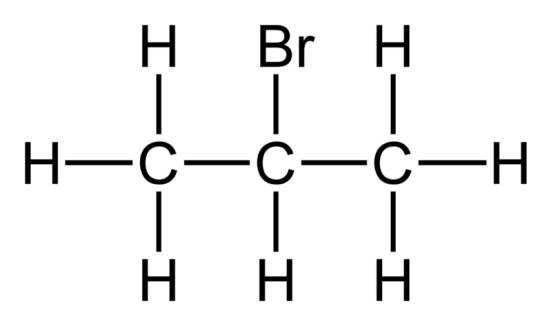
What type of compound is this?
Haloalkane.
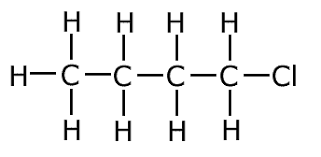
Name this haloalkane.
1-chlorobutane.
What is an intermolecular force?
The force between molecules.
What are dispersion forces?
Temporary dipoles form, non-polar molecules due to movement of electrons.
What are dipole-dipole forces?
Permanent dipoles form due to electron sharing, polar.
What is hydrogen bonding?
The type of dipole-dipole bond where hydrogens bond with an O, N, or F.
Are all hydrocarbons non-polar?
Yes.
How is the boiling point of molecules determined?
Boiling point is determined by the strength of the intermolecular forces. The more carbons/atoms, the more dispersion forces. It then requires more energy to boil as the forces increase.
What can affect the boiling point of molecules?
Straight chained molecules have higher boiling points than branched chains becasue branching increases surface area.
Are haloalkanes stronger than hydrocarbons?
Yes, because they have dipole-dipole bonds that increase their strength.
What is the imputs of a combustion reaction?
A compound and oxygen.
What is a complete combustion reaction?
There is plentiful oxygen, shown by a blue flame, and no soot produced. Carbon Dioxide and water are produced.
What is an incomplete combustion reaction?
The oxygen is limited, shown by an orange flame, and soot is produced. Carbon monoxide and water are produced.
What is an addition reaction?
A recation where a double bond is broken and converted to a single bond due to the addition of a small molecule.