ANBI Module 1
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
Endocrinology
the study of the endocrine glands and their secretions
Endon + krinein =
within + to secrete
Endocrine glands
ductless glands that secrete hormones into the blood
Classical endocrine secreting glands
Thyroid
pituitary
Clinical endocrinology
Ethiology and treatment of human endocrine diseases
comparative endocrinology
Learn more about the functions of hormones
How animals adapt to dissimilar enviros
Behavioral endocrinology
how hormones regulate behaviour
Endocrine toxicology
endocrine disrupting chemicals and impact on humans and animal health
Hormone classical definition
A substance secreted by specialized cells and released into a vascular system (bloodstream) or tissue fluid causing a response in target cells elsewhere in the body
Response is mediated by receptors specific to hormone in target tissues
Issues with the hormone definition
not always produced by glands
not unihormonal
multiple production sites
transport not only thru blood
Major functions of hormones
growth and dev
homeostasis
metabolism
behavioral regulation
immune function
Why do we have endocrine system
multicellular forms need a way to coordinate and comm
chemical signalling
compliments nervous system
3 components of endo system
Gland/cell (secrete hormones)
Hormone (chemical products, released upon stimulation)
Target organ (express hormone specific receptors, biological response)
Exocrine glands
release secretions via a duct into an epithelial surface
Epithelial cells
skin cells but not necessarily on outside
GI tract, resp tract
Endocrine glands
ductless and release substances directly into blood/lymph
water sol (exocytosis)
lipid sol (diffusion)
Hormone classification based on
type of signaling
chemical structure
solubility
solubility of hormones
water vs fat sol (type of receptor)
blood is mostly water
water sol receptors on outside of cells bc cant go thru lipid membrane
Endocrine signaling
hormones enter bloodstream/lymph and bind to hormone receptors in target cells of DISTANT organs
Endocrine signaling ex.
Beta cells in islets of Langerhans in pancreas produce and release insulin into blood where it travels to many tissues including liver signaling it to store glucose in form of glycogen
Paracrine signaling
hormones bind to cells near the cell that released them (same organ/tissue), often degrade quickly or taken up regularly (interstitial space)
Autocrine signalling
hormone produced biological effect on same cell that it has released it
Autocrine signaling ex
lining of mammalian endometrium responds to oxytocin to cause production of prostaglandins (cause contractions)
tumor cells (estrogen in breast cancer cells)
growth hormone in pituitary cells
Intracrine signaling
when hormone is synthesized and acts intracellularly
DOES NOT leave cell
Intracrine ex
Precursor sex steroid hormones are synthesized and then are converted by enzymes to active androgens/estrogens which bind to receptors within the same cell
Vit D (calcitriol) converted to its active form within target cells and acts intracellularly
Neuroendocrine
chemical is produced by neuron or nervous tissue and is released into bloodstream to act on another cell type
Neuroendocrine ex
Adrenalin, dopamine, oxytocin
Hormones vs neurotransmitters
endocrine cells vs neurons
vesicles, diffusion vs action potential, vesicles
variable distance vs short
slow speeds vs fast
depends on receptor vs specific to post synaptic neuron
Peptide and protein hormones
proteins are more complex
common hormone type
made of chain aa
preprohormones → prohormones → active hormones
stored in secretory vesicles and released by exocytosis
water sol
act quickly, short half life
hormone processing
uses enzymes on aa hormone
until end product, are inactive
Preprohormone
large, inactive precursor
Prohormone
smaller, inactive (proteolytic, post translational mod)
Peptide/protein hormones
bind surface membrane receptors, cellular response thru signal transduction system
peptide/protein hormone processing and release steps
mRNA on ribosome binds aa into peptide chain called preprohormone, chain directed into ER lumen by signal sequence of aa
Enzymes in ER chop off signal sequence creating inactive prohormone
Prohormone passes from ER thru golgi
Prohormone passed from Er through golgi
Vesicles contain enzymes and prohormone bud off golgi, chop again into active peptides
Vesicles release contents by exocytosis into extracellular space
Hormone moves into circulation for transport
Processing of insulin
Preprohormone of insulin translated in ER and peptidase cleaves the signal peptide
Folding of prohormone and formation of disulfide bonds, C -peptide plays essential role in orenting 2 chains of insulin during step
Prohormone secreted into golgi
Packaged into secretory vesicles
Prohormone convertases create separate and distinct insulin and c peptide molecules
Insulin and c peptide remain in secretory vesicles of B-cell until release
Blood glucose stimulates insulin release
Where is insulin produced and what cells make it
pancreas and langerhan cells
Insulin is an example of
regulated secretion
c-peptide
is released w insulin and goes into blood
important in metabolism and used as measurement guide for blood insulin and glucose to diagnose diabetes
Peptide/protein hormone secretion
can be regulated or constitutive
Regulated secretion
hormone waits until signaled to release (insulin, growth hormone)
Constitutive secretion
hormone is always being secreted (ex. euthropretin RBC production in kidneys)
aa derivatives (amine hormones)
Derived from aa, normally tyrosine but also tryptophan (precursor to serotonin and melatonin) and glutamic acid (converted to histamine)
Sig smaller
ex of amine hormones
Norepinephrine and epinephrine, dopamine, thyroid hormones (metabolism regulators) and melatonin (circadian rhythms)
catcholamines
need vesicles for exocytosis - hydrophillic (water loving)
Thyroid hormones
lypophillic (fat loving), like steroid hormones
steroid hormones
Cholesterol derived
Lipophilic and easily crosses membranes
Not translated from DNA - use cholesterol available in cells
Fat
Lipophilic and can cross cell membrane
Blood is aq so need carrier proteins in blood to move
Act on receptors inside cells
Bind carrier proteins in blood
Longer half life
Cytoplasmic or nuclear receptors
Genomic effect to activate or repress genes for protein synthesis
Slower acting process
But can also bind to cell membrane receptors
Nongenomic responses
Ex of steroid hormones
Glucorticoids
Mineralocoricoids
Androgens
Estrogens
Progestrogens
Cholesterol importance
parent compound for all steroid hormones
cascading effect depends on converting enzymes
cortisol chronic stress hormone is in
mammals
corticosterone is in
verts other than mammals
Eicosanoids
Modified 20 C fatty acids w complete/partial C ring and 2 long C tails
All derived from arachidonic acid (part of phospholipid bilayer of membrane)
Lipophilic
important in many physiological processes
Prostoglandins
constriction and dilation of smooth muscle cells
asthma and anaphylaxis
Leukotrienes
inflammation compounds immunity
NSAIDS and COX2 inhibitors
drugs to prevent making of prostaglandins and leukotrienes to block enzymes, preventing inflammation
Eiocasinoid hormone ex
Prostoglandins
Leokotrines
NSAIDs and COX2 inhibitors
rapid acting and paracrine
Arachidonic acid cascade
Phospholipase A2 catalyzes the hydrolysis of a bond In membrane phospholipids
Rxn released arachinonic acid and free fatty acid
AA precursor to eicosanoids including prostoglandins and leukotrienes
Rapidly inactivated by being metabolized -> typically active for only a few seconds
Estrous cycle
Estrogen (steroid) goes up right before LH (release of egg - developing in follicle of ovary) tertiary follicle
Progesterone (steroid) goes up from corpus luteum (shell from which egg ovulated from) mid cycle also prevents another ovulation
Thickening of uterine lining, in prep for potential embryo dev
Fert may or may not happen
Prostaglandin released from endometrium cells to cause corpus luteum to degrade and tell repro tract no pregnancy
Includes
Ovary + egg
Smooth muscle cells of uterine lining that secretes hormones
hormone structure importance
Transport and solubility - structure (polar vs nonpolar) dictates whether it travels freely in blood or requires carrier
Stability and duration - structural features influence degradation rate and half life, affecting how long the hormone lasts
Cell entry and signalling - hydrophobic hormones can cross membranes easily, while hydrophilic hormones need receptors on cell surface
Receptor binding and function - shape chemical groups determine receptor specificity, which drives physiological effects
Evolutionary insights - conserved structural motifs across species reveal evolutionary relationships and functional importance
physiologic effects of hormones depend largely on
their conc in blood/extracellular fluid
disease arises when hormone conc are
to low or to high
Male and female reference ranges are diff bc
they have other hormones circulating and they interact diff in the body
conc of hormone as seen by target cells determined by
Rate of production
Rate of delivery
Rate of degradation and elimination
elimination or hormones
kidneys → urine
liver → fecal excursion thru GI tract
hormone lifecycle
Endocrine cell -> hormone (pink sphere) -> released into circulation (blood)
-> bind to binding protein in blood (lipophilic hormones, steroid, thyroid)
-> liver and excreted via GI tract, liver can change hormone to do something else (shape) act on target cell to fit receptor
-> maybe not changed/metabolized and go directly to target cell
-> kidney and excursion by urine
-> feedback regulation (specific control) alter cell that made it to turn on more synthesis or turn down
rate of production/secretion
pos and neg feedback circuits
stimulation of hormonal production
humoral
neural
hormonal
Humoral stimulus
hormone release caused by altered levels of certain critical ions or nutrients
not an endocrine signal but something in blood tells endocrine cells to make hormones (glucose and Ca2+)
neural stimulus
hormone release caused by neural input
nervous system/cell send messaged to endocrine cell to produce hormone (acetylcholine is NT, released at end of nerve that inervate adrenal gland to make hormone fight or flight)
Hormonal stimulus
hormone release caused by another hormone
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) - thyroid gland
ACTH
Testosterone - stimulated by LH
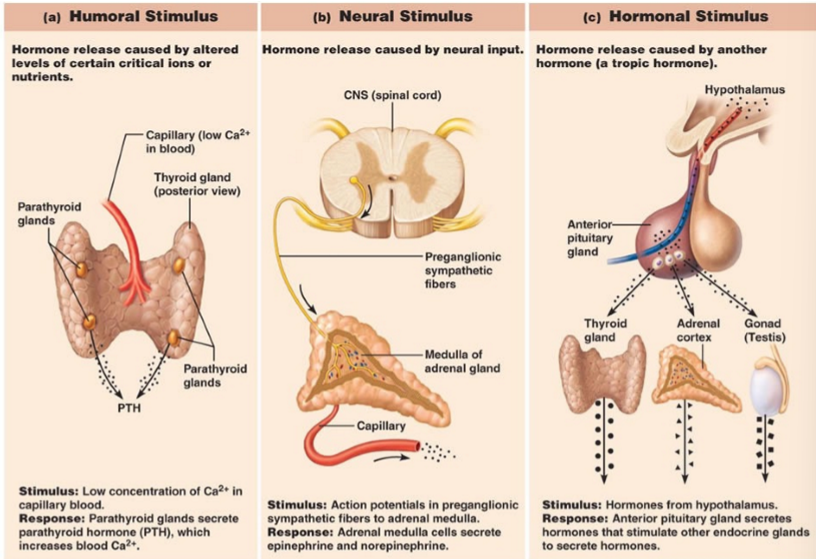
JUST KNOW THIS
Feedback regulation
allows the body to correct any type of hormone release after a stimulus
Negative feedback regulation steps from homeostasis
Imbalance of endocrine gland or tissue hormone level
Hormone release
Correction
Negative feedback
Glucocorticoid negative feedback ex
gluco low conc of stress hormone detected by hypothal via sensors in blood vessels
hormone release of CRH and ACTH cascade triggers adrenal gland to release more gluco into blood
conc of gluco in blood increases to normal and hypothal senses normal conc and stops CRH
Negative feedback …
shuts off and happens most of the time
Positive feedback
further stimulation of the hormone which was the og source of the signal
positive feedback vs stimulation
positive feedback reinforces that hormone release
stimulation is the original stimulus that triggered the hormone release
Positive feedback estrous/menstral cycle ex
Follicular phase- hypothal releases GnRH to anterior pituitary, release of FSH, LH to ovary, estradiol neg feedback to pituitary
Midcycle same thing except estradiol is pos feedback to pituitary
Luteal phase - same except neg feedback of progesterone to pituitary
Positive feedback in estrous cycle leads up to
ovulation
estradiol stimulates more FSH and LH production so eggs grow
albumin and transthyretin
bind small ligands, gen transport mol
moves basically everything in body
Delivery
higher blood flow → delivers more hormones than low blood flow
circulate free or bound to large protein
specific transport proteins
Corticosteroid binding globulin (CBG)
Thyroxine binding globulin (TBG)
Sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG)
Plasma proteins
control lipid sol hormones to get thru capillaries and be delivered to tissues
Why do males and females have diff drug dosages
diff amounts of binding proteins in bodies
drug delivers needs binding proteins, hormone delivery will be diff
Which hormones sol can travel freely but cant enter cells without receptors
hydrophilic
free hormones is the _____ form and can
bioactive form, leave blood into target tissues and is free to bind receptors
% of free proteins is
2
when free hormones go into tissues what happens
bounded hormones are released to balance the conc and stimulate tissues to make more hormones
hormones change from what sol when metabolized and excreted from body
lipophilic → hydrophilic
How are hormones degraded
Some are metabolized by their target cells
Some metabolized by enzymes in circulation
Many metabolized by enzymes in liver and kidneys
Most excreted via kidneys (some via liver -> bile)
half life
time during which the conc of hormone decreases to 50% initial volume
half lives of amines vs thyroid vs polypeptide/protein vs steroid
amines - very short min
Thyroid - long days
Pp and proteins short - min
Steroids - medium min to hours
Metabolic clearance rate
removal of hormones from circulation, the volume of plasma cleared of the hormone per unit time
Short half life =
leaves quick, high MCR
long half life =
leaves slow, low MCR
Thyroid has a ____ protein binding, _____ half life and _____ MCR
high, long, low
Steroids have a _____ protein binding, _____ half life and _____ MCR
low, short, high
Metabolic degradation is mainly in the ____ thru enzymatic processes
liver
Liver metabolic degradation processes
Phase I - breakdown (oxidation, reduction)
Phase II - adding something (methylation, sulfuration)
Excretion of hormones thru
bile or urine
hormone breakdown not excreted
target cell may internalize hormone and degrade it and use for other processes