Alkanes and Alkenes
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
hydrocarbons
compounds made from only carbon and hydrogen atoms
alkanes
homologous series of saturated hydrocarbons
homologous series
a group of chemicals which have similar chemical properties and can be represented by a general formula.
saturated meaning
has the maximum amount of hydrogen atoms for each carbon atom i.e doesn’t have a double bond
general formula for alkanes
CnH2n+2
1 carbon atom alkane
methane
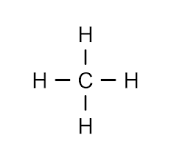
2 carbon atom alkane
ethane
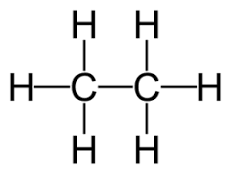
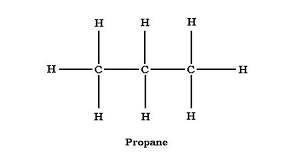
3 carbon atom alkane
propane
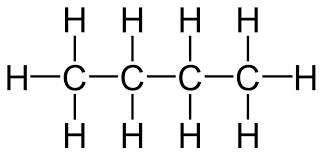
4 carbon atom alkane
butane
anagram for alkanes
my enormous penis bulges
cracking
a method used to break longer chain alkanes into shorter chains which are more in demand
this will always make one shorter alkane and 1 alkene
types of cracking
thermal cracking - using heat
catalytic cracking - using catalysts
alkenes
a homologous series of unsaturated hydrocarbons
general formula for alkenes
CnH2n
unsaturated
a molecule containing carbon-carbon double bond
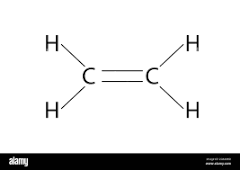
2 carbon atom alkene
ethene
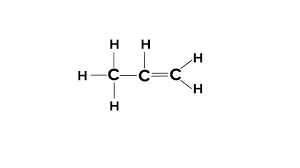
3 carbon atom alkene
propene
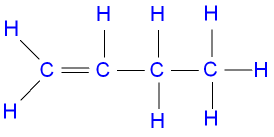
4 carbon atom alkene
butene
5 carbon atom alkene
pentene
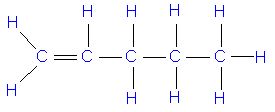
when do alkenes go under complete combustion
when there is a plentiful supply of oxygen
complete combustion of alkene symbol equation
C2H4 + 3O2 = 2CO2 + 2H2O
Test to distinguish alkenes and alkanes
Add bromine water, if alkenes are present the ln solution will go from orange to colourless, if alkanes are present then it wont turn colour
polymer
very large molecules made from many small molecules joined together in repeating units
monomer
small molecules that join together to make polymers
polymerisation
formation of polymers - small monomers joining together
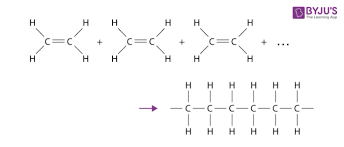
additional polymerisation
process where many unsaturated monomers join together to make a saturated polymer
thermosetting
melt/soften on heating as chains are not joined together
thermosoftening
do not melt/sofetn on heat as chains are joined together
repeating unit in polymerisation