Animal Cells and Tissues
1/76
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
Homeostasis
[similar] + [condition] -maintain a stable internal environment despite changes in external environment
Homeostasis examples
body temp regulation, blood glucose regulation, osmoregulation
biological hierarchy
cell → tissue → organ → organ system → organism
cell specialization
certain cells are formed into specific tissues to perform specific tasks e.g. muscle cells → muscle tissues
primary tissues
epithelial, nervous, connective, muscle
epithelial tissues
Sheets of cells that cover surfaces and form barriers which must allow for secretion, absorption, and transportation of other molecules
Simple squamous epithelium
A
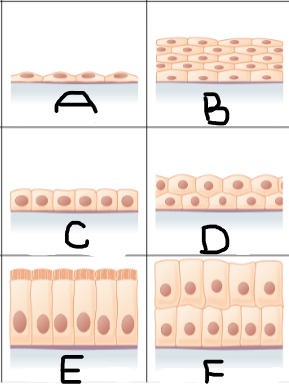
Stratified squamous epithelium
B
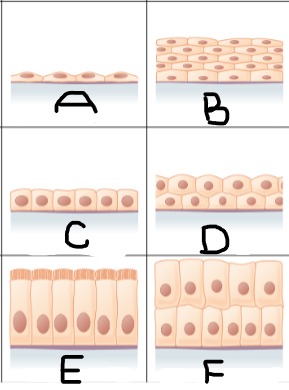
Simple cuboidal epithelium
C
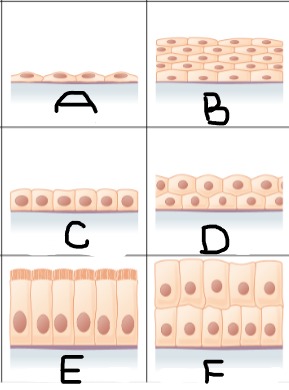
stratified cuboidal epithelium
D
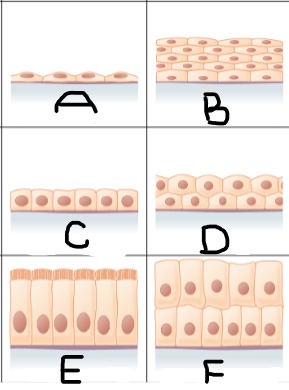
simple columnar epithelium
E
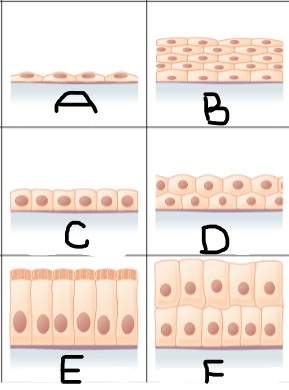
Stratified columnar epithelium
F
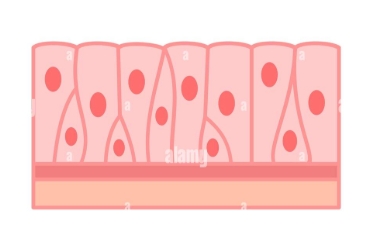
Pseudostratified
Name this special epithelial cell type
Transitional
Name the epithelial cell type
Connective tissue
Supports, binds, and protects other tissues and organs. Characterized by having relatively few actual cells.
Types of connective tissue
fibroplasts, adioplasts, extracellular substance (ground substance)
Extracellular substance
collagen, elastin, reticulin
loose and dense
2 characterizations of connective tissue
cartilage (chondrocytes) and bones (osteocytes)
specialized connective tissues
skeletal muscle tissue (striated)
majority of muscle tissue in animal body, voluntary contraction, multinucleated
cardiac muscle (striated)
only found in heart, involuntary contraction, branched and connected by intercalated discs, mononucleated
smooth muscle
found in most organs, involuntary, spindle shaped, mononucleated
nervous tissues
tissues responsible for communication, control, coordination
soma
cell body
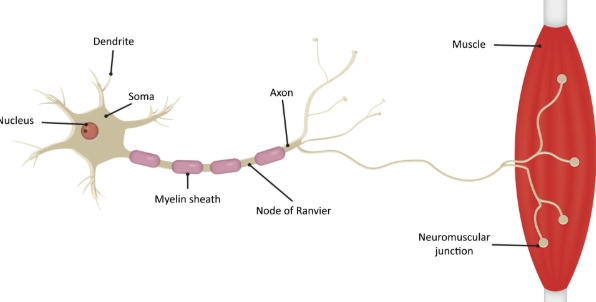
dendrites
input region
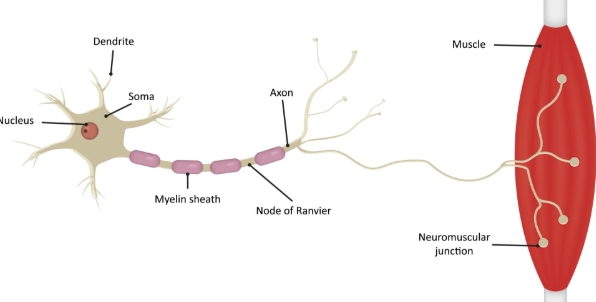
axon
output region
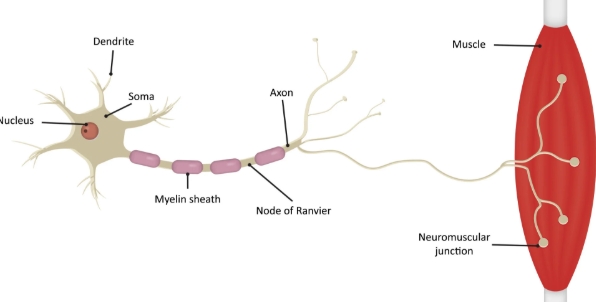
myelin sheath
A fatty later that acts as electrical insulation
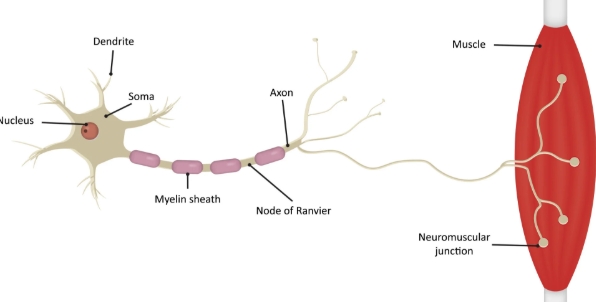
axon terminals
where a neuron forms a synapse
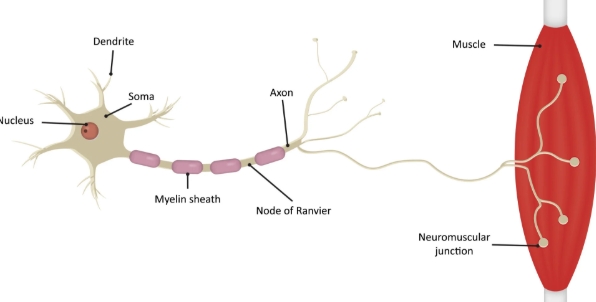
nerve signal
aka action potential, triggers a series of reactions that allow the muscle to contract
digestive system
mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas
circulatory system
heart, blood vessels, blood
respiratory system
nose, trachea, lungs
nervous system
brain, spinal cord, nerves
reproductive system (male)
testes, vas deferens, prostate gland, penis
reproductive system (female)
ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina
Water cell composition
70-90%
Protein cell composition
7-22%
Lipid cell composition
1-95%
Inorganic matter cell composition
1-2%
Carbs and others cell composition
1.5%
Water in cells
Largest constituent in cells, universal solvent, reaction medium, structural support, transport, thermal regulation
Universal solvent
Water’s ability to dissolve most substances and transport components around the body
Osmotic pressure
Pressure exuded by water on a cell when it moves to a place of high solute concentration from low solute concentration
Osmosis
The movement of water across a concentration gradient
Thermal regulation
Water’s high specific heat helps to maintain homeostasis
Intracellular fluid
Water inside of cells account for 40% of body weight
Extracellular fluid
Water outside of cells accounts for ~20% of body weight
Interstitial fluid
ECF surrounding cells accounting for 15% of body weight
Blood plasma
ECF in the blood counting for 5% of body weight
Conjugated proteins
Proteins that are attached to another molecule (prosthetic group)
Glycoprotein
A conjugated protein with a carbohydrate
Chromoprotein
A conjugated protein with with a colored substance able to be lit up
Structural and reactive
2 protein classifications
Structural protein
Provide support, strength, and cell shape. Examples include connective tissue and keratin
Reactive protein
Provide biochemical reactions and regulation. Examples include pepsin (enzymes), insulin (hormone), hemoglobin (transportation), and myosin + actin (contraction)
Lipids
Play roles in energy storage, cell signaling, membrane structure, and are insoluble in water
Fatty acids
main building block of lipids composed of carbon and hydrogen tails with a carboxyl group head
Triacylglycerol
Forms 90% of acylglycerols, consists of a glycerol head with 3 fatty acid tails. Must be further metabolized in order to be used in the body as glycerol and fatty acids.
Diacylglycerol
metabolic intermediate and signaling molecule with 2 fatty acid tails
Monoacylglycerol
Digestion and absorption intermediate with one fatty acid tail
Phospholipid
Similar structure to a triglyceride with the addition of a phosphate group in the head alongside more unsaturated fatty acid tails. Known for making up semi permeable membranes.
Steroids
Lipid not built from fatty acids, rather 3 six-membered rings and 1 five-membered ring. Examples include cholesterol, bile salts, and hormones like testosterone
Deoxyribose
DNA carbohydrate backbone
Ribose
Carbohydrate backbone in RNA
C, H, O, N
99% of elements in animal cells
P, Ca, Cl, K, Na, Mg
1% of elements in animal cells (with special emphasis for in class)
Cell membrane
Outer boundary of the cell that separates the cytoplasm from the external environment. Serves as a barrier, transport regulation, communication, signaling, and structural support
Fluid mosaic model
Model to describe cell membrane composed of a patchwork with phospholipids, membrane proteins, and cholesterol
Phospholipid bilayer
Thin barrier around all cells that comprises 50% of the total membrane. Key characteristics are amphipathic (hydrophobic and philic), selective permeability, and fluidity
Integral proteins
Proteins wedged into the the membrane among the phospholipids
Transmembrane proteins
A special type of integral protein that goes fully into the membrane to be exposed to the cytosol and out into the external environment.
Peripheral proteins
Proteins bound only to the surface of the membrane
Transporter protein
Integral protein (transmembrane) that moves molecules across the membrane
Recognition protein
Peripheral/glycoprotein that acts as identification of cell type or origin by other cells
Receptor protein
Integral protein that binds to hormones outside the cell and activates signaling inside the cell
Anchor or structural protein
Integral or peripheral protein that connects the cell membrane to the cytoskeleton or extracellular matrix for stability and shape
Cholesterol
A steroid that helps to regulate membrane fluidity by keeping phospholipids from separating under hot conditions or prevents them from bunching up under cold conditions.