Korean Phonetics Exam 1
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
What is the IPA letter and description of the following letter:ㄱ
[k]
voiceless velar stop
What is the IPA letter and description of the following letter: ㄲ
[k*]
voiceless tense velar stop
What is the IPA letter and description of the following letter: ㅋ
[kʰ]
voiceless aspirated velar stop
What is the IPA letter and description of the following letter: ㄴ
[n]
voiced alveolar nasal
What is the IPA letter and description of the following letter: ㄷ
[t]
voiceless alveolar stop
What is the IPA letter and description of the following letter: ㄸ
[t*]
voiceless tense alveolar stop
What is the IPA letter and description of the following letter: ㅌ
[tʰ]
voiceless aspirated alveolar stop
What is the IPA letter and description of the following letter: ㄹ
[l/ɾ]
voiced alveolar liquid
What is the IPA letter and description of the following letter: ㅁ
[m]
voiced bilabial nasal
What is the IPA letter and description of the following letter: ㅂ
[p]
voiceless bilabial stop
What is the IPA letter and description of the following letter: ㅃ
[p*]
voiceless bilabial tense stop
What is the IPA letter and description of the following letter: ㅍ
[pʰ]
voiceless aspirated bilabial stop
What is the IPA letter and description of the following letter:ㅅ
[s]
voiceless alveolar fricative
What is the IPA letter and description of the following letter: ㅆ
[s*] |
voiceless tense alveolar fricative
What is the IPA letter and description of the following letter:ㅇ
[ŋ]/∅
voiced velar nasal (coda) / null onset
What is the IPA letter and description of the following letter: ㅈ
[tɕ]
voiceless alveolo-palatal affricate
What is the IPA letter and description of the following letter: ㅉ
[tɕ*]
voiceless tense alveolo-palatal affricate
What is the IPA letter and description of the following letter: ㅊ
[tɕʰ]
voiceless aspirated alveolo-palatal affricate
What is the IPA letter and description of the following letter:ㅎ
[h]
voiceless glottal fricative
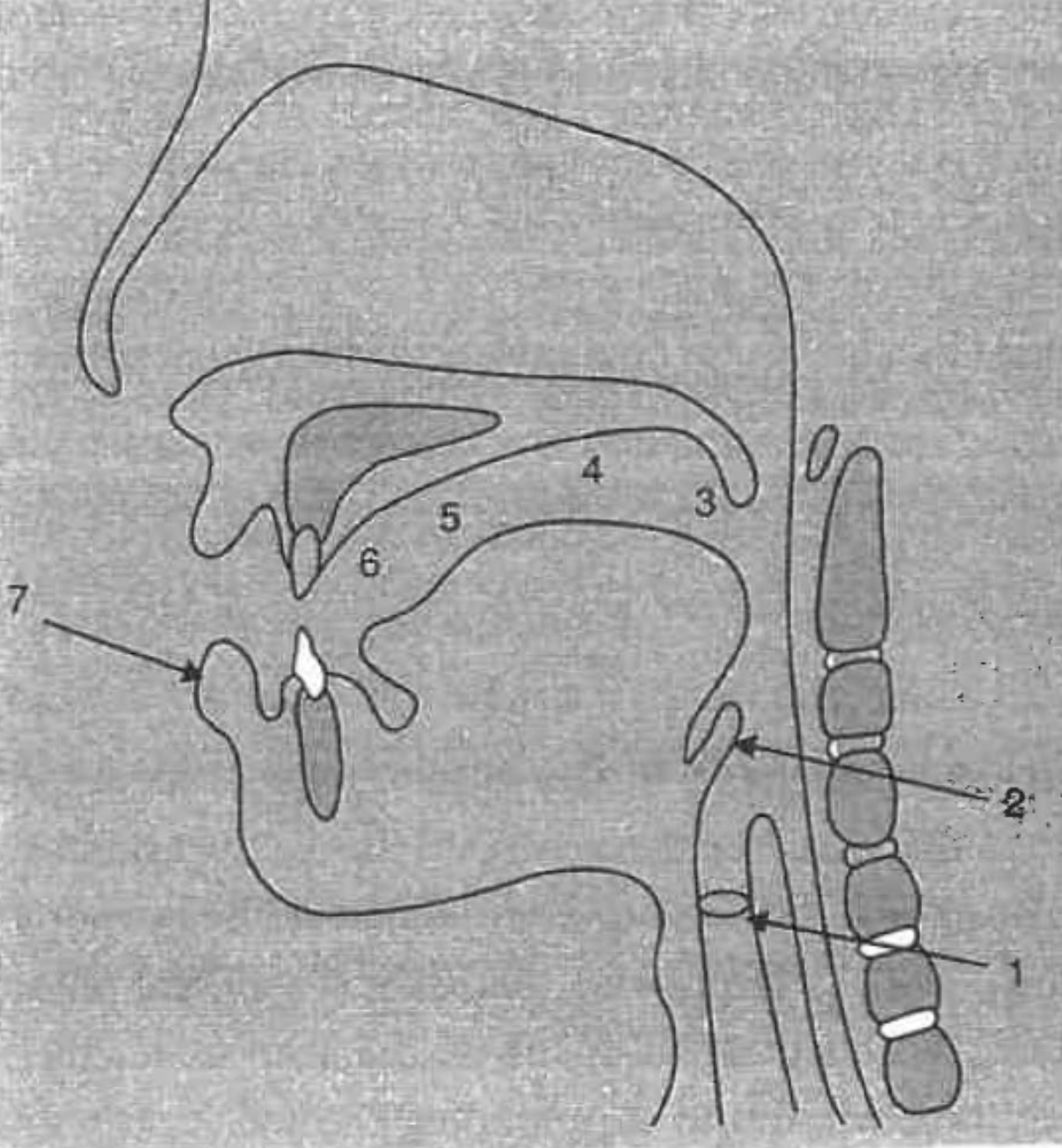
What is the structure at #1?
glottis
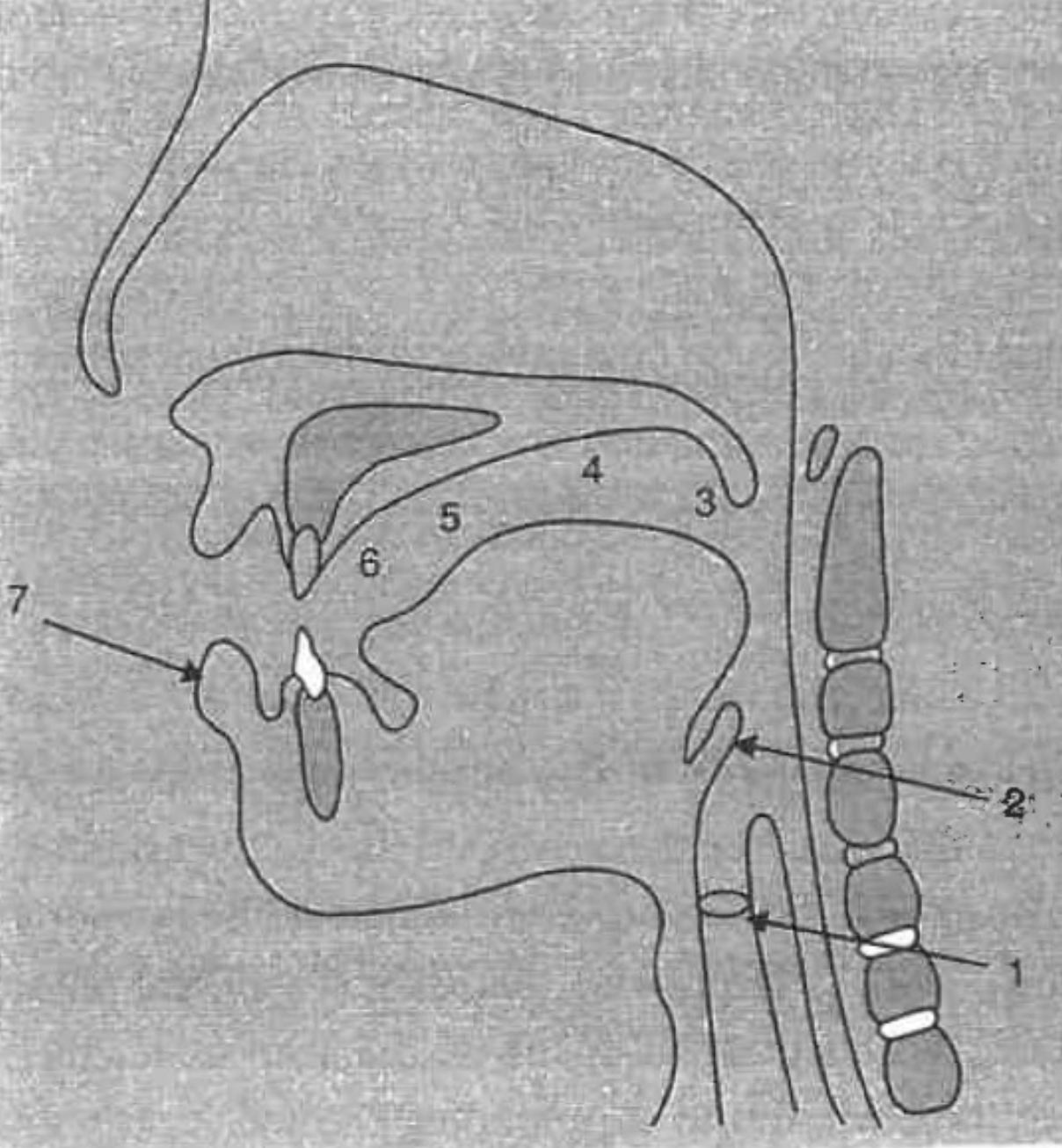
What is the structure at #2?
epiglottis
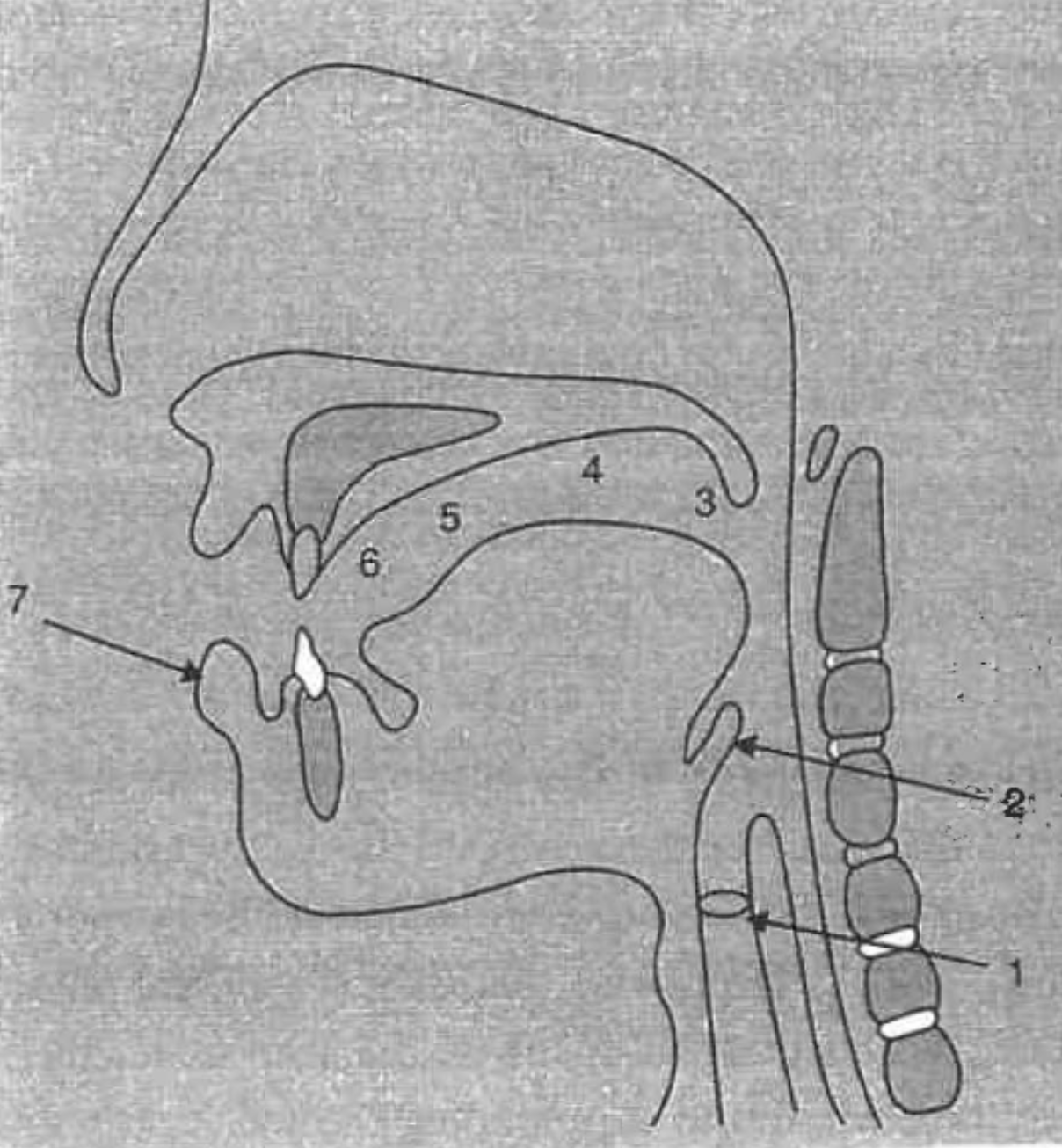
What is the structure at #3?
uvula
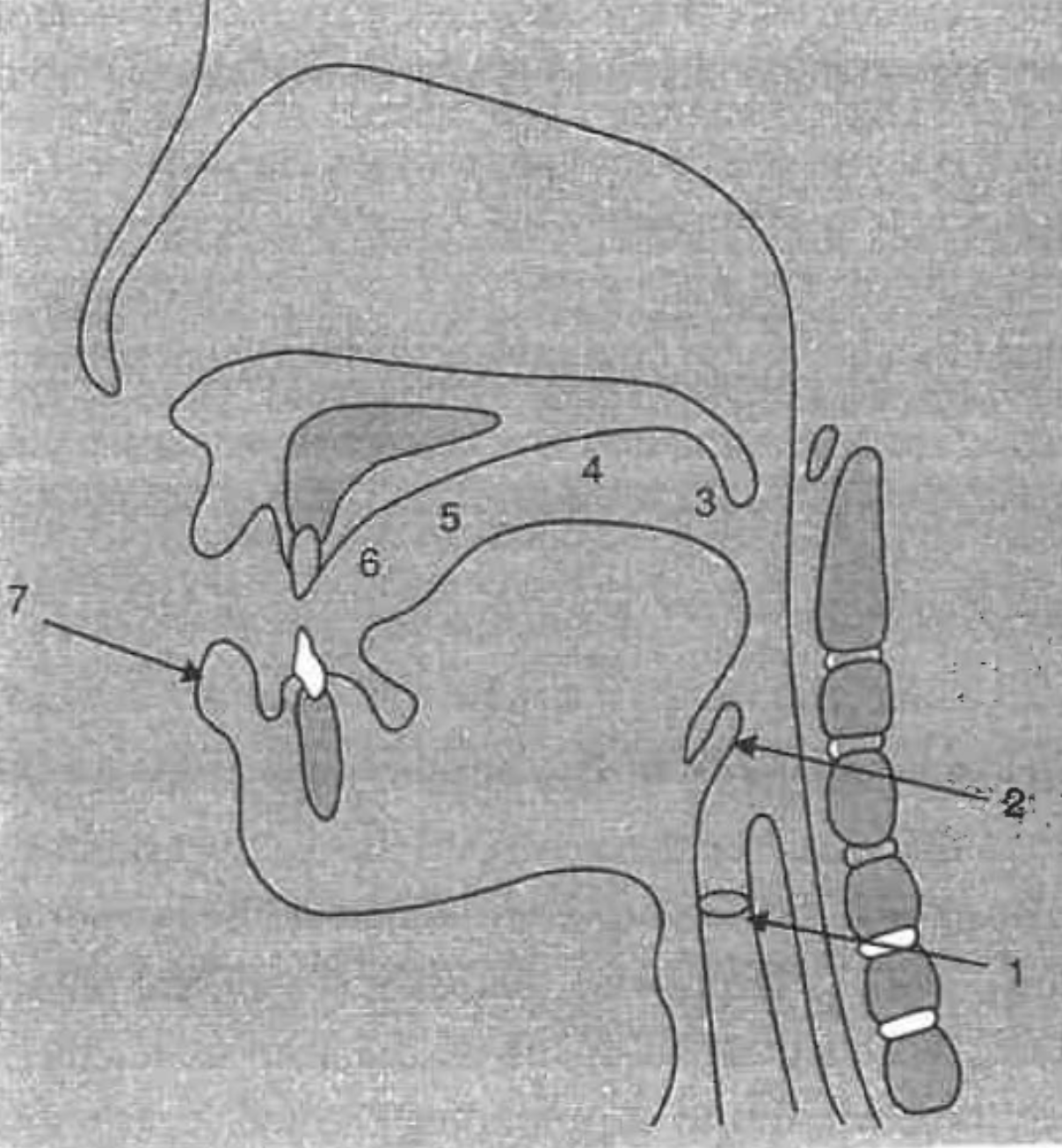
What is the structure at #4?
velum (soft palette)
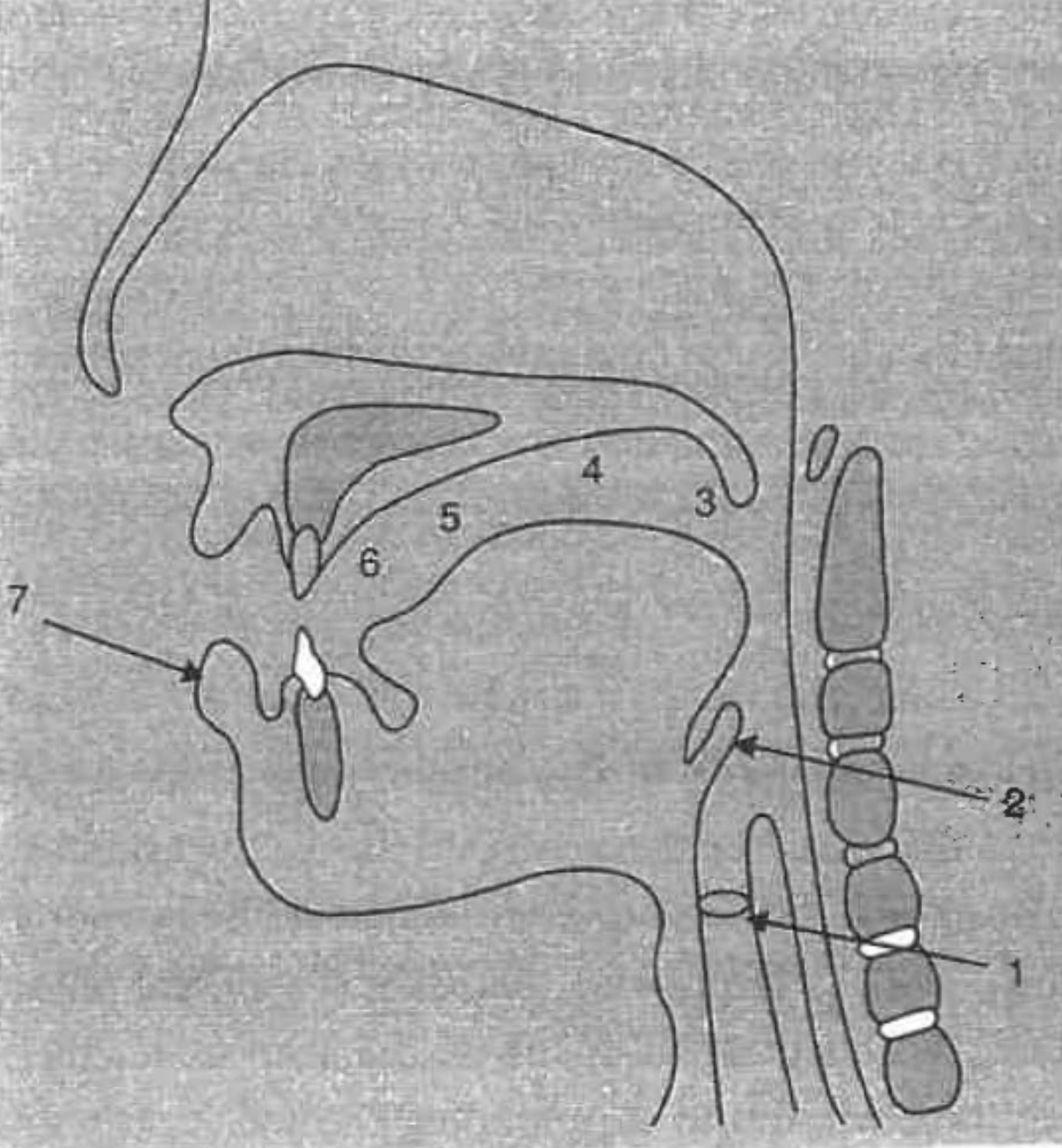
What is the structure at #5?
hard palette
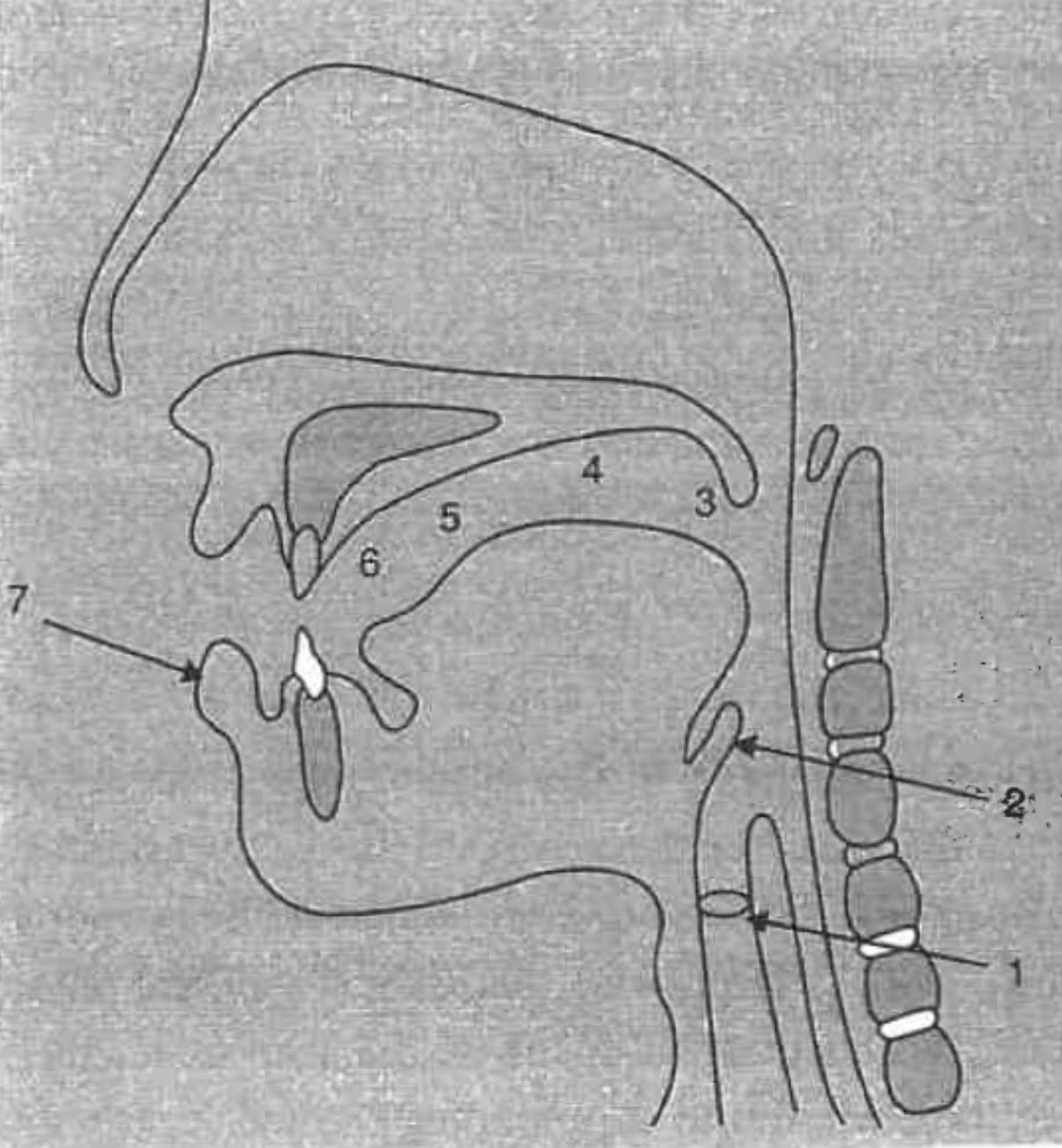
What is the structure at #6?
alveolar ridge
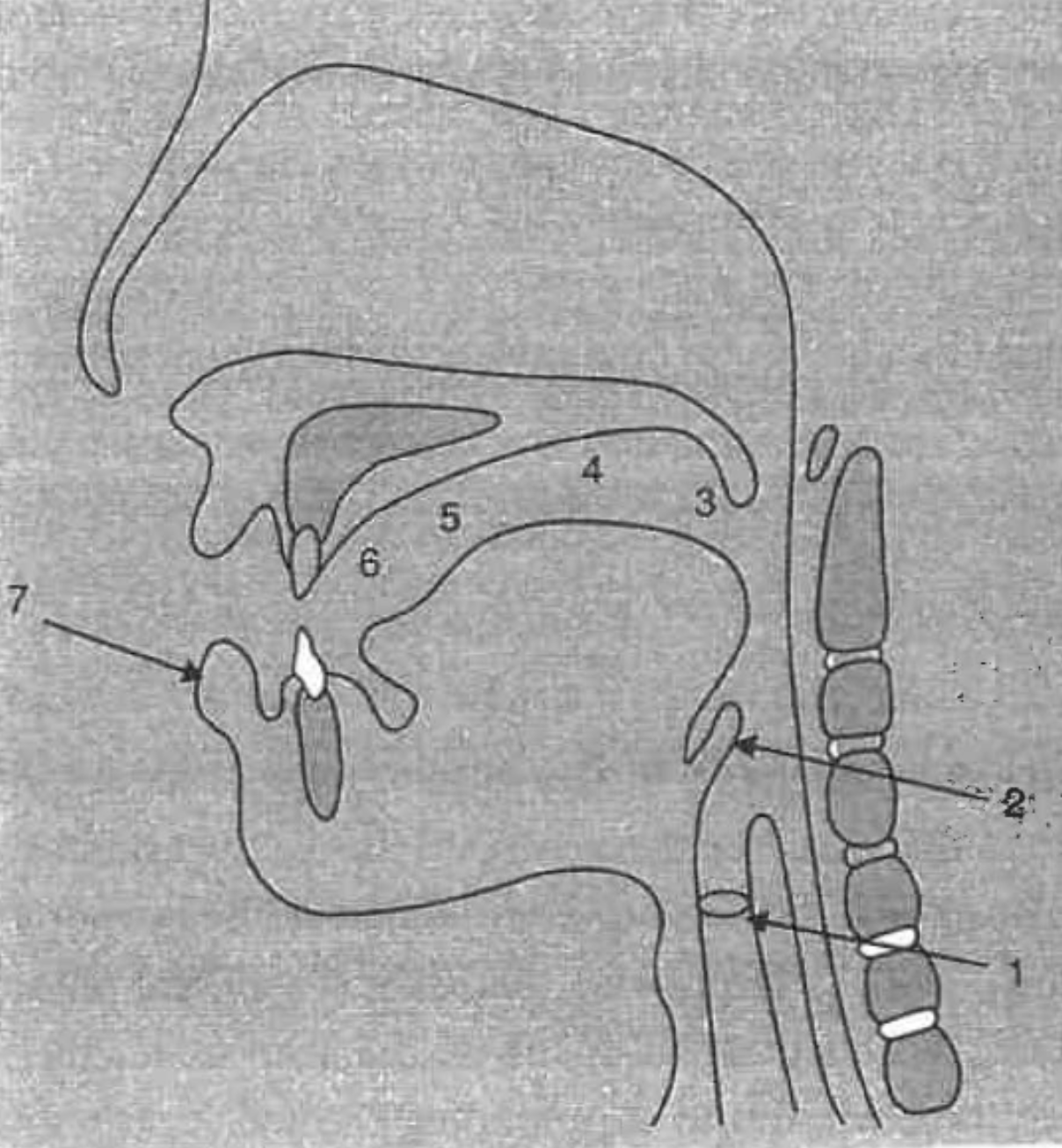
What is the structure at #7?
lips
Spell the following word in IPA letters: 영웅
[jᴧŋuŋ]
What is the IPA letter and description of the following letter:ㅏ
[a]
Low central unrounded vowel
What is the IPA letter and description of the following letter:ㅓ
[ʌ]
mid central unrounded vowel
What is the IPA letter and description of the following letter: ㅗ
[o]
Mid back rounded vowel
What is the IPA letter and description of the following letter: ㅜ
[u]
High back rounded vowel
What is the IPA letter and description of the following letter: ㅡ
[ɯ]
high central unrounded vowel
What is the IPA letter and description of the following letter:ㅣ
[i]
High front unrounded vowel
What is the IPA letter and description of the following letter:ㅐ
[ɛ]
Mid front unrounded vowel
What is the IPA letter and description of the following letter:ㅔ
[e]
Mid front unrounded vowel
What is the IPA letter and description of the following letter: ㅚ
[ö]
Mid front rounded vowel
What is the IPA letter of the following letter:ㅑ
[ja]
What is the IPA letter of the following letter:ㅕ
[jʌ]
What is the IPA letter of the following letter: ㅛ
[jo]
What is the IPA letter of the following letter: ㅠ
[ju]
What is the IPA letter of the following letter:ㅒ
[jɛ]
What is the IPA letter of the following letter: ㅖ
[je]
What is the IPA letter of the following letter: ㅘ
[wa]
What is the IPA letter of the following letter: ㅙ
[wɛ]
What is the IPA letter of the following letter: ㅝ
[wʌ]
What is the IPA letter of the following letter: ㅞ
[we]
What is the IPA letter of the following letter: ㅟ
[wi]
What is the IPA letter of the following letter: ㅢ
[ɰi]
Compare word-initial and word/syllable-medial (intervocalic) stops in Korean. How do the stops in Korean change sounds in two different environments?
Stops are voiceless in initial position in Korean while voiceless stops change to voiced when they are intervocalic.
List examples of the words which illustrate the three-way contrast (lax, tense, and aspirated) in Korean affricates. Please use IPA
[tɕata] ‘to sleep’
[tɕʰata] ‘to be cold’
[tɕ*ata] ‘to be salty
Explain the differences between the articulation of fricatives and that of affricates.
Fricative sounds are produced by forcing air through a partial obstruction passage in the mouth, causing friction. Affricates are produced by stopping the airstream and then releasing the air slightly. This is a stop sound (like a plosive) and is followed by a fricative.
List examples of the words which illustrate the three-way contrast (lax, tense, and aspirated) in Korean stops. Please use IPA.
[pul] 'fire'
[pʰul] 'grass'
[p*ul] 'horn’
What vowel is not distinguishable from [e] in casual speech in Korean? list example of the each word, using IPA.
[ɛ] and [e] are very similar in Korea. Examples are 게 [ke] ‘crab’ vs. 개 [kɛ] ‘dog’
Which consonants are found in Korean, but not in English? Please use IPA.
[tɕ tɕʰ tɕ*]
Which monophthong(s) can be found in Korean, but not in English? Please use IPA.
ɯ
True/False: Tense and lax features are distinctive in certain consonants in Korean.
True
True/False: Aspirated consonants are always voiceless in Korean.
True
True/False: /si/ and /s'i/ do not show meaning differences in Korean.
False
True/False: Nasal sounds are made by raising the velum to block the nasal cavity.
False
True/False: Since there is no !zl in Korean, English zoo by a Korean speaker might be heard as Jew by an English speaker
True
True/False: Korean shows differences of vowel length in certain vocabs.
True
Complete Korean aspirated consonants. [ph, th, ______, _____]
kh & tɕh
Complete Korean tensed consonants. [p*, t*, k*, _____, _____]
s*, tɕ*
Complete Korean bilabials. [p, p*, _____, _____]
ph & m
Complete Korean fricatives. [s, _____, _____]
s* & h
In class, we discussed some major allophonic variations (phonology!) of the consonants under certain sound environments in Korean.
For example, a voiceless stop becomes voiced when it is located between voiced sounds (intervocalic).
Please put appropriate IPA(s) in the data below.
/tap/ ‘answer’ → [____ ap]
pa.po/ ‘fool’ → [___ a ____ o]
/kuk] ‘soup’ → [____u___]
/tap/ ‘answer’ → [ tap ]
/pa.po/ ‘fool’ → [ pabo ]
/kuk] ‘soup’ → [kuk¬]
Define: Oral sounds
The velum is raised to block the nasal cavity (so, the air flows out through the mouth)
Define: Nasal Sound
lowering the velum to open the nasal cavity (so, the air can flow out through both the mouth and the nose)
Define: Liquid [l]
Partial obstruction of the airstream in the mouth, but air still passes through without any friction
The tongue tip touches the alveo-dental area, the air escapes on the two sides of the tongue body.
Which consonants are changed when there is an intervocalic and how are they changed?
/p, t, tɕ, k, l/ → [b, d, dɕ, g, r]
What is the IP for the following word?
다리
달
/tali/ ‘bridge’ → [tari]
/tal/ ‘moon‘ → [tal]
What phonetics are available in the American inventory but not the Korean one?
[f] → [ᄑ]: five → “파이브”
[v] → [ᄇ]: violin → “바이올린”
[θ] → [ᄊ] (sometimes [ᄄ]): thanks! → “쌩쓰” (“ 땡쓰”)
[ð] → [ᄃ]: father → “파더”
What are some examples of words that have no contrast and affect romanization of Korea?
[부산] → “Pusan” or “Busan”
[대구] → “Taegu” or “Daegu”
[김밥] → “Kimpap” or “Gimbab”