Science - Chapter 6 (Chemistry)
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
What is an atom?
building block of matter
smallest particle possible
What are molecules?
more than one atom (plural)
What is an element?
pure substance that consists of only one type of atom (same)
Example
1 carbon atom = C
2 oxygen atoms = 02
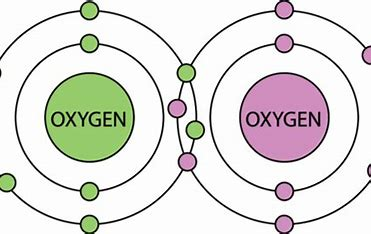
What is a compound?
pure substance made up of two or more elements that are chemically combined (different)
can be broken down into molecules
Example
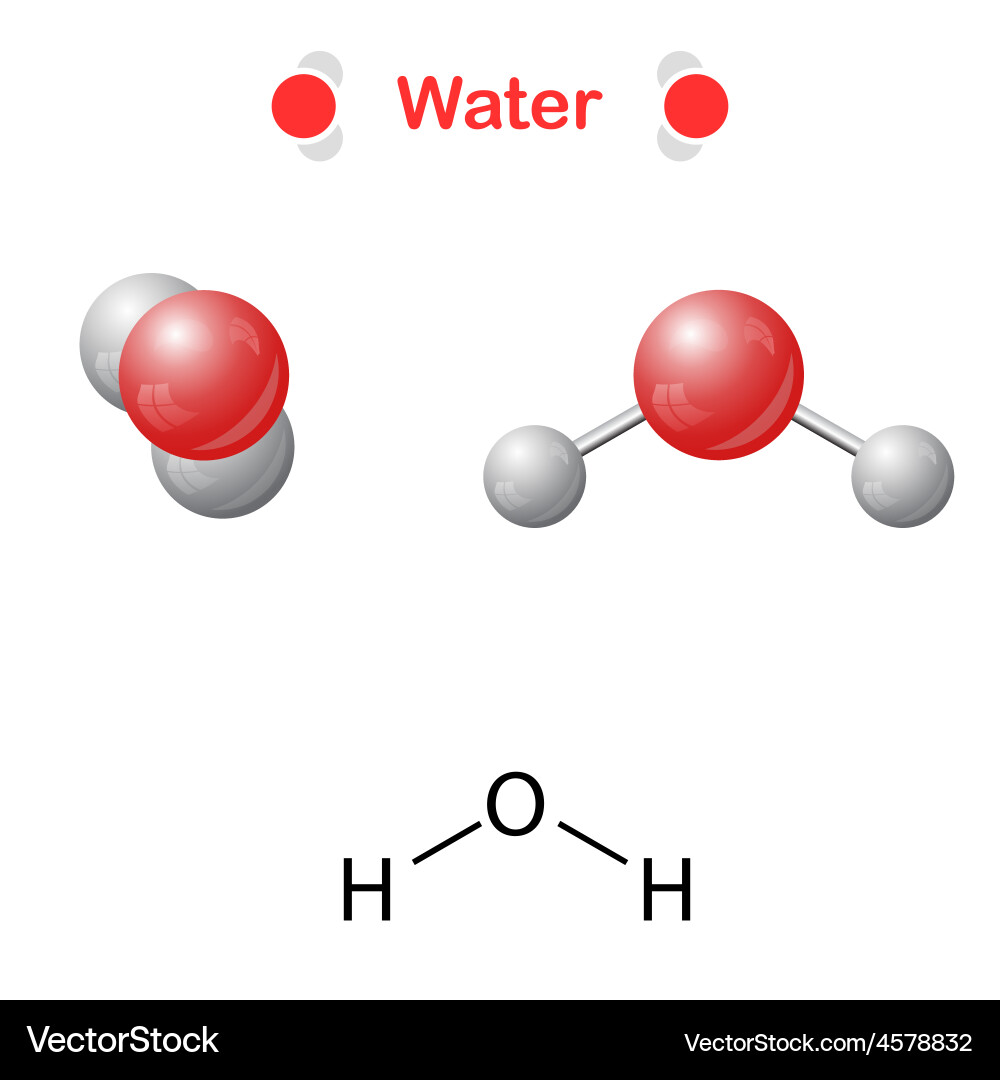
2 hydrogen + 1 oxygen = H20 **NOTE: water is pure BUT has different types of atoms
Who invented the Chemical Symbols?
It was invented be a Swedish chemist, Jon Jacob Berzelius
What are the rules?
First letter of element name
Ex. C - carbon H- hydrogen
First two letter of element name
Ex. Ca - calcium He - helium
First & third letter of element name
Ex. Cl - chlorine Cr - chromium
First & later letters of Latin name
Ex. Cu - cuprum = copper
- Different Kinds of Elements -
Metals, Non-Metals, & Metalloids
Metals:
conduct electricity & heat
shiny
malleable & ductile
solid at room temperature (except mercury)
Non-Metals:
does not conduct electricity & heat (insulator)
not shiny
brittle & not ductile
solid, liquid, gas at room temperature
Metalloids:
properties between metals & non-metals
conduct electricity, NOT heat (semi-conductor)
shiny or dull
brittle & not ductile
solid at room temperature
What is a chemical family?
It is a group of related elements sharing common chemical properties
Example: gold, silver, copper
Who is Demitri Mendeleev?
made a card for each known element with it’s properties (only 63)
arranged cards by increasing mass
noticed group elements had similar physical and chemical properties
predicted properties of undiscovered elements
this formed a pattern periodically → periodic table
Name of the Chemical Families:
Alkali Metals (Group 1)
Alkaline Metals (Group 2)
Halogens (Group 17)
Noble Gases (Group 18)
Alkali Metals (Group 1)
most reactive metals
react quickly when exposed to air & water
Alkaline Metals (Group 2)
2nd most reactive metals
Halogens (Group 17)
most reactive non-metals
Noble Gases (Group 18)
inactive/does NOT react
very stable
Column =
Group
Row =
Period
Find the element: Group 2 - Period 3
The element is Magnesium (Mg)
- Famous scientists and their theories of atoms -
Democritus (400 BCE)
all matter can be divided into smaller and smaller pieces until it is a single invisible particle
there are different sizes
in constant motion
separated by empty spaces (the void)
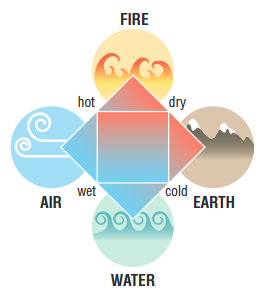
Aristotle (450 BCE)
all matter is made up of four basic substances: earth, water, air, and fire
four specific qualities - dry, wet, cold and hot
John Dalton (1807)
all matter is made up of tiny, invisible particles called atoms
all atoms of an element are identical
atoms of different elements are different
atoms are rearranged to form new substances in chemical reactions, but they are never created or destroyed

J.J. Thomson (1897)
atoms contain negatively charged electrons
since atoms are neutral, the rest of the atom is a positively charged sphere
negatively charged electrons are evenly distributed throughout the atom
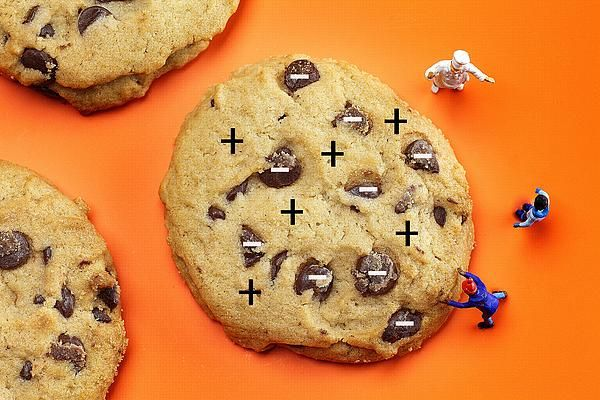
What 3 things did Ernest Rutherford (1909) discover?
Discovered metal atoms of gold have:
1) Nucleus - center of atom with positive charge
2) Electron Cloud - surrounds nucleus with negative charge
3) Most of the atom is empty space
What did James Chadwick (1932) discover?
Discovered that the nucleus also has a neutral particle with a mass called neutrons
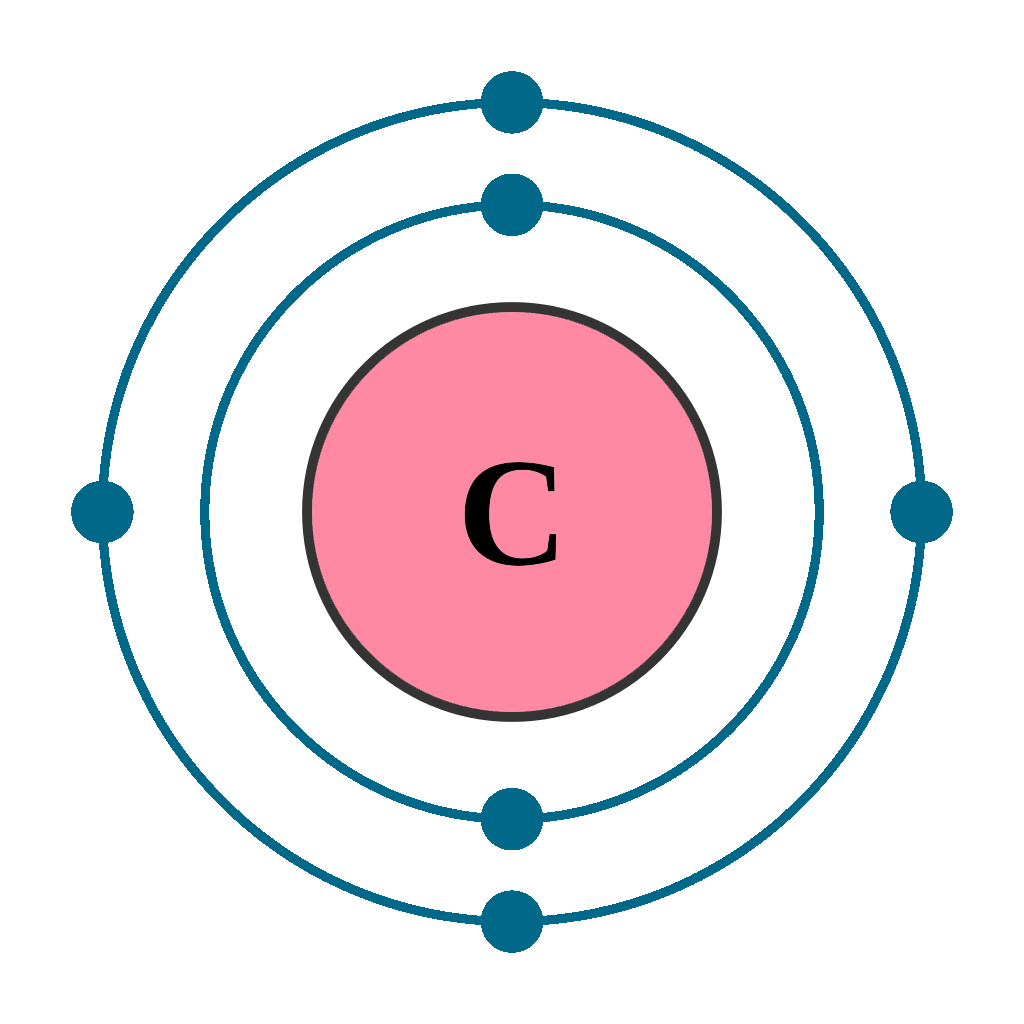
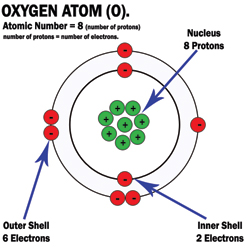
What did Niels Bohr (1913) discover?
electrons move rapidly around nucleus (orbit) in electron
more energetic electrons, the further the shells
each shell holds maximum amount of electrons
Bohr-Rutherford Atom Example:
What is a proton?
found inside the nucleus
has a positive charge (+)
represented by “p” in the nucleus
Example: 11P
What is an neutron?
found inside the nucleus
has a neutral charge (-)
represented by “n” in the nucleus
Example: 12N
What is an electron?
found outside the nucleus
has a negative charge
represented by “ē”
What is a atomic number?
Number of protons/electrons in the nucleus
What is a mass number?
The number of protons + neutrons in the nucleus
How do you solve for the number of neutrons in an atom?
Number of Neutrons = Mass Number - Atomic Number

How to draw standard notation:
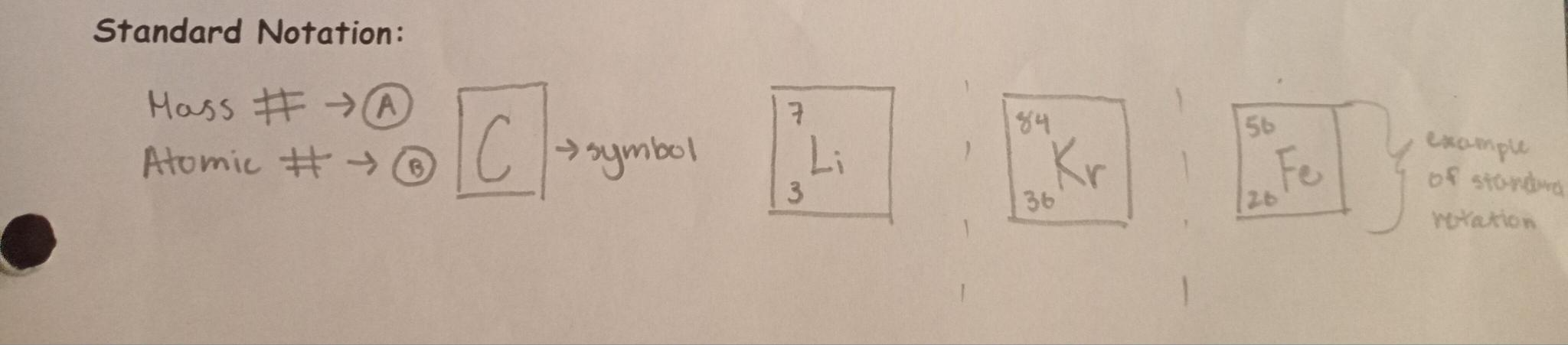
What are the patterns found in the periodic table?
same period # have the same number of shells
same group # have the same number of electrons in the outer shell
- Alkali Metal → 1 electron
- Alkaline → 2 electrons
- Halogens → 7 electrons
- Noble Gases → Full shell (2 electrons of 8 electrons)
smaller period # → fewer number of shells
smaller group # → smaller radius of atom
Elements with electrons(s) further from the nucleus are more reactive
What is charcoal?
shapeless, disorganized arrangement of carbon atoms which creates a soft black solid
forms an unending structure
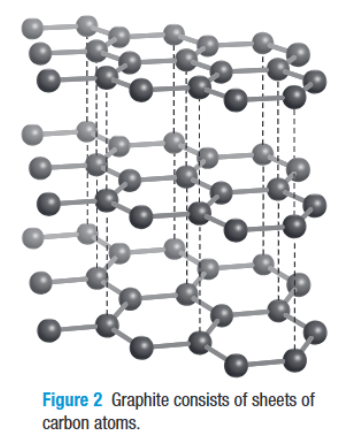
What is graphite?
the arrangement is organized
each carbon atom joins with three other carbon atoms to form a sheet of interconnected hexagons
flat sheets are loosely layered on top
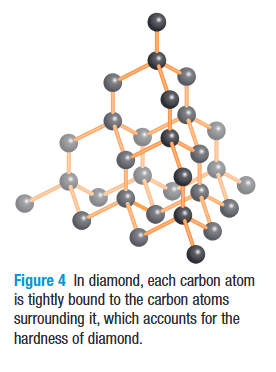
What is diamond?
due to extremely high pressure, carbon atoms arrange themselves into regular patterns
they are interconnected in three dimensions