Aerobic & Anaerobic Respiration (plants + animals)
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
Respiration (cellular)
A series of oxidation reactions taking place in all living cells. It results in the release of energy from organic compounds such as glucose
Aerobic Respiration
A type of cellular process that consumes organic molecules and oxygen to yield ATP. It occurs with oxygen in the mitochondria.
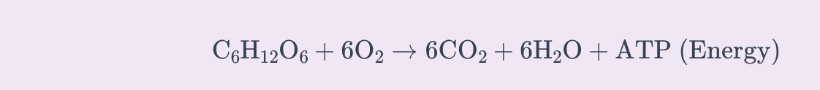
Anaerobic respiration
A type of cellular respiration that occurs without oxygen to produce lactic acid and energy in the cytoplasm for animals, while for plants: alcohols and carbon dioxide (in plants and yeast).
Some organisms carry out aerobic respiration in the presence of oxygen but are able to change to anaerobic respiration in its absence. Some bacteria can thrive only in the absence of oxygen.
When oxygen supply is limited, glycolysis occurs for a quick supply of energy (glucose into pyruvic acid)
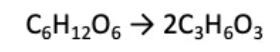
products: small amount of ATP + lactic acid in animals
Lactic acid
Lactic Acid:
Lactic acid is toxic and requires an oxygen debt to be broken down into useful monomers for anaerobic respiration
Lactic acid is either excreted through breakdown on a cellular level or turned into pyruvic acid for a quick source of energy
Glycolysis
The process of breaking down glucose into pyruvic acid in the cytoplasm. This step occurs in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration. In anaerobic conditions, the pyruvic acid is then converted into lactic acid (in humans) or alcohol and CO2 (in plants).
When oxygen supply is limited, glycolysis occurs for a quick supply of energy (glucose into pyruvic acid.
Alcohol fermentation (example of anaerobic respiration)
Alcohol fermentation (plant):
Pyruvate is converted into ethanol and CO2.
Glycolysis can still operate in the absence of oxygen, but the energy yield is low.
Pyruvate is converted into waste products.
Lactic acid fermentation (animals - anaerobic respiration)
Occurs in human muscles when oxygen is scarce (e.g., during intense exercise).
Buildup of lactic acid creates a burning sensation in muscles.