Chapter 4: Electric Potential and Capacitance
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
It deals with the potential associated with electric charges and the capacitance associated with capacitors.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
1
New cards
Electrical Potential Energy
We is the work done by the electric force, then the change in the charge’s electrical potential energy is defined by:
* Ue = electrical potential energy
* We = work done by electric force
* Ue = electrical potential energy
* We = work done by electric force
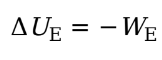
2
New cards
Electrical Potential Energy from a point charge
Electrical potential energy required to move along the field lines surrounding a point charge is given by:
* q1 and q2 = charges
* e0 = permeability of free space
* Ue = electrical potential energy
* r = distance
* q1 and q2 = charges
* e0 = permeability of free space
* Ue = electrical potential energy
* r = distance
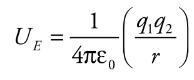
3
New cards
Electric Potential
Electric potential is the electric potential energy per unit of charge at a point in an electric field, measured in volts (V). It's the work done per unit charge in bringing a test charge from infinity to that point.
***V = U/q***
***V = U/q***
4
New cards
Electric Potential Energy from a point charge
Consider the electric field created by a point source charge Q. If a charge moves from a distance rA to a distance rB from Q, then the change in the potential energy is:
* Ub and Ua = electrical potential energies for a and b
* ra and rb = distances for a and b
* e0 = permeability of free space
* Ub and Ua = electrical potential energies for a and b
* ra and rb = distances for a and b
* e0 = permeability of free space
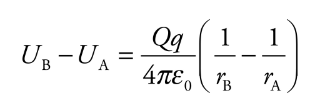
5
New cards
Equipotential Surface
An equipotential surface is a surface in a region of space where every point on the surface is at the same potential. In other words, no work is required to move a charge along an equipotential surface. Equipotential surfaces are perpendicular to electric field lines and can be used to visualize the electric field in a given region.
6
New cards
Addition of electric potential
***V = kQ/r***
* V = electric potential energy
* q = point charge
* r = distance between any point around the charge to the point charge
* k = Coulomb constant; k = 9.0 × 109 N
* V = electric potential energy
* q = point charge
* r = distance between any point around the charge to the point charge
* k = Coulomb constant; k = 9.0 × 109 N
7
New cards
Equipotential Curve
Equipotential curves are curves of constant elevation. If you walk along any of the contour lines and you neither ascend nor descend, then the curve is known as the equipotential curve.
8
New cards
Equipotential Map
A drawing of several equipotential curves at various values of the potential for a charge distribution is called an equipotential map.
9
New cards
Capacitor
Two conductors, separated by some distance carry equal but opposite charges +Q and -Q. The pair comprises a system called a capacitor.
10
New cards
Parallel-Plate Capacitor
The capacitor is in the form of parallel metal plates or sheets.
11
New cards
Capacitance
The capacitance measures the capacity for holding charge.
***C = κε₀A/d (k = dielectric constant)***
***C = κε₀A/d (k = dielectric constant)***
12
New cards
Fringing fields
Fringing fields extend beyond conductor or magnetic material edges. They weaken as the distance from the edge increases. They're important in device design but can cause interference and affect performance.
13
New cards
energy stored in capacitor
The energy stored in a capacitor can be calculated using the formula
***Uc = ½QV = ½CV²***
where U is the energy stored in joules, C is the capacitance of the capacitor in farads and V is the voltage across the capacitor in volts.
***Uc = ½QV = ½CV²***
where U is the energy stored in joules, C is the capacitance of the capacitor in farads and V is the voltage across the capacitor in volts.
14
New cards
Dielectric
To keep the plates of the capacitor apart they are filled with dielectric which increases the capacitance of the capacitor.
15
New cards
The amount of work done by a uniform electric field
***W = q E d***
* W = work done
* q = charge
* E = electric field
* d = distance
* W = work done
* q = charge
* E = electric field
* d = distance
16
New cards
A dielectric always _______ the capacitance of a capacitor
increases
17
New cards
the __________ of the capacitance of a collection of capacitors in series is found by adding the reciprocals of the individual capacitances
reciprocal
18
New cards
Collection of capacitors are said to be in ______ if they all share the same charge magnitude
series
19
New cards
The equivalent capacitance of a collection of capacitors in parallel is found by _______ the individual capacitances
adding
20
New cards
The equivalent capacitance of a collection of capacitors in parallel is found by _______ the individual capacitances
parallel
21
New cards
1 C/V = ?
1 Farad
22
New cards
Ratio of charge to potential difference \n (C=Q/∆V)
capacitance
23
New cards
Magnitude of the potential difference between two plates of a distance d
***∆V = -Ed***
24
New cards
How does the electric field relate to electric potential difference?
***E = -dV/dr***
25
New cards
1 volt = ?
1 J/C
26
New cards
Wₑ = Fₑ\*distance\*cosθ = qE\*distance; ∆U =?
\-qEd\*cosθ
27
New cards
When a charge moves in an electric field, unless its displacement is always perpendicular to the field, the electric force does _______ on the charge.
work
28
New cards
Factors on which capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor depend on?
1\. Area of the plates (C ∝ A) \n 2. Distance between the plates ( C ∝ 1/d) \n 3. Permittivity of medium ( C ∝ ε0)
29
New cards
What is the dimensional formula of capacitance?
M-1L-2T4A2
30
New cards
Potential energy of a dipole in a uniform electric field?
U = -pEcosθ
31
New cards
How to solve for capacitance?
C = q/V
32
New cards
What factors does capacitance depend on?
1\. Size and shape of conductor \n 2. Nature (permittivity)
33
New cards
How to find total capacitance in a series combination?
1/Cs = 1/C1 + 1/C2 + 1/C3
34
New cards
How to find total capacitance in a parallel combination?
Cp = C1 +C2 + C3