Biology - Nutrition in Plants
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 1:20 AM on 10/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
1
New cards
- nutrition
process by which living organisms obtain food
2
New cards
- photosynthesis
the process by which green plants convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose by using sunlight energy absorbed by chlorophyll in chloroplasts
3
New cards
- What is the equation for photosynthesis?
6H₂O (l) + 6CO₂ (g) → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
4
New cards
- What conditions are necessary for photosynthesis? (6)
Carbon dioxide; Water; Sunlight energy; Chlorophyll; Enzymes (in chloroplasts); Optimum temperature for enzymes
5
New cards
- Describe the light stage of photosynthesis
In the light stage, the light energy absorbed by chlorophyll is used to split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen — releasing oxygen as a waste product
6
New cards
- What conditions are necessary for the light stage of photosynthesis to occur? (3)
Light, chlorophyll and water
7
New cards
- evolution of oxygen
fundamental process in which oxygen is created and released into the atmosphere as a consequence of photosynthesis
8
New cards
- Describe the dark stage of photosynthesis
In the dark stage, the hydrogen atoms produced in the light stage reduce the carbon dioxide molecules forming glucose via enzymes
9
New cards
- What conditions are necessary for the dark stage of photosynthesis to occur? (3)
Hydrogen atoms, carbon dioxide molecules, enzymes
10
New cards
- chlorophyll
green pigment found in chloroplasts that absorbs light which is used as energy in photosynthesis
11
New cards
- chloroplast
a rod-shaped organelle that produces chlorophyll and houses photosynthesis
12
New cards
- What are the four main environmental factors affecting the photosynthesis rate? (4)
Light; carbon dioxide; temperature and water
13
New cards
- How does light affect the photosynthetic rate? (2)
Light limits the rate between dusk and dawn, and during the winter months in temperate climates due to the lack of light for energy
14
New cards
- How does temperature affect the photosynthetic rate?
Temperature limits the rate during the winter months — destabilizing enzymes used to assemble glucose
15
New cards
- How does water affect the photosynthetic rate? (2)
Water limits the rate during the dry season in tropical climates and when the ground is frozen in temperate climates
16
New cards
- How does carbon dioxide limit the photosynthetic rate?
It limits the rate during the day in most climates since the concentration of carbon dioxide in the air is very low
17
New cards
- glucose
a sugar that is used as a source of energy in the plant
18
New cards
- Where is glucose found/used in the plant? (4)
In the leaf cells in respiration; Condensed into starch for ease of storage; Converted into other organic substances; Converted into sucrose
19
New cards
- Where is sucrose found/used in the plant? (5)
Reconversion into glucose for respiration; Conversion into cellulose to make cell walls in growing plants; As starch for storage; Converted into amino acids and proteins by the addition of nitrates and sulfates; As lipids in seeds
20
New cards
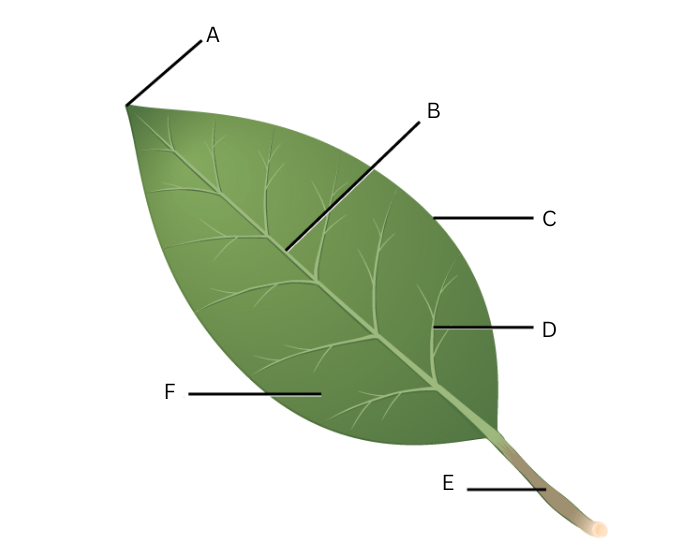
Label this diagram (6)
A-apex; B-midrib; C-margin; D-vein; E-petiole; F-lamina
21
New cards
- apex
the protruding part of the leaf
22
New cards
- margin
the outline of a leaf blade
23
New cards
- lamina
flat, typically green, expanded part of the leaf blade
24
New cards
- midrib
the central, thicker, linear structure, which runs through the lamina
25
New cards
- vein (leaf)
small channels made of vascular tissue that are responsible for transporting minerals and water throughout the leaf
26
New cards
- petiole
stalk that attaches a leaf to the plant stem
27
New cards
- Briefly describe the external adaptions made by the leaf to maximize photosynthesis (4)
The lamina is broadly held out flat by veins to increase surface area for absorption; Lamina is thin so that sunlight energy and carbon dioxide can easily reach all cells; Laminas are usually held 90° to the sunlight — maximizing its exposure to the sunlight; Laminae are spaced out around stems — maximizing each one’s exposure to the sunlight
28
New cards
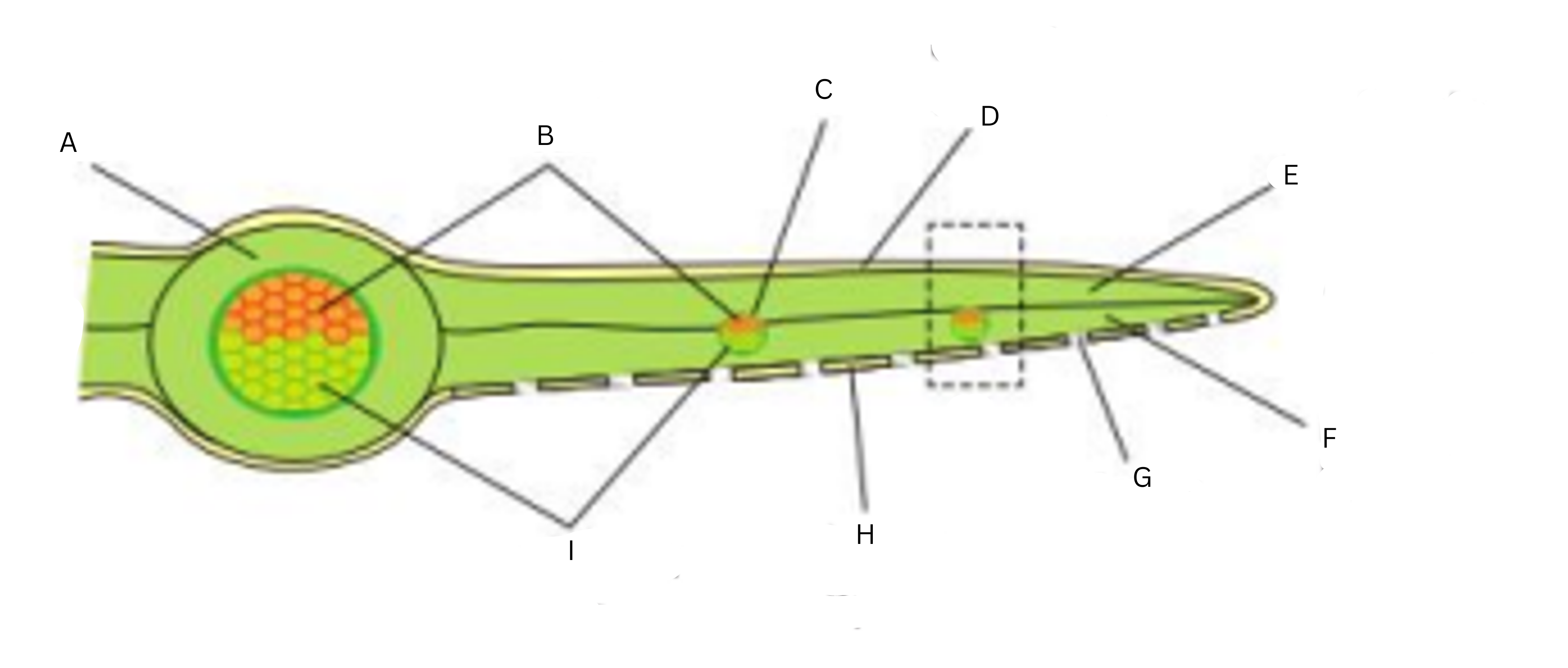
Label this diagram (9)
A-midrib; B-xylem tissue; C-vein; D-upper epidermis; E-palisade mesophyll layer; F-spongy mesophyll layer; G-stoma; H-lower epidermis; I-phloem tissue
29
New cards
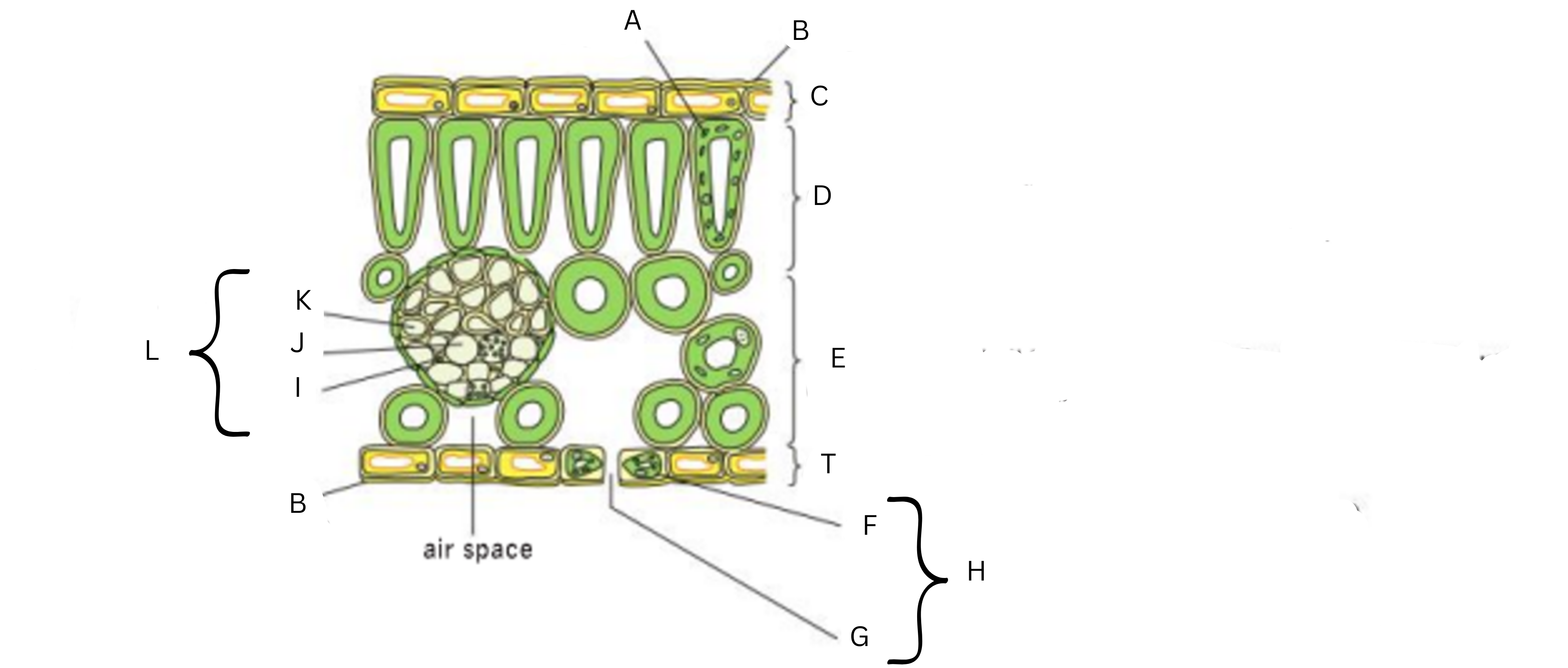
Label this diagram (13)
A-chloroplast; B-wavy cuticle; C-upper epidermis; D-palisade mesophyll layer; E-spongy mesophyll layer; T-lower epidermis; F-guard cell; G-stomatal pore; H-stomata; I-companion cell; J-phloem sieve tube; K-xylem vessel; L-vein
30
New cards
- waxy cuticle
a waxy, waterproof layer which prevents water from leaving the leaf
31
New cards
- palisade mesophyll cells
plant cells found beneath the upper epidermis of the leaf responsible for absorbing a majority of the sunlight for photosynthesis
32
New cards
- spongy mesophyll cells
plant cells which facilitate gaseous exchange for photosynthesis and aid the palisade cells in absorbing light
33
New cards
- guard cells
plant cells which have adapted their structure to open and close stomatal pores when they are turgid or not, respectively
34
New cards
- stomatal pore
pores on the surface of leaves that facilitate the gaseous exchange for photosynthesis
35
New cards
- xylem cells
plant cells which are responsible for transporting water across the plant
36
New cards
- phloem cells
plant cells which are responsible for transporting food substances across the plant
37
New cards
- Briefly describe the internal adaptations made by the leaf to maximize photosynthesis (7)
Waxy cuticles prevent the loss of water; Stomatal pores facilitate gaseous exchange; Palisade mesophyll cells house a majority of the chloroplasts for photosynthesis; Palisade mesophyll cells arrange themselves at 90° to allow chloroplasts to concentrate at the top of the cells in dim light; Spongy mesophyll cells are irregularly shaped in order to house gaseous exchange in intercellular spaces; Xylem vessels supply mesophyll cells with water and mineral ions for their processes; Phloem tubes transport glucose from photosynthesis to other parts of the plant
38
New cards
- nitrogen
a mineral used to form chlorophyll and make proteins in plants
39
New cards
- In what form is nitrogen found in the plant, and what are the results of its deficiency? (1/3)
Nitrate ions/poor growth; chlorosis; underdeveloped leaves
40
New cards
- magnesium
a mineral used to form chlorophyll in plants
41
New cards
- In what form is magnesium found in the plant, and what is the result of its deficiency? (1/1)
Magnesium ions; Chlorosis
42
New cards
- phosphorus
a mineral used to make ATP and some proteins
43
New cards
- In what form is phosphorus found in the plant, and what are the results of its deficiency? (1/3)
Phosphate ions/dull, purple-green leaves with curly brown edges; Poor root growth; Stunted growth
44
New cards
- potassium
a mineral used to help maintain the correct salt balance in plant cells and to help in photosynthesis
45
New cards
- In what form is potassium found in the plant, and what are the results of its deficiency? (1/2)
Potassium ions/yellow-brown margins and brown spots; Premature death of leaves
46
New cards
- sulfur
a mineral used to make proteins in plants
47
New cards
- In what form is sulfur found in the plant, and what are the results of its deficiency? (1/2)
Sulphate ions/Poor growth; Chlorosis
48
New cards
- calcium
a mineral used to make cell walls in the tips of growing roots and shoots
49
New cards
- In what form is calcium found in the plant, and what are the results of its deficiency? (1/3)
Calcium ions/Poor, stunted growth; Death of the growing tips of roots and shoots; Poor bud development
50
New cards
- chlorosis
yellowing of normally green leaves due to lack of chlorophyll