Biodiversity and Classification of Microorganisms and Plants
1/240
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
241 Terms
Biodiversity
Variety of life forms in ecosystems.
Microorganisms
Tiny organisms visible only under a microscope.
Five Kingdoms
Classification system: Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia.
Prokaryotes
Organisms without a true nucleus.
Eukaryotes
Organisms with a true nucleus.
Monera
Kingdom including bacteria.
Protista
Kingdom including unicellular eukaryotes.
Fungi
Kingdom including yeasts and molds.
Plantae
Kingdom including multicellular plants.
Animalia
Kingdom including multicellular animals.
Pathogens
Microorganisms causing diseases.
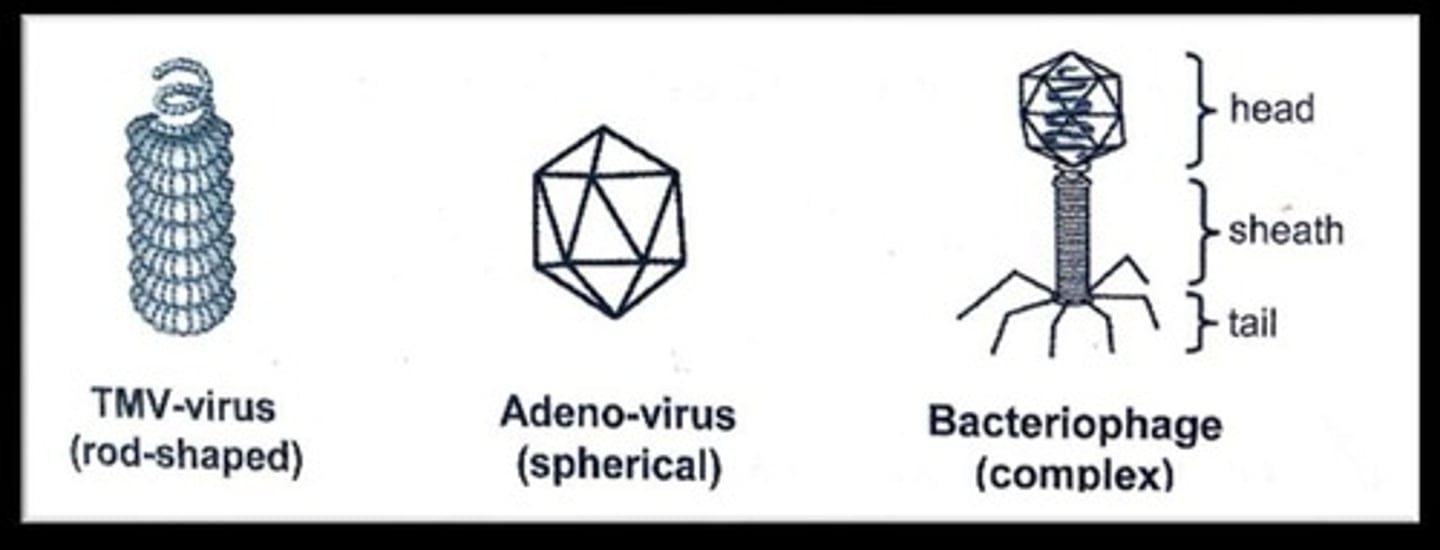
Viruses
Acellular entities requiring host cells to reproduce.
Acellular
Lacking cellular structure or organization.
Host-specific
Viruses infect specific types of host cells.
Bacteriophage
Virus that infects bacterial cells.
Asexual reproduction
Reproduction without sexual processes.
Binary fission
Asexual reproduction method in bacteria.
Heterotrophic bacteria
Bacteria that cannot produce their own food.
Autotrophic bacteria
Bacteria that produce their own food.
Saprophytic bacteria
Bacteria feeding on dead organic matter.
Parasitic bacteria
Bacteria obtaining food from living hosts.
Mutualistic bacteria
Bacteria benefiting from symbiotic relationships.
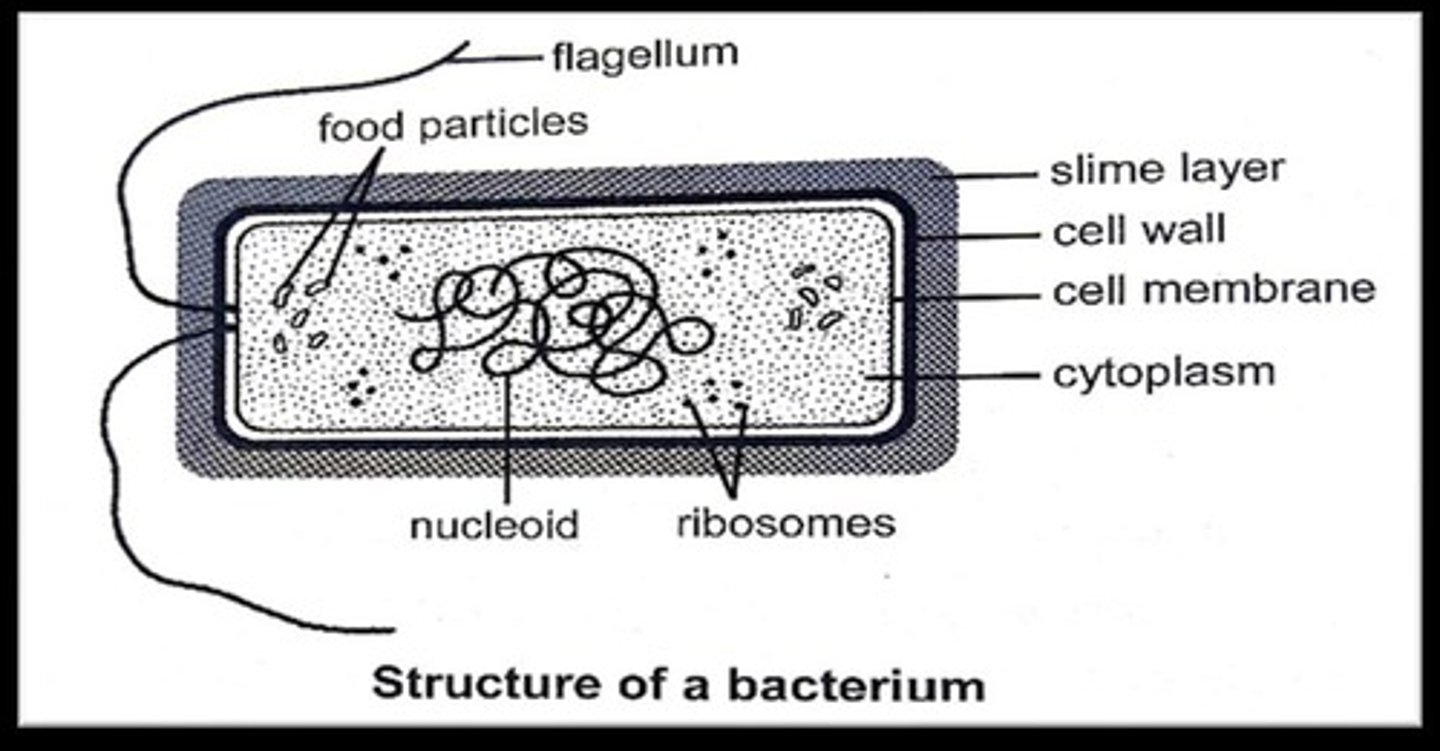
Cell wall
Structure providing protection to bacterial cells.
Slime layer
Protective layer surrounding some bacterial cell walls.
Plasma Membrane
Encloses cytoplasm, located beneath cell wall.
Cytoplasm
Fluid containing ribosomes, no membrane-bound organelles.
Nucleus
True nucleus is absent in bacteria.
Nucleoid
Concentration of DNA in bacterial cells.
Flagella
Whip-like structures for bacterial movement.
Bacillus
Rod-shaped bacteria, plural: bacilli.
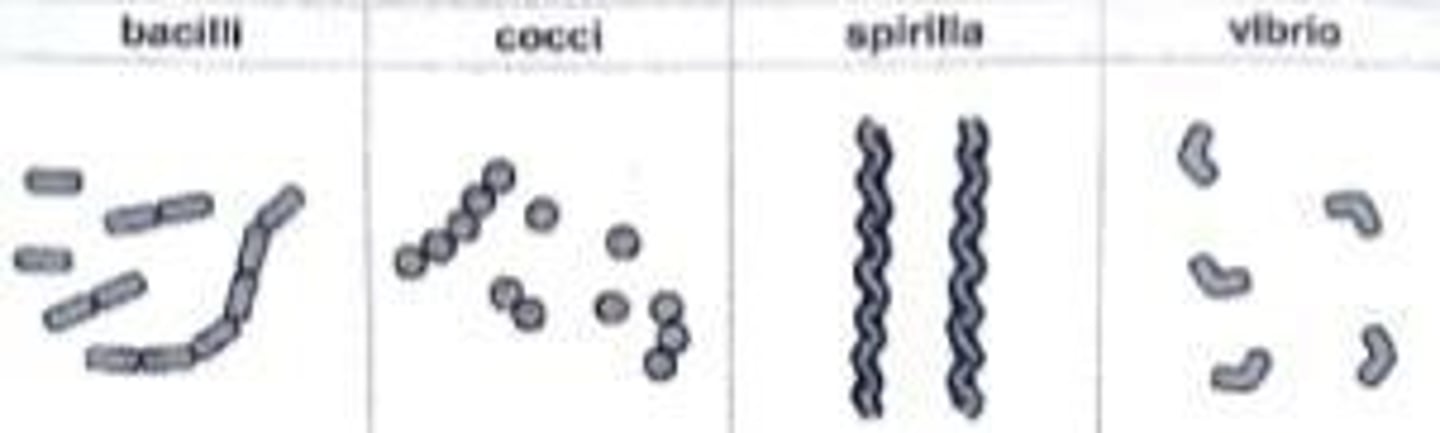
Coccus
Spherical bacteria, plural: cocci.
Spirillum
Spiral-shaped bacteria, plural: spirilla.
Vibrio
Comma-shaped bacteria.
Protists
Diverse unicellular organisms not fitting other kingdoms.
Eukaryotic
Organisms with true nuclei, like protists.
Protozoa
Animal-like, unicellular, heterotrophic protists.
Algae
Plant-like, autotrophic protists, uni- or multicellular.
Slime Moulds
Fungus-like, multicellular, heterotrophic protists.
Amoeba
Example of protozoa, uses pseudopodia for movement.
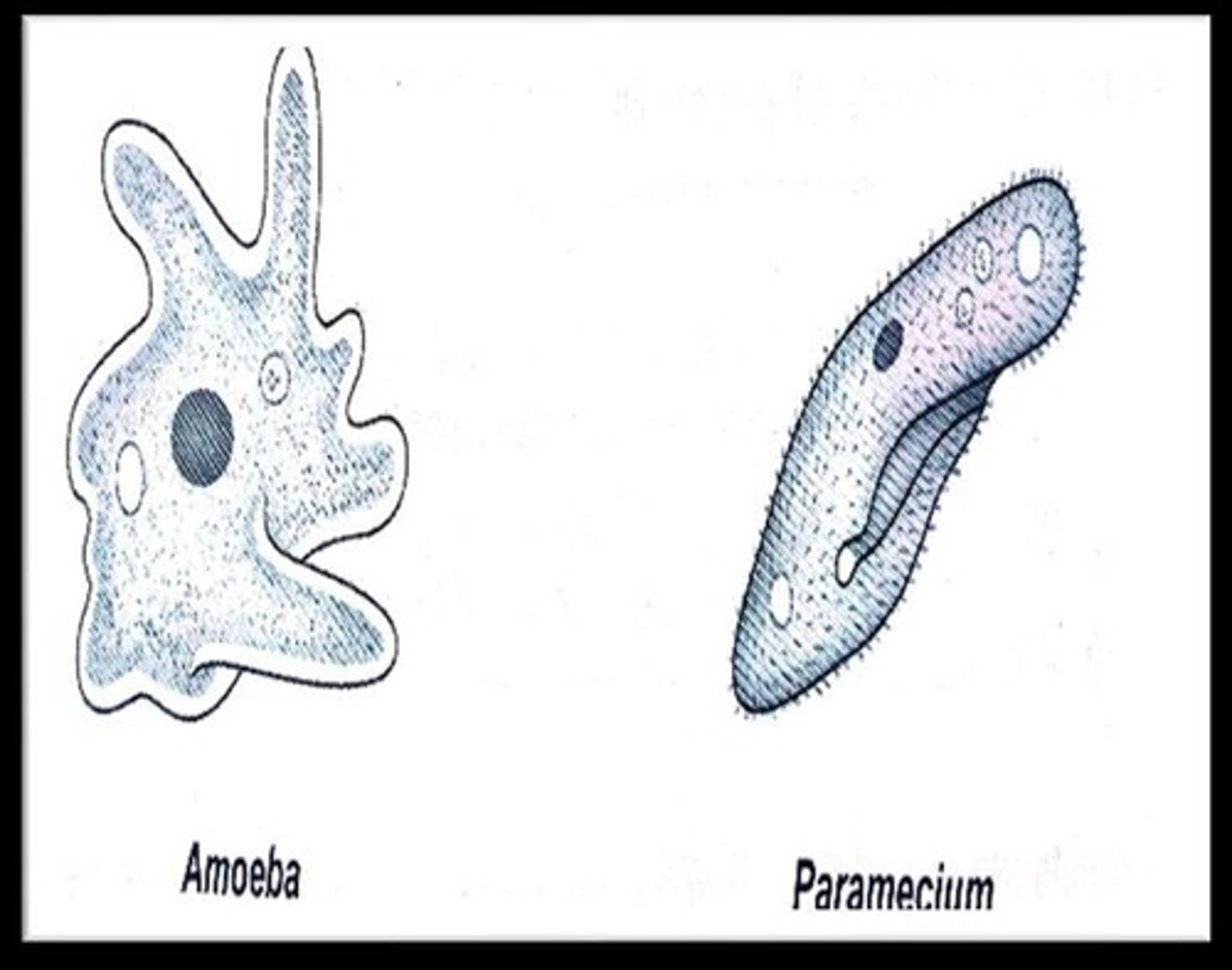
Paramecium
Ciliated protozoa, uses cilia for locomotion.
Euglena
Flagellated protist, capable of photosynthesis.
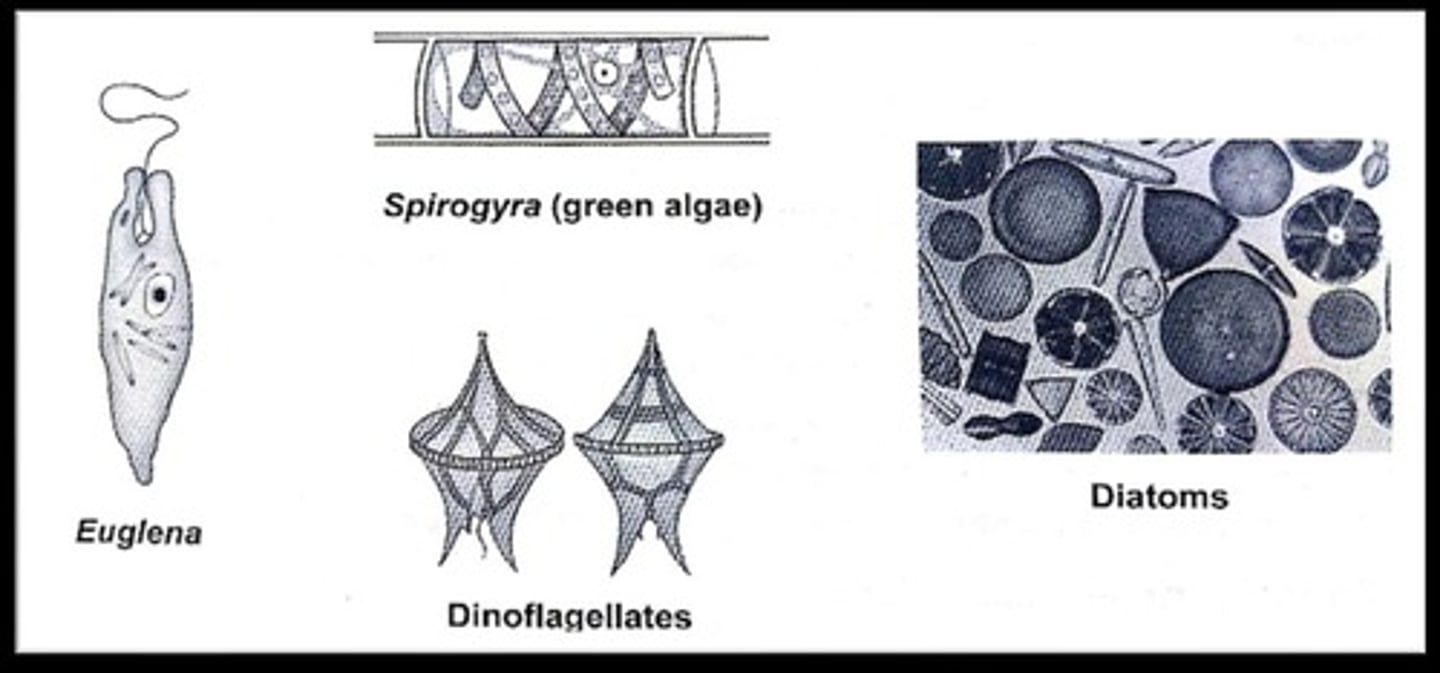
Diatoms
Microscopic, unicellular algae with silica walls.
Chloroplasts
Organelles enabling photosynthesis in algae.
Hyphae
Branched filaments making up fungal structure.
Mycelium
Mass of interwoven hyphae in fungi.
Chitin
Polysaccharide in fungal cell walls.
Saprophytes
Fungi that decompose dead organic matter.
Mutualistic Fungi
Fungi that benefit from symbiotic relationships.
Decomposers
Organisms that break down dead organic matter.
Nitrogen Cycle
Process converting nitrogen for plant uptake.
Nitrifying Bacteria
Convert ammonia to nitrites and nitrates.
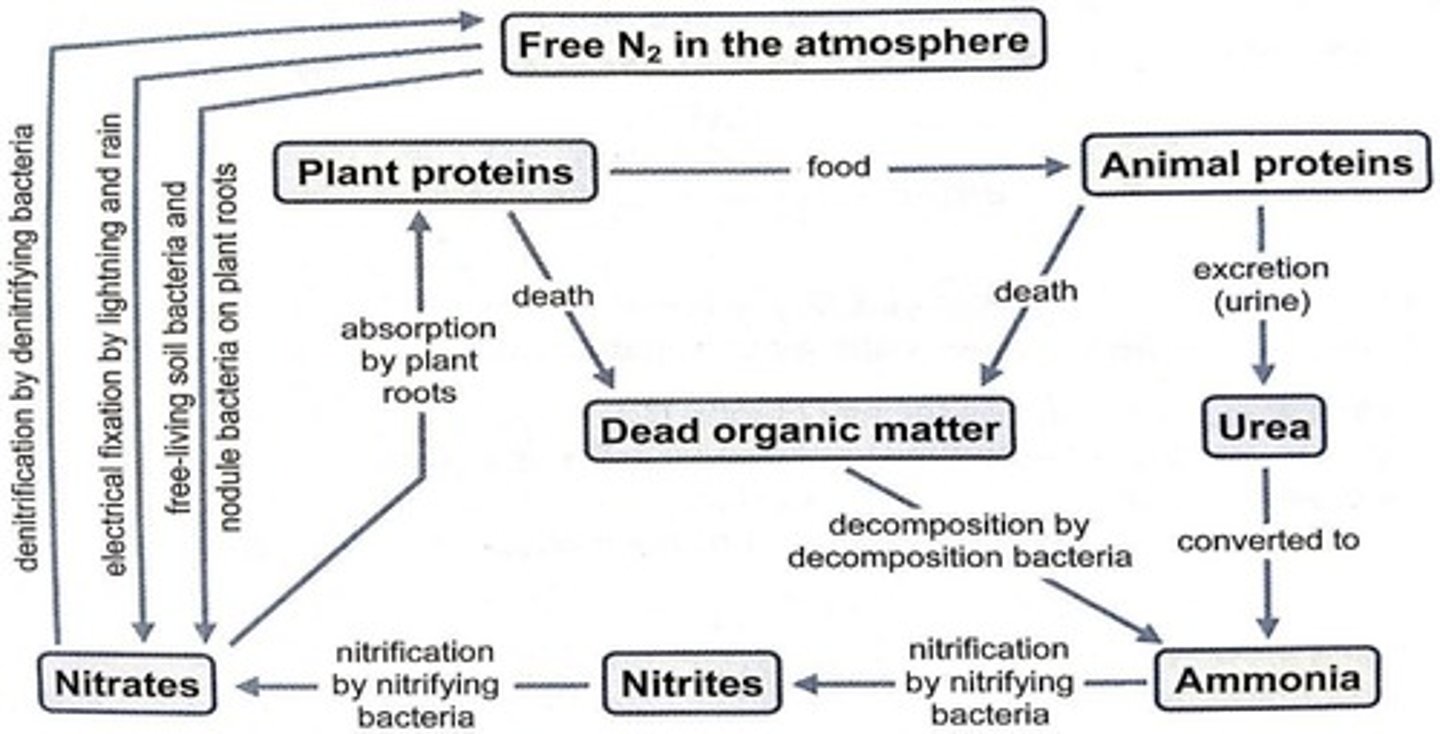
Denitrifying Bacteria
Convert nitrates back to atmospheric nitrogen.
Photosynthesis
Process converting light energy into chemical energy.
Nitrogen-Fixing Bacteria
Convert atmospheric nitrogen into plant-usable nitrates.
Escherichia coli (E. coli)
Bacteria producing vitamin K in human intestines.
Opportunistic Infections
Infections occurring when immune system is weak.
HIV/AIDS
Disease caused by Human Immunodeficiency Virus.
CD4 Cells
Immune cells targeted by HIV virus.
Symptoms of HIV
Flu-like symptoms in early infection phase.
AIDS
Final phase of HIV infection with severe symptoms.
Impact on Families
HIV affects health, income, and productivity.
Orphans
Children without parents due to HIV/AIDS.
Economic Impact
HIV reduces labor force and affects industries.
Direct Costs of HIV
Medical care and medication expenses.
Indirect Costs of HIV
Costs from lost productivity and orphan care.
Testing for HIV
Knowing one's HIV status is crucial.
Antiretroviral Drugs (ARVs)
Medications that lower viral load in HIV patients.
Healthy Diet
Essential for supporting immune system in HIV.
Prevention of HIV
Education and avoiding sexual intercourse are key.
Thrush (Candidiasis)
Fungal infection caused by Candida species.
Tuberculosis (TB)
Bacterial infection affecting lungs and other organs.
Malaria
Disease caused by Plasmodium parasites transmitted by mosquitoes.
Safe sex practices
Engaging in sexual activity with protection to prevent STDs.
HIV-negative partner
A sexual partner who is not infected with HIV.
Condom use
Using condoms to reduce STD transmission risk.
STD treatment
Addressing sexually transmitted diseases like syphilis.
Blood contact avoidance
Preventing exposure to blood to reduce infection risk.
Drug abuse effects
Substance misuse leading to risky sexual behaviors.
TB transmission
Spread through inhalation of infected droplets.
Poverty-related disease
Illness exacerbated by poor living conditions.
TB symptoms
Cough, fatigue, weight loss, night sweats, chest pain.
Active TB
Severe form of TB with widespread infection.
Income loss from TB
Financial impact due to inability to work.
TB stigma
Social discrimination against individuals with TB.
TB management
Treatment involves antibiotics over six months.
BCG vaccine
Immunization against TB given shortly after birth.
Drug-resistant TB
TB that does not respond to standard medications.
Multi-drug resistant TB
Requires expensive long-term chemotherapy for treatment.
TB and HIV/AIDS
TB accelerates progression of HIV to AIDS.
Anopheles mosquito
Primary vector for malaria transmission.
Malaria infection process
Parasites enter bloodstream via mosquito saliva.
Secondary host
Organism that supports parasite development after primary host.
Malaria effects
Parasites multiply in the liver after bloodstream infection.
Symptoms of Malaria
Fever, headache, shivering, joint pain, vomiting, convulsions.
Cerebral Malaria
Severe complication causing brain damage.
Vector Mosquitoes
Insects responsible for transmitting malaria.
Prophylactic Medication
Drugs used to prevent malaria infection.
Natural Immunity
Innate defense present at birth.
Acquired Immunity
Immunity developed after pathogen exposure.
First Line of Defence
External barriers preventing pathogen entry.