biological molecules
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
What are DNA and RNA types of?
Nucleic acids
What are nucleic acids made of?
Nucleotides
What are DNA and RNA nucleotides made of?
Pentose sugar - deoxyribose or ribose
Phosphate group
Nitrogen containing base
How are nucleotides joined together?
joined by phosphodiester bonds
in condensation reactions
What groups do the phosphodiester bonds form between?
The deoxyribose sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate group of another
What is the structure of a DNA molecule?
double helix
What is the structure of a RNA molecule?
Single helix/relatively short polynucleotide chain
Which bonds form between DNA bases?
Hydrogen
How many H bonds form between C and G?
3
How many H bonds form between A and T?
2
What is the chain of nucleotides, not including bases, called in a DNA molecule?
Phosphodiester backbone
what are the two polynucleotide strands of DNA described as?
Anti Parallel
Which carbons do phosphodiester bonds form between?
3 and 5
Which way is a strand with a phosphate group at the end bonded?
3 prime to 5 prime
Which way is a strand with an OH molecule on the end bonded?
5 prime to 3 prime
How does DNA replicate?
Semi conservatively
What were the other two theories for DNA replication?
Conservative, dispersive
What kind of bases are A and G?
Purine
What kind of bases are C, T and U?
Pyramidine
describe the process of DNA replication
DNA helicase breaks the hydrogen bonds between bases on the two polynucleotide strands
helix unwinds to form two strands
free nucleotides diffuse and bind to complementary exposed bases via hydrogen bonds when they happen to hit them by chance
the sugar-phosphate backbones of the new nucleotides are joined together by DNA polymerase to form 2 new DNA molecules
each DNA molecule is one old strand and one new strand
which direction does DNA polymerase work in?
moves down the template strand 3’ to 5’, new strand formed is 5’ to 3’
this is because the active site is only complementary to the 3’ end of the newly forming DNA strand
what experiment was done to prove that DNA replicates semi-conservatively?
the most beautiful experiment in biology
two samples of bacteria were grown on different types of nitrogen broth - 14N and 15N (light and heavy)
this nitrogen became a part of the bacteria’s DNA
a sample of DNA was taken from each batch of bacteria, and spun in a centrifuge tube - 14N DNA was lower than 15 N
bacteria containing heavy nitrogen were taken out and put in a broth containing light nitrogen
they were left for one replication of DNA and then spun in a centrifuge, then left and spun again
describe the results of the experiment that showed DNA replicated semi conservatively
first spin: DNA will settle in one block in between where the 14N and 15N had settled previously
2nd spin: half of the DNA will settle in the same place, the other half will settle higher up
describe the results of the experiment IF DNA replicated conservatively
first spin: the DNA would be in 2 distinct sections, one 14N and higher, the other 15N and lower
2nd spin: 75% of the DNA would be high up where the 14N was, and 25% would be low down where the 50% was
describe the results of the experiment if DNA replicated dispersively
1st spin: all DNA in the middle of where the 14N and 15N DNA had settled previously
2nd spin: all the DNA in between where the 14N and 15N had been, but skewed upwards (less 15N)
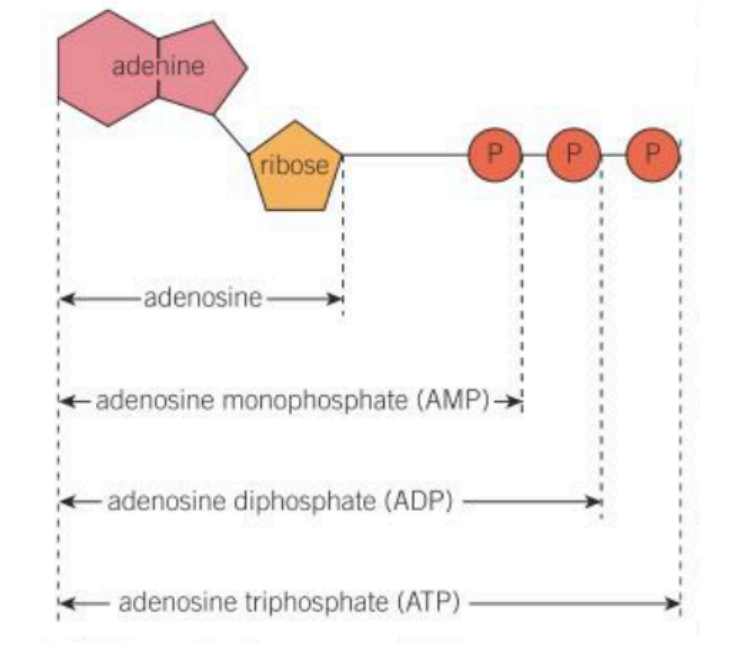
what does ATP stand for?
adenosine triphosphate
what does ADP and AMP stand for?
ADP - adenosine diphosphate
AMP - adenosine monophosphate
what is ATP made up of?
ribose
adenine
three phosphate groups (ADP has 2, AMP 1)
how is energy released from ATP?
ATP is hydrolysed
this forms ADP and a phosphate molecule
this requires the presence of water
which enzyme catalyses the process of energy release by ATP?
ATP hydrolase
how does the hydrolysis of ATP release energy?
bonds between phosphate molecules are very unstable and have a low activation energy
one of these bonds is broken, which is a quick process and releases a lot of energy
what can the phosphate group produced from ATP hydrolysis be used for?
phosphorylation of other compounds
this makes them more reactive
which process occurs to form ATP?
condensation of ADP and inorganic phosphate
when does condensation of ADP and inorganic phosphate occur?
during photosynthesis and respiration
which enzyme catalyses condensation of ADP?
ATP synthase
write an equation for hydrolysis of ATP
ATP + H2O → ADP + Pi
write an equation for condensation of ADP
ADP + Pi → ATP + H2O
why is ATP useful?
it is an immediate source of energy and can be broken down in a single step
releases a small, manageable quantity of energy
doesn’t require a lot of space/need to be stored as it can be formed easily - recyclable
phosphorylation
small and soluble - easy to store
what properties does water have?
polar
metabolite
solvent
high specific heat capacity
high latent heat capacity
strong cohesion and adhesion
strong surface tension
different density in ice than water
why is water polar?
it has an uneven distribution of charge within the molecule
this gives the oxygen ends slightly negative charges and the hydrogen atoms slightly positive charges
why is water being polar beneficial?
means it has hydrogen bonds
this enables pretty much all of its other properties
why does water act as a solvent?
is polar
helps ions to dissociate in water as charges on molecule attract charged ions
means it is a solvent
why is the property of water being a solvent important?
allows for transport of dissolved substances around the body
either in xylem/phloem/blood
why is the property of water being a metabolite important?
metabolite = allows chemical reactions take place
means it allows reactions such as condensation and hydrolysis to take place
why does water have strong surface tension?
hydrogen bonds on the surface of the water make it very cohesive
this means it has strong surface tension
why is water having a strong surface tension important?
allows sweat to form droplets, which evaporate from the skin
allows pond skaters to move on surface of water
allows water droplets to form on leaves
why does water have a high specific heat capacity and what does it mean?
it means a lot of energy is required to raise the temperature of water by 1K
this is because of the collectively strong hydrogen bonds between molecules which require a lot of energy to overcome
why is water having a high specific heat capacity beneficial?
can act as a buffer solution in cells/tissues
helps to maintain a constant internal temperature
also makes water a good habitat for aquatic organisms
why does water have strong cohesion/adhesion and what does this mean?
cohesion is attraction between molecules of the same type, adhesion is of different types
hydrogen bonds that form between molecules make this possible
why is water having strong cohesion beneficial?
helps water to flow, making it good for transporting substances
means water can move up columns like the xylem
why does water have a high latent heat of vaporisation and what does this mean?
lots of energy is required to change the state of the water
this is because of the many hydrogen bonds it contains
why is water having a high latent heat of vaporisation beneficial?
means that lots of energy can be lost through sweating, but without using too much water
means that it helps with temperature regulation
what are 4 types of inorganic ions?
hydrogen ions
iron ions
sodium ions
phosphate ion
what are the functions of hydrogen ions?
concentration impacts levels of enzyme activity
pH changes alters H+ ion concentration and so ionic bonding in tertiary structure
this changes the shape of the active site
what are the functions of iron ions?
found in haemoglobin and myoglobin
these are proteins which allow molecules to hold and transport oxygen
incorporated in some enzymes
circulated in blood
what are the functions of sodium ions?
required for cotransport of glucose and amino acids across membranes
helps to regulate blood pressure and volume
contributes to maintenance of turgidity
what are the functions of phosphate ions?
used in essential molecules (ATP, ADP, RNA, DNA, NADP, phospholipids, phosphorylated sugars)
part of main inorganic component of human bone (calcium phosphate)