CRISPR-Cas9 Gene Editing
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
CRISPR
formed as defense mechanism in bacterium against DNA virus
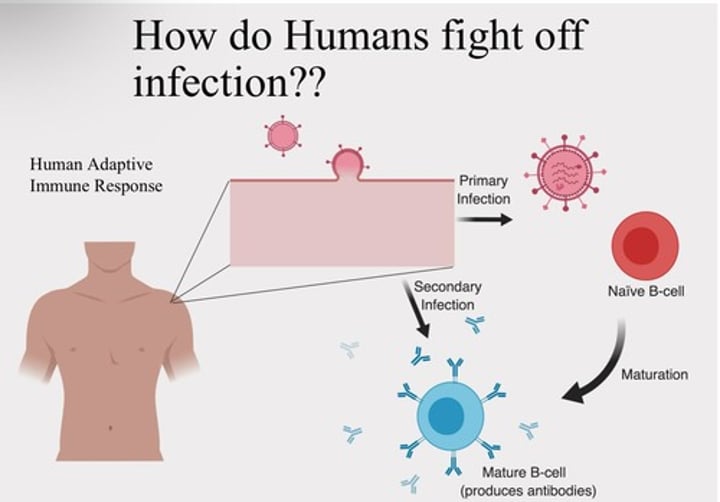
How do Humans fight off infection?
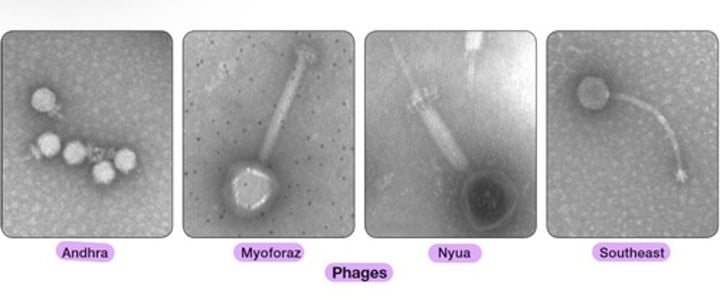
Phages
- Andhra
- Myoforaz
- Nyua
- Southeast
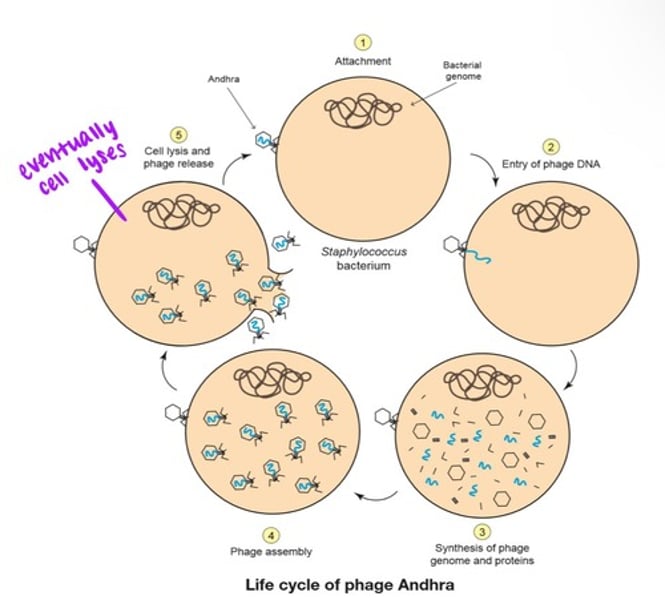
Life cycle of phage Andhra
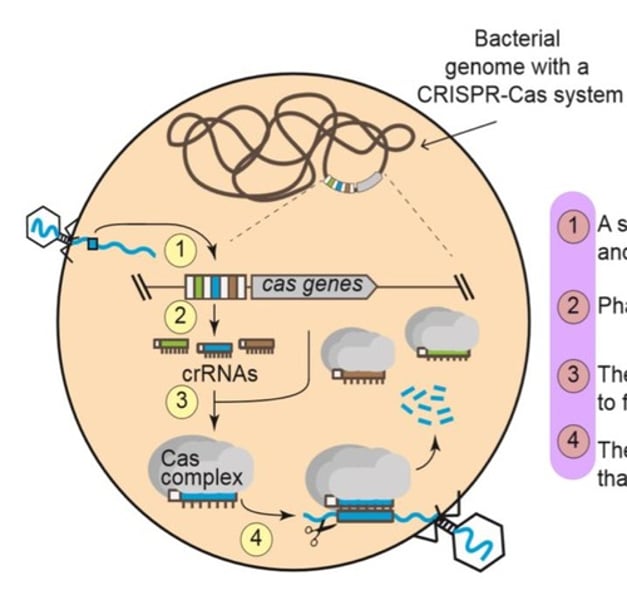
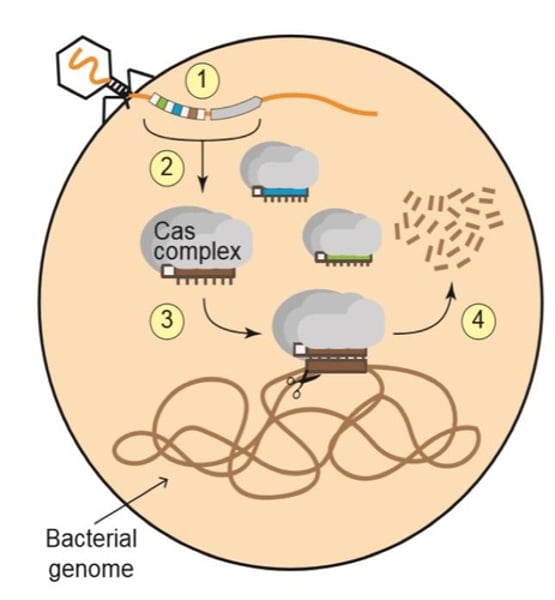
The CRISPR-Cas immune system mechanism
1. a short piece of phage DNA is captured (blue square) and inserted into the bacterial chromosome when have an infection.
2. phage DNA is transcribed into small crRNAs.
3. the crRNAs combine with Cas proteins (grey circles) to form a Cas complex
4. the Cas complex seeks and destroys phages DNA (DNA virus) that matches the crRNA.
crRNA (Crispr RNA)
scans protein
Cas9
exonuclease
CRISPR application
- gene editing
- gene drive
- transcription regulation
- infection treatment
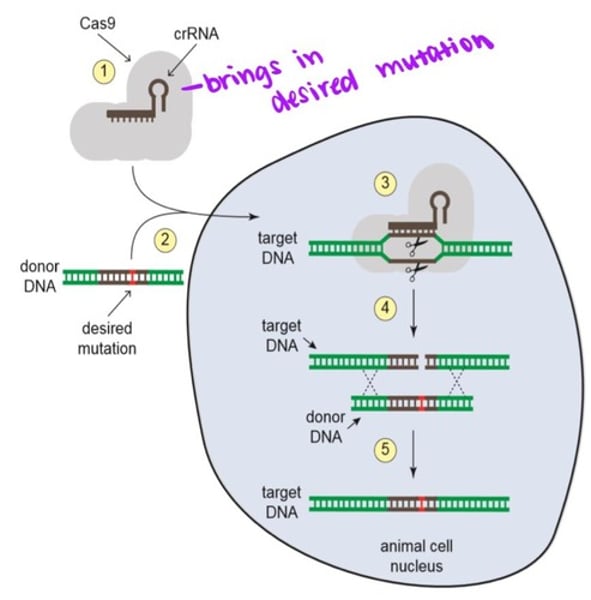
Gene editing mechanism
1. Cas9 is programmed to cute a specific DNA sequence by combining it with a crRNA that matches the target DNA.
2. The Cas9-crRNA complex is introduced into the nucleus of an animal cell along with a donor DNA, which contains a portion of the targeted sequence plus the desired mutation.
3. The Cas9-crRNA complex will bind the targeted DNA in the region that matches the crRNA, and then Cas9 will cut both strands of the DNA.
4. The cut target DNA will get repaired by the cell's repair machinery using the donor DNA as a repair template.
5. After the repair process is complete, the targeted DNA will have acquired the desired mutation.
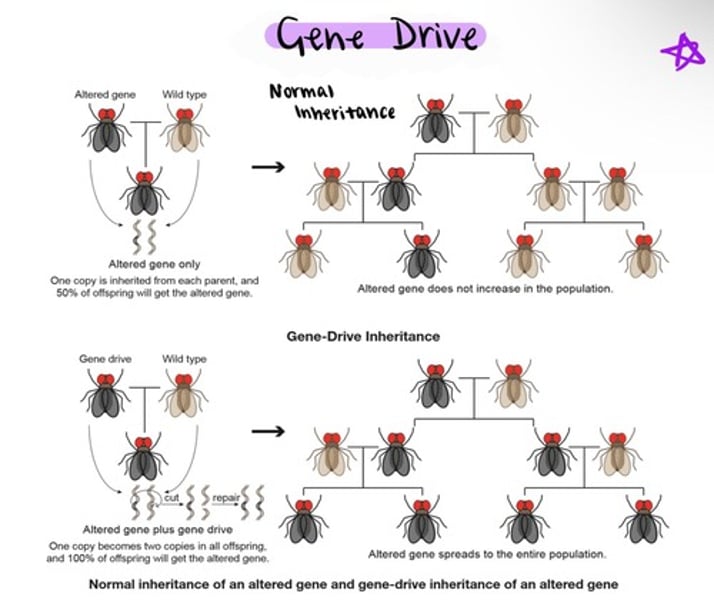
Gene drive
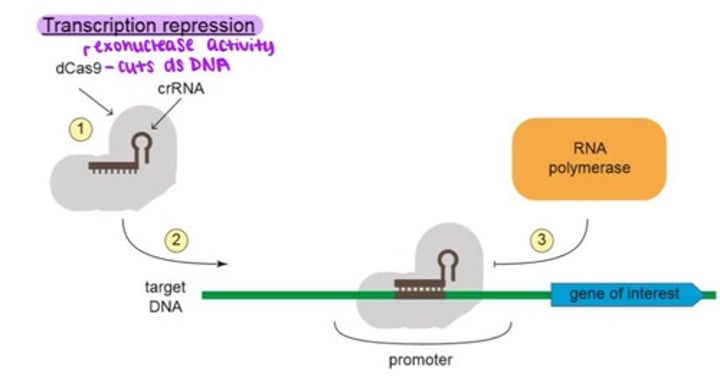
Transcription Regulation - transcription repression mechanism
1. A mutant version of Cas9 that cannot cut DNA (dCas9) is combined with a crRNA that matches the promoter region of the gene of interest.
2. The dCas9-crRNA complex is introduced into the cell where it binds the target DNA.
3. The dCas9-crRNA complex prevents RNA polymerase from building the promoter, which causes the gene to remain silent and no transcription occurs.
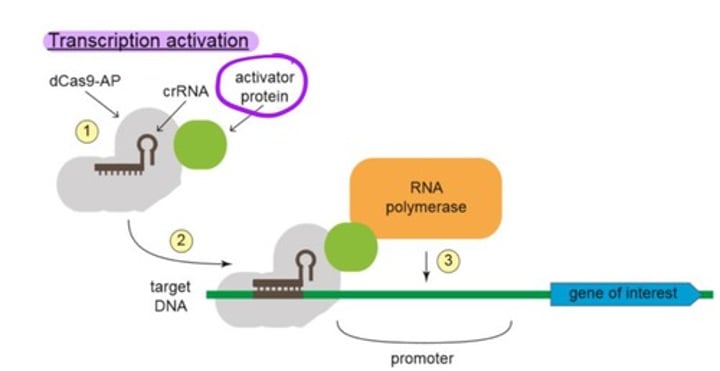
Transcription Regulation - transcription activation mechanism
1. A dCas9 mutant fused to a transcription activator protein (dCas9-AP) is combined with a crRNA that matches the region next to the promoter of the gene of interest.
2. The dCas9-AP-crRNA complex is introduced into the cell where it binds the target DNA.
3. The fused activator protein recruits RNA polymerase to the promoter, which then transcribes the gene of interest. After this, Cas9 leaves.
Infection treatment mechanism
1. Pathogenic bacteria are infected with an engineered phage that encodes a CRISPR-Cas system in its genome. The CRISPR-Cas system has a crRNA that targets the bacterial chromosome.
2. The CRISPR-Cas system is transcribed and the Cas complexes are assembled.
3. The Cas complex carrying the crRNA that matches the bacterial genome will bind to its target in the genome.
4. The Cas complex shreds the bacterial genome and kills the cell.
Restriction enzyme
endonuclease
- an enzyme that cuts at a specific nucleotide sequence once it is identified
Cas9 recognizes what as a PAM sequence
NGG (TGG) or its complementary ACC