Module 1, Units 1-3
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Define transducer
Any device that converts one form of energy into another form
Piezoelectric effect
Bidirectional ability to convert electrical energy to mechanical energy
Crystals
PZT
PZT
Piezoelectric material used in transducer
PureWave Crystals
Philips technology for higher efficiency PZT
Currie point
300C
the temperature at which dipoles of piezoelectric materials can be adjusted
Electromagnetic coupling efficiency
Bidirectional efficiency of converting electrical energy to mechanical energy
Dipoles
Material with charged ends
Polarization
Alignment of dipoles within a piezoelectric material to create an overall direction (positive and negative end)
Sensitivity
Amplitude of a signal that can be detected by a transducer
Why do U/S transducers use PZT?
High coupling coefficient
High frequency of natural resonance
Stable design
What are the frequency determinants for PW applications?
Crystal thickness
Propagation speed of sound in the crystal
Drive voltage
Electrical stimulation applied to the crystal must be at or near the operating frequency
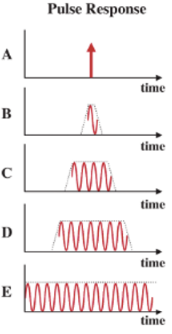
Impulse response
Response of a crystal to a single short-duration pulse
Name an advantage and disadvantage to crystal resonation.
Advantage: efficient voltage excitation
Disadvantage: crystals resonate longer than desired
Composition and location of damping material on a transducer?
Metal powder and plastic or epoxy resin
Attached to rear face of the crystal
Explain how the PD and SPL of a transducer is controlled.
Backing material limits the number of cycles in a pulse through limiting the impulse response
What are some effects of backing material?
↓PD → ↑BW
↓SPL → ↑axial resolution
↓electromagnetic coupling efficiency
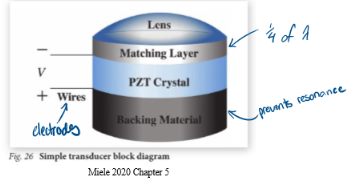
Describe the thickness of the matching layer. Why is this thickness chosen?
¼ of the wavelength of sound leaving the crystal.
¼ = 90° → GRT makes it 180°
180° creates destructive interference of reverberation artifact caused by the matching layer → no reverberation artifact from matching layer
Describe the ideal Z value of the matching layer.
Zcrystal > Zmatching layer > Zmedium
Explain how transducers improve sound transmission across the BW of the transducer.
Multiple matching layers to improve transmission over the large range of frequencies emitted during a PW.
Draw a simple transducer block diagram.
Bandwidth
Range of frequencies over which a device can operate
What is the expected PD with backing material?
n=2-3
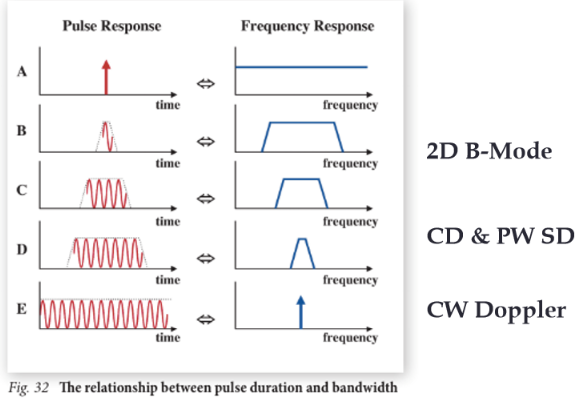
Draw the BW of the given PDs. Label which PD would be used for the following: 2D imaging, CD and PW, and CW.
Provide some advantages of a wider BW.
Multi-Hertz operation
Dynamic frequency tuning
Harmonic imaging
Frequency compounding (frequency tuning)
Describe the expected BW for Doppler applications and explain why.
Narrow BW, high sensitivity.
Doppler application require receiving signals from Rayleigh scatter, which is extremely faint.
In a patient with large body habitus, would you prefer the transducer has a wide or narrow BW? Explain.
A narrow BW would be more beneficial because of the increased need for penetration.
↑penetration → ↑attenuation → ↓returning signal strength
Decreasing the BW allows for more sensitivity, which is necessary for detecting the returning signals
Draw a representation of dynamic frequency tuning.

BW =
fmax - fmin
fractional BW (FBW) =
BW / fcenter
A broad BW is considered to be ___% FBW.
80
A high QF indicates ___ BW whereas a low QF indicates____ BW.
narrow, broad
Is 3MHz equivalent on a L12-3 transducer and a C5-1 transdicer?
No
Transducers are more effective closer to their center frequency.
List the advantages of a high electromechanical coupling coefficient.
Increases penetrability of SW
Improves SNR and overall contrast resolution
Aids in tissue harmonic production
List the advantages of high sensitivity.
Detect echoes from farther away → increased penetration
Detect more Rayleigh scatter → Doppler imaging improvements
List some goals for improving PZT.
Reduce acoustic impedance to better match soft tissue
Increase efficiency
Wider BW without sensitivity comprimise
Describe a method for reducing PZT’s acoustic impedence.
Piezoceramics
break PZT block into hundreds of components and set in polymer epoxy
Z-value = 8-12MRayls
Describe a method for improving PZT efficiency.
Poling: aligning regions of positive and negative magnetic charges
List the steps associated with poling a piezoelectric material.
crystals are heated above Currie temperature (300)
magnetic field applied to align dipoles
crystals cooled while magnetic field is still applied
dipoles set in a new orientation
What is the difference between piezoceramics and Philip’s PureWave Crystal Technology?
Piezoceramic alignment ~70%
PureWave alignment ~100%
List some benefits to PureWave technology.
Improved electromechanical efficiency
Improved sensitivity
Improved penetration and image quality
Wider BW without compromising sensitivity