Biochem Ch. 9 Hemoglobin
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
The ability of myoglobin and hemoglobin to bind oxygen depends on what?
the presence of a heme group
What is the form of iron in the heme group?
Fe2+, ferrous
What is the central atom in a heme group?
iron
pyrrole ring
N-C ring in heme
proximal histidine
occupies the iron’s lower binding site
what binds to the Fe2+ upper site?
oxygen
hemoglobin structure
2 identical a chains and 2 identical beta chains
oxygen binding curve
fractional saturation vs oxygen concentration
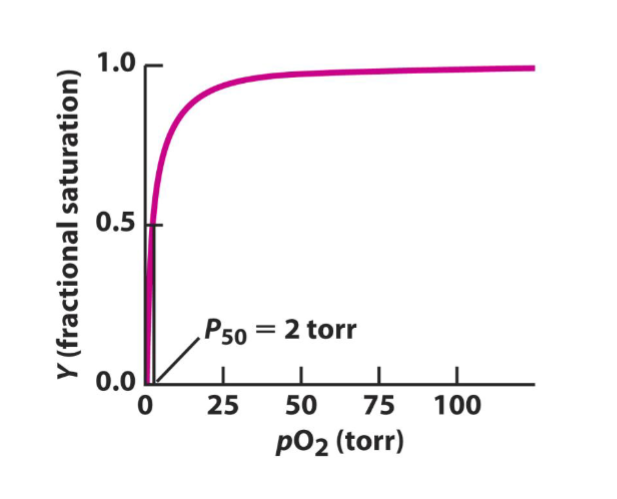
Myoglobin has what kind of oxygen binding curve?
hyperbolic, increases sharply at the beginning
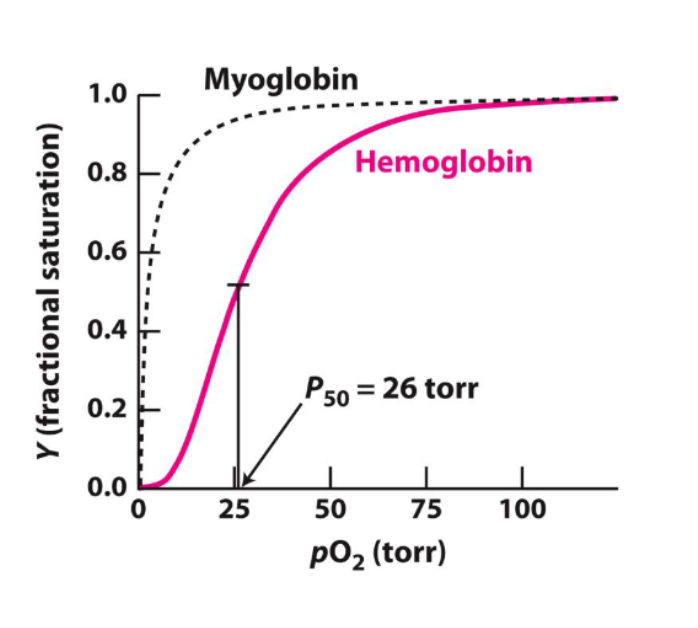
hemoglobin has what kind of oxygen binding curve?
sigmoid curve, s shape
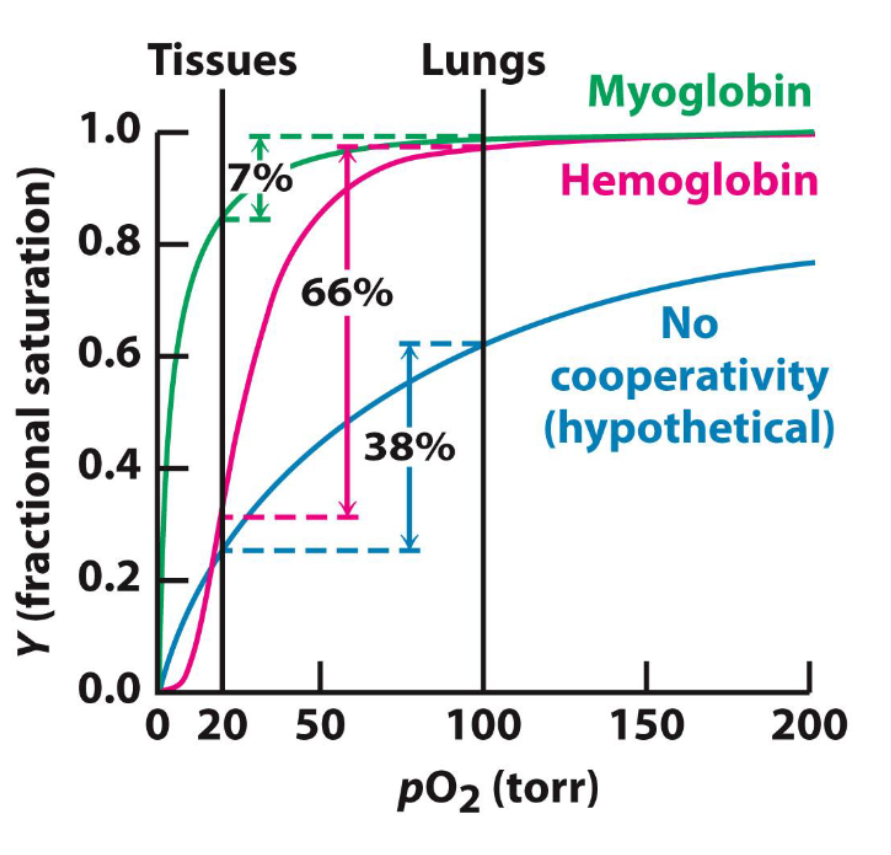
What is cooperativity?
it allows hemoglobin to bind oxygen in the lungs and release oxygen at the tissues
what is the pressure of oxygen in the lungs?
100 torr
what is the pressure of oxygen in tissues?
20 torr
T state
tense, quaternary structure of deoxyhemoglobin
R state
relaxed, quaternary structure of oxyhemoglobin
In what state is oxygen binding weaker?
t state
In what state is oxygen binding higher?
r state
2,3-BPG
stabilizes the t state of hemoglobin and facilitates the release of oxygen
What is crucial in red cells to determine the oxygen affinity of hemoglobin?
2,3 BPG
What must occur for oxygen to bind to hemoglobin?
transition from t state to r state
carbon monoxide
binds tightly to iron on hemoglobin so that it can’t transition from R to T state
What enhance oxygen release? (allosteric effectors)
CO2 and H+
Bohr effect
stimulation of oxygen release by CO2 and H+
What causes Sickle-cell anemia?
replacement of Glu with Val at position 6 of the beta chains; can’t facilitate oxygen binding
When is oxygen binding low and oxygen releasing high?
in T state
The t-state is stabilized by what?
2,3-BPG, CO2 and H+
The t-state shifts the curve to the?
right, good for tissues
When is oxygen binding high and oxygen release low?
in the R state
What stabilizes the R-state?
CO
The r-state shifts to the?
left, good for lungs