Analytical Chemistry
1/151
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Test 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
152 Terms
What is interference?
When 2 or more waves meet at the same point in space and time
What is constructive interference? What are the phase differences?
When two waves are in phase (peaks/troughs line up), amplitudes add together. Phase difference: multiples of 360 degrees
What is destructive interference? What are the phase differences?
When two waves are out of phase, difference between two amplitudes = resulting. Phase difference: multiples of 180 degrees
What is partial interference?
somewhere in between constructive interference (in phase) and destructive interference (out of phase)
What are the units of frequency?
waves/sec (Hz)
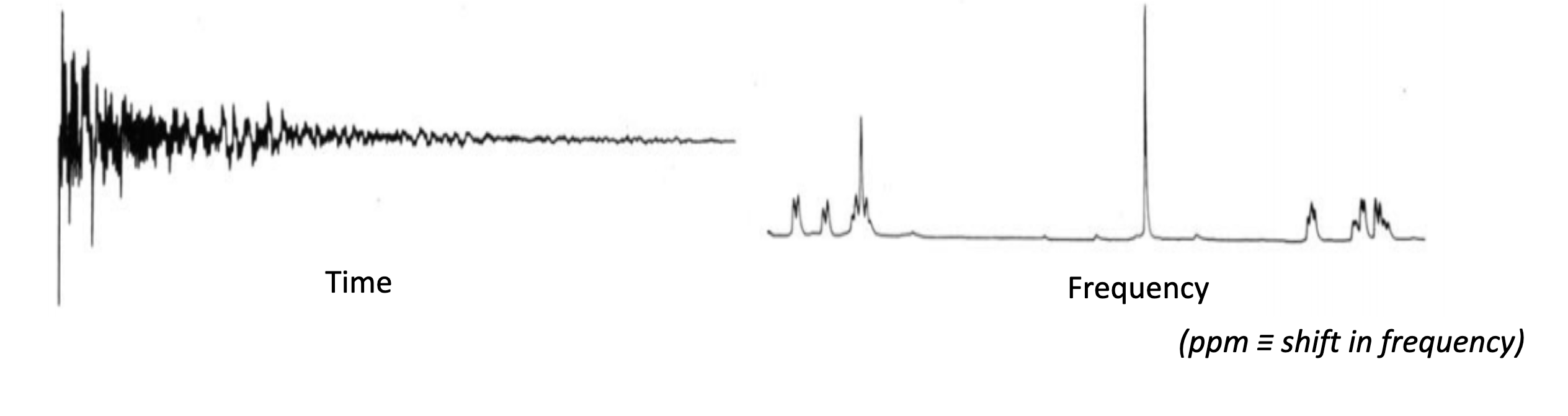
What does Fourier Transform do?
converts time domain to frequency domain
What are characteristics of FT calculations?
overall slow, but there are fast FT algorithims
What is a signal?
response due to a phenomenon of interest
What is noise?
unwanted response that intersects w signal measurements
What would FT look like in terms of NMR?
Draw a noise power spectrum?
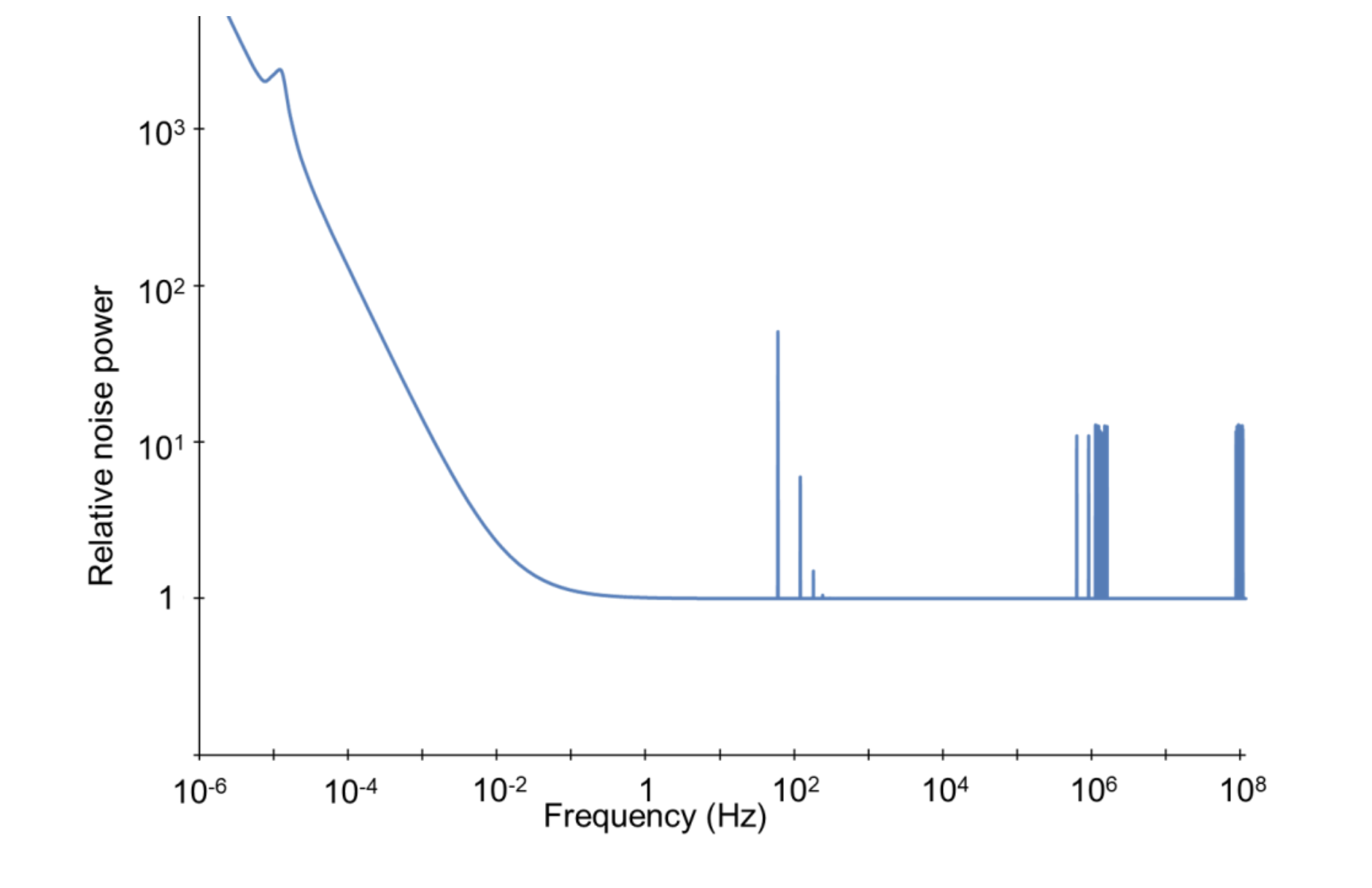
Three types of noise
white, 1/f, environmental
What is a noise power spectrum used for.
Shows how energy of noise is distributed across different frequencies, can be used to diagnose where noise is coming from in order to design filters to remove frequencies
Draw the noise power spectrum of each type of noise.
top - 1/f
middle - white
bottom - environmental
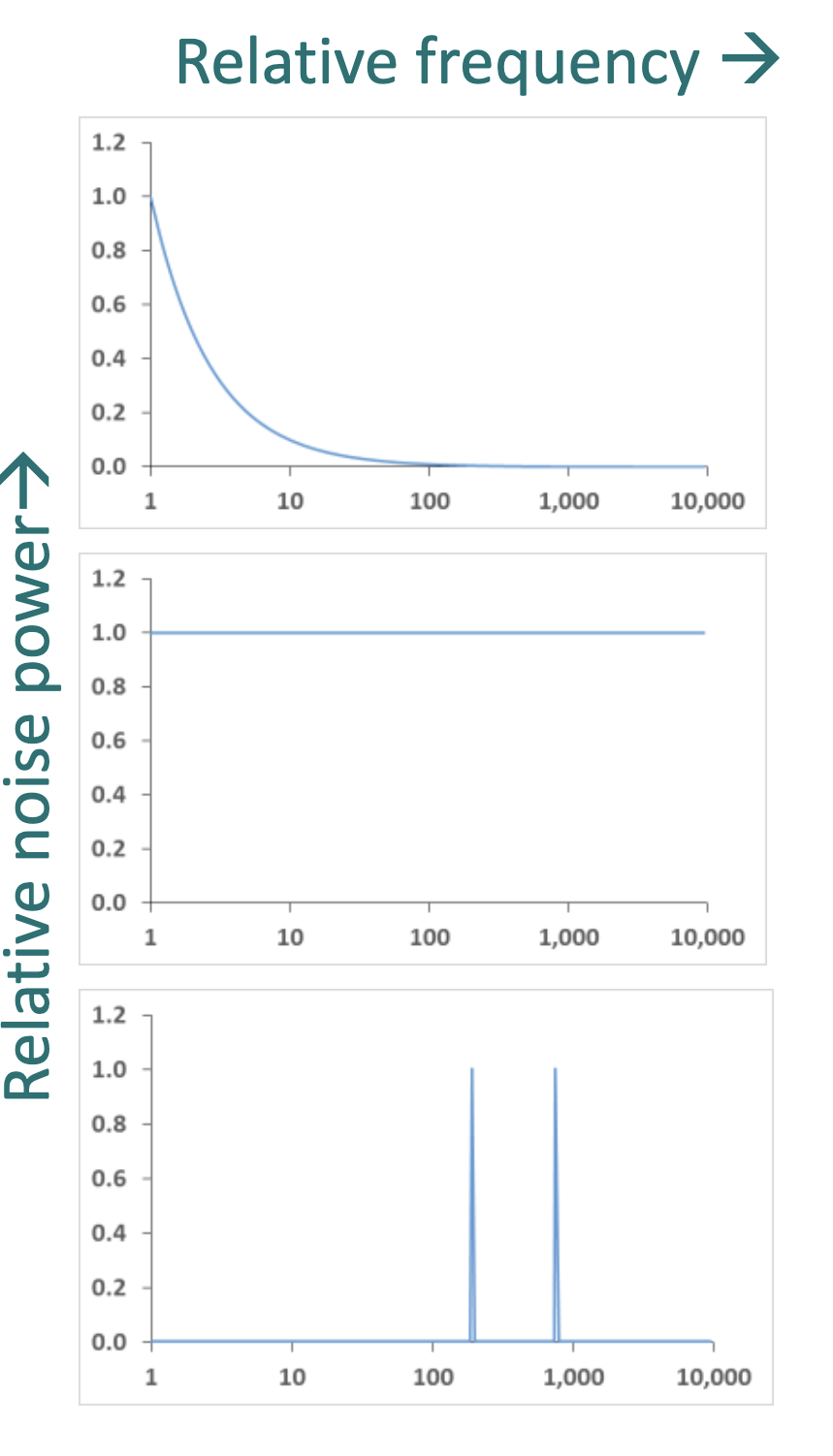
How do the different types of noise relate to time?
1/f noise has a slow drift if data is taken over time (hours/days), quick/rapid measurements are limited by white noise
How can you reduce 1/f noise?
move to higher frequencies by regularly calibrating/blanking or chopping (or other forms of modulation)
How can you reduce white noise?
decrease the bandwidth (frequency range) by removing low and high (via low pass filter) frequencies
What is simultaneous detection?
Sample and reference signals are measured simultaneously and the background noise is subtracted.
Equation for simultaneous background subtraction
V = A(Va-Vb)
A = amplification factor
V = voltage out
Va = signal voltage
Vb = reference voltage
What is additive noise?
a noise that adds to the signal, but independent of the signal
How do you correct additive noise?
By subtracting background through blanks, modulation, or simultaneous background measurement
What is multiplicative noise?
noise that multiplies the signal and is dependent on the strength of the signal
How do you correct multiplicative noise?
divide by an internal standard that carries noise (and is in correlation)
What is the difference between digital and anlog information?
Digital information has discrete states and analog information has continuous states.
What does bit mean?
binary digit
what number is this: 1101101
109
what number is this: 1101
13
What number is this: 1000011
67
Why is digital data noise resitant?
Because digital data is easy to store and process. Techniques like averaging and frequency filtering are easily employed.
What is signal averaging?
The signals of multiple measurements are averaged. The more the measurements, the better the signal to noise ratio.
What is frequency filtering?
Isolating frequency of interest, used by digital data
# of possible binary digits =
2^#ofbits
what is the formula for resolution in terms of # of bits?
resolution = range/2^#ofbits
What does resolution means in terms of digital data?
smallest difference detected
What is the sampling rate?
The number of times per second a signal is recorded
What is the Nyquist Criterion?
To accurately capture a signal, the sampling rate must be twice as the highest frequency of the signal.
What happens as a result of undersampling?
Aliasing: signal will appear at much lower frequencies than its true waveform
Energy formula and what each variable is
E = hv , h=planks constant (6.626×10^-34 Js), v = frequency (Hz)
List the types of waves with their wavelengths and quantized transition
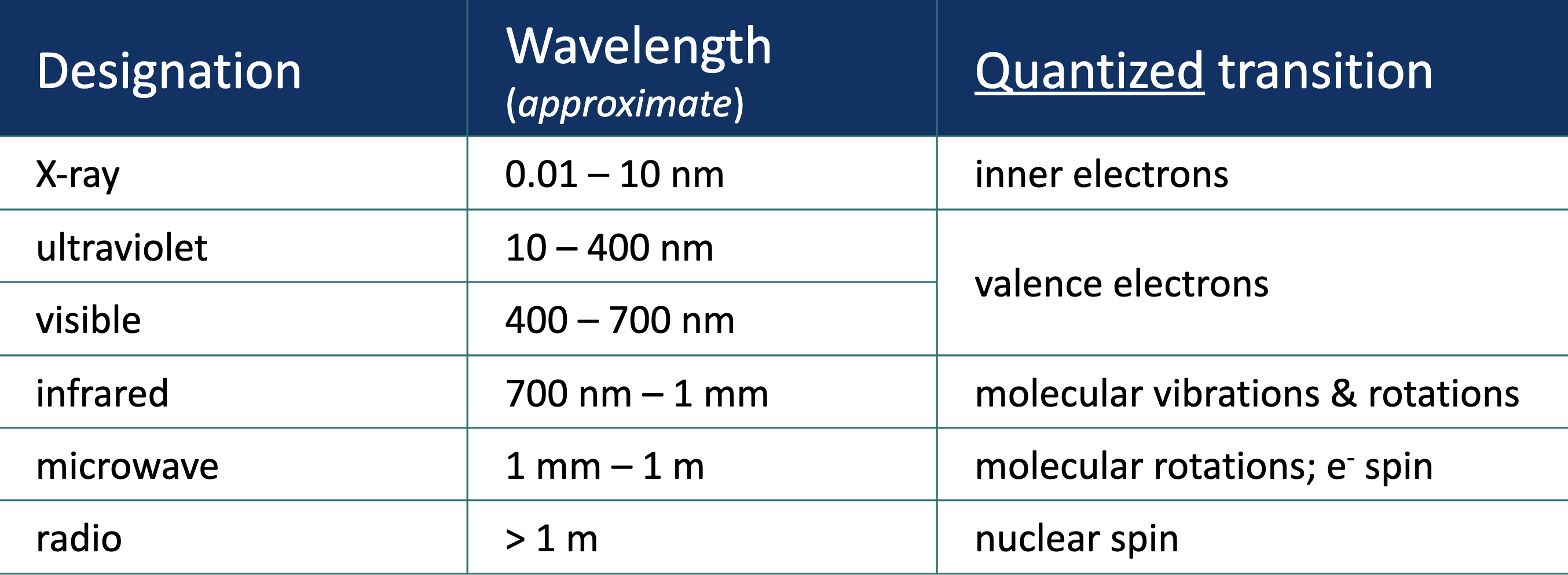
What is a typical spectroscopy spectrum characteristic of (in terms of axes)
X-axis : mostly qualitative, energy of electron transitions
y-axis : mostly quantitative, # of transitions
Define the three major types of spectroscopy.
Absorption, transmission, and reflectance : molecules absorb energy and move to a higher energy state
Emission and luminescence : molecules emit energy and move to a lower energy level
Scattering : measures interactions not involving a quantized excited state
What is wavelength and what is it measure in?
the length of 1 full wave, typically measured in nm or m
Speed of light in a vacuum
c = 2.9979 × 10^8 m/s
What is the formula for speed of light?
c = λν
Speed & wavelength change in a material “i” (formula)
vi = λiν
Refractive index equation
ni = c / vi
What is polarization?
The orientation of the electric field of a light wave
What does superposition of polarized light mean?
When two waves overlap, their electric field vectors combine forming a different angle of oscillation
Explain what you get if you have two waves that are in phase and of equal amplitudes (in terms of polarization)? Of different amplitudes?
45 degree angle, different amplitudes will result in an angle other than 45
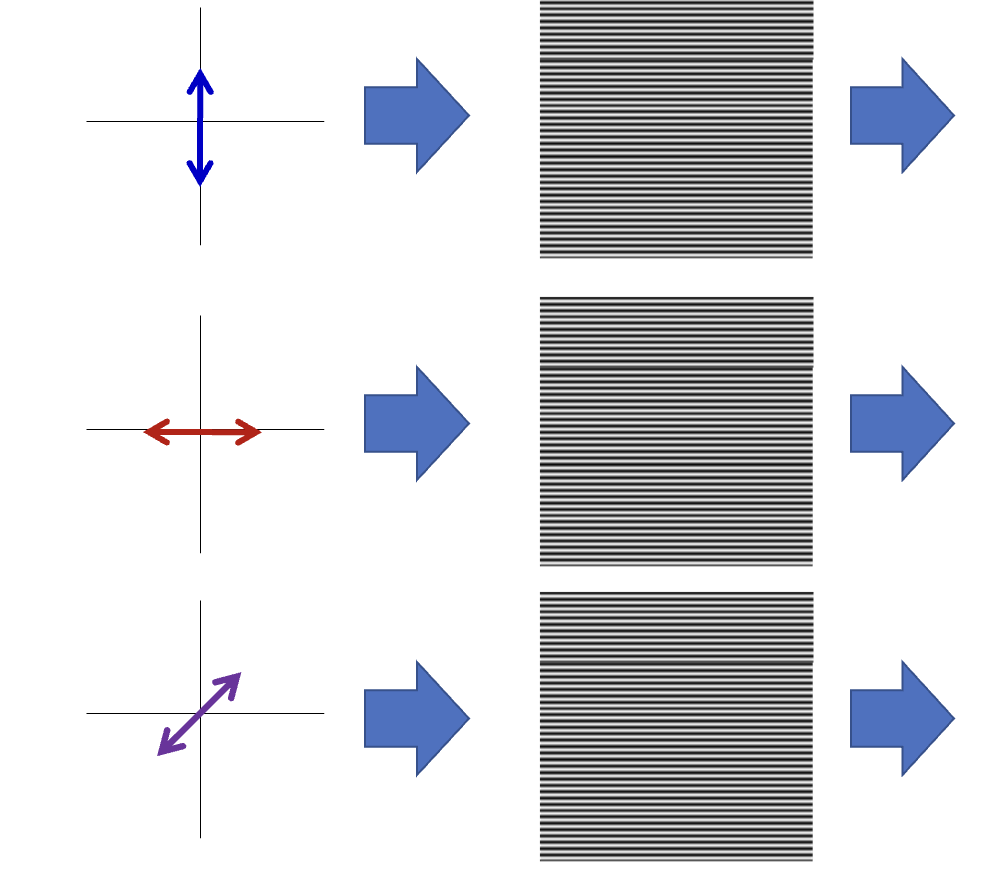
What are polarizers?
An optical filter that only allows light waves vibrating in a specific direction to pass through.
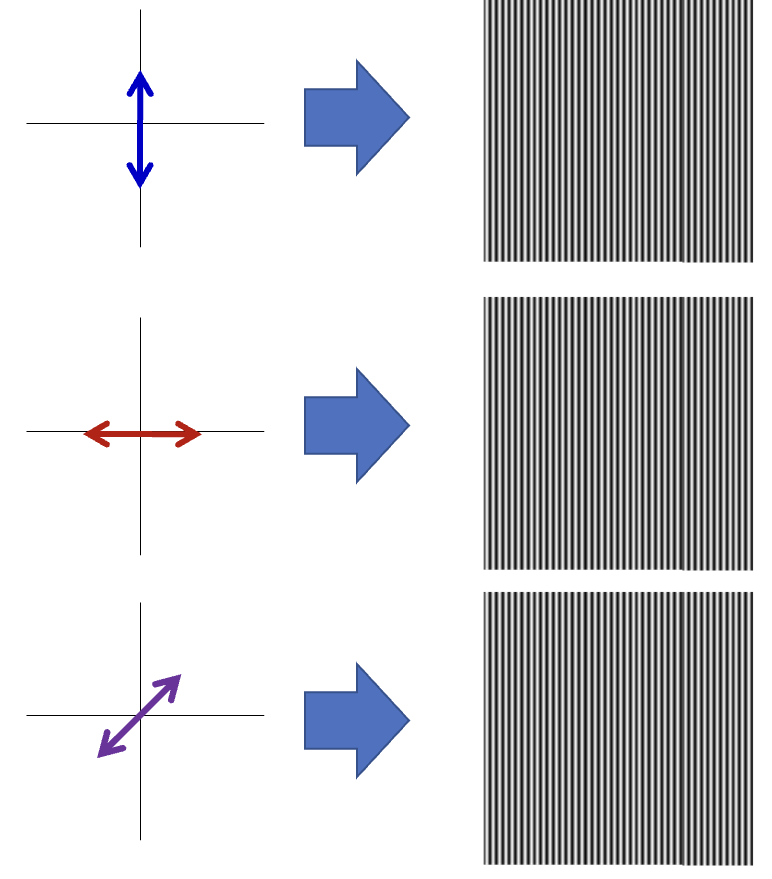
What will the resulting light look like?
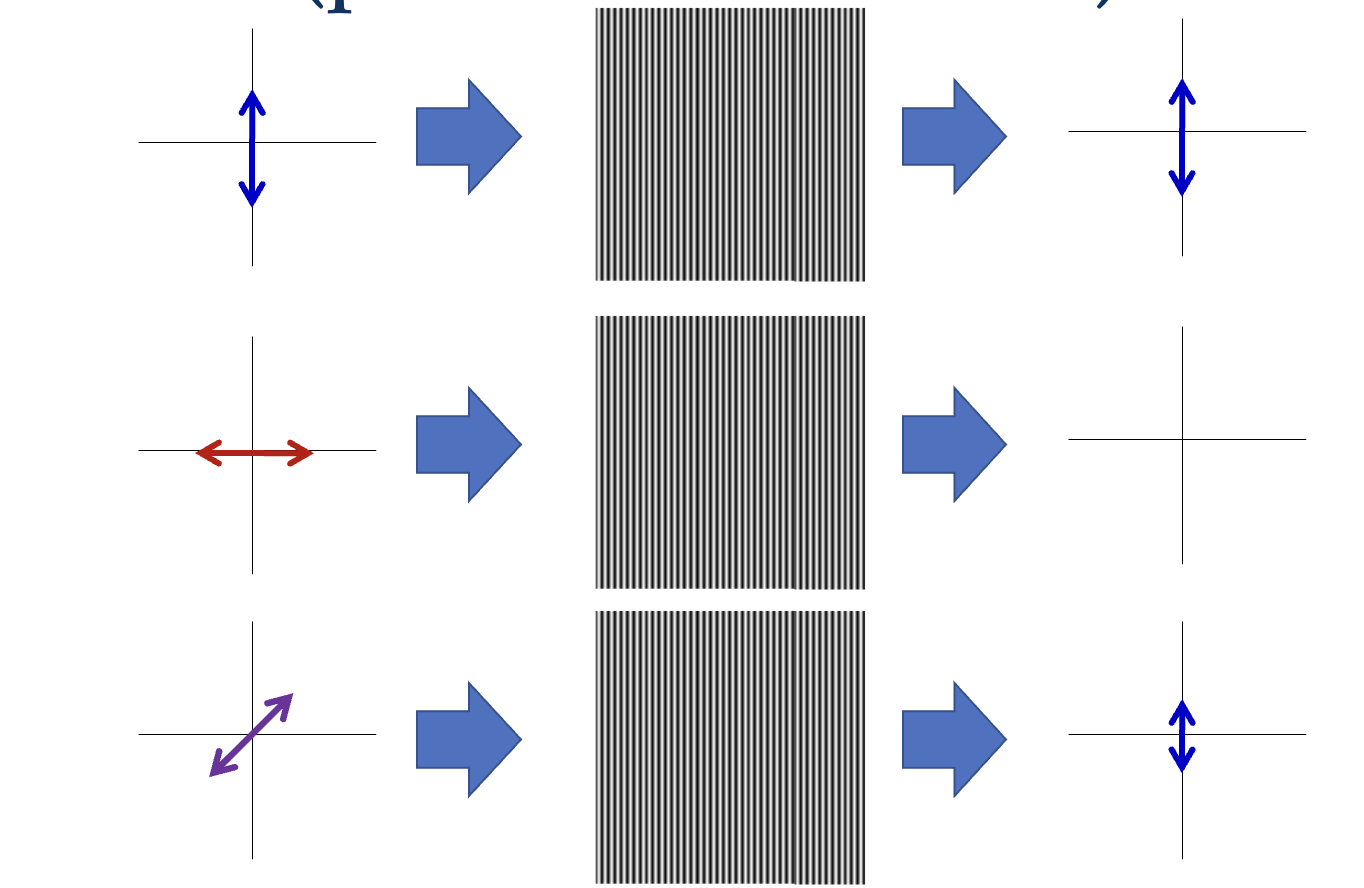
What will the resulting light look like?
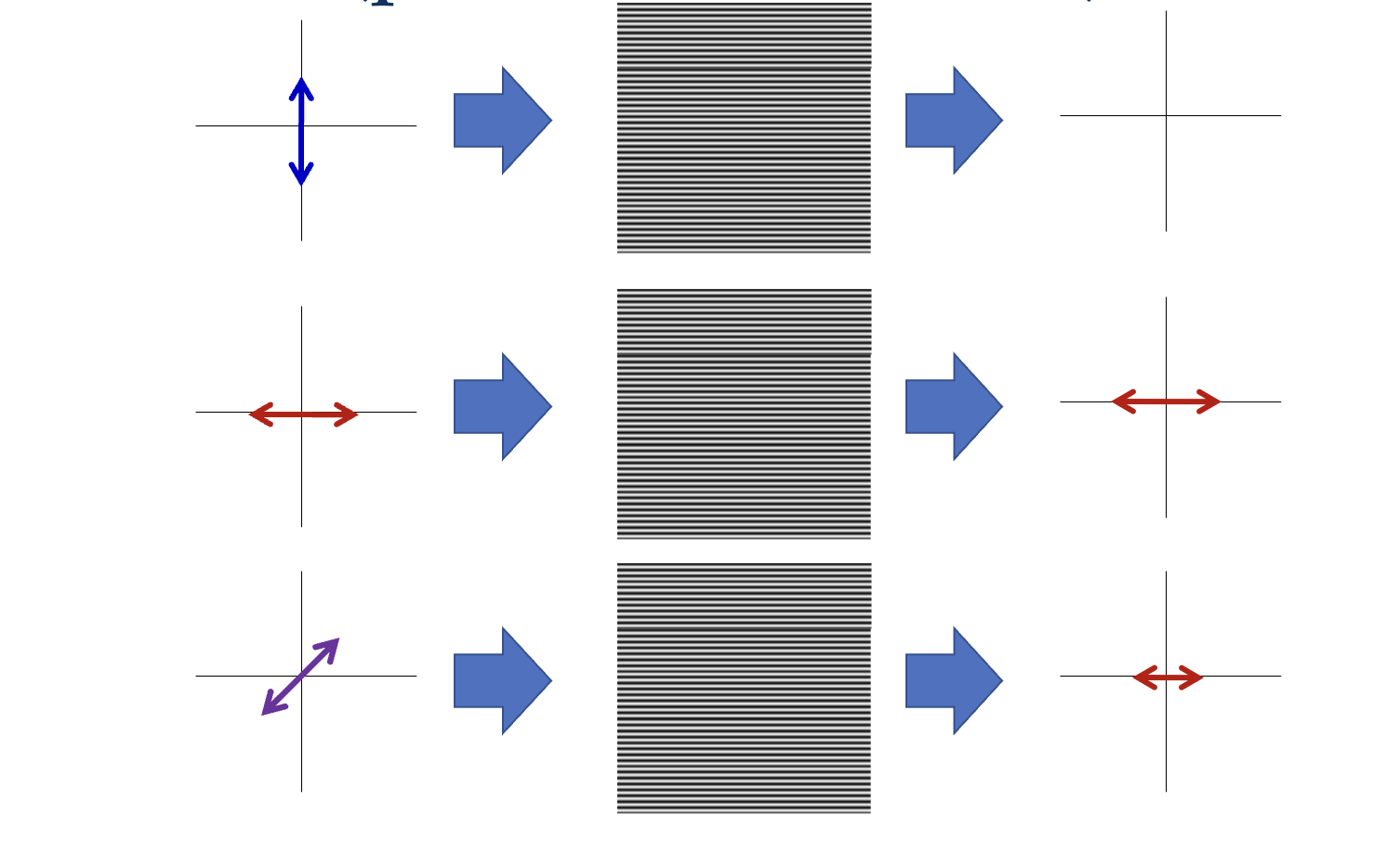
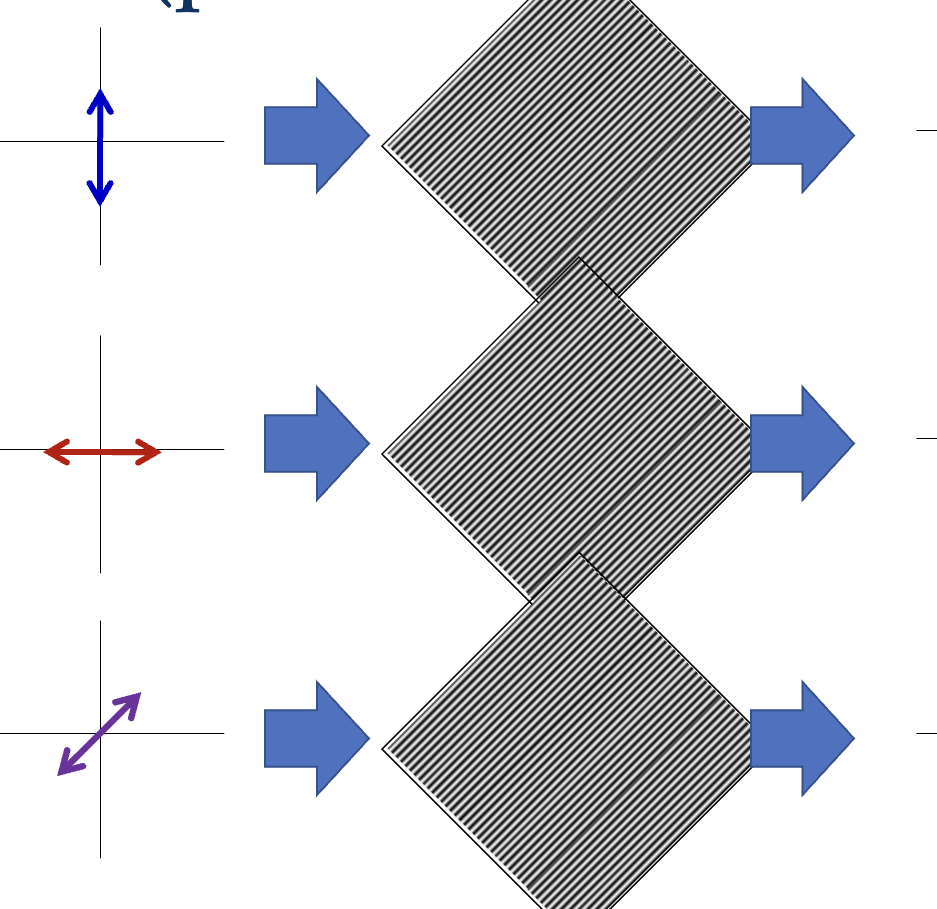
What will the resulting light look like?
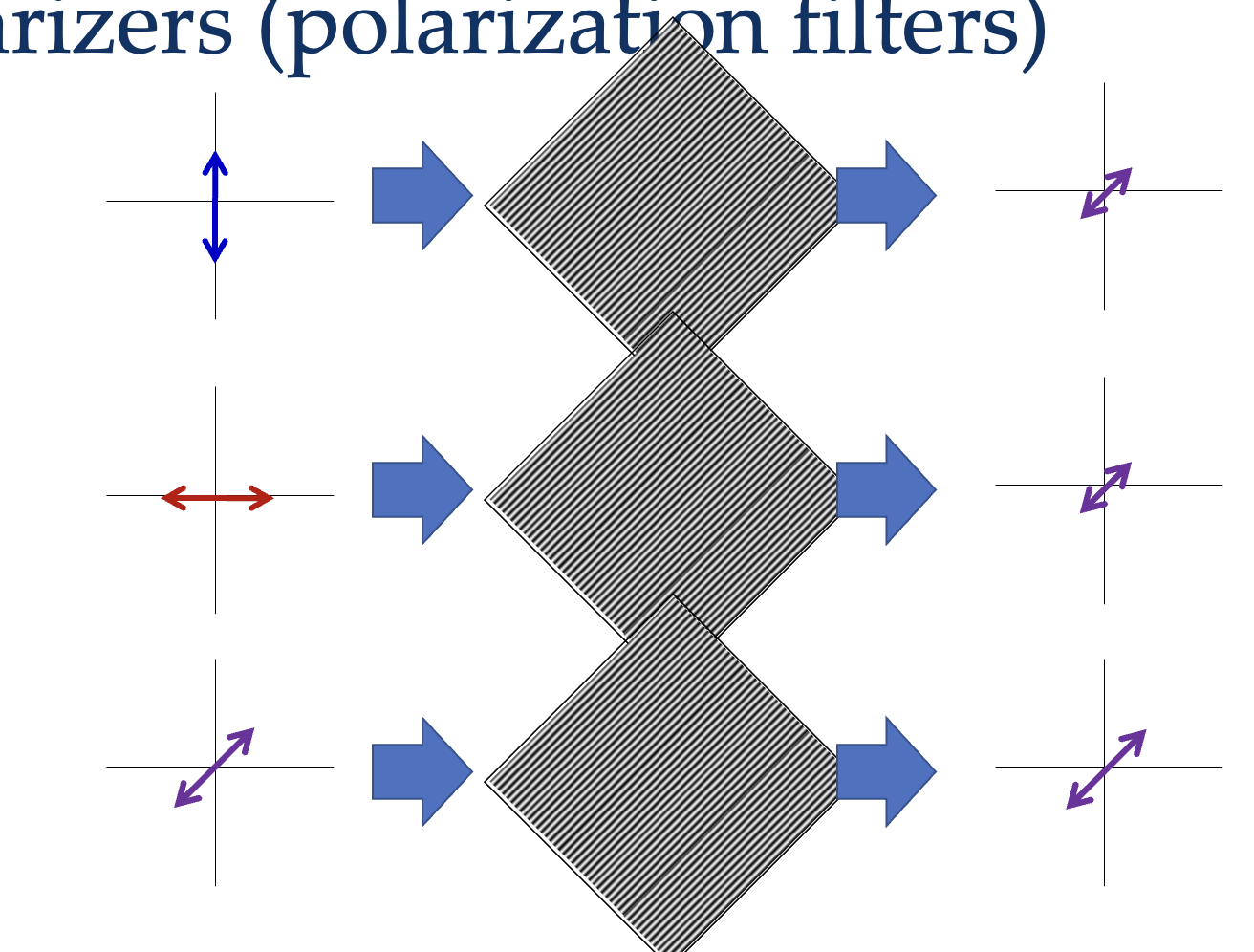
Explain what you get if you have two waves that are out of phase and of equal amplitudes (in terms of polarization)? Of different amplitudes?
Equal amplitudes : circular superposition
Unequal amplitude : elliptical superposition
Define refraction
Bending due to change in n
Snell’s Law
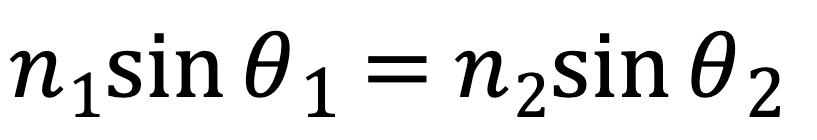
What is refractive index?
how much light slows down and bends when it enters a substance
What is the relationship between refractive index and wavelength?
For most materials, the shorter the wavelength, the greater the refractive index
What is dispersion and what causes it?
spread of light by wavelength, caused by variation of n with wavelength
What is a prism monochromator?
a device used to select a single wavelength of light from a broad spectrum using a prism
Shortcomings of prism monochromators
Non-linear dispersion (doesn’t spread wavelengths evenly) making it harder to calibrate
Low dispersion, especially at higher wavelengths (poor resolution in red/IR region)
Light loss due to absorption and reflection, especially at lower wavelengths
What is a grating monochromator?
a device used to select a single wavelength of light from a broad spectrum using a diffraction grating
Define diffraction.
Bending of light as it passes by a sharp edge or narrow slit
Describe how diffraction gratings use interference.
The diffracted waves overlap. Each wavelength has its own set of angles where constructive interference occurs. The many waves from all these slits reinforce each other exactly at the constructive angles, and cancel elsewhere.
Formula for constructive interference in terms of refraction grating (and what each term means).
m = diffraction order
d = space between slits
lambda = wavelength
alpha = angle of incidence
beta = angle of diffraction
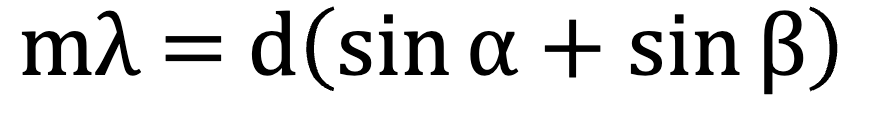
Draw the Czerny-Turner design.
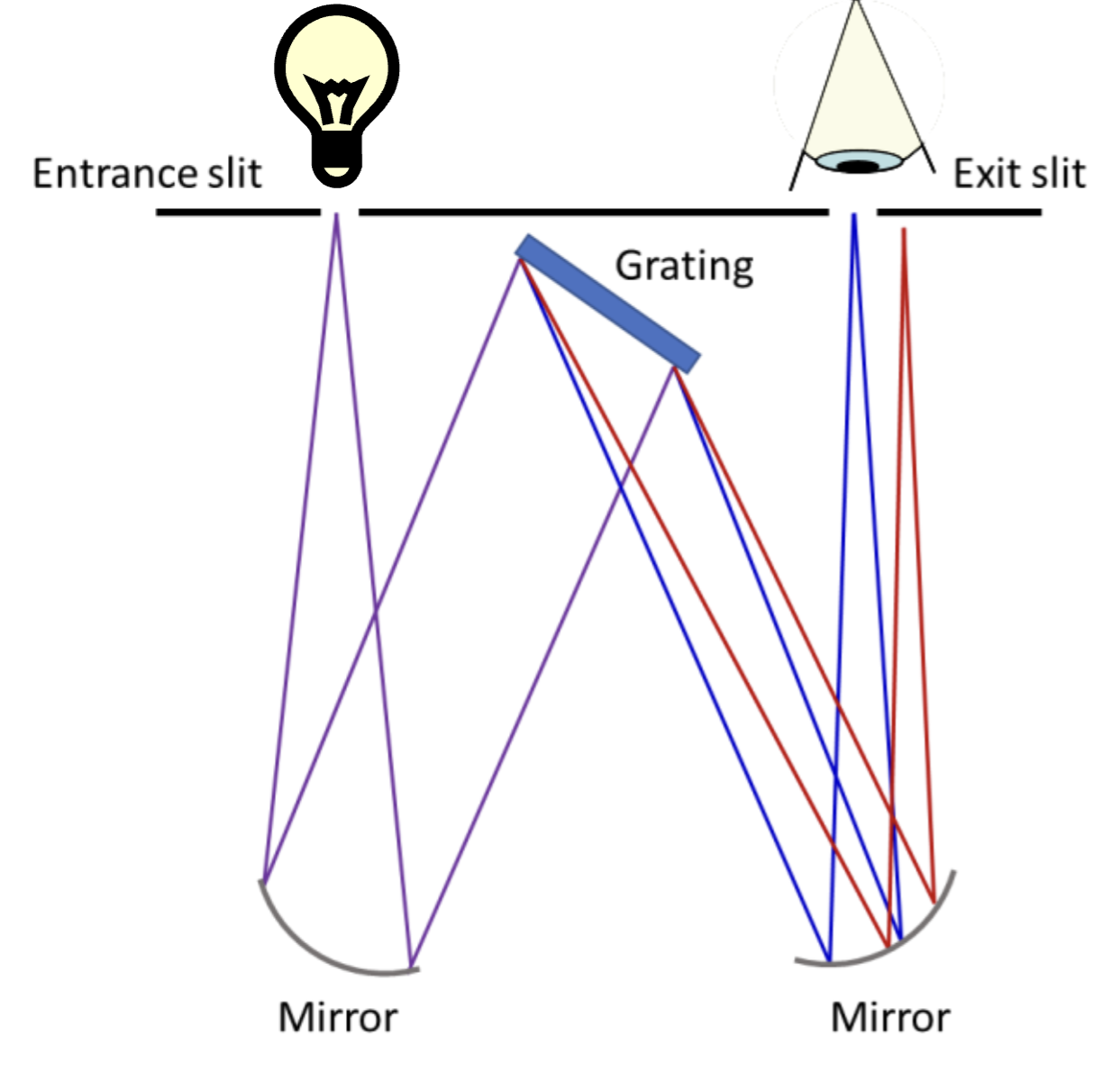
What is the reciprocal linear dispersion?
Spread of wavelength on exit slit
Reciprocal linear dispersion formula and units
d = grove spacing
beta = diffraction angle
m = order
f = focal length
units = nm/mm
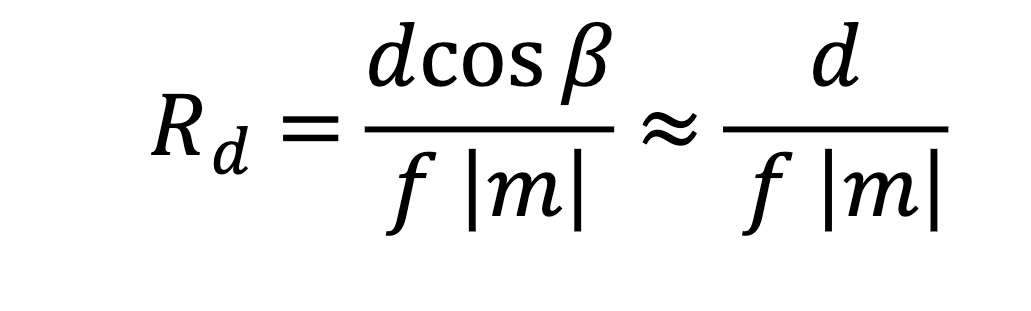
Effective bandpass formula
Rd = reciprocal linear dispersion
Ws = width of slit
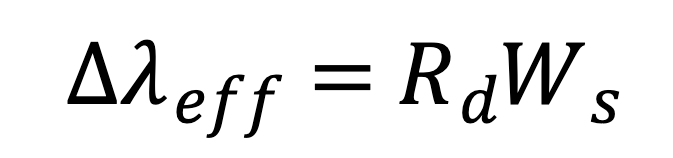
How does effective bandpass relate to resolution and intensity?
The lower the effective bandpass, the higher the resolution, the lower the intensity
What is the significance in bandpass and baseline resolution.
Having a separation of 2 effective bandpass between two wavelengths ensures baseline resolution
What is an interferometer?
Splits light into two or more beams and recombines them and the waves interfere w/ one another
When does constructive interference occur in an interferometer?
S = pathlength difference

What is the effect of the placement of the mirror in an interferometer on resolution?
The further the mirror is, the more wave cycles the interferometer can detect, the higher the resolution.
What is the significance of throughput?
The more light that passes through, the stronger the signal, the better the signal to noise
What is the difference between throughput in a monochromator and an interfermoter?
In a monochromator, light is limited by the slit width. An interferometer has a wide opening (no slits).
What is the advantage of interferometers in terms of accuracy?
The interferometer’s scale is constantly being calibrating by a second source and detector, limiting the delay after calibration, thus limited the uncertainty of wavelength and frequency measurements.
What is the advantage and disadvantage of multiplex in an interferometer?
Advantage : noise from detector is shared and can be reduced by averaging
Disadvantage : noise from one wavelength can effect others
What is a multichannel detector?
A detector that measures multiple wavelengths and/or spatial positions simultaneously
Relationship between x # of pixels and time and noise
1/x time for equivalent measurement
1/square root of x for noise for same total time
What is a photodiode array and how is it setup?
A type of multichannel detector. It is a piece of a semiconductor (usually Si) with p-type regions. Each p-n junction acts as a photodiode and is 1 “pixel” in a linear array.
What is a charged transfer device and how does it work?
A type of multi-channel detector. When a photon hits the detector, the energy moves an electron to the conduction band of the semi-conductor trapping the electron in a potential well near a positive voltage to hold it in place.
What is a charge-coupled device and how does it work?
A type of charge transfer device. Photon-generated electrons are moved from one position to another leading the charges along the array to shift until they reach a single readout point.
What are the three types of charge-coupled devices and how are they different.
Full Frame = entire sensor is detected to light and rows are readout sequentially with pixels still exposed to light, can lead to smearing (if readout time is similar to exposure time)
Transfer Frame = exposed pixels are shifted down to storage area rapidly and read out from there, reduces change of smearing
Interline Transfer = entire imaging is shifted to interline pixels, least change of smearing due to least amount of light collected
What is blooming and what are it’s effects?
Too many electrons in one potential well spill over into others, can cause distorted imaging
What is a complimentary metal oxide semi-conductor and how does it work?
A type of charge transfer device. Pixel readout is circuitry through the use of a rolling shutter
CCD vs CMOS
speed : CMOS = faster
cost : CMOS - cheaper
Signal/noise : CCD = higher signal, less noise
common artifacts : CCD = blooming, CMOS = rolling shutter
Where does most of the noise come from in charge transfer devices and how can you improve it?
Most of the noise comes from the readout step. You can improve by increasing the signal without increasing the noise.
What is more effective for S/N ratio (in terms of charge coupled devies), long exposure or averaging and why?
long exposure, because readout noise is added once rather than multiple times from multiple exposures (averaging)
What is binning and what is its purpose?
Addition pixels together before readout in order to increase signal strength and decrease readout noise.
What are ways to improve signal to noise ratio in charge transfer devices?
Binning and long exposure
What is a back thinned charge transfer device and what is an advantage and disadvantage of it?
The silicon layer of the sensor is made thin by removing material from the back side allowing for light reach the photosensitive region more efficiently.
Advantage = avoids electrodes
Disadvantage = expensive
What is an intensified charge coupled device, how does it work, and what is its benefit and disadvantage?
A CCD that amplifies the electrons before the CCD pixels. It transmits the photons, converts the photons to electrons, amplifies the electrons, converts the electrons back to photons and then transmits the photons. Its benefit is that is increases sensitivity. However, image degradation can occur.
How are the electrons amplified in an intensified charge coupled device?
Via a micro channel plate, containing many parallel electron multipliers
What is an electron multiplied charge coupled device and what is its benefit?
Amplified electrons in between CCD pixels and readout. Its benefit is better image resolution.
How are electrons amplified in electron multiplied CCDs?
Through impact ionizations, similar to avalanche photodiodes
What is the photoelectric effect? List some key details regarding energy, wavelength, noise, and the amount of electrons.
When radiant energy hits a metal surface, electrons are ejected.
Photon energy must be larger than energy binding electron
typically occurs at the uv/vis range with a 600-900 nm cutoff
1 electron per photon
electron is excited thermally which can lead to noise
What is a phototube and how does it work?
A type of single channel detector. Photons hit the photocathode and electrons are ejected and attracted towards the anode, creating a current proportional to the light’s intensity.
What is a photomultiplier tube and how does it work?
A photomultiplier tube is a type of single channel detector. Photons hit the photocathode and electrons are ejected. The electron then bounces off multiple dynodes, ejecting even more electrons each time. The electrons are collected by the anode and outputs as a current. Gain is 10^6 electrons per photon.
What region are photomultiplier tubes used in?
Works best in UV (if in quartz) and shorter wavelength vis. However, can detect longer wavelength vis and NIR with the right photocathode material.