Social Studies Unit 3 Quiz
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/48
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
1
New cards
Know the meaning of Mesopotamia, which it was named from the ancient Greeks
“land between rivers”
2
New cards
Know the 9 characteristics of a civilization
Centralized State, Complex Social Hierarchy, Dense Population, Cities, Writing
System, Specialization of Labor, Monumental Buildings, Dominant Belief System,
Agricultural Economy
System, Specialization of Labor, Monumental Buildings, Dominant Belief System,
Agricultural Economy
3
New cards
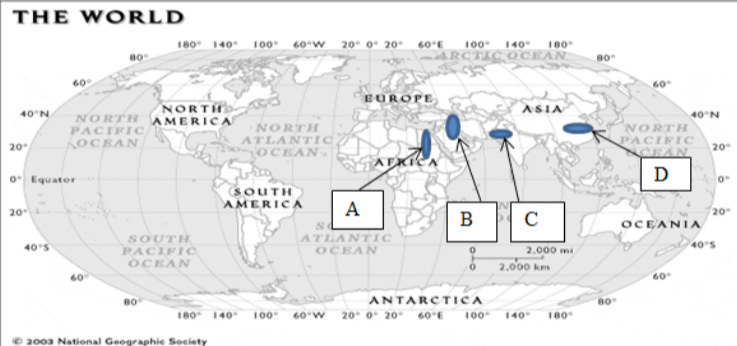
Know the location and which river belongs to each letter A,B,C,D
A – Nile River, B – Tigris and Euphrates River, C – Indus River, D – Yellow River
4
New cards
Based on the latitude of each of the four river valley civilizations, you can make the
assumption that they had what in common?
assumption that they had what in common?
All four have similar climates
5
New cards
Who separated drinking water from waste water in the first known sewage system?
Indus River civilization
6
New cards
Who used bronze for wheels and pots?
Yellow River civilization
7
New cards
Who had scribes who would record information on an early form of paper called papyrus?
Nile River civilization
8
New cards
Who created temples for major gods and goddesses called ziggurats?
Tigris and Euphrates Rivers civilizations
9
New cards
Know which form of writing we use today that is similar to Egyptian hieroglyphics
Emoji’s
10
New cards
Know four important details about scribes
They didn’t have to do hard labor, They were educated for 12 years, They didn’t
have to join the military and fight the pharaoh’s enemies, Their education wasn’t
free
have to join the military and fight the pharaoh’s enemies, Their education wasn’t
free
11
New cards
Know which civilization that King Hammurabi lead
Babylonians
12
New cards
Know what the pharaoh’s had built that they would eventually be entombed in
Pyramids of Giza
13
New cards
Know the roles of men and women in Mesopotamia
Women were responsible for maintaining the household, while men worked outside
the household
the household
14
New cards
Know the six Sumerian firsts
60 seconds in a minute, 24 hours in a day, Developed the first known form of
mathematics, a number system based on 12, 60 minutes in an hour, written language
mathematics, a number system based on 12, 60 minutes in an hour, written language
15
New cards
Know which two river valley civilizations that had Sumerian seals found there suggesting
trade
trade
Nile River and Indus River
16
New cards
Know one of the most important non-military achievements by the Assyrian
They built the royal library at Nineveh
17
New cards
Know what present day country Babylon was located in
Iraq
18
New cards
Know which of Hammurabi’s Code that is most like a law used in present day
Code 55 If a man opens a canal for irrigation and neglects it and the water floods a
nearby field, he shall pay grain to the owner of the adjacent field
nearby field, he shall pay grain to the owner of the adjacent field
19
New cards
Know what advantages the Hittites developed
They used iron weapons and chariots in battle
20
New cards
Know why Nebuchadnezzar was the most famous Chaldean
He rebuilt Babylon and his grand palace featured the Hanging Gardens
21
New cards
Sheep
Staple livestock for nomadic people, require protection from predators and fresh pasturelands
22
New cards
Goats
Provided milk, meat, hide, and wool, adapted to mountainous
environments
environments
23
New cards
Dogs
Non-livestock, kept predators like wolves at bay, admired for their loyalty and courage
24
New cards
Horses
Most beloved by nomadic people, mane and tail used for rope or
hides, used as tribute for Chinese emperors
hides, used as tribute for Chinese emperors
25
New cards
Camels
Beasts of burden in the deserts, made travel along the Silk Road possible
26
New cards
Bovines
Cows/Yaks/Ox, Yaks meat could be consumed fresh or dried, Cows
are not used for transportation
are not used for transportation
27
New cards
Know what polytheistic or polytheism means
The belief in more than one God
28
New cards
Know which metal was formed by combining 2/3 copper and 1/3 tin
Bronze
29
New cards
Know what all four world zones had in common in 3500 BCE
All four world zones had foraging
30
New cards
Know the structure of the Egyptian social hierarchy pyramid from highest to lowest
Pharaoh, Nobles (Officials and Priests),Scribes and Craftspeople, Farmers, Servants, Slaves
31
New cards
King Tutankhman
Tomb was discovered in 1922 by Howard Carter and
taught us much about Egyptian burial practice and beliefs
taught us much about Egyptian burial practice and beliefs
32
New cards
King Enzana
Aksum's most famous ruler and made Christianity the
kingdoms official religion
kingdoms official religion
33
New cards
Piankhi
Believed that the gods wanted him to rule Egypt. By 716 BCE, his
kingdom extended from Napata to the Nile Delta
kingdom extended from Napata to the Nile Delta
34
New cards
Ramses the Great
Had the temples at Karnak, Luxor, and Abu Simbel built
35
New cards
Queen Shanakh-dakheto
She is believed to be the first woman to rule Kush
36
New cards
Khufu
Best known for the monuments that were built to him (pyramids)
37
New cards
Queen Hatshepsut
Sent Egyptian traders to Punt and Asia Minor and was
an Egyptian female pharaoh
an Egyptian female pharaoh
38
New cards
Cuneiform
characters formed by the arrangement of small wedge-shaped
elements and used in Sumerian, Akkadian, Assyrian, Babylonian, and
Persian writing
elements and used in Sumerian, Akkadian, Assyrian, Babylonian, and
Persian writing
39
New cards
Domestication
the process by which people change plants and animals over
time at a genetic level to increase their productivity or other desired traits
time at a genetic level to increase their productivity or other desired traits
40
New cards
Herds
Large groups of domesticated animals like sheep and goats
41
New cards
Hieroglyphics
writing system that uses symbols or pictures to denote
objects, concepts, or sounds, originally and especially in the writing system of
ancient Egypt
objects, concepts, or sounds, originally and especially in the writing system of
ancient Egypt
42
New cards
Scribe
a person who was able to read and write, allowing for the creation of
written records and messages
written records and messages
43
New cards
Social Hierarchy
an order of social classes with producers at the bottom and
leaders or kings at the top
leaders or kings at the top
44
New cards
Chariot
A wheeled carriage powered by horses that was essential for trade
and warfare throughout AfroEurasia beginning in about 3000BCE
and warfare throughout AfroEurasia beginning in about 3000BCE
45
New cards
Metallurgy
The art and science of producing metal goods, all the way from
mining and extracting metal from mineral ores to the shaping of metal
objects
mining and extracting metal from mineral ores to the shaping of metal
objects
46
New cards
Textile
Cloth or fabric that is woven, knitted, or otherwise manufactured
47
New cards
Geographic Luck
Jared Diamond's theory that some regions developed
rapidly and expanded and conquered much of the world because the natural
resources available to them, climate, and geography gave them a early
advantage into agriculture before people in other places
rapidly and expanded and conquered much of the world because the natural
resources available to them, climate, and geography gave them a early
advantage into agriculture before people in other places
48
New cards
Pastoral Nomads
People who depend on domestic livestock, migrate in an
established territory to find pasture for their animals
established territory to find pasture for their animals
49
New cards
Great Arid Zone
The belt of dry and semi-arid land that extends across
AfroEurasia from the Sahara Desert in the west to Manchuria in northern
China
AfroEurasia from the Sahara Desert in the west to Manchuria in northern
China