G202 Exam 1
1/164
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
165 Terms
Assume that the socially efficient output level in the residential solar panel market is 1,000units per week, but the industry is only producing 800 units per week at current capacity. Theindustry's under-production is causing
society to lose out on a net benefit, as the next panel produced would have more consumer value than productive costs.
3 multiple choice options
Auto manufacturers are currently offering flex-fuel vehicles that are designed to run on ethanol gasoline mixtures. An economist recently analyzed the cost versus value consideration of these vehicles and found that the market is currently buying approximately the socially efficient amount of flex fuel vehicles. Under lobbying pressure from the car manufacturers and environmental groups, the federal government is considering a $3,000 subsidy paid per flex fuel vehicle sold. If this subsidy goes through, what would be the most likely impact on market efficiency?
Efficiency decreases
3 multiple choice options
Given an industry is producing the socially efficient output level, a tax placed on the industry will result in inefficiency because the market will produce
too few units, giving up some units that have more consumer value than productive costs
3 multiple choice options
Given what happens to the price buyers pay and the price sellers ultimately receive after a productive regulation is enforced on sellers, what happens to the level of consumer and producer surplus after the productive regulation takes effect?
Both consumer surplus and producer surplus decrease.
3 multiple choice options
You produce flat-screen televisions and sell them currently at a price of $1,000. The government is planning to enact a tax based on your chemical use and cause you to incur $100 worth of tax costs per unit. Which of the following is a likely outcome of the tax?
You raise the television buyer's price to $1,050 while your seller's price becomes $950 and your sales decrease 3%.
3 multiple choice options
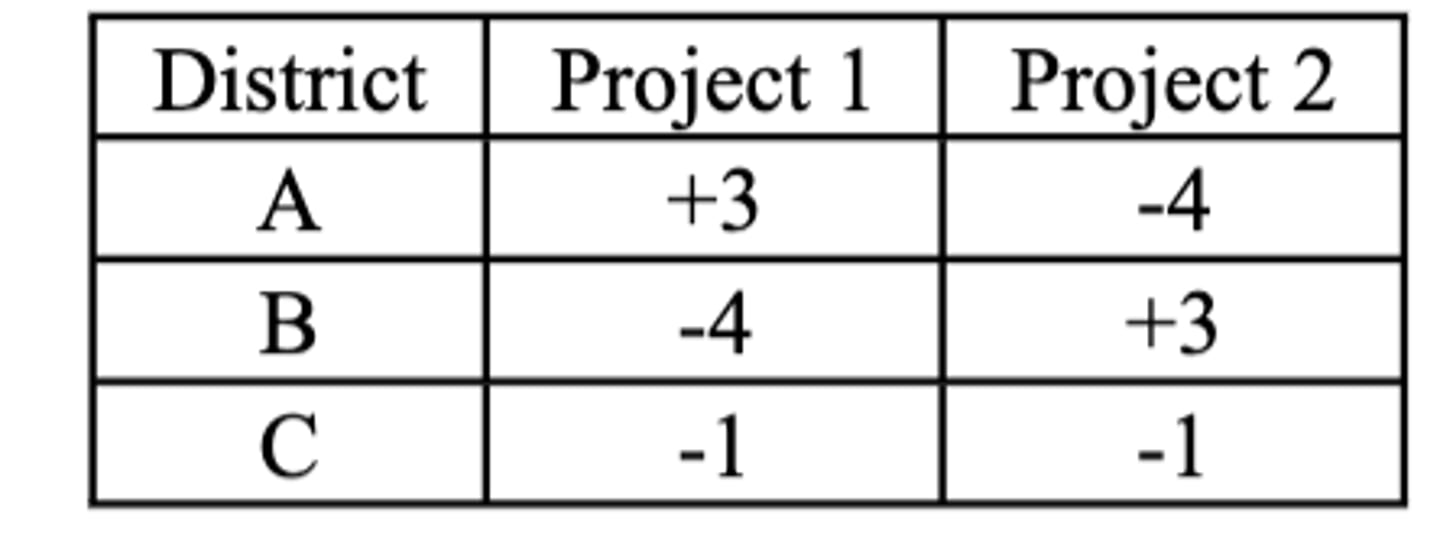
Below is a table on the Net Benefits (+) and Net Costs (-) incurred by the different districts ofa city considering two municipal projects
Districts A and B will not be willing to use log-rolling to pass both projects.
3 multiple choice options
For any particular special interest group, lobbying over a specific political issue will likely besuccessful when the issue is classified as
client issue
3 multiple choice options
The political action surrounding the location of federal nuclear waste dump sites in the US,can best be described as having
concentrated costs and widely dispersed benefits
3 multiple choice options
The 'special interest effect' refers to the bias of government in favor of policies that
support small groups at the expense of large groups
3 multiple choice options
Voters are rationally ignorant because of the
costs of obtaining political information that exceed the benefits of casting an informed vote.
3 multiple choice options
A U.S. trade policy that restricts the sale of foreign goods in the U.S. market will
reduce the demand for U.S. exports since foreigners will have less income
3 multiple choice options
If the world price of steel is $20, compare the pricing impact of the US enacting a $10 tariff per unit of steel imported versus the US imposing an import quota of 150 units of steel with a $10 per unit licensing fee.
The after tariff price would be Pt = $30, while the after quota price would be Pq = $40.
3 multiple choice options
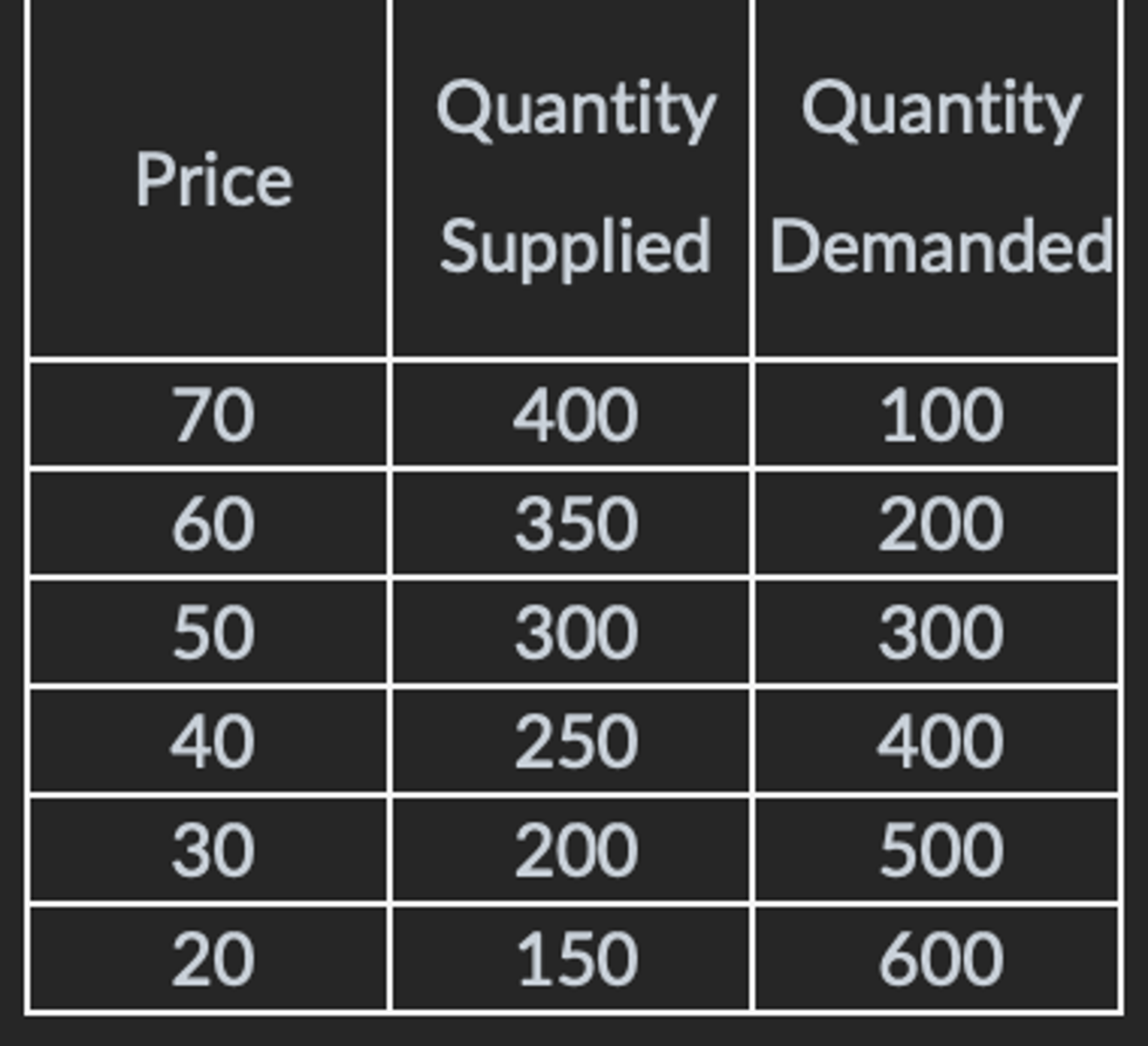
For a given product that the US imports from the world market at a price of $40, which of the following quotas enacted in the US market has the potential to cause the least amount of lobbying inefficiency?
A 3,000 unit quota with a license fee of $20 per unit that increases the product's price in the US market to $60.
3 multiple choice options
For a given product, which of the following trade restrictions would likely result in the least overall inefficiency?
A $20 tariff that resulted in 5,000 units of imports.
3 multiple choice options
1. Assume that sugar is initially traded freely in the US at the world price of $20 and at this world price the US imports 5,000 units of sugar. Then assume that the US enacts a quota of 2,000 units of imported sugar that raises the domestic price of sugar to $45. What is the most amount of revenue that the government can generate if it combines this quota with a licensing fee?
$90,000
3 multiple choice options
Which of the following is most likely to have patent protection?
Lipitor (pharmaceutical drug for lowering cholesterol sold by Pfizer)
3 multiple choice options
Consider an individual with a current income of $40,000 that is considering committing a crime that has a payoff of $20,000 and a fine of $20,000 if the individual is caught. Based on the standard Becker criminal decision rule, which of the probabilities of getting caught listed below is the highest probability that would still give the individual incentive to commit the crime?
33%
3 multiple choice options
Which of the following is not one of the benefits of well defined and enforced private property rights
owners will devote less resources to developing new technology
3 multiple choice options
Within the Becker model of crime, which of the following variables does government completely control?
The size of the punishment
3 multiple choice options
Crime 1:
Payoff=$50,000
Probability of getting caught=3/5
Punishment=$20,000 fine
Crime 2:
Payoff=$20,000
Probability of getting caught=1/4
Punishment=$20,000 fine
Above are some characteristics of potential corporate crimes that an individual with a current income level of $60,000 is considering committing. If the individual can only commit one of the above crimes due to time and resource constraints, which one will the individual rationally commit using the decision rule to only commit crime if utility is expected to increase by at least 10% after committing the crime?
a) Crime 1
b) Crime 2
c) Either Crime 1 or Crime 2 as they both have expected utility 10% greater than current utility.
d) Neither Crime 1 nor Crime 2 as they both do not have expected utility 10% greater than current utility.
B
3 multiple choice options
Social effiency occurs at
Market equilibrium
Demand is based on ...
value to consumers
1 multiple choice option
supply is based on...
cost to producers
1 multiple choice option
In underproduction, is cost less than or great than value?
less than
1 multiple choice option
the demand curve can be called the ...
value curve
1 multiple choice option
the supply curve can be called the...
cost curve
1 multiple choice option
In overproduction, cost is...
greater than value
1 multiple choice option
What are tools that can fix an inefficiency?
taxes, subsidies, and regulations
Taxes Imposed on Sellers shift the supply curve which way?
to the left
2 multiple choice options
Tax example: Soda is $1 a can and the government places a 10 cent tax on each can. How much money do you now make off selling the soda can now?
Pbuyer = $1.06 (because they will not front all the money coming from the tax)
$1.06-$0.10 = $0.96
Price increases
Consumption decreases
Market decreases
Do taxes fix overproduction or underproduction?
Overproduction
1 multiple choice option
Subsidies given to sellers shift the supply curve which way
To the right
3 multiple choice options
Subsidy Example: Solar Panels are $1000 each, but the government wants more, so they subsidize each one by $100, what is the seller's new revenue?
Pbuyer = $925 (Just like they won't pay all the money for the taxes, they will not reap all the benefit of the subsidy either)
Seller new revenue = $925 +$100 = $1025
Price decreases
Consumption increases
Market increases
Do subsidies fix over or underproduction?
Underproduction
2 multiple choice options
Why were the taxi medallions so expensive?
The government was not selling anymore of them. In the last 50 years, 11 new medallions have been sold.
Demand was going up, but supply was staying the same.
What did Uber recognize that they took advantage of?
Uber recognized the inefficiency the taxi market was creating, so Uber created a two sided market
Uber created a...
Two sided market, meaning it acted as a bridge between drivers and passangers
Uber is valuable for....
drivers and passangers
2 multiple choice options
How does Uber demonstrate efficient scaling in a two sided market?
Surge pricing, meaning that it is during a time that is inconvient for drivers so like holiday or something like that.
It works because the higher prices encourage drivers to come out, while discouraging passangers from ordering ubers?
Tech-based solutions reduced...
the search costs
What is a specific feature that reduces search costs and outcompetes taxi?
the hot map
What were Uber's competitive advantages?
- Efficient scaling in a 2-sided market
- Tech-based reductions in search costs
- Avoidance of regulatory costs
Uber's avoidance of regulatory costs
Uber operates in a grey area of the law that has it so it does not have to pay insurance, licensing fees and other traditional regulations ride services would have to do
Who initially had the relative strength in the Uber vs Taxi issue, and why?
The taxi drivers because they helped elect all the local politicians
How did Uber gain relative strength ?
They ran social media campaigns and got their customers to lobby for them.
How did Uber gain political and cultural legitimacy?
Uber partnered with Mothers Against Drunk Driving / MADD (who had experience lobbying (political) and had experience in making local communities safer (cultural))
Why isn't Uber able to turn a profit?
- High legal, lobbying, and start up costs
- unable to replicate political strategy across cities, states, and countries
- each location's campaign has come with unique legal and lobbying costs
What are the court cases that Got Uber in trouble that escalated their costs?
- Department of Justice / DOJ investigation into use of 'greyball' software that hides Uber driver locations
- FBI investigation into whether or not it was tracking Lyft drivers
- DOJ investigation into possible violation of Foreign corrupt practices act
- Acquisition of self-driving car start up, which landed itself in a IP-lawsuit over stealing trade secrets from Waymo
- California legislation that classifies gig-drivers as employees
Has Uber's bet on regulatory cost avoidance paid off?
No
1 multiple choice option
What is one way Uber has increased revenue?
Uber Eats
How is Uber gaining local legitimacy?
- Partnering with public Transportation systems across many metropolitan areas that suffer from congestion and under-utilized public transportation
- Uber can alleviate congestion as an extension of public transportation system
- Subizidation from cities has allowed passangers to receive discounted fares for using Ubeer to connect to an existing transportation hub
Sample Case Questions: Uber
According to the Uber case, which of the following is not one of the features of Uber’s technology that gives Uber a 2-sided-market convenience gain over taxi cabs?
Increaser insurance coverage and stricter labor screening for all new Uber Drivers
3 multiple choice options
Sample Case Questions: Uber
Which of the following is not one of the competitive advantages that allowed Uber to disrupt the taxi industry?
Incumbent advantage with shaping local regulations?
3 multiple choice options
special interest effect
small group of people, with incentive to take political action, receive benefits at the expense of a large unorganized group of people
Are small or large groups more likely to organize politically?
Small groups
1 multiple choice option
Why do large groups not take political action?
Because individual costs exceeds individual benefit of taking action
Every single government action introduces a ...
cost and benefit
3 multiple choice options
Types of political action chart
***
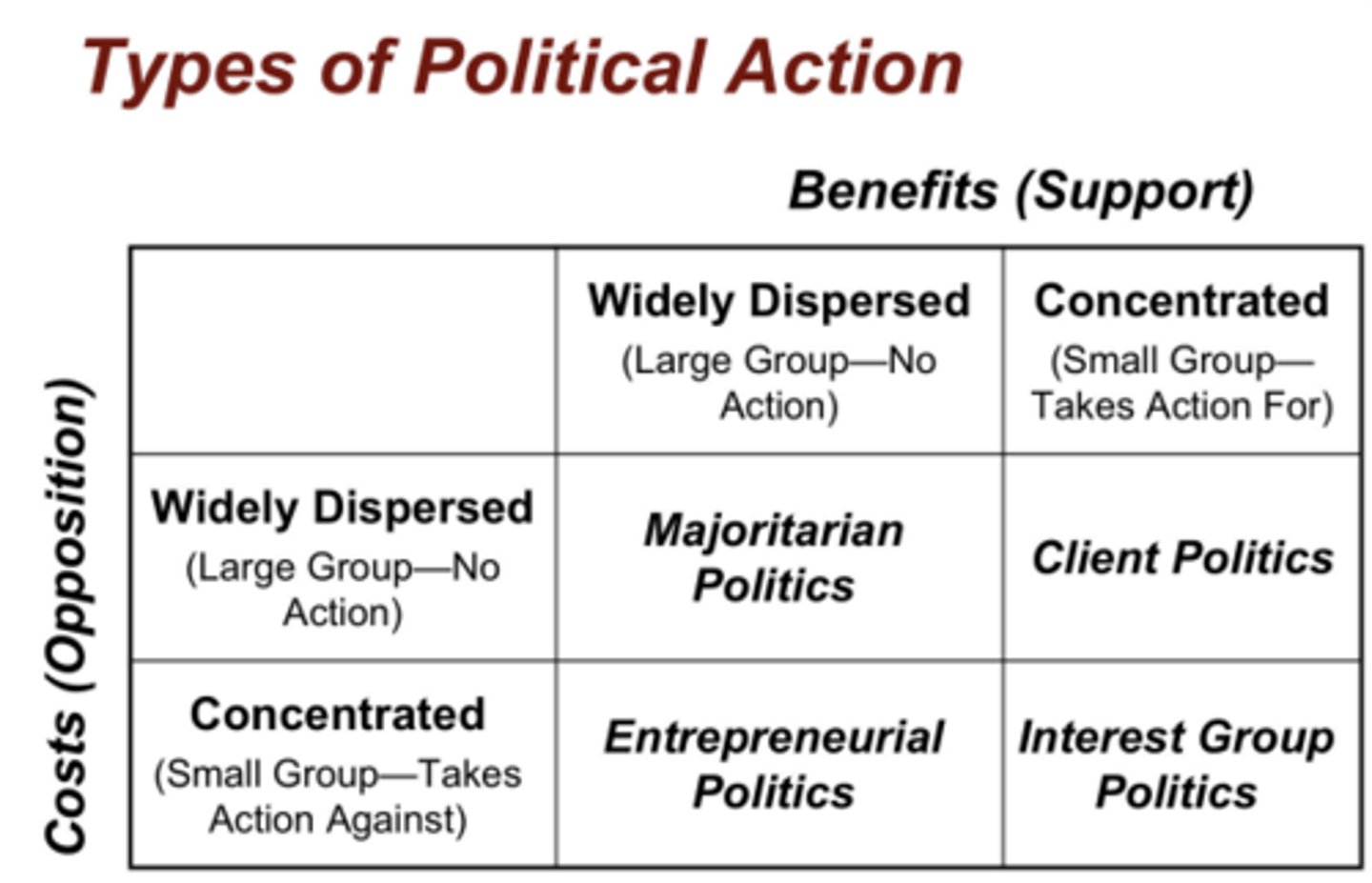
Majoritarian Politics
- Widely dispersed costs
- Widely dispersed benefits
- No small group action
- No lobbying
- Ex: social security
- Social security is the ONLY example
Client politics
- Widespread costs
- Concentrated benefits
- The concentrated benefits allow a small group to take action and organize to fight in favor of the issue
- No large group action
- Example: USDA Foreign advertising Funds
Interest Group Politics
- Concentrated costs
- Concentrated benefits
- Small groups on both sides of the issue
- Outcome depends on relative strength of lobbying
- Ex: Uber, Legalization of Weed
Entrepreneurial Politics
- Concentrated Costs
- Widespread benefits
- One small group is against issue
- These issues typically would involve a change to the status quo that most people benefit from
- Successful lobbying will be costly
- Ex: Dumping nuclear waste
Another term for lobbying
Rent Seeking
Coalition voting techniques
log rolling and pork barrel
Logrolling
- Politicians trading support for issues they both care about
- involves risk as voting on the separate projects are spread over time
- Tit for tat
- "If you vote for my bill I will vote for yours"
pork barrel
- Politicians bundling different regional projects into a package
- Less risk
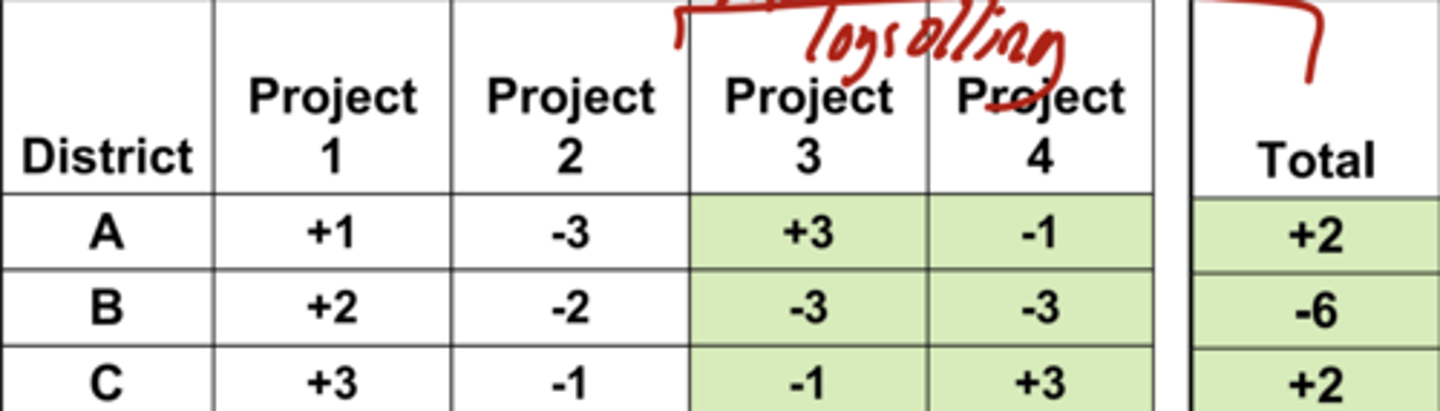
Chart that displays how log rolling could be used
For Projects 3 and 4, the issue would not pass if everyone was voting in their own self interest, but if District A and C log rolled it would pass because it would end up being a net benefit for them
Is Ventria a big or small company?
Small- they have around 20 employees
2 multiple choice options
What does Ventria do?
They genetically modify ride to produce more proteins to increase rehydration because over 2 million kids die a year from dehydration problems via diarrhea
Who are Ventria's potential clients?
UNICEF, Red Cross, WHO
What is the risk of growing Ventria's genetically modified rice?
Contamination of crops / wildlife
What three things is rice mainly used for?
Human food, animal food, and beer
Which US state values rice the most?
California, rice brings in around $500 million dollars for the rice industry annually
What is the only state with a rice committee to advise on rice issues?
California
What did Ventria not do that they should have done before starting their company?
A stakeholder analysis
Ventria Allies
- Employees and Investors (Investors have poured in $4 million dollars for 11 years)
- Pharma and Infant formula
- Red Cross, UNICEF, WHO
- Biotech Industry Organization
- UC Davis
- California Rice Comission
Ventria Neutral parties
- Federal Government
- EPA, FDA, and USDA
- State government (Rice Comission is an ally, but Secretary of Agriculture is against)
Ventria Adversaries
- Japanese Rice retailers association
- Traditional Rice farmers
- Anti-GMO activist coalition
- California secretary of agriculture
What type of political issue is growing GMOs in California?
Interest Group Politics => issue is going to come down to relative lobbying strength
Ventria's Options
- fight = relative strength of opposition is growing
- compromise = compliance costs are increasing and becoming an obstacle to business
- leave = find another place with less adversaries
What did Ventria do after it left California?
Moved to Missouri, but Missouri is a rice producing state. It would have been smarter for them to move to a non-rice producing state. Especially because Anhesuer-Busch is based in Saint Louis.
After Northwest Missouri State University pulled Ventria's funding, where did it go?
Kansas, which is a non-rice producing state. Its first harvest was in 2007, and since then has been profitable.
Takeaways from Ventria
- Activists had leverage over Ventria in rice producing states
- By locating to a non-rice producing state, Ventria gained political leverage by removing threat to state economy and providing jobs and attracting more biotech firms
Ventria Sample Case Question 1
Based on Ventria Bioscience case; which of the following was considered to be part of the potential stakeholder allies of Ventria?
WHO
3 multiple choice options
Based on the Ventria case, which of the following risks materialized to help block Ventria from planting rice in California?
Policy makers, traditional rice, and NGO activists all created barriers to Ventria's operations in California
3 multiple choice options
Rules of social efficiency under imports
Consumption rule and Production Rule
Consumption Rule
Domestic consumers should consume as long as value (DUS) is greater than or equal to production cost (PW)
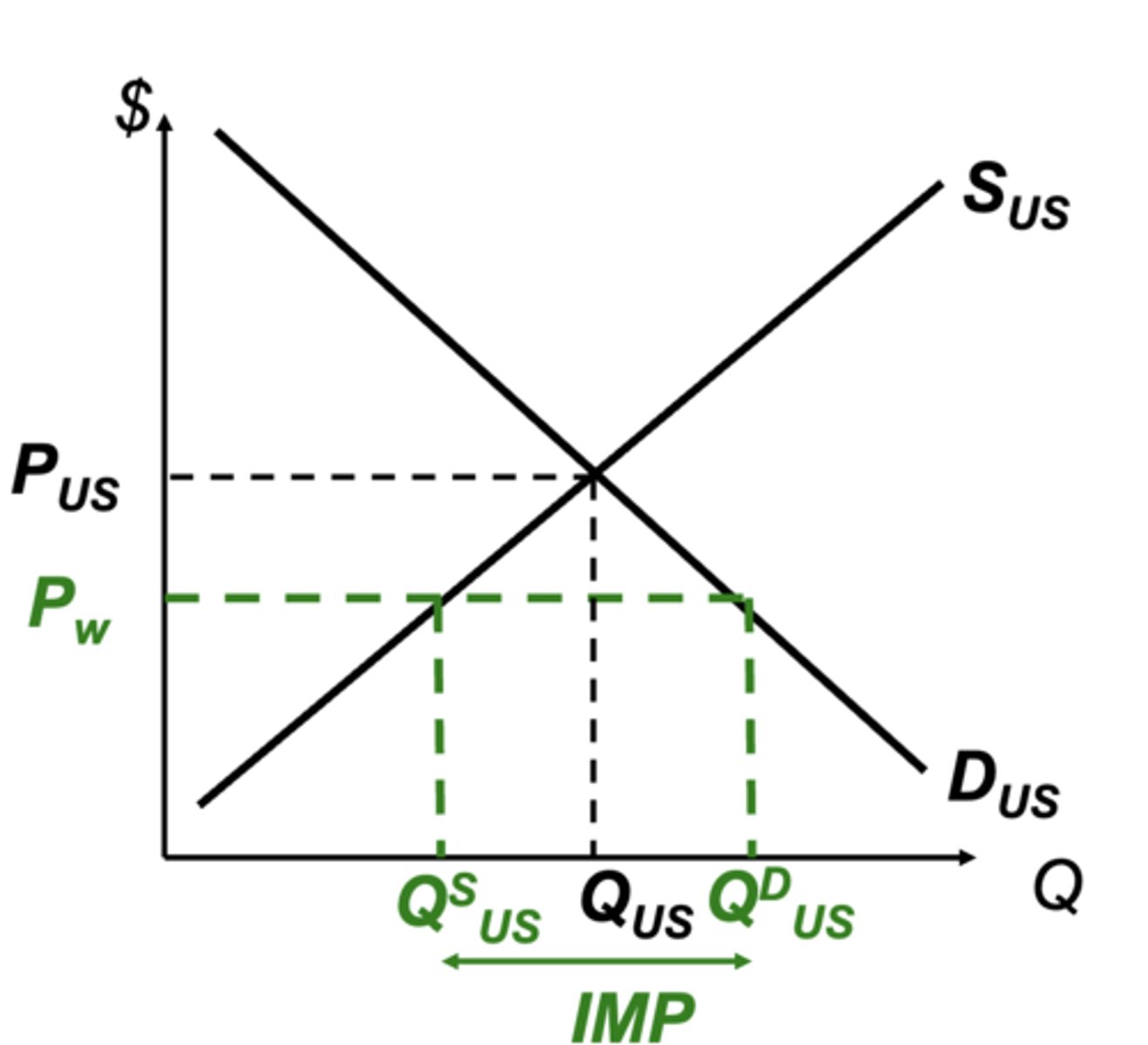
Production Rule
Domestic producers should produce as long as their production costs (SUS) are less than or requal to the world's cost (PW)
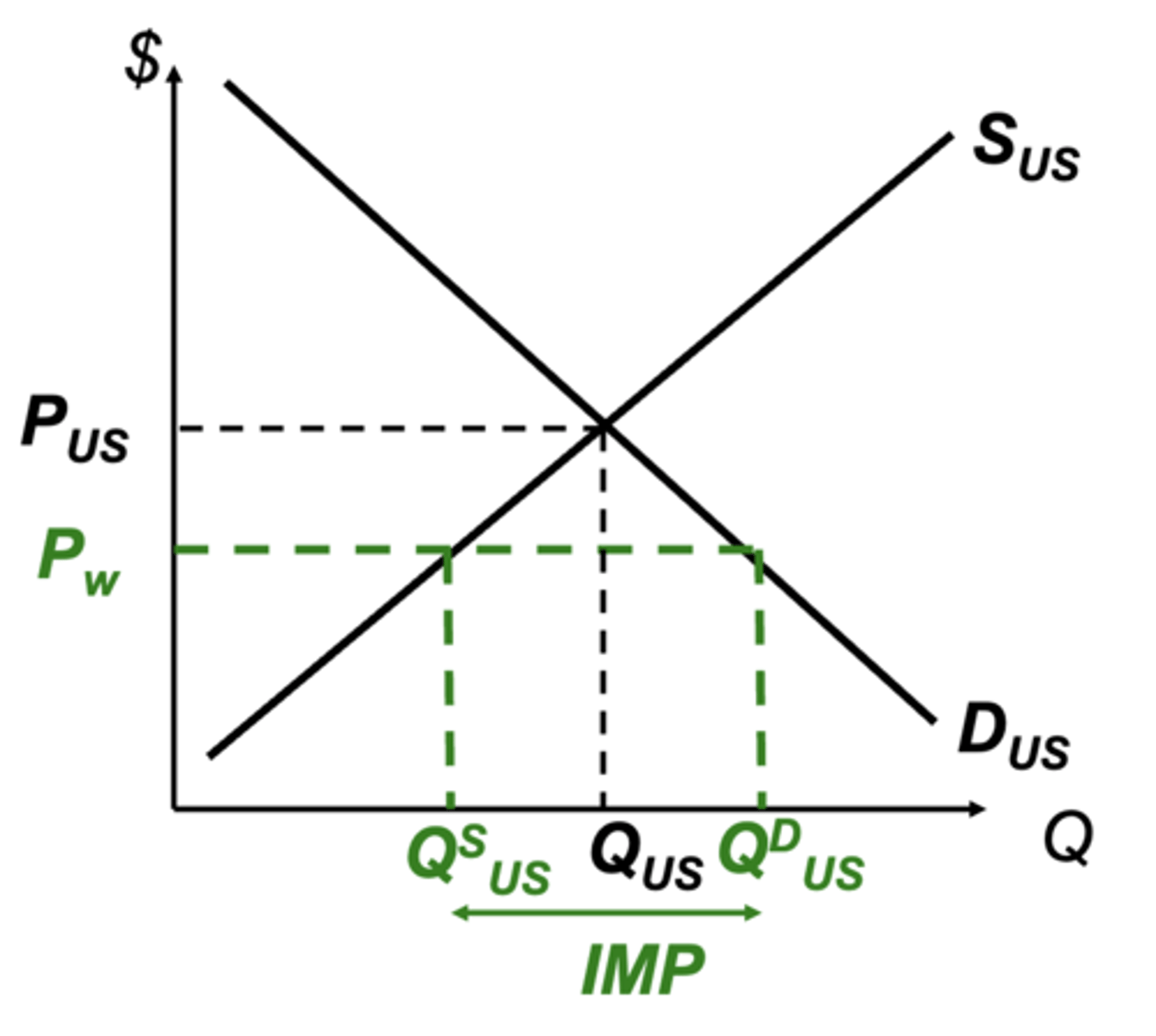
Free trade on a chart
What is US production, consumption, and imports?
300, 1100, 800
3 multiple choice options
Tariff Graphically
- a tariff will push the price up
- to find the government revenue, you plot the new QS and QD points. You then find the difference between them and multiply that by the amount of the tariff.
- a tariff goes on each unit of import so it basically comes down to amount of imports * price of tarrif
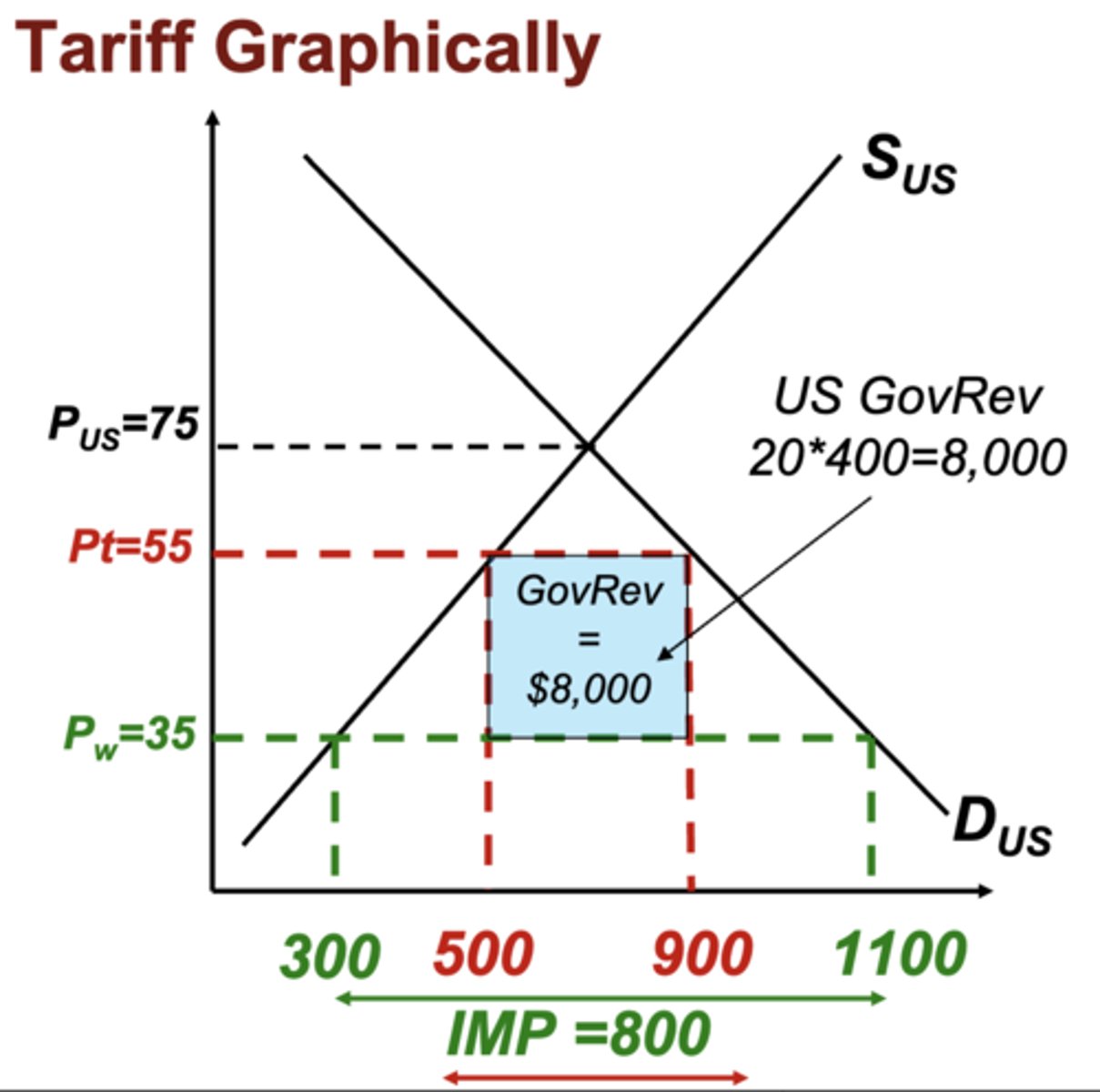
Impact of $20 tariff on US price, production, consumption, imports, gov rev?
Price: Up $20
Production: US Production is quantity supplied, so 500
Consumption: US consumption is quantity demanded, so 900
Imports: Consumption-Production, so 400
Gov Rev: Price of tariff * imports, so $8,000
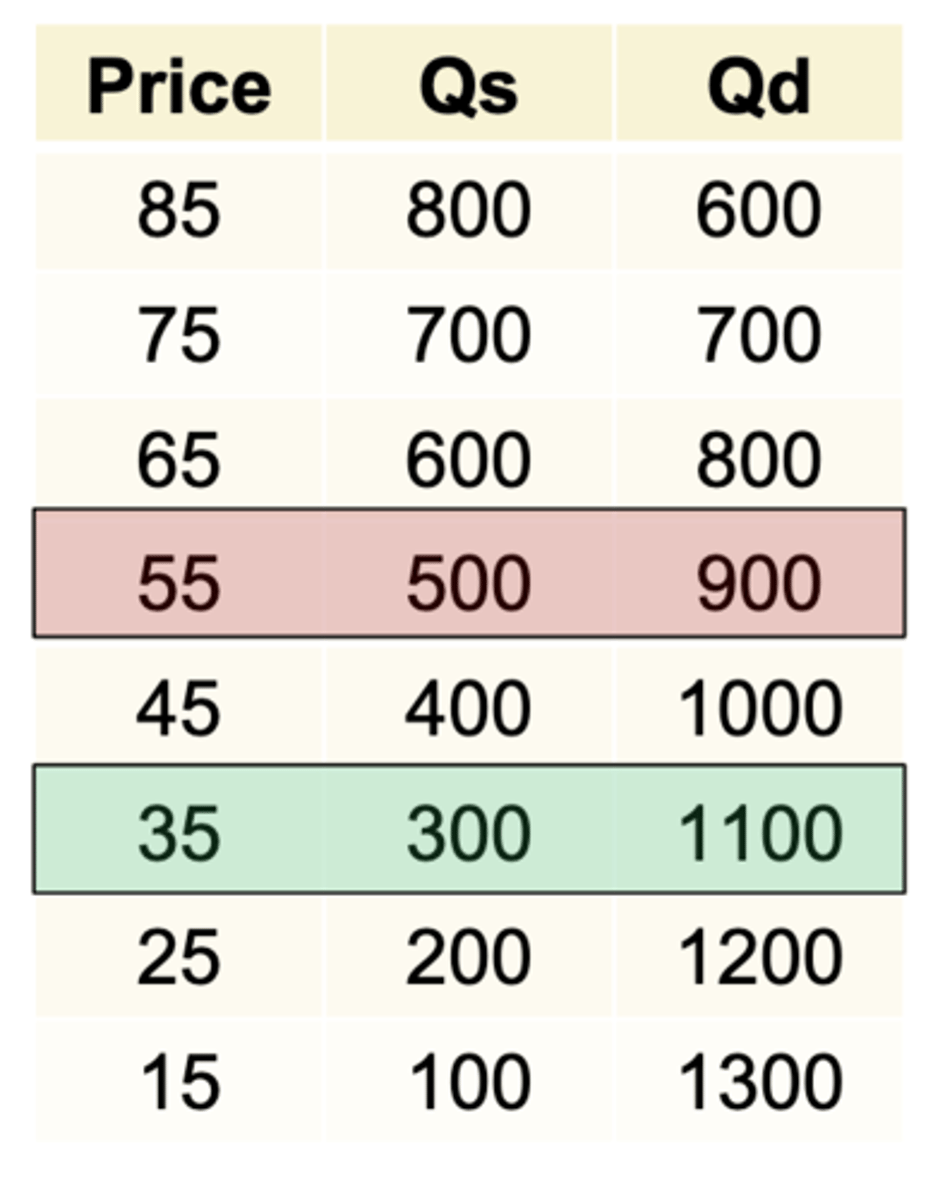
Tariff's are great for ___________ producers
domestic
1 multiple choice option
Why are tariff's good for domestic producers?
- Sell at a higher price and sell more units
Quota
Limitation on imports
A quota creates
excess demand
3 multiple choice options
Quota Graphically
Impact of a 600 unit quota, with a $5 license fee
1. US imports
2 US production
3. US consumption
4. US price
5. US GovRev & Foreign Gain
1. 600 (down from 700)
2. 400 (up from 300)
3. 1000 (down from 1100)
4. $45 (up from $35)
5. Both are $3,000 in this case
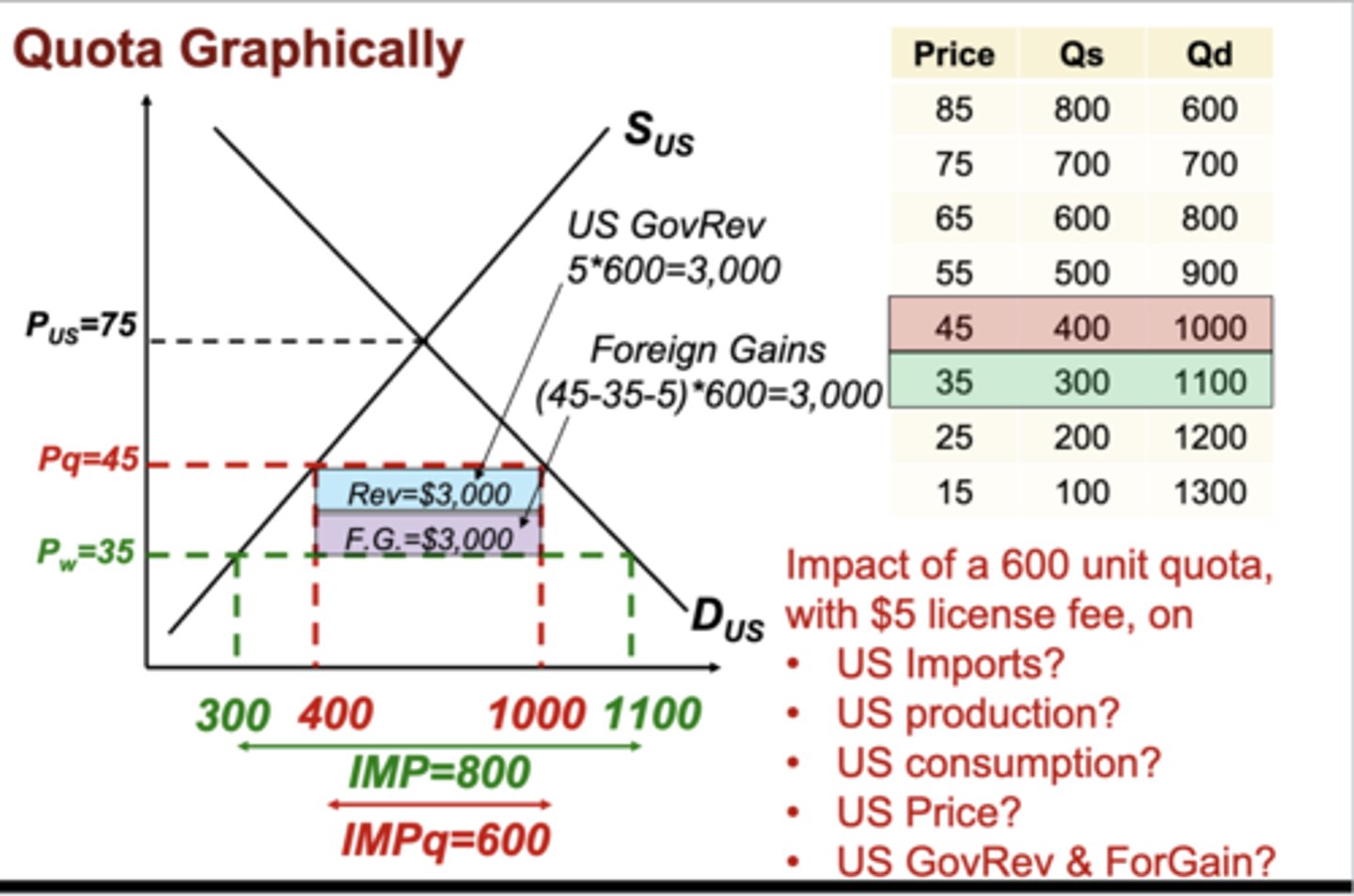
How to solve Quota problems
A question may be given as what is the impact of a ______ unit quota. To find what the number is, lets say 500, you need to find where the number of imports is 500. The number of imports is equal to QD-QS.
Foreign gains formula
[(After quota price)-(Before quota price))-licensing fee]*# of imports
Alternate way to find foreign gains
- You could find the change in price and multiply that by the amount of imports. Then, find the government revenue, which is licensing fee * imports. The total number from price change - gov rev will also be foreign gains.
3 types of trade restriction inefficiencies
1. Under consumption
2. Over production
3. Lobbying