Ap Gov Unit 2
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Mandates
official orders or requirements imposed by a higher authority, often referring to federal requirements that states must follow to receive funding or support
Ex: federal minimum wage
Spin
the attempt to control or influence communication in order to deliver one's preferred message
Impact of Social Media
made it easier to divide people and manipulate them
Midterm
happens mid-way through every 4-year presidential election cycle; gives voters a chance to decide which party controls Congress, and determines who represents your state
(1/3 of the Senate and every seat in the HOR are up for election; Senators serve 6-year terms while HOR serve two-year terms)
Approval Ratings
a rating based on a percentage of people (as voters) who think someone (as a politician) is doing a good job
Ex: Gallup Polls
Pork Barrel
the use of government funds for projects designed to please voters or legislators and win votes
Logrolling
the practice of two or more lawmakers trading votes on different issues to get their preferred bills or projects passed (quid pro quo arrangement)
Commerce Clause
gives Congress broad power to regulate interstate commerce and restricts states from impairing interstate commerce (Article I, Section 8)
Partisanship
a strong adherence, dedication, or loyalty to a political party; accompanied by a negative view of an opposing party
Bully Pulpit/State of the Union
The platform that a President of the United States has to advocate for their agenda and influence public opinion
Ex: Annual State of the Union
Super PACs
organizations that can raise and spend unlimited amounts of money to influence elections, as long as they do not coordinate directly with candidates or political parties
Citizens United vs. FEC
the government can't restrict independent political spending by corporations and unions in candidate election, violating the First Amendment
Participatory Democracy
democracy that emphasises the active, direct participation of citizens in the policies and decisions that affect their lives and communities
Ex: Surveys and polls
Pluralist Democracy
multiple groups, interests, and organizations compete for power and influence within the government
Elite Democracy
a small number of individuals or groups hold significant power and influence over the decision-making process
Base
a candidate or party's base or core support refers to the voters who support them for elected office based on core values
Congressional Leadership
the elected members of the House of Representatives and the Senate who guide their respective chambers and political parties.
Moderates
political views or policies that fall in between the extremes of the ideological spectrum, often characterized by a blend of liberal and conservative beliefs
Single-issue Voting
casting a vote based solely on a candidate's or a political party's stance on one particular public policy issue
K Street
area in downtown Washington, DC where many lobbyists, lawyers and advocacy groups have their offices
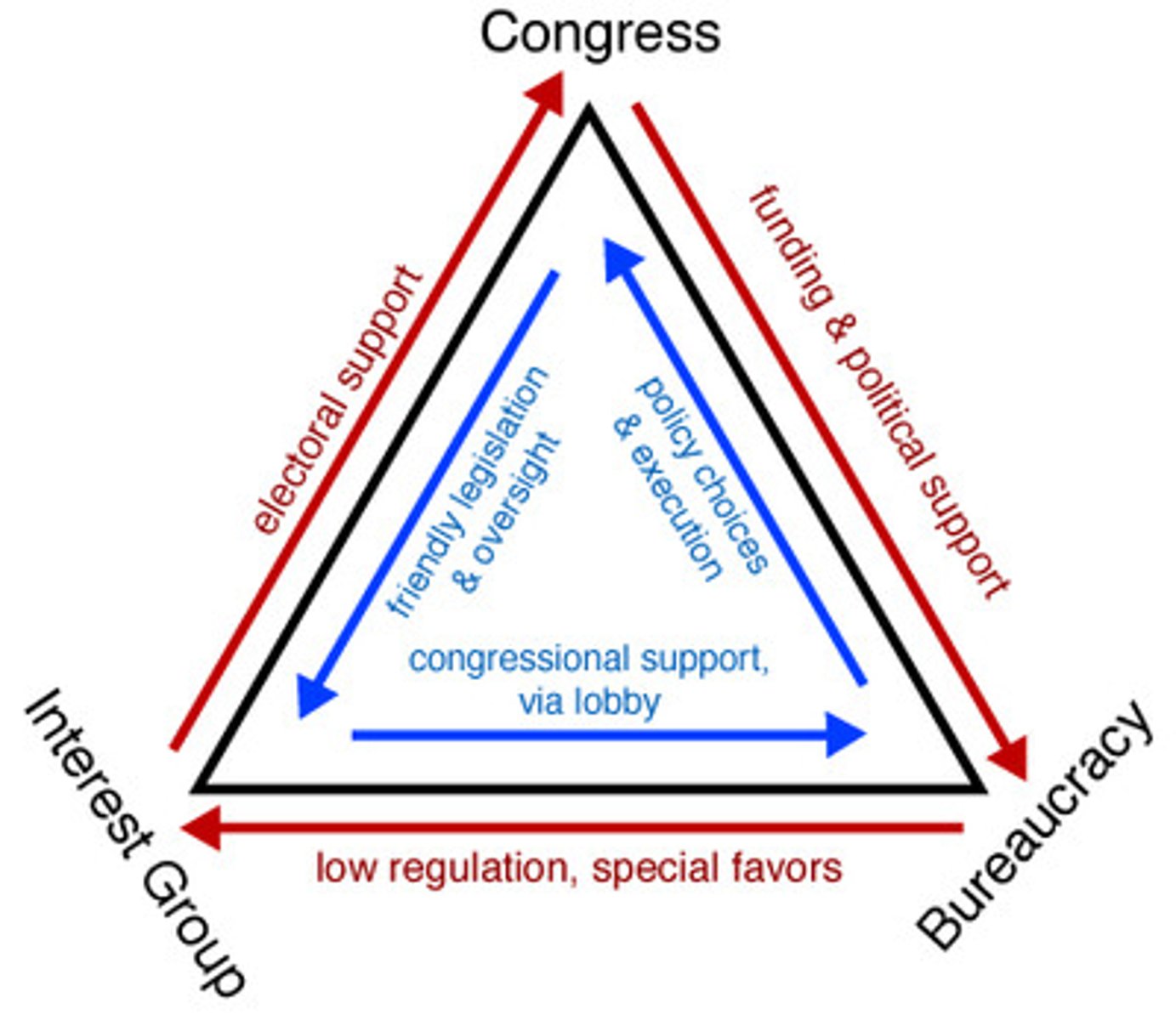
Iron Triangle
congress + agency + interest group = policy loop
relationship that develops between congressional committees, the federal bureaucracy and interest groups during the policy creation process. The relationship between these three actors occurs naturally over time down to close proximity in which all of them work together. They are all seeking to maximise their gain during the policy process, and iron triangles help them to do this.
Issue Networks
a loose, informal, and temporary alliance of various individuals and groups who come together to influence policy around a specific issue. nlike the stable, mutually beneficial relationships of an iron triangle, issue networks are fluid and involve a diverse range of participants.
Lobbying
the act of attempting to influence government decision-making, such as legislation, regulations, or other official actions, through communication with public officials
Linkage Insitutions
structures that connect individuals to the government and facilitate communication between citizens and policymakers
Ex: elections, political parties, the media
Baker v Carr
one person, one vote
Shaw v Reno
No racial gerrymendering without strong reason
Federalist 70
Hamilton advocated for strong president = energy + accountabilityF
Federalist 78
Hamilton argued for an independent judiciary.
Courts need judicial review for checks
Marbury v Madison
Established judicial review.
Supreme court gains power to say “unconstitutional”
Power of the Purse
The ability of congress to control money —> biggest weapon
Discretionary Rulemaking
Congress writes broad laws —> agencies fill in details
allows for flexibility for the agencies
Bicameralism
Two house legislature structure(house + senate)
House of Rep
2 year terms, strict debate rules, represents districts, originates revenue billsSen
Senate
6 year terms, unlimited debate, represents states, approves treaties & nominees
Apportionment
dividing house seats based on population after the census
Incumbency Advantage
existing members of congress have higher re-election chances
Standing committee
permanent committee focused on one policy area
Select committee
temporary committee created for investigation or a specific issue
joint committee
members from both chambers conduct oversight or researchconf
conference committee
resolves differences between house and senate version of a bill
markup
committee edits a bill before voting it out
discharge petition
house method to force a bill out of committee with 218 signatures
committee of the whole
house meets with relaxed rules to speed up debate
appropriations
congress allocating money to programs
authorization bill
creates or continues a government program
mandatory spending
required spending like social security, medicare
discretionary spending
optional spending decided in annual budget. Ex: education, defense
continuing resolution
temporary funding to avoid shutdown when budget isn’t passed
omnibus bill
large bill that packages many funding bills together
earmarks
funds set aside for specific local projects
pocket veto
president takes no action on a bill at the end of a session, killing it
signing statements
president comments on how laws should be enforced
war powers resolution
requires president to notify congress within 48 hours of troop deployment and get approval after 60 days
writ of certiorari
supreme court agreeing to hear a case
amicus curiae brief
friend of the court brief by outside groups tyring to influence decision
administrative descretion
agencies decide how to enforce laws
notice and comment rulemaking
agencies publish proposed rules for feedback
red tape
excessive bureaucracy or rules that slow processes
independent regulatory commission
agency designed to be shielded from politics
cabinet department
major agency head advising president(DHS, state, defense)