biomed respiratory system
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
nose
heats and moistens air
turbinates
three pairs of long thin bones covered with a layer of tissue that can expand. if swollen, can block airflow
cilia
projections in the nasal cavity that beat in a coordinated manner to clear foreign bodies
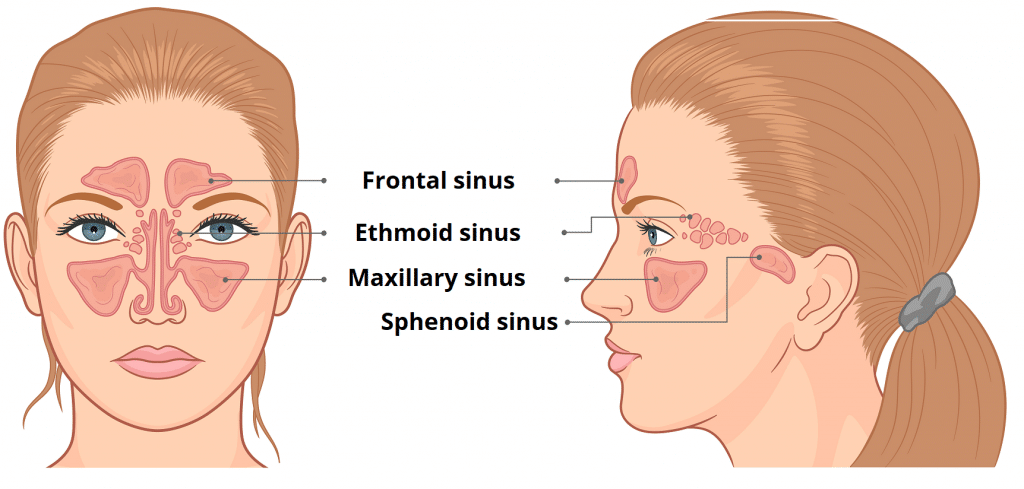
sinuses
hollow cavities within bone including frontal, ethmoidal, sphenoidal, maxillary
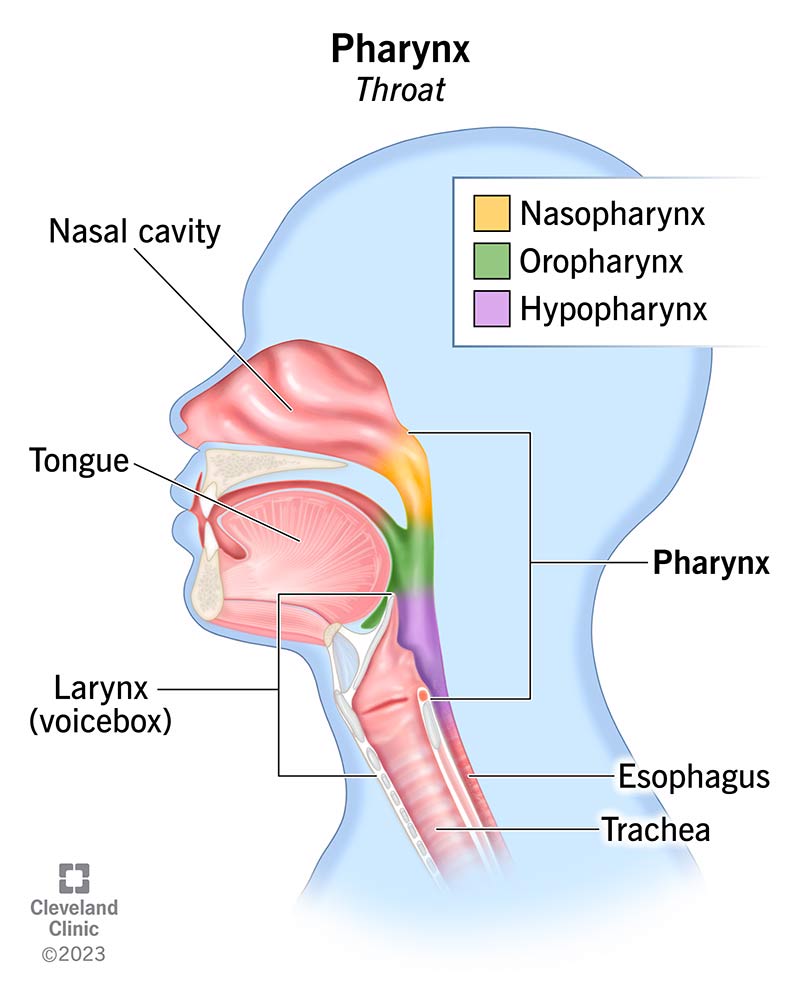
pharynx
passageway for air and food between the nasal cavity, mouth and esophagus also known as throat
epiglottis
flap of cartilage that closes the opening to the larynx when food is swallowed
larynx
a space near the pharynx that aids in voice production; also known as the voice box - the adams apple
trachea
the tube that leads from the larynx to the lungs , also known as the windpipe
lobes
right lung has 3, left has 2
pleura
membrane that lines the surface of the lungs
bronchi
tubes that branch out from the trachea into the right and left lungs
bronchioles
tubes that branch out from the bronchi and travel down to the air sacs in the lungs
alveoli
tiny hollow air sacs clustered like bunches of grapes at the ends of the bronchioles, which exchange gas with surrounding capillaries - smallest blood vessels. gas exchange occurs here
surfactant
mixture of fat and proteins that line the pulmonary system, specifically alveoli
mediastinum
intrapleural space separating the sternum in the front and the vertebral column behind
diaphragm
dome shaped muscle separating thorax from the abdomen that plays major role in breathing. it contracts on inhale, expands on exhale.
external respiration
gas exchange between alveoli and the external environment, or breathing
internal respiration
the gas exchange between the blood and the tissues throughout the body
medulla oblongata
senses levels of oxygen and CO2 to level basic rhythm of breathingph
phrenic nerve
sends impulses to stimulate the diaphragm
apnea
without breathd
dyspnea
difficulty breathing
eupnea
normal breathing
hyperpnea
excessive breathing
orthopnea
difficulty breathing when lying down
tachypnea
fast breathing
hyperventilation
sudden change to quicken breathing
asthma
a person’s airways become inflamed, narrow, swell, and produce extra mucus. causes bronchodilation, airway inflammation, and mucous impaction.
treatment includes bronchodilator, steroids, anti inflammatory, antihistamines
bronchodilator
helps open airways of the lungs to make breathing easier
steroids
stimulates hormone effects, often to reduce inflammation or for tissue growth and repair
anti inflammatory
prevents or counteracts swelling in joints and tissues
antihistamines
reduces or blocks histamine release
COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder)
lung diseases that block airflow and make breathing difficult. risk factor is smoking, asthma, over 40. medicatins are bronchodilator and steroids
pneumothorax
air leaks into the space between lung and chest wall ; a collapsed lung. treatment is needle/tube used to remove excess air
hemothorax
blood collects in the pleural space. without treatment, blood can continue to accumulate and collapse the lung.
thoracentesis
draining of pleural fluid through a needle or catheter
thoracostomy
drainage of pleural fluid through a chest tube
tension pneumothorax
when mediastinal structures in thoracic cavity shift. treatment is immediate needle decompression