DNA + Polypeptide
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/83
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:05 AM on 1/30/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
1
New cards
What is it called when DNA copies itself?
Replication
2
New cards
What is transcription?
Transcription is the process a specific gene being copied onto an RNA strand.
3
New cards
What is translation?
Translation is the process of the genetic code on the mRNA being decoded to synthesise a polypeptide.
4
New cards
What are the 2 stages of polypeptide synthesis?
The first stage is called Transcription.
The second stage is called translation.
The second stage is called translation.
5
New cards
What initiates the process of polypeptide synthesis?
Gene expression initiates the process of polypeptide synthesis.
6
New cards
When does replication occur in DNA?
1. Cell division
2. Protein synthesis
2. Protein synthesis
7
New cards
What are the 3 forms of RNA?
1. t-RNA
2. r-RNA
3. m-RNA
2. r-RNA
3. m-RNA
8
New cards
What is the role of mRNA?
Carries information from DNA in the nucleus to ribosomes in the cytoplasm
9
New cards
What is the role of rRNA?
Acts as an structural component of ribosomes
10
New cards
What is the role of a tRNA?
Carries amino acids to the ribosome during translation to help build an amino acid chain
11
New cards
What is a codon?
A sequence of three nucleotides that corresponds with a specific amino acid or start/stop signal during translation
12
New cards
What is an anticodon?
Anticodons are codons that are a part of an tRNA and are considered as complementary codons of the specific codon of the mRNA.
13
New cards
What is an RNA?
Single-stranded nucleic acid that carries out the instructions coded in DNA
14
New cards
What is a polypeptide?
A singular linear chain of amino acids
15
New cards
What passes the information from a DNA to an RNA?
The triplet code (a sequence of three nucleotides) passes the information from the DNA to the mRNA.
16
New cards
When does a pre-RNA turn into an mRNA?
A pre-RNA turns into an mRNA when it goes through splicing.
17
New cards
For a polypeptide synthesis to occur what does the free floating bases do?
The free floating bases bond to each other and form an mRNA (messenger RNA). The mRNA transcribes the DNA information.
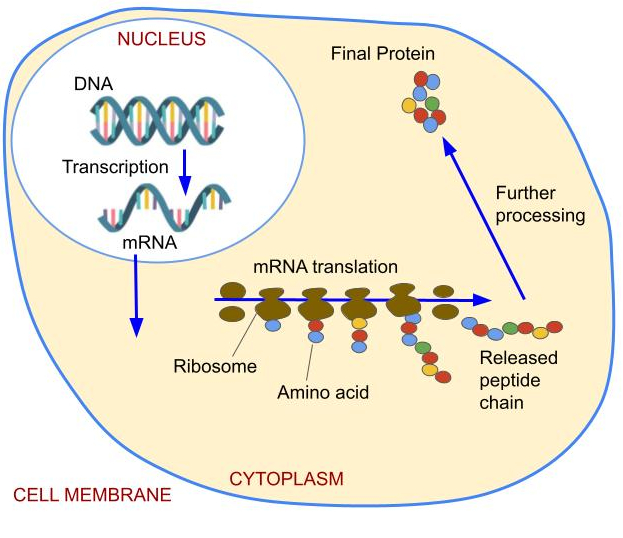
18
New cards
For polypeptide synthesis to occur what does the ribosome do?
The ribosome attracts tRNAs that act as anti-codons and have picked up amino acids. These amino acids then bond together by peptide bonds as the anti codons attach themselves to the codons.
19
New cards
During mRNA formation which base of the DNA is replaced by another nucleotide?
Thymine is replaced with Uracil.
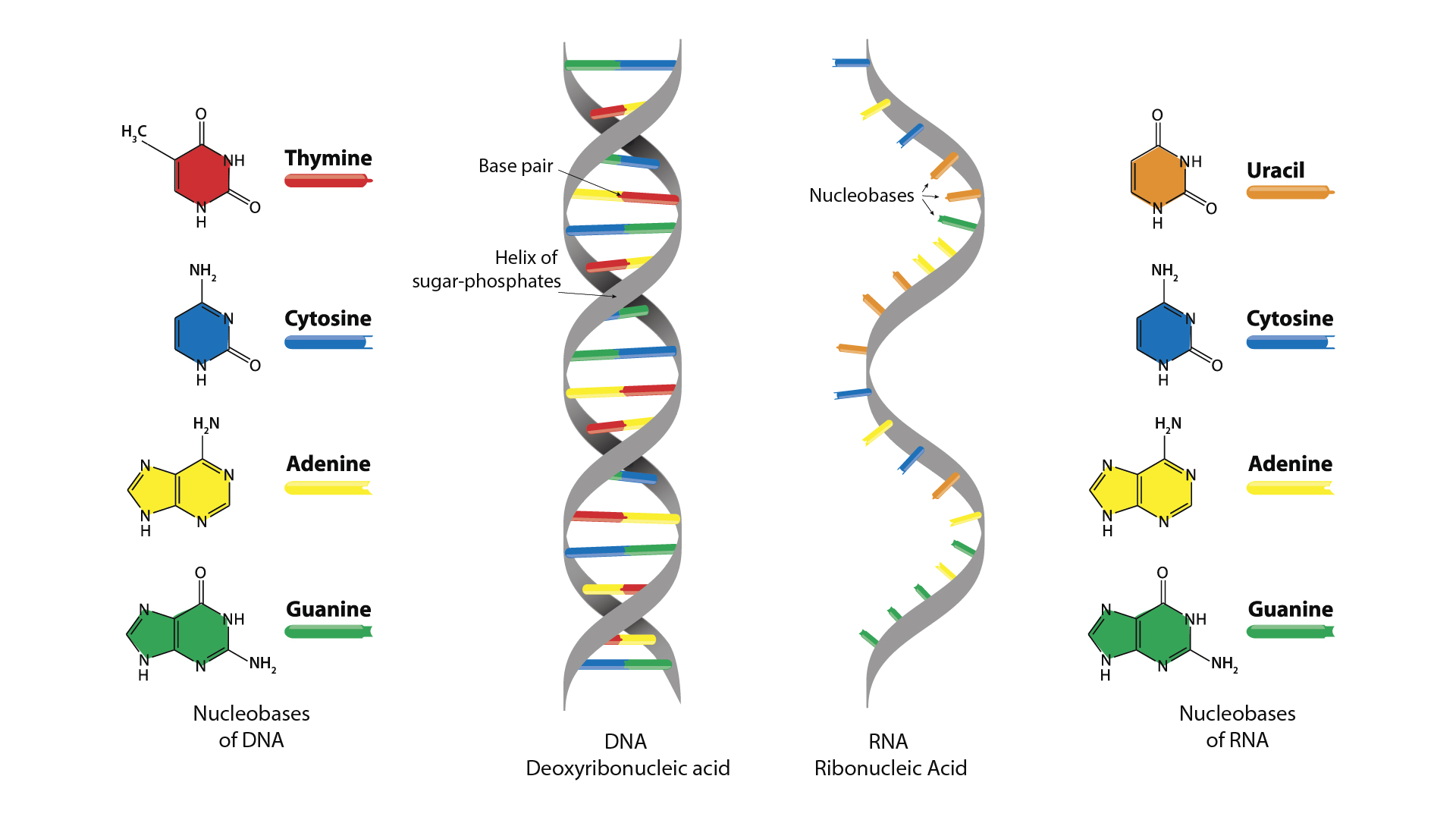
20
New cards
What are introns?
Introns are non-coding segments of nucleic acid found in eukaryotic DNA.
21
New cards
What are exons?
Exons are coding segments of nucleic acid found in eukaryotic DNA.
22
New cards
What do condones code for?
Amino acid
23
New cards
In which organelle is polypeptides created?
Ribosome aka rRNA
24
New cards
What does ribosomes attract?
The ribosome attracts tRNA that is tethered to an amino acid
25
New cards
How is amino acids bonded together with?
Peptide bonds
26
New cards
How is a folded protein bonded to create its fold?
Hydrogen bonds
27
New cards
What is template strand?
Template strand is the strand that is being transcribed/copied in the polymerase.
28
New cards
What is a promotor?
Promotor is a specific codon or a sequence of nucleotides that signals the beginning of replication of a gene.
29
New cards
What is a terminator?
Terminator is a specific codon or a sequence of nucleotides that signals the end a gene that is being replicated.
30
New cards
What is RNA polymerase? And what is it's job?
RNA polymerase is an enzyme and it's job is to seperate the 2 DNA strands from each other and link the RNA nucleotides to form a mRNA.
31
New cards
From which prime does a RNA polymerase start and end transcription? from?
5' (Five prime) and ends transcription at 3' (Three prime)
32
New cards
What do the primes of an mRNA strand do?
The prime 5' is capped and the prime 3' is a poly-a tail. These primes prevent the mRNA from degrading.
33
New cards
What is the difference between pre-mRNA and mRNA? What process takes place when an pre-mRNA is transformed into mRNA?
Pre-mRNA includes non-coding introns with no primes (5 capped and 3 poly-a-tail) but mRNA does NOT include the non-coding introns instead it had the 5' and 3'. The process of an pre-mRNA transforming into an mRNA is called RNA splicing.
34
New cards
What is RNA splicing?
RNA splicing is the process in which the non-coding segments (introns) of an RNA strand are removed from the pre-mRNA and the exons are joined together forming codons. It is also when the 5' cap and 3' poly-a tail is formed on the 2 ends of the RNA. In this process the pre-mRNA transitions into mRNA.
35
New cards
What does r-RNA stand for? What is it's role?
r-RNA stands for ribosomal RNA. The role of r- RNA is to provide a site for translation to occur by providing biding sites for the m-RNA and t-RNA.
36
New cards
What is a polysome?
Polysome is when multiple ribosome attach to an mRNA to produce a faster amino acid chain.
37
New cards
What are the 3 sites for tRNA in a ribosome called?
1. P site holds tRNA with the growing chain of amino acids.
2. E site holds the tRNA that has delivered the amino acid.
3. A site holds the tRNA that is carrying the amino acid.
2. E site holds the tRNA that has delivered the amino acid.
3. A site holds the tRNA that is carrying the amino acid.
38
New cards
On the large subunit how many binding spots are there for tRNA?
3
39
New cards
On which subunit does tRNA bind to?
large subunit
40
New cards
On which subunit does mRNA bind to?
small subunit
41
New cards
Where does translation occur?
Translation occurs in the cytoplasm, specifically in ribosome
42
New cards
What are the 3 stages of translation?
The 3 stages of translation are:
1. Initiation
- Refers to the 2 subunits of ribosomes coming together to provide
a site for tRNA to attach to it's complementary codon.
2. Elongation
- Refers to the amino acids being brought to the mRNA to continue
the growing chain of amino acids (polypeptide)
3. Termination
- Refers to the stop codon (terminator) releasing protein which
causes the polypeptide to be complete.
1. Initiation
- Refers to the 2 subunits of ribosomes coming together to provide
a site for tRNA to attach to it's complementary codon.
2. Elongation
- Refers to the amino acids being brought to the mRNA to continue
the growing chain of amino acids (polypeptide)
3. Termination
- Refers to the stop codon (terminator) releasing protein which
causes the polypeptide to be complete.
43
New cards
On which prime is the amino acid attached to on a tRNA.
3'
44
New cards
What happens during gene expression?
The gene of a DNA that has the code for a polypeptide expresses (switches on) and then the cell starts to produce that specific polypeptide.
45
New cards
What is alpha helix?
An alpha helix is a polypeptide chain that has it’s backones coiled anti clockwise
46
New cards
what is beta sheet?
A beta sheet is a polypeptide chain that has it’s backbone nearly fully extended.
47
New cards
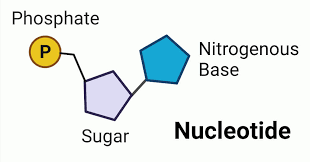
What three things make up a
nucleotide?
nucleotide?
1. Nitrogenous base
2. Phosphate
3. - Deoxyribose sugar (For DNA)
- Ribose sugar (For RNA)
2. Phosphate
3. - Deoxyribose sugar (For DNA)
- Ribose sugar (For RNA)
48
New cards
What does the Purines group consist of?
Adenine and Guanine
49
New cards
What does the pyrimidines group consist of?
Thymine and Cytosine
50
New cards
What is RNA constructed of?
RNA is constructed of a single strand of ribose sugar and nitrogenous bases of Adenine, Uracil, Guanine and Cytosine.
51
New cards
What is the name of each stage in polypeptide folding?
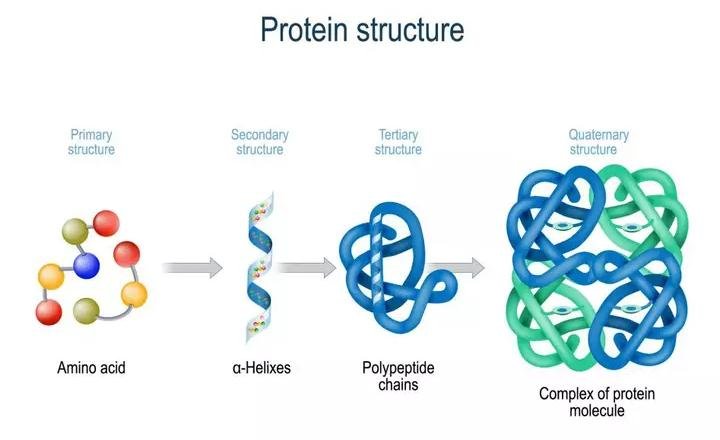
52
New cards
53
New cards
What is DNA constructed of?
DNA is constructed of a double strand of of deoxyribose sugar, phosphate and nitrogenous bases of Adenine, Thymine, Guanine and Cytosine.
54
New cards
How do nucleotides bond to each other?
With hydrogen bonds
55
New cards
What is the backbone of a DNA made of?
Sugar phosphate
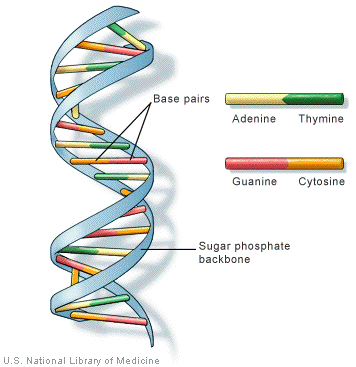
56
New cards
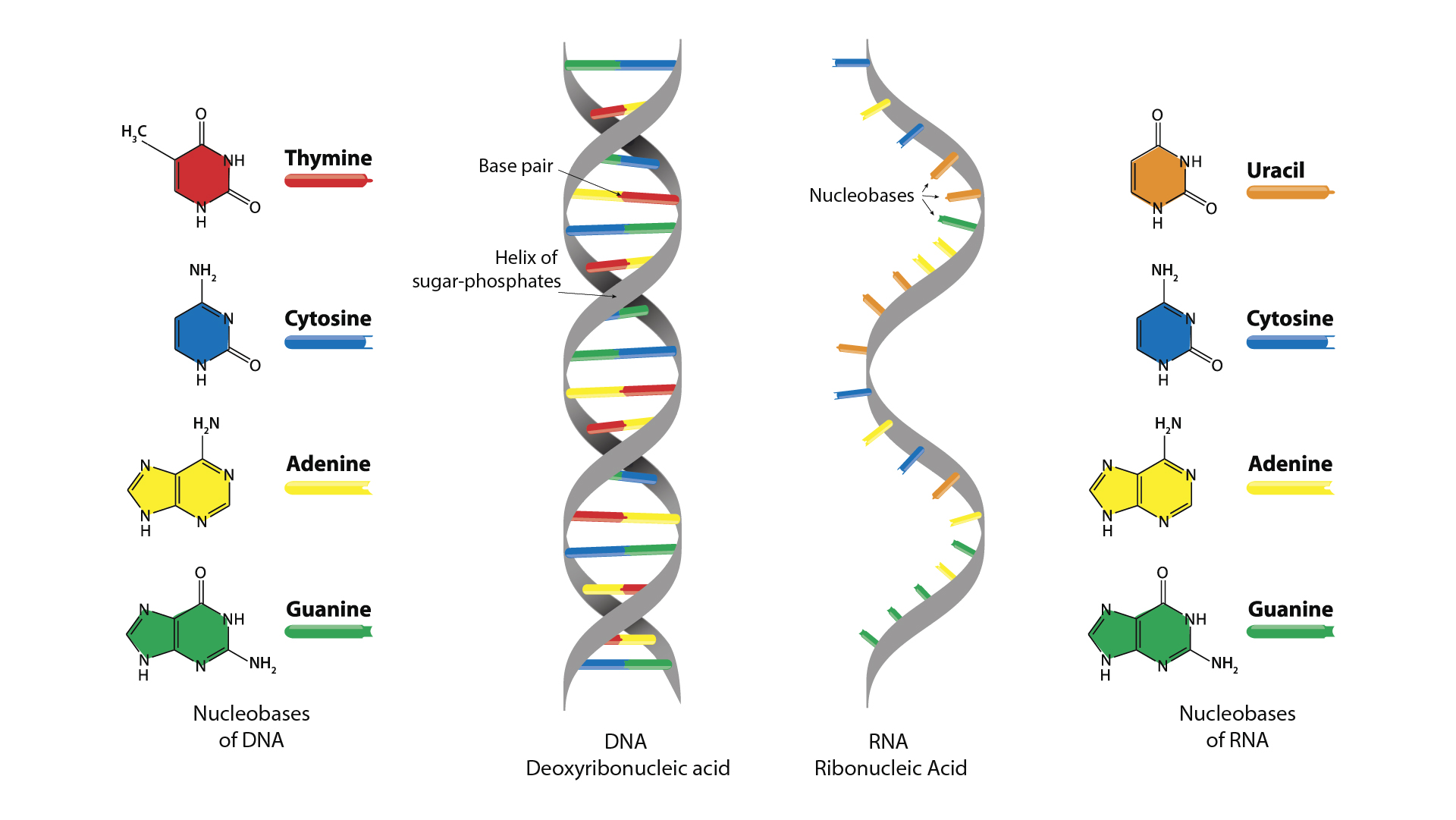
What are the four bases/rungs of a DNA?
1. Adenine (A)
2. Thymine (T)
3. Cytosine (C)
4. Guanine (G)
2. Thymine (T)
3. Cytosine (C)
4. Guanine (G)
57
New cards
What are the four bases/ rungs of an mRNA?
1. Adenine (A)
2. Uracil (U)
3. Cytosine (C)
4. Guanine (G)
2. Uracil (U)
3. Cytosine (C)
4. Guanine (G)
58
New cards
What do the bases/rungs of DNA consist of?
Nitrogen
59
New cards
What does the base G stand for and what does it correspond with?
G stands for guanine and it corresponds with C- cytosine
60
New cards
What does the base C stand for and what does it correspond with?
C stands for cytosine and it corresponds with G- guanine
61
New cards
What does the base T stand for and what does it correspond with?
T stands for thymine and it corresponds with A- adenine
62
New cards
What does the base A stand for and what does it correspond with?
A stands for adenine and it corresponds with T- thymine
63
New cards
What does the base U stand for and what does it correspond with?
U stands for uracil and it corresponds with A- adenine
64
New cards
What does a nucleotide consist of?
A nucleotide consists of a sugar, a phosphate and one of the 4 nitrogenous bases.
65
New cards
What is a DNA?
DNA is a heredity material that is made of genes.
66
New cards
What is gene?
A gene is a section of a DNA that carries a specific code of function.
It is a certain length of a DNA is called a gene and this gene determines a different characteristic of the individual organism such as the hair colour.
It is a certain length of a DNA is called a gene and this gene determines a different characteristic of the individual organism such as the hair colour.
67
New cards
Where is DNA found in a cell?
* In the nucleus
* In the mitochondria
* In the chloroplast (plant cells)
* In the mitochondria
* In the chloroplast (plant cells)
68
New cards
What is a chromosome?
Chromosomes are long spiral strands that carry DNA.
69
New cards
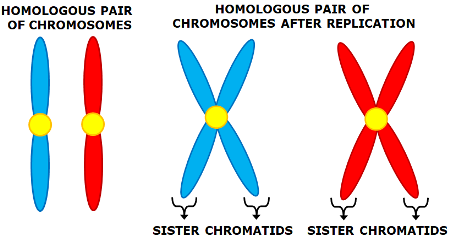
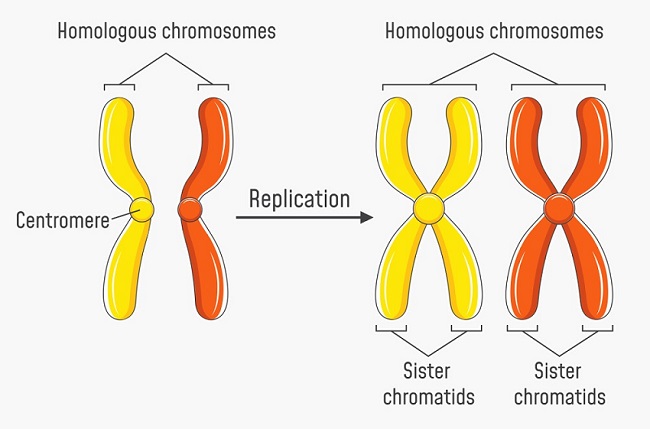
What is a chromatid?
A chromatid is one of the two identical halves of a chromosome that has been replicated in preparation for cell division.
70
New cards
How are chromatids formed?
When homologous chromosomes replicate themselves they form chromatids. Resulting in 4 chromatids.
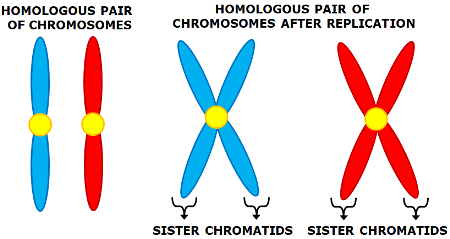
71
New cards
What is a homologous chromosome?
Homologous chromosomes are composed of two different chromosomes that are not genetically identical despite containing the same sets of genes. It is one paternal and one maternal chromosomes that contain the same set of genes.
72
New cards
what is a sister chromatids?
The sister chromatids are pairs of identical copies of DNA joined at a point called the centromere. It is when a single stranded chromosome replicates itself during interphase, specifically S phase.
73
New cards
What is a gene loci?
A fixed position on a chromosome where a specific gene is found.
74
New cards
What is an allele?
An allele is a gene loci of two chromosomes that are identified as two identical genes but are different versions .
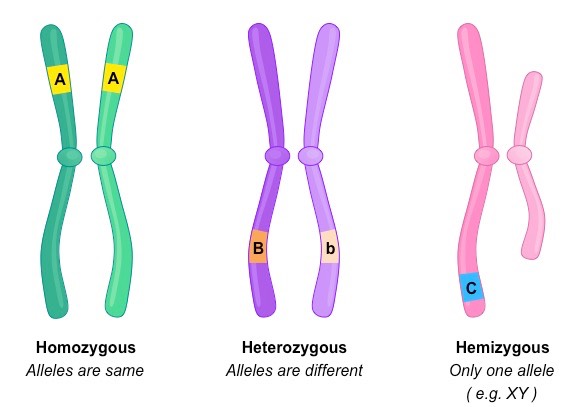
75
New cards
What causes mutation?
Mutation is a change in the genetic sequence of a DNA. Mutations are caused due to errors in DNA replication. It is when a change occurs in the sequence of a gene.
76
New cards
What is somatic mutation?
A mutation that occurs in an individual’s ‘body cell’ and is not passed on to the offspring.
77
New cards
What is gametic mutation?
A mutation that occurs in sex cell and is heritable.
78
New cards
What are the 4 types of mutations? Explain each.
1. Substitution nonsense mutation
when a nucleotide is exchanged with another during replication, as a result a stop or start codon is formed.
2. Frameshift deletion mutation
when a nucleotide is completely removed from sequence during replication without being replaced with another.he
3. Silent mutation
when a nucleotide is exchanged with another during replication, however no major change occurs as the same amino acids is still produced
4. Substitution missense mutation
when a nucleotide is exchanged with another during replication, as a result a new amino acid and a gene is produced
\
79
New cards
What is a homozygous allele?
The presence of two identical alleles at a particular gene locus.
80
New cards
What is a heterozygous allele?
The presence of two different alleles at a particular gene locus.
81
New cards
What is a nucleoid?
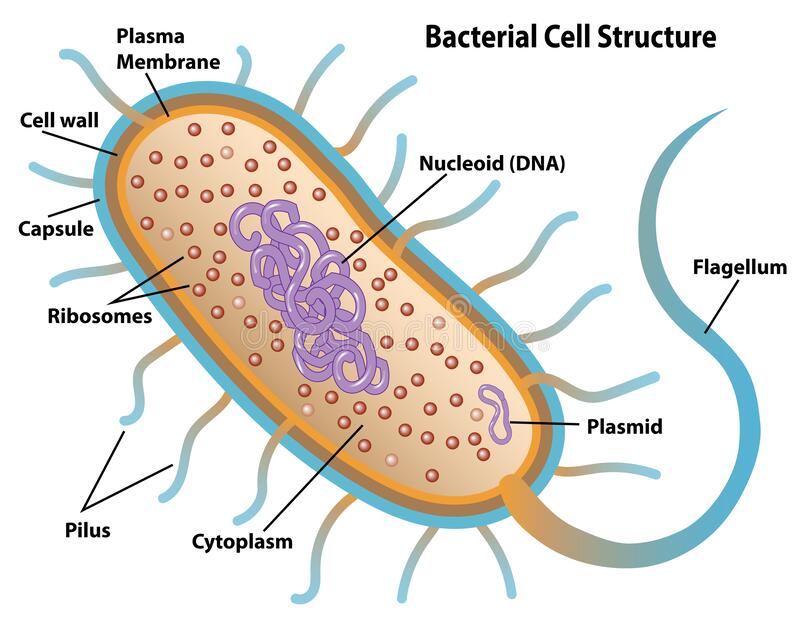
The nucleoid is an irregularly shaped region within the prokaryotic cell that contains all or most of the genetic material
82
New cards
What is a plasmid?
Circular, independent, self replicating and double stranded DNA molecule. Plasmids can frequently be transmitted from one bacterium to another.
83
New cards
Name the 5 main characteristics of DNA in prokaryotic cells.
1. DNA is found in the cytoplasm (nucleoids) of the cell, as the cell does not have a nucleus. The DNA is also found as plasmids.
2. The DNA sequence does not have introns
3. The chromosome is circular
4. Most cells don’t have histones except archaeas
5. Single chromosome and plasmids in the entire cell
84
New cards
Name the 5 main characteristics of DNA in eukaryotic cells.
1. The major amount of DNA is found in the nucleus and in small amounts it is found in the mitochondria and chloroplast.
2. The DNA sequence has introns
3. The chromosome is linear rather than circular
4. The DNA is wrapped up around histones
5. Billions of chromosomes in the entire cell