Y11 Comp Sci 1.3 & 1.4 test
1/77
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
network definition
a system that allows computer systems to communicate and share resources with each other. Usually 2 or more devices
standalone computer
a computer thats not connected to any network (e.g. the internet)
LAN
Local Area Network
computers connected over a small geographical area e.g. a single building or site
owner is responsible for the connections (cabling, wifi, hotspots etc)
examples of lans - home networks, school networks, networks in shops
cheaper than wans (only costs are devices & networks) + cost less to maintain (smaller area)
more secure than WANs (smaller area)
WAN
computers connected over a large geographical area - several sites, town, country, or international
owners use existing network infrastructure to connect sites together e.g. phone lines, satellite connections
examples of wans - city, university campus with several sites, the internet (biggest wan)
cost more than lans (sophisticated hardware) & are less secure (larger area)
network hardware: network interface card (NIC)
allows computers to connect to other computers by allowing them to connect to a wired network and data packets to travel to & from it
contains a MAC address (Media Access Control) - physical hardware address
allows an ethernet cable to be plugged into it
network hardware: transmission media
different types of cabling you need to connect to other computers
ethernet cable - aka twisted pair, networking standard
fibre optic cable - very fast but expensive, often used in WANs / big LANs
coaxial cable - older networking cable
packet definition
a message containing data that is sent from one device to another
network hardware: switch
connects multiply devices (printers, computers, servers) in a network & allows them to communicate with each other
when a device sends data to another device it forwards the data packet to the correct destination device using the MAC address of each device to see where to sent it
if 2 or more computers place a packet onto a network at the same time a data collision occurs. a switch helps solve this by examining the destination device and creating a direct connection to that device
as far as the 2 devices are concerned, there are no other computers on the network - no other devices exist
how switches send packets
each device on a network has a unique MAC address, given to them when they are manufactured
switches don’t initially know which device is connected to which one of its ports but will build up a MAC address table by learning from the traffic that passes through it
network hardware: router
interconnection device used on a network
contains routing table with a list of IP addresses & common routes for packets to take. examines the IP adresses of data packets, identifies a network, and determines which network / host the packet should be forwarded to
router allows computers to access the internet - allow packets from different network types to be exchanged
home broadband routers
network hardware device that combines features of a switch, WAP and router in one
network hardware: wireless access point (WAP)
allows for wireless devices to connect to a network using a switch. includes connections through wifi & bluetooth
can also provide internet access in public places e.g. wifi hotspot
benefits of a WAP
no need for cables - allow devices to connect to networks wirelessly so no need for physical cabling. beneficial in environments where cables would be impractical e.g. big buildings, conference rooms, public spaces
mobility & flexibility - users can connect laptops, smartphones, tablets etc to the network from anywhere in the WAP’s coverage area
cost saving - cables can be costly & labour intensive to set up - save on infrastructure costs
limitations of WAPs
bandwidth limitations - all devices must share available bandwidth - network congestion
capacity - limited total bandwidth which is split between all devices. can slow down network
radio interference - wireless signals are susceptible to interference from other devices that operate on similar frequencies (microwaves, cordless phones, bluetooth devices). can lead to packet loss, signal degradation, retries, leading to reduction in overall speed & reliability of network.
signal strength - as distance between device & WAP increases, signal strength decreases leading to slower speed & higher latency (time it takes for packet to travel from one device to another). devices far away can experience packet loss / need to reconnect
factors affecting network poerformance
bandwidth - how much data can be transferred in a unit of time (in bits per second). smaller bandwidth = less data can be sent & network slows down
latency - time it takes for a packet to arrive. big delay = more data on network = more data collisions = more packets on network
number of users - too many can cause network to slow down if there’s not enough bandwidth / can cause data collisions
error rate - how many packets don’t reach their destination. higher rate = less reliable connections
transmission media - type of cable used as some have higher bandwidth (fibre optic is the best
client definition
a device capable of obtaining information from a server
server definition
a computer that manages a centralised resource
peer defintion
a computer of the same status / ability
client-server network
relies on a centralised server that all clients request services from. additional hardware is also needed e.g. high end powerful servers
useful if there are lots of computers & a high traffic environment
all computers can update central databases, backups are easily managed as they are done centrally in one go
centralised security can be installed & configured from the server (e.g. antivirus / firewall)
peer-peer network
all computers have equal status - each device can act like a client & a server. all devices can request & provide network services
useful for a small number of computers & low traffic environment
if it’s a home network no additional software would be needed, but in a corporate situation additional hardware may be needed
all files can be accessed by anyone and individual computers need to back up their own files
individual security needs to be installed on individual machines
topology definition
the way devices are arranged & connected on a network
node definition
any device connected to a network
server
powerful computer that provides service / resources
stores files, hosts websites, runs apps, manages emails
other devices can be added & access the server
star topology
the most common type of topology where every message goes through a central device. typical layout for classrooms, home networks, large organisations
can look the same as a client-server network but can run applications in either client-server or peer-to-peer model
benefits & limitations of star topology
benefits
fast & reliable as each device has its own connection to central node, reducing data collisions
if one device fails the rest won’t be affected
easy to add new devices by connecting them to just the central node
increased security - central node can screed data packets & reject corrupt ones
management of network can be done centrally
signal doesn’t need to be transmitted to all computers
simple to understand & troubleshoot
fewer cables needed (compared to mesh)
limitations
requires lots of cabling so can be expensive
if central node fails the whole network fails
bottlenecks can be caused
mesh topology
devices are connected to lots of devices with no central switch
expensive as more cables & maintenance is required
mostly used by military & emergency services to avoid a breakdown in communications as data can be rerouted
partial vs full mesh - in a partial mesh, most devices are connected to several other devices. in a full mesh, every device is connected to every other device
benefits & limitations of mesh topology
benefits
allows packets/data to be rerouted around a bottleneck
more reliable & robust - single failure won’t stop the rest of the network
limitations
needs more cabling (more connections)
more complicated to add/remove devices
more complicated to understand & troubleshoot
expensive
the internet
a worldwide collection of computer networks that are all linked together
internet protocols (IP)
a set of rules that ensure that devices can work together
URLs
we use URLs (Uniform Resource Locators, aka domain name) to access webpages as IP addresses are hard to remember
‘http’ tells the computer to use hypertext transfer protocol which puts packets together in the same web browser
‘www’ tells the webpage that it’s located on the world wide web
DNS servers
Domain Name Server / Domain Name System Server
when you type a URL into the web browser the computer will query a DNS server which has a list of all domain names and their associated IP addresses
all packets are addressed to IP addresses so to access the server you need to know the IP address. this is what DNS servers do. without them you would have to type IP addresses in to access a webpage
you search for something
it goes to the DNS server that attributes your search to an IP address
it finds the computer with that IP address
it sends the data pack to your computer using your IP address
hosting
when you place your website on a web server to let other people see it
a company can host different types of content like files, web pages, email, video, or game servers
you need to register the domain name with a domain registrar who ensures the domain name is unique & not already registered. each registered domain name has an associated IP address that is registered on a DNS
hosting companies charge a fee and provide facilities depending on the price e.g. storage space
the cloud
a network of servers that are accessed via the internet rather than being stored locally on a device
benefits
access files from anywhere in the world
collaborate and share data around the world easily
has the most up to date software & minimal user requirements
reduces reliance on network managers
flexible file storage
data is backed up & secure
limitations
no internet = no files
users have little control over your data - could be hacked
unclear who owns the data (user or provider?)
providers can increase their fees - too expensive
web servers & clients
every website is hosted on a web server - a dedicated computer on the internet that stores web pages. it holds the data needed for the website, content & layout
when someone wants to view the page their web browser sends a request to the web server which processes the request and prepares the data before sending it back. the web browser receives the data and displays the webpage
anyone can set up a web server but people typically use web hosting companies. they provide the space while web servers have the website files
the web server acts as a host, controlling access to a centralised resource. the web browser is a client, requesting access to that resource
wired connections: ethernet
aka LAN ethernet cable - the most common type of cable, uses wires to carry electrical signals between devices. common in offices & classrooms
advantages
more secure - you need physical access to the cables to get onto the network
connections are more stable, faster, less susceptible to interferences
disadvantages
requires physical cables to be connected - harder to move around
cables can be trip hazards - need to be routed along walls, under floors, through the ceiling
wireless connections: wi-fi
the most common type of wireless used in LANs
devices communicate with a WAP - often the centre of a home network. many schools & offices have wi-fi access + ethernet
advantages
don’t need to buy extra cables - devices have wifi adapters built in
no physical connections = ease of movement
disadvantages
vulnerable to hacking as radio waves can be intercepted
walls & obstructions reduce signal strength, electrical objects (e.g. fridges & microwaves) cause interference
transfer speeds are slower than ethernet
wireless connections: bluetooth
shorter range than wi-fi so is typically used for direct connections between 2 devices e.g. headphones, mice, keyboards. it’s possible to send files over bluetooth but its slow
advantages
ideal for personal devices
small range makes it harder to intercept data
uses less power than wi-fi
designed to make quick ad-hoc connections
disadvantages
only works over a very short range
slow transfer speeds
can still be intercepted by anyone in range
encryption on the internet
a method of scrambling data with a key code so it makes no sense and is protected
if encrypted data is intercepted e.g. on a public wi-fi network it will have no meaning - only devices with the correct key can read the data.
when visiting a secure website encryption is applied to keep details safe. this is called SSL - secure socket layer
you know data is encrypted when you see the padlock in your browser window and the website starts for htpps
IP addressing
IP (internet protocol) addresses are used for uniquely defining a computer within a network. they are dynamic (can change)
if you connect a device to one network it will be given an IP address and if you move it to another network, the IP address will change
IPv4
Internet Protocol Version 4
type of IP address that uses 32-bit numbers written as four 8-bit sections separated by full stops, each representing a number between 0-255
provides over 4 billion unique addresses but there are over 8 billion people on the planet (and people may have more than one device) so IPv6 is now used
IPv6
Internet Protocol Version 6
used now due to shortage of IPv4 addresses. new devices have both version 4 & 6 addresses so can work on any network
IPv6 addresses are represented by 128 bits divided into eight 16-bit sections written in hexadecimal and separated by colons
MAC addressing
Media Access Control
a MAC address is made up of 48 bits shown as 6 groups of 2 hexadecimals separated by colons or hyphens
every MAC address is completely unique and MAC addresses are static - they never change. they are printed on the NIC of the device by the manufacturer
standards
a set of guidelines that when used with different hardware & software allows them to work with each other (compatibility) and allow data exchange (interoperability)
standards give manufacturers & software developers the ability to create hardware and software that will function together
countries that use different plug sockets and devices that use different charger cables are examples of where standards are not used
examples of computer standards:
HTML - standard for creating websites, allows them to be viewed on the world wide web using browser software
ethernet - standard for wired network cables that allows the network to function
USB - standard defining physical connector used for connecting peripheral devices to computers
wi-fi - standard allowing wireless devices to communicate on a LAN
protocols
a set of rules that govern communication on a network
standards outline the broad guidelines and protocols focus on specific procedures
protocols: http & https
http (hypertext transfer protocol) is used for accessing and receiving web pages on the internet which are made in HTML (hypertext mark up language). it requests a web page from the web server. the server then sends its response including the web page
https (hypertext transfer protocol secure) encrypts the information so it can’t be understood by an eavesdropper. most websites use it to deal with personal data e.g. banks, online shops and social networks
protocols: FTP
file transfer protocol - used for sending / retrieving files to / from a FTP server, allowing files to be taken from a computer to the server
how an email is sent with protocols
when an email is sent from a computer it will first be sent to a mail server using the SMTP protocol. it’s then forwarded on by other SMTP servers. when it reaches its destination server it’s stored and the user computer can use POP or IMAP to access the email
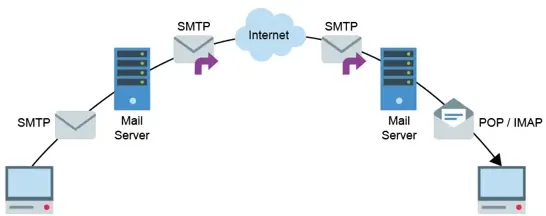
protocols: SMTP
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol - email protocol used for sending emails
email software send the email to the SMTP server used by the person, which relays the message through various other servers (mail relays), eventually arriving at the destination mail server
protocols: POP
post office protocol - downloads every new message to your device, leaving them no longer available on the server (like sending a letter through a post office)
protocols: IMAP
internet message access protocol - downloads an email from a server but will leave a copy of it there which can be accessed by multiple devices and is only removed if the user deletes them
communication protocols
a set of rules for transferring data over the internet
protocols: TCP & IP
TCP (transmission control protocol) breaks up messages sent over the internet into small chunks (packets) and reassembles the packets at the other end. also detects errors and resends lost messages
IP (internet protocol) routes the individual packets from one IP address to another
the TCP & IP protocol stack has four layers and enables communication on the internet
layers
networks rely on many complex parts all working together at the same time. managing the complexity of networks is helped with layers
a layer is a sub part of a more complex task. dividing the network tasks into layers reduces the complexity and makes each layer more manageable. example is the TCP/IP protocol stack (4-layer model)
advantages of layers
self contained - managing, repairing, upgrading is easier as each one can be worked on independently
allow focus on specific parts of a protocol without affecting other parts
promotes data exchange / interoperability between hardware & software
malware
an executable program that runs on a computer and is usually installed without the user’s knowledge
viruses, worms, trojans, ransomware, spyware
malware: viruses & worms
viruses infect computers and can then replicate their code in other programs & infect other computers. harm the computer by deleting / corrupting / modifying files
worms replicate themselves to spread to other computers. can slow down networks and computers but cause no damage to attacked computers
malware: trojans
a program / game / cracked file that’s something the user wants so they are tricked into installing the program. have negative program code which causes damage / takes control / provides access to computer
malware: ransomware
holds a computer hostage by locking / encrypting data and denying access to it
if data is encrypted you can’t recover it unless backups are available. but there’s no guarantee that files will be released once you pay the ransom
malware: spyware
installed without the user’s knowledge (usually bundled in legitimate looking software downloads)
collects personal / sensitive data (e.g. login details & browsing habits) and can monitor user activity like keystrokes (keylogging) to obtain passwords & login details. sends data to a remote attacker
vulnerabilities in systems that hackers exploit
unpatched software - if software updates / security updates aren’t installed software will be vulnerable
out of date anti malware software - if antivirus isn’t regularly updated it can’t detect more up to date viruses
social engineering
the art of manipulating people into providing confidential data / unauthorised access to a computer system.
impersonation - pretend to be someone to trick someone into giving personal info
baiting - leave a drive in plain sight / offer free downloads to trick people into downloading malware
social engineering: shoulder surfing
the ability to get information / passwords by observing as someone types them in
e.g. looking over someone’s shoulder, using cameras, observing from a distance
social engineering: phishing
sending emails/texts/phone calls pretending to be from a trusted organisation to get personal information (usernames, passwords, credit card details)
social engineering: pharming
a type of cyberattack that redirects users from a real website to a fake one, either with malware (using a virus/trojan) or with DNS server poisoning (harder way of exploiting DNS server vulnerabilities)
denial of service attacks (DoS)
hacker will use/infect a computer so it sends as many requests to the server as it can (flood the server). the server can’t respond fast enough so it slows down / goes offline
distributed DoS attack (DDoS) - many computers are used to send requests all at the same time
man in the middle attack (MITM)
attacker intercepts communications between user & server, and can eavesdrop, find passwords / personal info, add info to web pages / emails, and see, steal, change data being sent
unencrypted wi-fi make it easy to perform a MITM attack, and fake websites are also used to trick users into entering details
MITM attacks can be prevented by encryption, secure wifi, VPNs, and digital certificates to verify trusted websites
baiting
criminals can leave USB sticks containing malware in public spaces. someone could pick it up & insert it into their computer, and a hacker can gain access to files, personal data, and system resources
data interception & theft
thieves/hackers can compromise usernames and passwords / other sensitive data by using devices like a packet sniffer
a packet sniffer will be able to collect the data that is being transferred on a network, and a thief can use this data to gain unauthorised access to websites, companies and more
attacks on digital devices
loss of mobile phone = loss of data stored on it - passwords, account numbers, card details
malware targeting digital devices can create back doors to give attackers access to your device
malicious apps can appear legitimate but lead to fraudulent charges on phone bill / theft of personal info
brute force attacks
hacker will try every combo until they find the right password - computer programs used (can try millions of passwords a second). purpose is usually to manipulate / delete data
prevent through strong passwords, account lockout after an amount of failed login attempts, 2FA, and CAPCHA to prevent bots
SQL injection
takes advantage of web input forms to access/destroy data. SQL commands are input into web forms instead of expected data and vulnerable web applications interpret it which can cause damage / release info
if a website doesn’t check inputs properly, malicious code can be run and the attacker could be able to view private data e.g. usernames / passwords. they can log in and delete / change data
prevent through input validation, not showing detailed database errors, and limiting access to the database / keeping it separate from user input
people as weak points
people are week points in systems because human errors can lead to issues
not locking doors to computer / server rooms
not locking devices
sharing passwords
not encrypting data
not keeping operating systems / anti-malware up to date
penetrating testing / pen testing
deliberately trying to find security holes in a system
someone is employed to try find vulnerabilities in a system - they attempt to break in and report back their findings. goal is to identify targets of attacks and possible entry points
anti malware software
will detect malware and send it to the antivirus company to verify it’s malware and create a signature of the virus. they add it to their virus database and tell computers to run an update
but viruses can morph to avoid detection so creating signatures can be hard
encrypting files etc
files can be encrypted individually on a computer using a password so they can only be viewed if you have the password
computer drives can be encrypted so a password is needed to access info and this can prevent a hacker from understanding the contents of the hard drive if it’s installed on a different computer
special hardware can be purchased which encrypts removable media on the disk
firewalls
monitors and controls network traffic between trusted internal and untrusted external networks
Blocks / allows data based on security rules to prevent unauthorised access or attacks
Uses packet filtering to drop data that doesn’t match rules
Can be hardware (e.g. built into home wifi router) or software
packet inspection (more advanced) examines contents inside data packets (not just header info) and checks for suspicious / harmful content and illegal / unwanted activities (malware, hacking attempts)
port bocking - firewall can block access to certain ports on the network
user access levels
can be set on disks, folders, or individual files
read (view/open), write (change info) or execute (run program applications / script, open file as a program)
password policy
make sure passwords have secure features e.g. minimum length & symbols. may also require password changes every so often
passwords are checked to make sure they conform to parameters of policy
physical security
hardware/software/networks are protected by physical methods e.g. CCTV, intruder alarms, locks, walls / fences, security guards, ID cards