6.2: Receptors
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
What is the function of a Pacinian Corpuscle and what does it demonstrate?
It is used as a pressure receptor in the skin
Demonstrates that
Receptors only respond to specific stimuli as the pacinian corpuscle only responds to mechanical pressure
Stimulation of a receptor leads to the establishment of a generator potential as when the threshold is reached, action potentials are sent
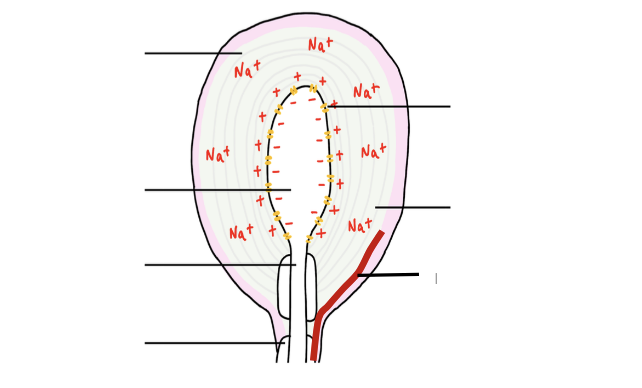
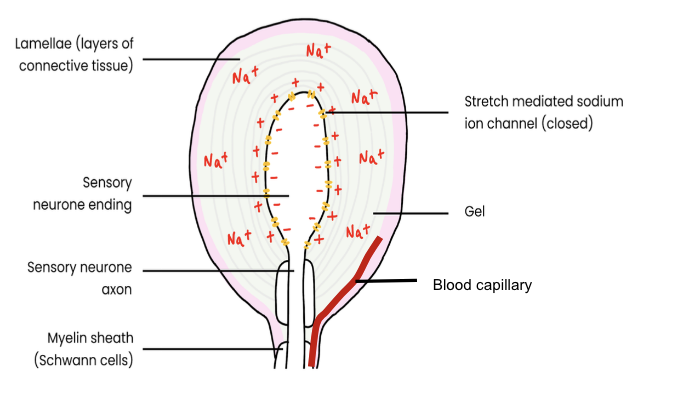
What is the structure of a Pacinian Corpuscle? (label diagram)
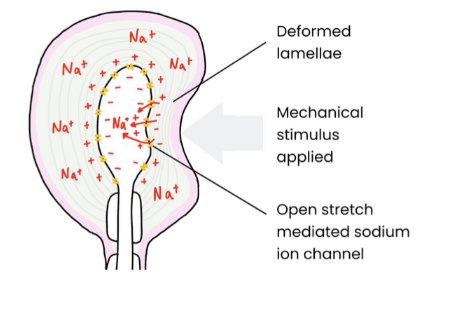
How is a generator potential established in a Pacinian Corpuscle?
A mechanical stimulus deforms the lamalle and stretch-mediated sodium ion channels
So sodium ion channels in the membrane open and Na+ diffuses into the sensory neuron
An increase in pressure causes more Na+ channels to open and more Na+ to enter
This causes depolarisation, leading to a generator potential
If the generator potential reaches threshold it triggers an action potential
What are the differences between rod and cone cells?
Greater number of cone cells than rod cells
Rod cells mainly at the periphery of the retina, cone cells mainly at the fovea with fewer at the retina
Rod cells give poor visual acuity, cone cells give good visual acuity
Rod cells are sensitive to low intensity light, cone cells are not sensitive to low intensity light
Only one type of rod cells, three types of cone cells responding to different wavelengths of light
What is spatial summation?
When multiple presynaptic neurons form a junction with a single neurone
Explain the differences in sensitivity to light for rods and codes in the retina
Several rods are connected to a single neurone
So spatial summation overcomes threshold to generate an action potential
One cone is connected to a single neurone
No spatial summation, so does not reach threshold, so no action potential produced
What is visual acuity?
How clearly a person can see at a specific distance
Explain the differences in visual acuity for rods and codes in the retina
Several rods are connected to a single nuerone
So several rods send a single set of impulses to the brain
So they cannot distinguish between seperate sources of light
One cone is connected to a single neurone
Sp they send separate sets of impulses to the brain
So they can distinguish between seperate sources of light
Explain the differences in sensitivity to colour for rods and codes in the retina
Rods have only 1 type with 1 pigment
So they allow for monochromatic vision
Cones have 3 types (red, green and blue sensitive)
Different optical pigments absorb different wavelengths
Stimulating different combinations of cones gives a range of colour perception