1. Methods in Neuroscience
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
sensory system
part of the NS that reports info about the state of the organism and environment
motor system
part of the NS that organizes and generates movement
associational system
part of the NS that provides higher order brain functions, such as perception, attention, memory, emotions, language, and thinking
central nervous system
part of NS subdivided into brain and spinal cord
peripheral nervous system
part of NS subdivided into sensory, somatic, and autonomic divisions
reticular theory
idea that all neurons form a continuously connected network
neuron doctrine
neurons communicate at synapses rather than through physical activity
neuron
NS cell which processes info, senses environmental changes, communicates changes via electrical signaling, and controls body responses
dendrite
branchy target for synaptic input from axon terminals of other neurons whose complexity increases with the number of inputs
axon
shaft responsible for signal transduction from cell body; reads out info
action potential
all or nothing changes in electrical potential made by Nodes of Ranvier, requiring Na to allow neuron to reach threshold and K to bring it back down
Node of Ranvier
gap between myelin that propagates action potentials
saltatory conduction
action potentials jumping between Nodes of Ranvier, enhancing velocity
presynaptic terminal
where molecules are secreted into synaptic cleft, immediately adjacent to dendrite of next cell
postsynaptic specialization
areas of dendrites w/ receptors for molecules to bind, immediately adjacent to axon terminal of previous cell
synaptic cleft
gap between pre- and post- synaptic terminals
glia
NS cell which supports the signaling function of, insulates, nourishes, and supports neurons; includes astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, Schwann cells, microglia, and stem cells
astrocyte
CNS glial cell maintaining appropriate chemical environment for neuronal signaling, including blood-brain barrier formation
oligodendrocyte
CNS myelin generator
Schwann cell
PNS myelin generator
microglia
scavenger cells that remove cellular debris from injury sites and cell turnover, secrete cytokines
glial stem cell
precursor to glia
afferent
carries info to CNS
efferent
carries info away from CNS
interneuron
CNS cell that participates in local aspects of circuit function, such as DRG
agonist
muscle that performs target movement (extensor in knee jerk reflex)
antagonist
muscle that opposes target movement (flexor in knee jerk reflex)
divergent circuit
neural circuit that spreads info
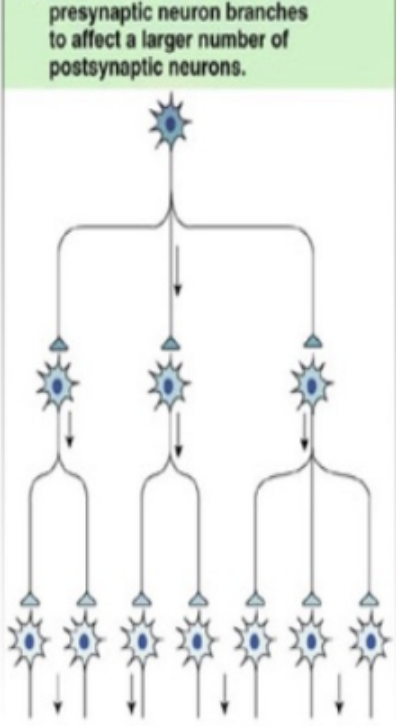
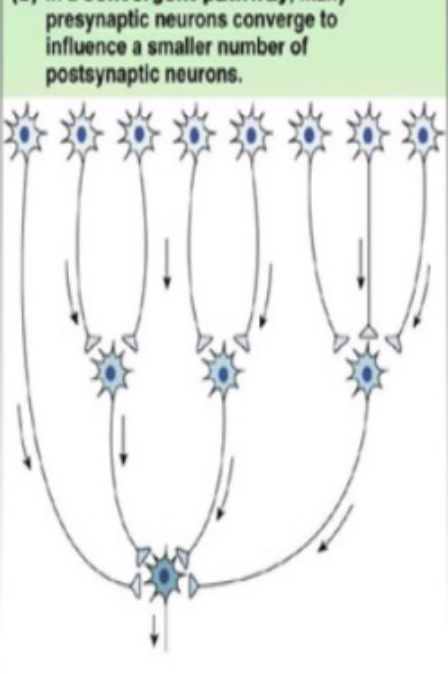
convergent circuit
neural circuit that integrates info
electrophysiological recording
technique to probe neural circuit function, subdivided into intracellular and extracellular recording
extracellular recording
an electrode is placed outside a neuron to detect temporal patterns of AP activity
intracellular recording
an electrode is placed inside a neuron to detect small. graded changes in electrical potential that can trigger APs and assesss communication among neurons w/in a circuit
calcium imaging
recording transient changes in [Ca] ion associated w/ AP firing to infer neural activity changes, where neurons are labeled w/ a Ca sensitive dye and then imaged
optogenetic
method introducing opsins into the NS so a neuron can artificially fire from light to assess neural circuit activity
opsin
bacterial channels transducing light energy into chemical signal activating channel proteins