ISDS 351 Ch 6
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Big data
data collections that are so enormous (terabytes or more) and complex (from sensor data to social media data) that traditional data management software, hardware, and analysis processes are incapable of dealing with them
Characteristics of Big Data
Volume: size of data
Velocity: the rate at which new data is being generated
Value: the worth of the data in decision making
Variety: structured v unstructured data
Veracity: a measure of the quality of the data
Sources of Big Data
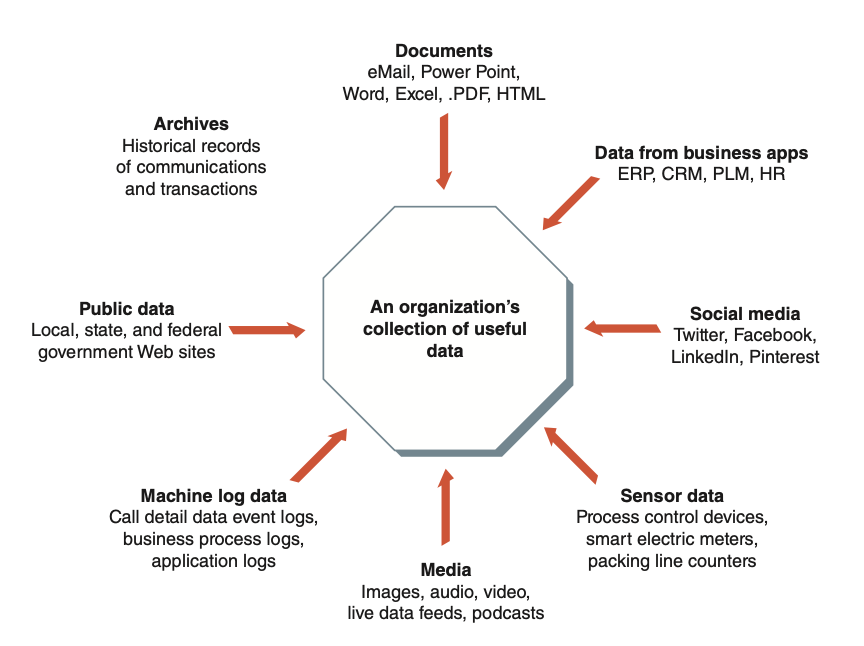
Challenges of Big Data
With so much data readily available business users can have a hard time;
Finding the information they need to make decisions.
Trusting the validity of the data they can access.
Data warehouse
A large database that holds business information from many sources in the enterprise, covering all aspects of the company’s processes, products, and customers.
Charactersitics of a data warehouse
Large: holds billions of records and petabytes of data
Multiple sources: data comes from many sources
Historical: typically 5+ years of data
Cross organizational access and analysis: data accessed, used, and analyzed by users across the organization to support multiple business processes and decision making
Supports various types of analyses and reporting: drill down analysis, development of metrics, identification of trends
Extract transform load (ETL) process
A data handling process that takes data from a variety of sources, edits and transforms it into the format used in the data warehouse, and then loads this data into the warehouse.
Data mart
A subset of a data warehouse that is used by small and medium-sized businesses and departments within large companies to support decision making.
Data lake
A “store everything” approach to big data that saves all the data in its raw and unaltered form.
NoSQL database
A way to store and retrieve data that is modeled using some means other than the simple two-dimensional tabular relations used in relational databases. impro
More flexible than relational database tables
Provide improved access speed and redundancy
Categories of NoSQL Databases
Key-value: two columns (“key” and “value”)
Document: Store, retrieve, and manage document-oriented information
Graph: Well-suited for analyzing interconnections
Column: store data in columns
Hadoop
An open-source software framework including several software modules that provide a means for storing and processing extremely large data sets.
* Limitation: can only perform batch processing
Hadoop Distributed File System
A system used for data storage that divides the data into subsets and distributes the subsets onto different servers for processing.
MapReduce program
A composite program that consists of a Map procedure that performs filtering and sorting and a Reduce method that performs a summary operation.
In-memory database
A database management system that stores the entire database in random access memory (RAM).
Faster access to data.
Enable the analysis of big data and other
challenging data-processing applications
Feasible
Business Intelligence (BI)
A wide range of applications, practices, and technologies for the extraction, transformation, integration, visualization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data to support improved decision making.
Analytics
The extensive use of data and quantitative analysis to support fact-based decision making within organizations.
Benefits of BI and Analytics
Detect fraud
Improve forecasting
Increase sales
Optimize operations
Reduce costs
Data scientist
An individual who combines strong business acumen, a deep understanding of analytics, and a healthy appreciation of the limitations of data, tools, and techniques to deliver real improvements in decision making.
Components required for effective BI and Analytics
Existence of a solid data management program
Creative data scientists
Strong commitment to data-driven decision making
BI and Analytics Tools
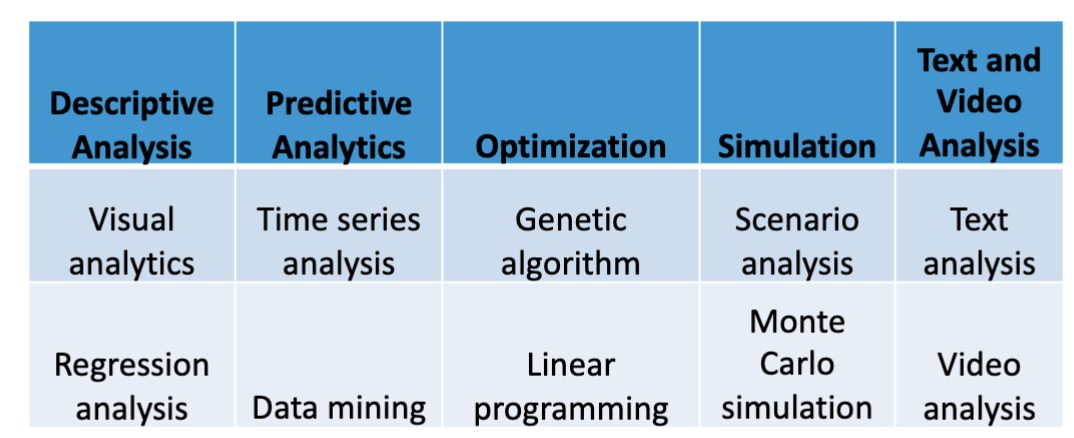
Descriptive analysis
A preliminary data processing stage used to identify patterns in the data and answer questions about who, what, where, when, and to what extent.
Two types:
Visual analytics
Regression analysis
Visual analytics
The presentation of data in a pictorial or graphical format.
Word cloud
A visual depiction of a set of words that have been grouped together because of the frequency of their occurrence.
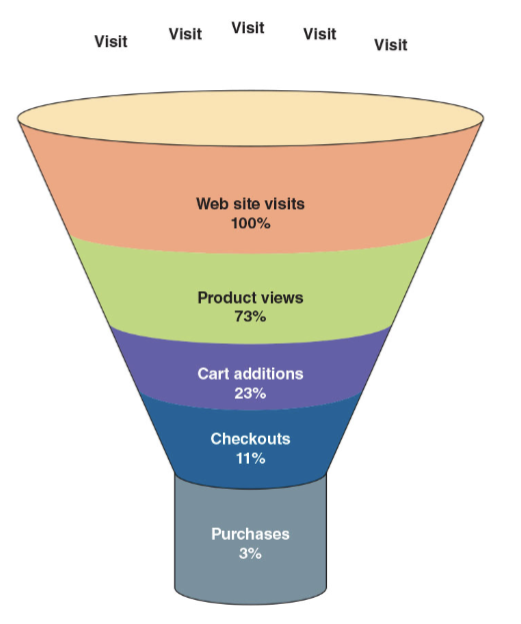
Conversion funnel
A graphical representation that summarizes the steps a consumer takes in making the decision to buy your product and become a customer.
Regression analysis
A method for determining the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables.
Predictive analysis
A set of techniques used to analyze current data to identify future probabilities and trends, as well make predictions about the future.
Time series analysis
The use of statistical methods to analyze time series data and determine useful statistics and characteristics about the data.
Data mining
A BI analytics tool used to explore large amounts of data for hidden patterns to predict future trends and behaviors for use in decision making.
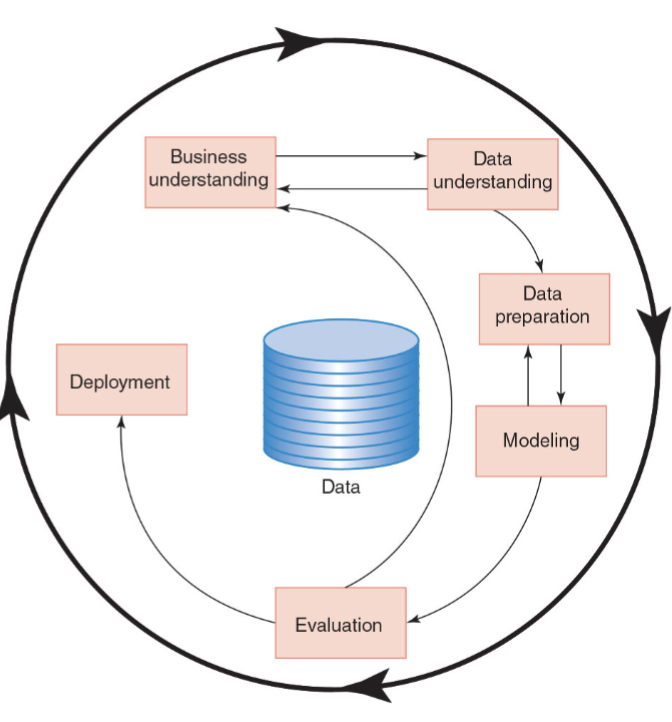
Cross-Industry Process for Data Mining (CRISP-DM)
A six-phase structured approach for the planning and execution of a data mining project.
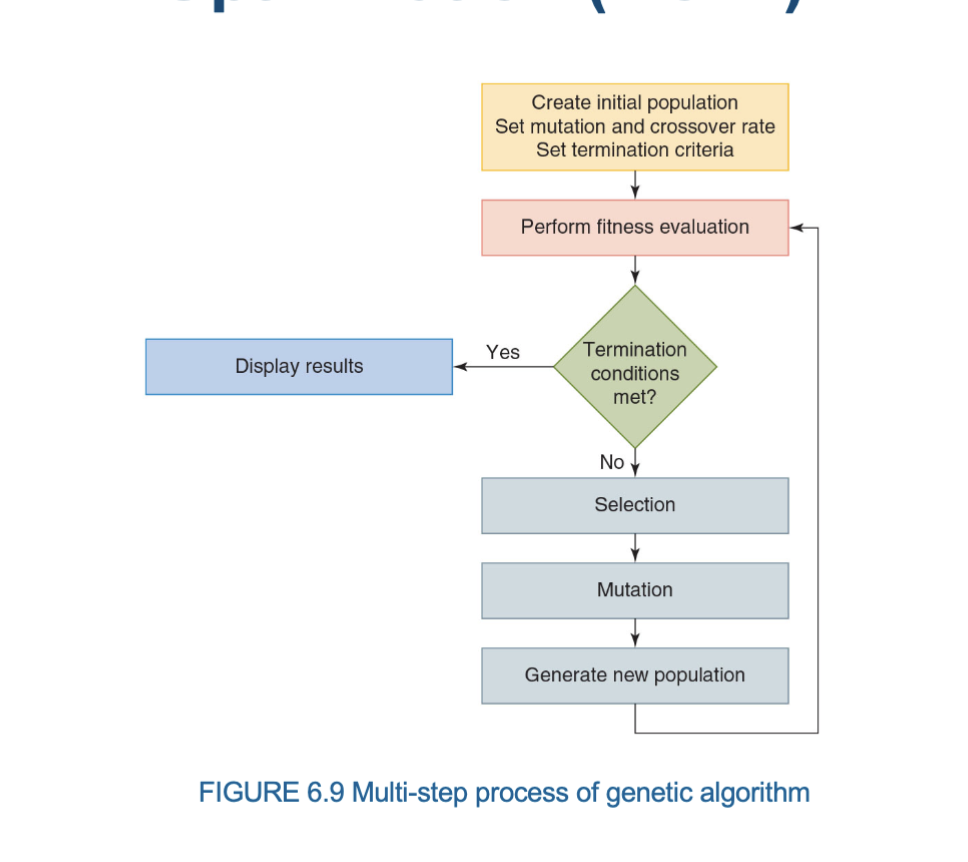
Genetic algorithm
A technique that employs a natural selection-like process to find approximate solutions to optimization and search problems
Linear programming
A technique for finding the optimum value (largest or smallest, depending on
the problem) of a linear expression (called the objective function) that is calculated based on the value of a set of decision variables that are subject to a set of constraints.
Computer simulation
involves using a model expressed in the form of a computer program to emulate the dynamic responses of a real-world system to various inputs.
Scenario analysis
A process for predicting future values based on certain potential events.
Monte Carlo simulation
A simulation that enables you to see a spectrum of thousands of possible outcomes, considering not only the many variables involved, but also the range of potential values for each of those variables.
Text analysis
A process for extracting value from large quantities of unstructured text data
Video analysis
The process of obtaining information or insights from video footage.
Self-service analytics
Training, techniques, and processes that empower end users to work independently to access data from approved sources to perform their own analyses using an endorsed set of tools.
Advantages of self-service analytics
Gets valuable data into the hands of end users
Encourages fact-based decision making
Accelerates decision making
Provides a solution to the shortage of data scientists