Reproductive A&P
1/32
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
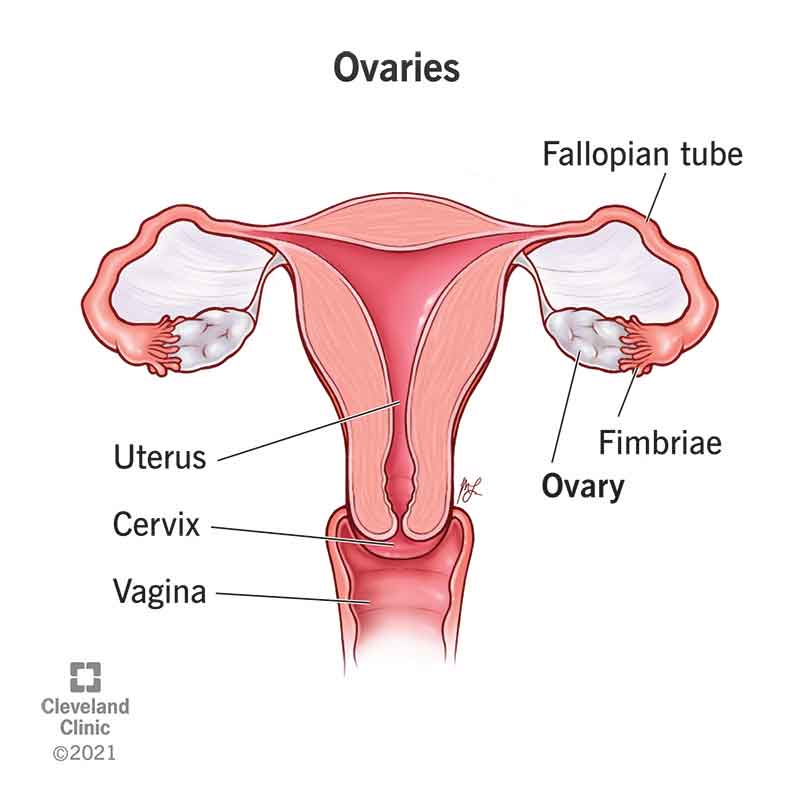
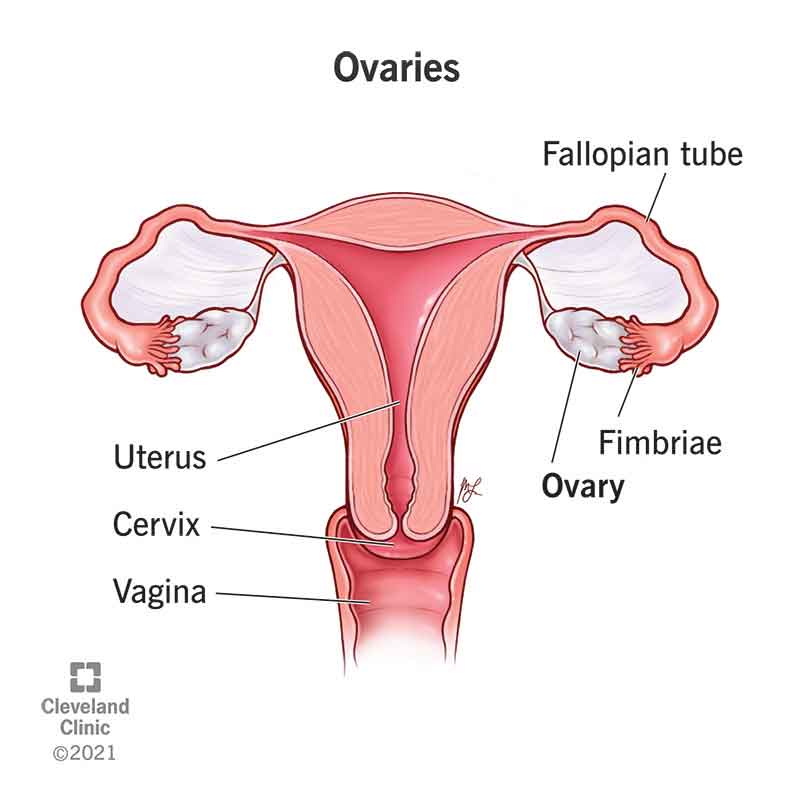
Ovary
paired, oval organs attached to the posterior surface of the broad ligament of the uterus; produce sex hormones (estrogen and progesterone); produce oocytes/eggs
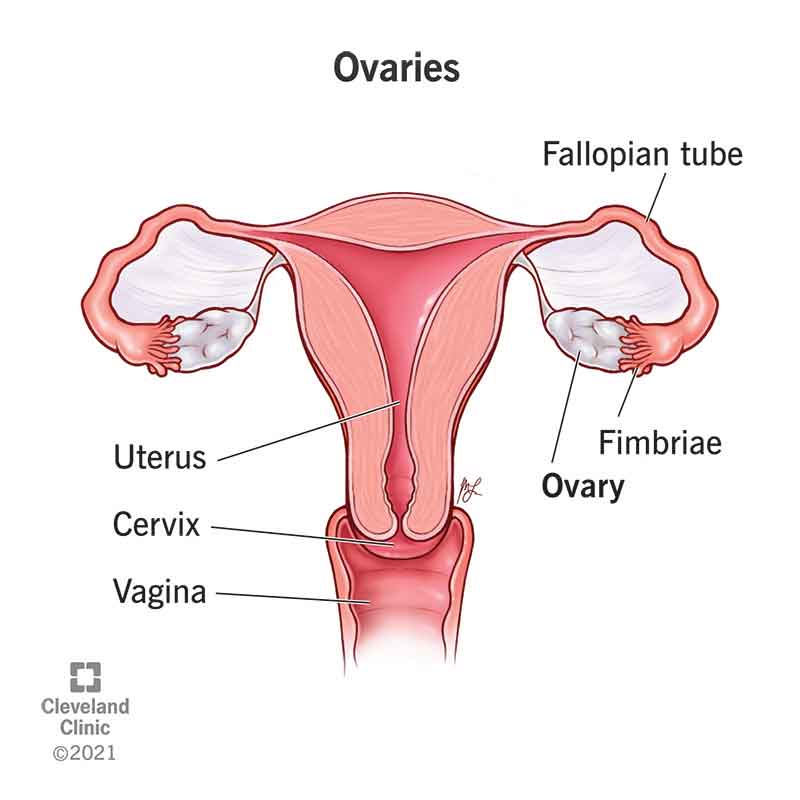
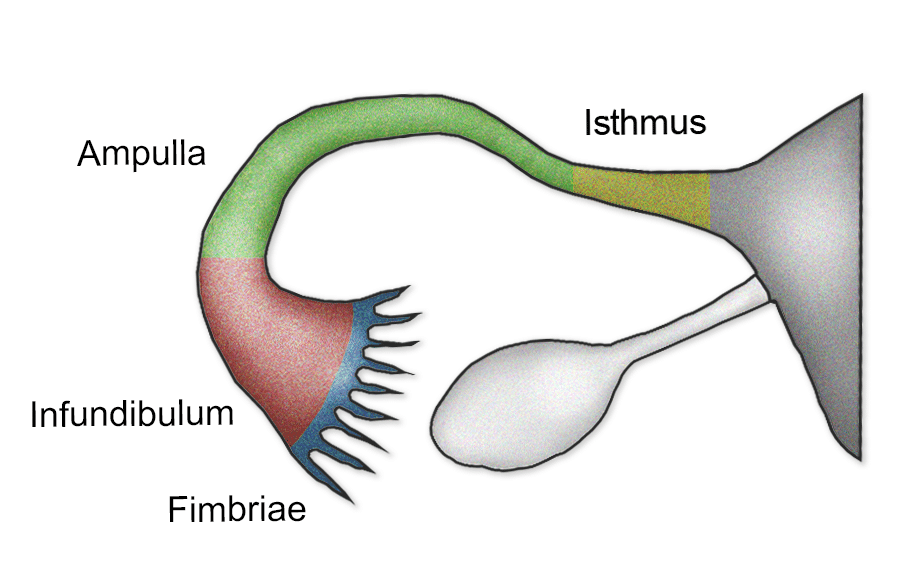
uterine tube
muscular tubes in the female reproductive system that transport eggs from the ovaries to the uterus; about 10-12 cm long and divided into fimbriae, infundibulum, ampulla and isthmus
fimbriae
finger-like projections at the end of the Fallopian tubes that catch and sweep eggs into the tubes for transport
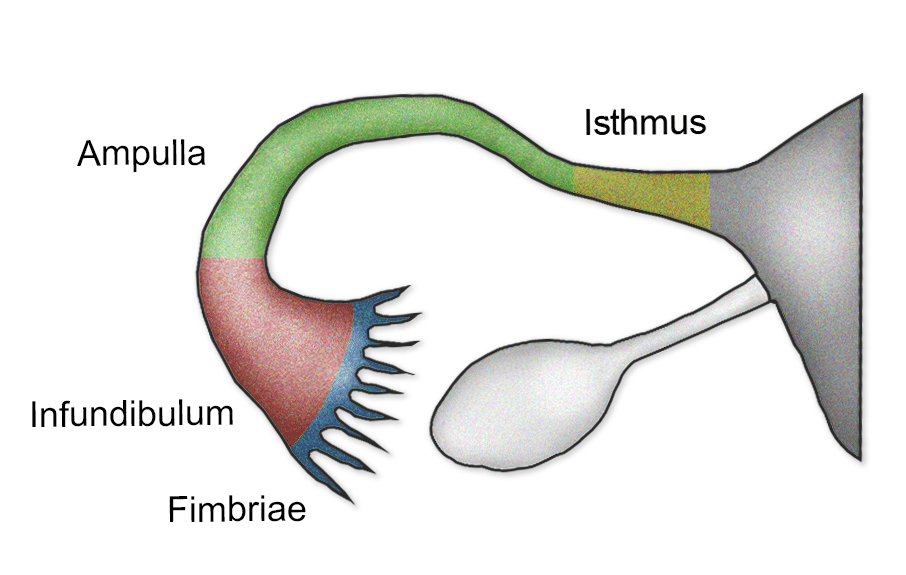
infundibulum
the funnel-shaped, outer end of the Fallopian tube; characterized by finger-like projections called fimbriae
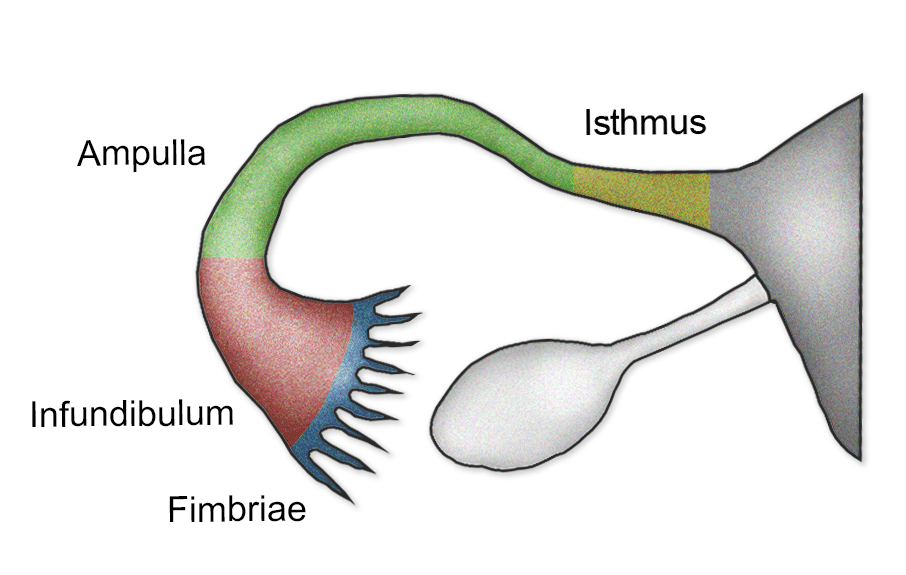
ampulla
the widest, longest section of the fallopian tube, located between the funnel shaped infundibulum and the isthmus
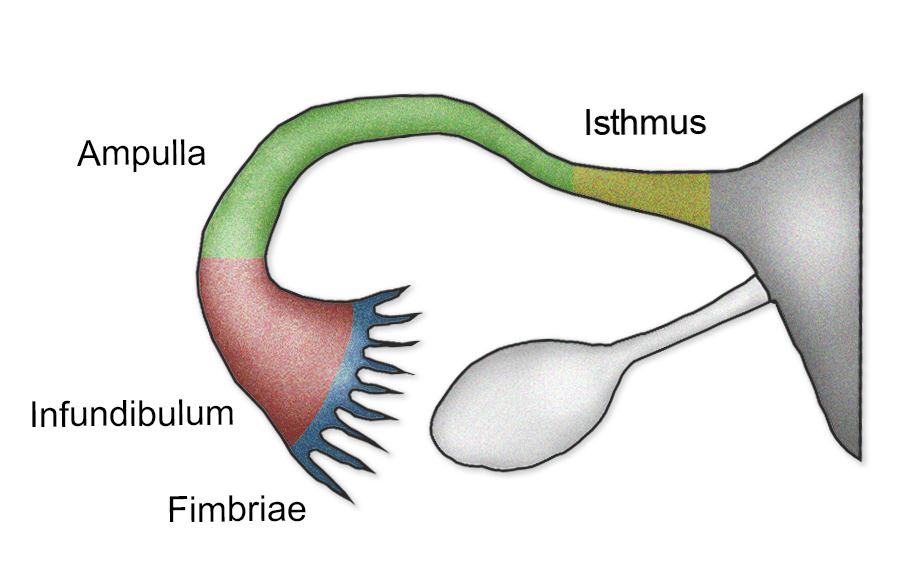
isthmus
narrow, constricted, and medial portion of the Fallopian tube, located between the ampulla and the intramural part that connects to the uterus
uterus
a pear-shaped organ that plays a critical role in menstruation, fertility and pregnancy; hollow and muscular and sits between the rectum and bladder in the pelvis
perimetrium
outer serous layer of the uterus— thin, protective membrane that reduces friction between the uterus and surrounding organs; main functions are to protect, provide structural integrity and anchoring to other pelvic structures
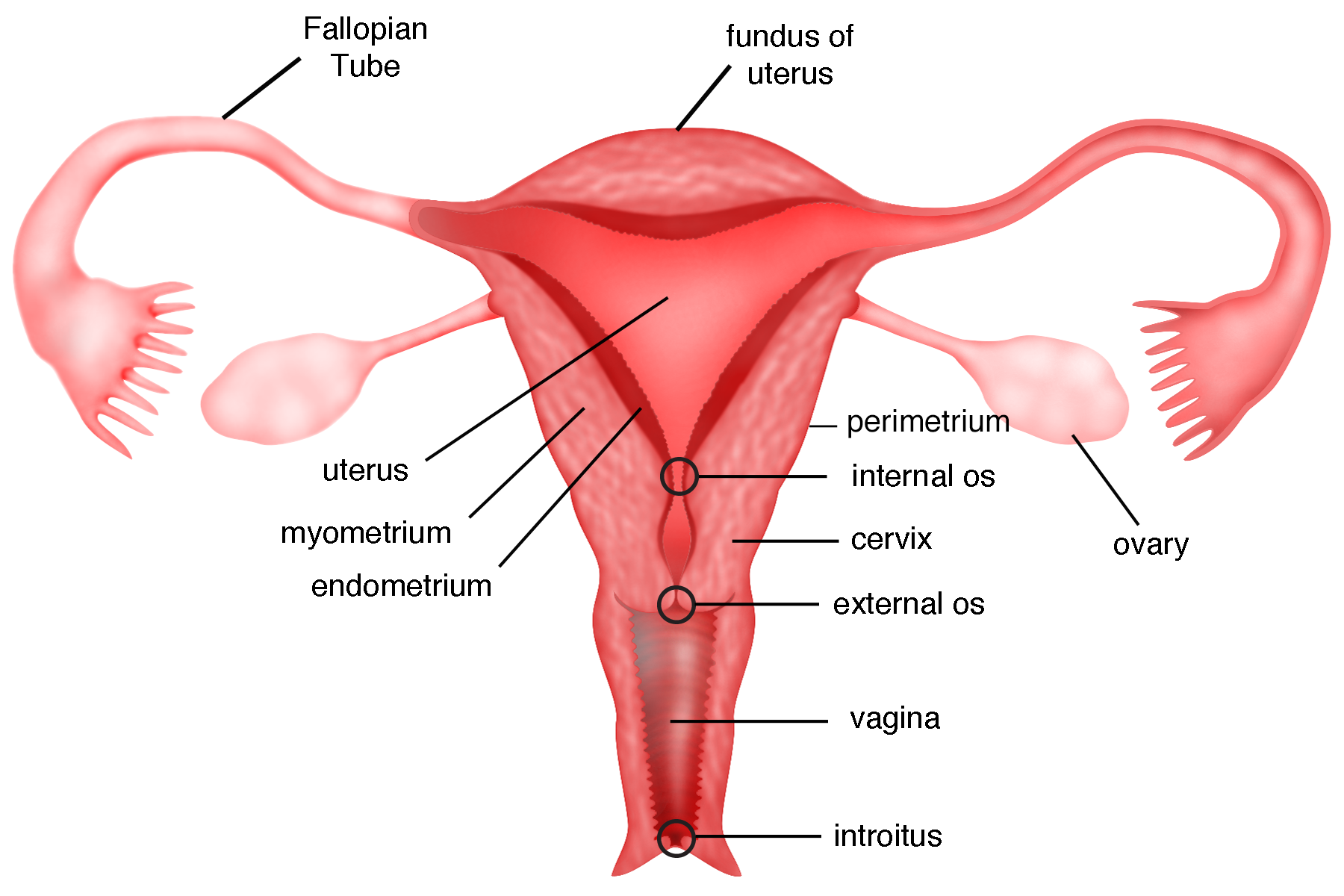
myometrium
muscular middle layer of the uterus, composed of smooth muscle cells arranged three layers that contract to expel the fetus during childbirth
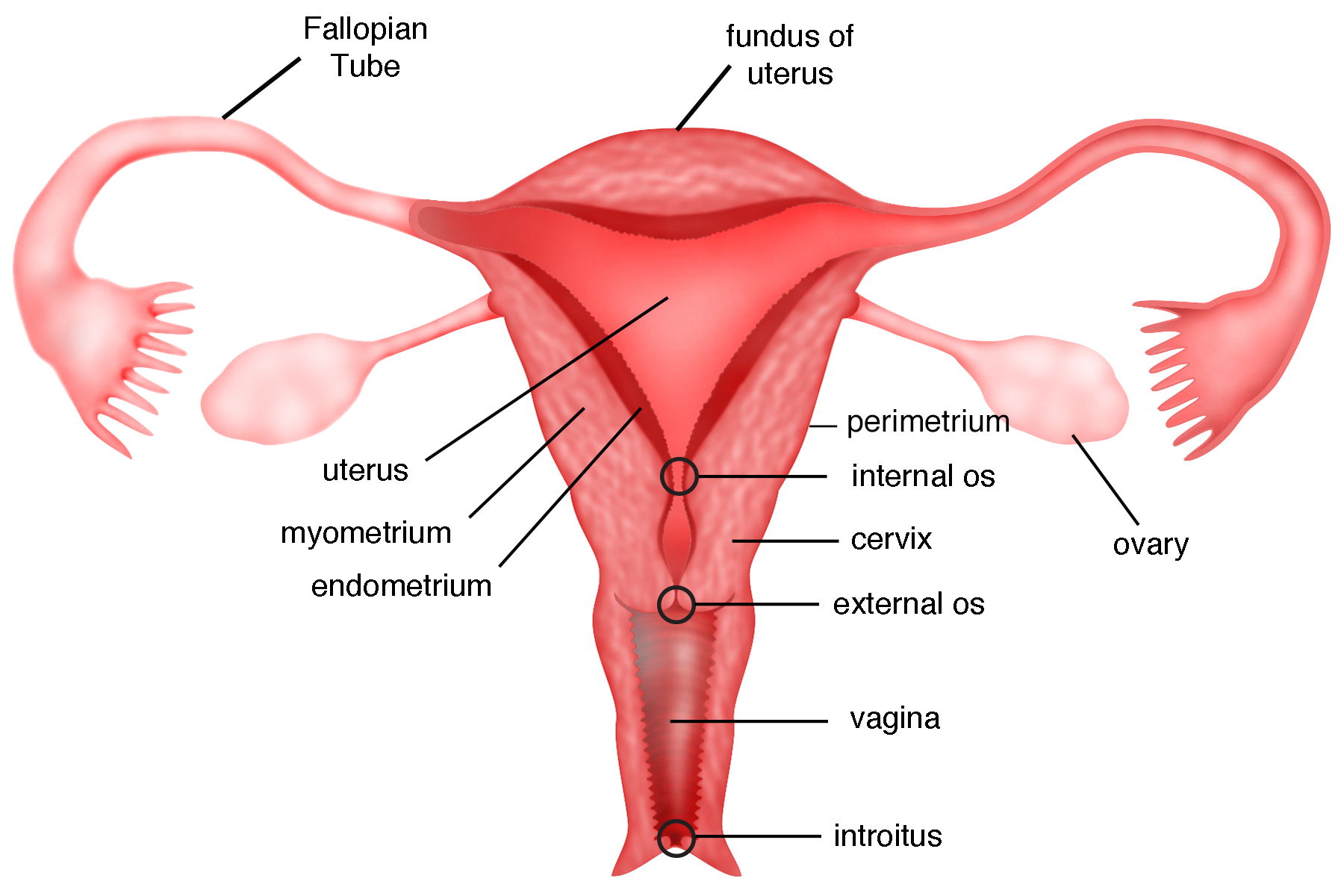
endometrium
the inner lining of the uterus that thickens each month to prepare for a potential pregnancy; sheds during menstruation if egg is not fertilized
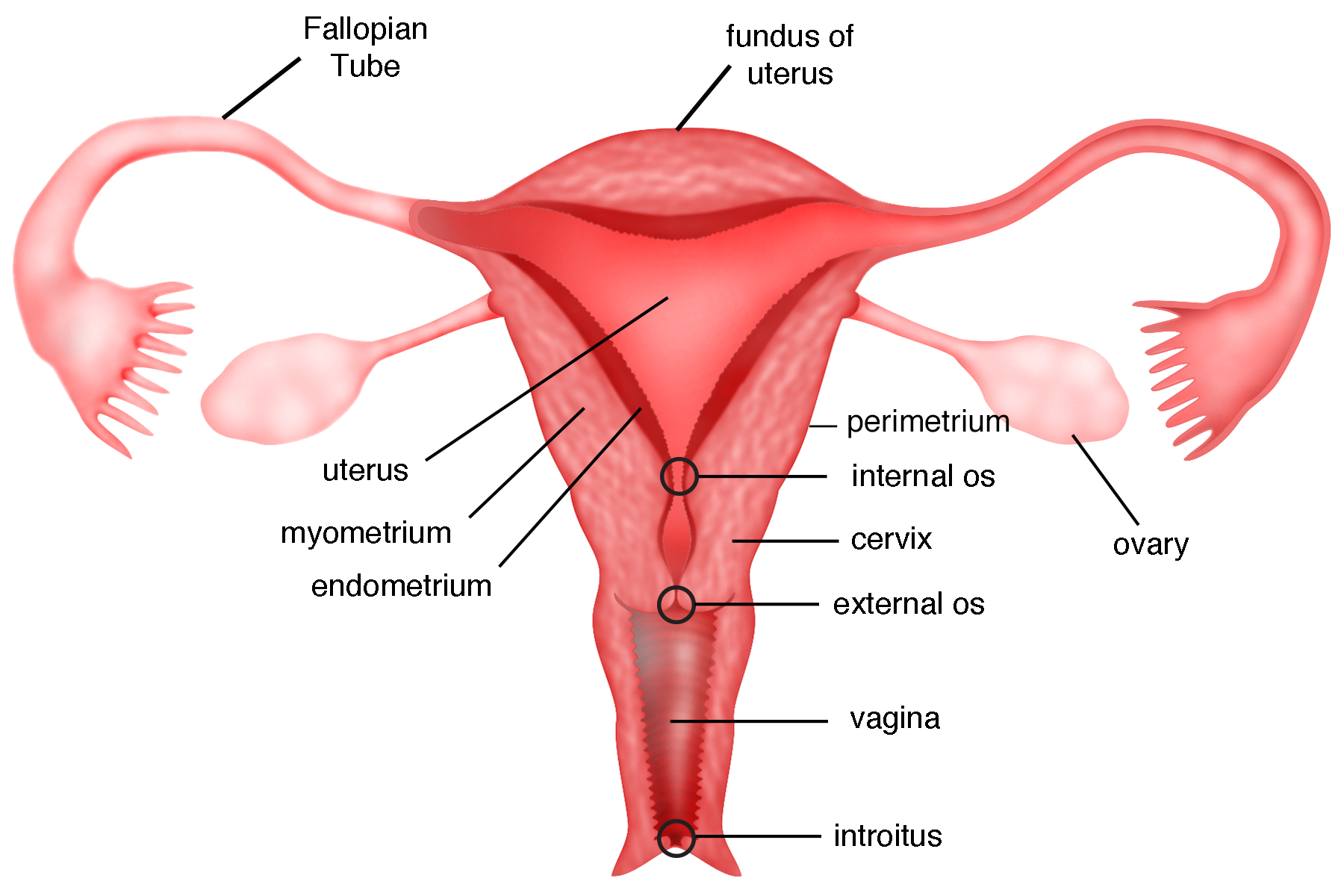
uterine cavity
the hollow space within the uterus lined by the endometrium; central space where the fertilized egg implants and a fetus develops
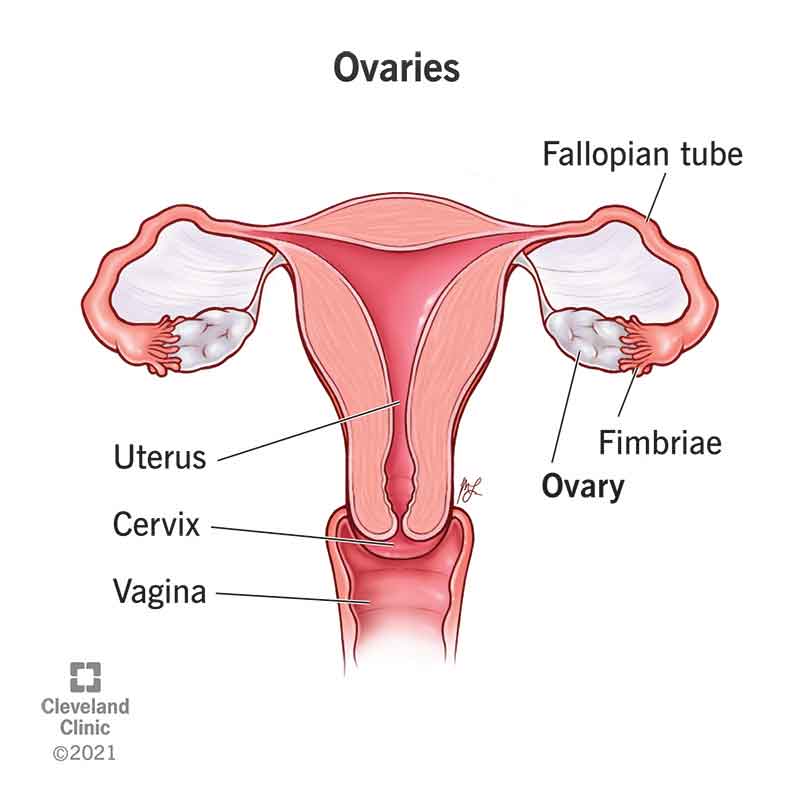
cervix
a small canal that connects the uterus and vagina; allows fluids to leave and enter the uterus; widens/dilates during childbirth to accommodate the fetus
vagina
a stretchy, muscular tube that plays important roles in conception, childbirth, menstruation and other sexual functions
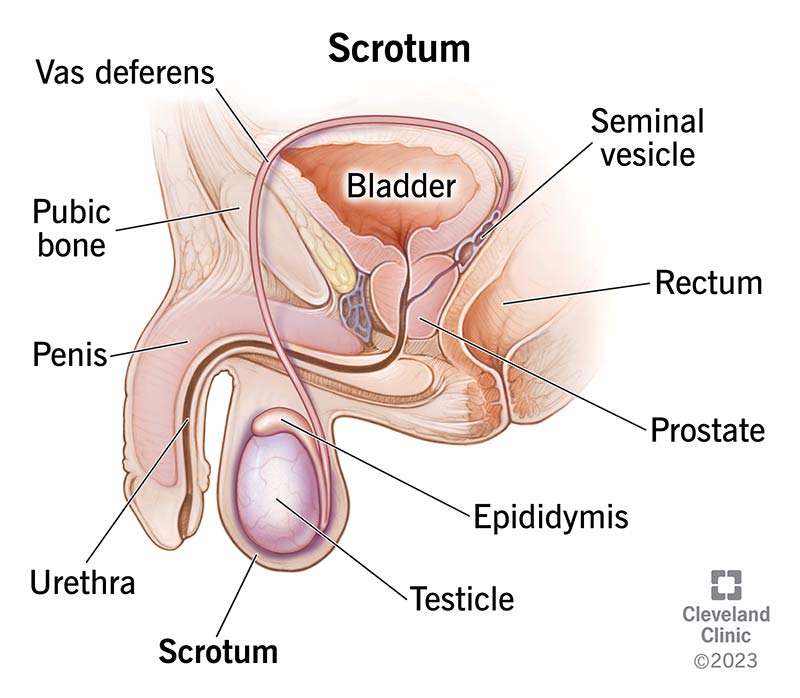
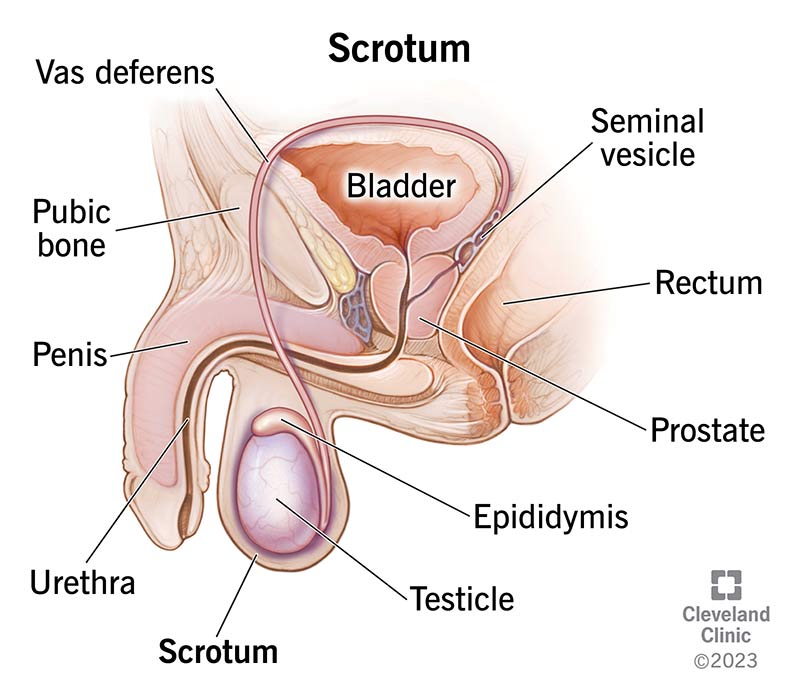
scrotum
a sac of skin and muscle that contains the testes, epididymis and the beginning of the spermatic cord
testes
male reproductive glands that produce sperm and testosterone; a fibrous capsule containing lobules with coiled seminiferous tubules
seminiferous tubules
highly coiled tubes located within the testes that transport sperm
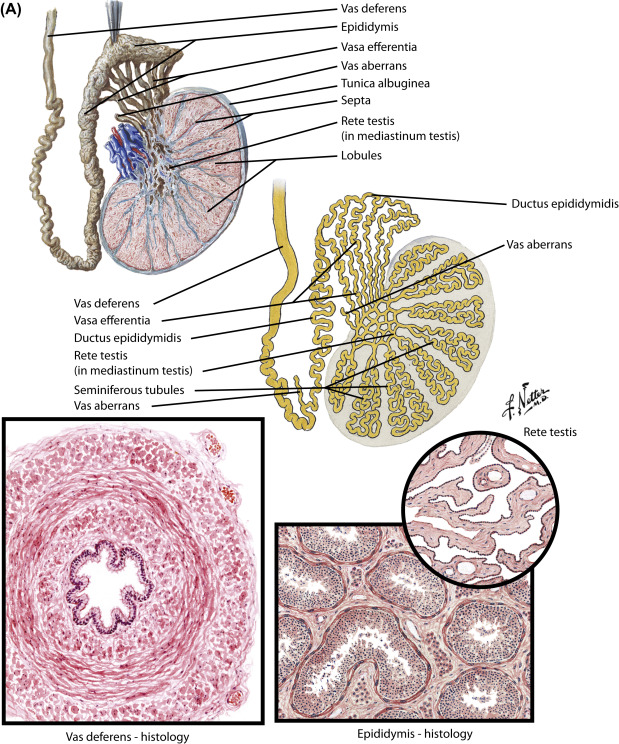
epididymis
a coiled tube located on the posterior part os the testis, divided into three regions (head, body and tail); where sperm mature and stored here as they travel from the testes with the walls gradually shining and reabsorbing fluid to concentrate the sperm as they move from head to tail; connected to vas deferens
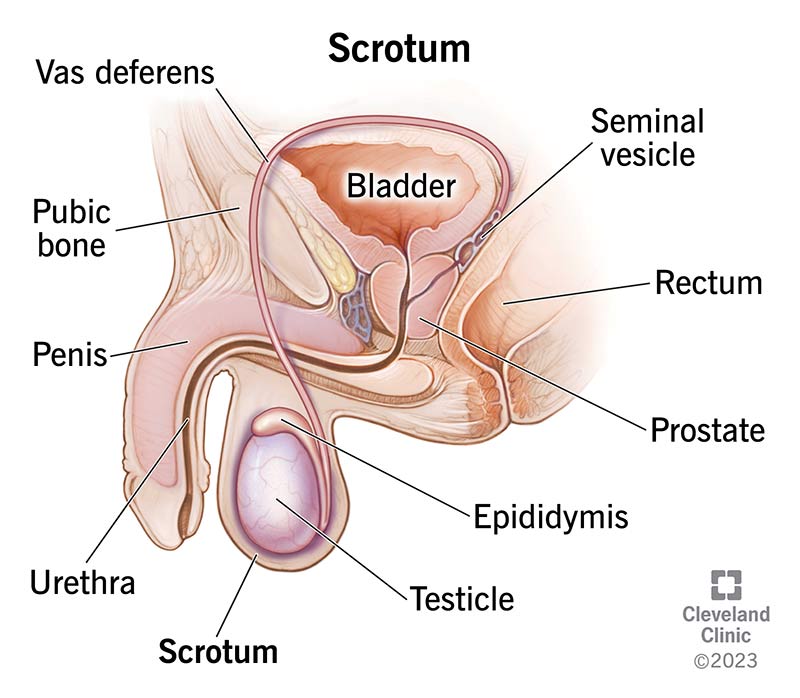
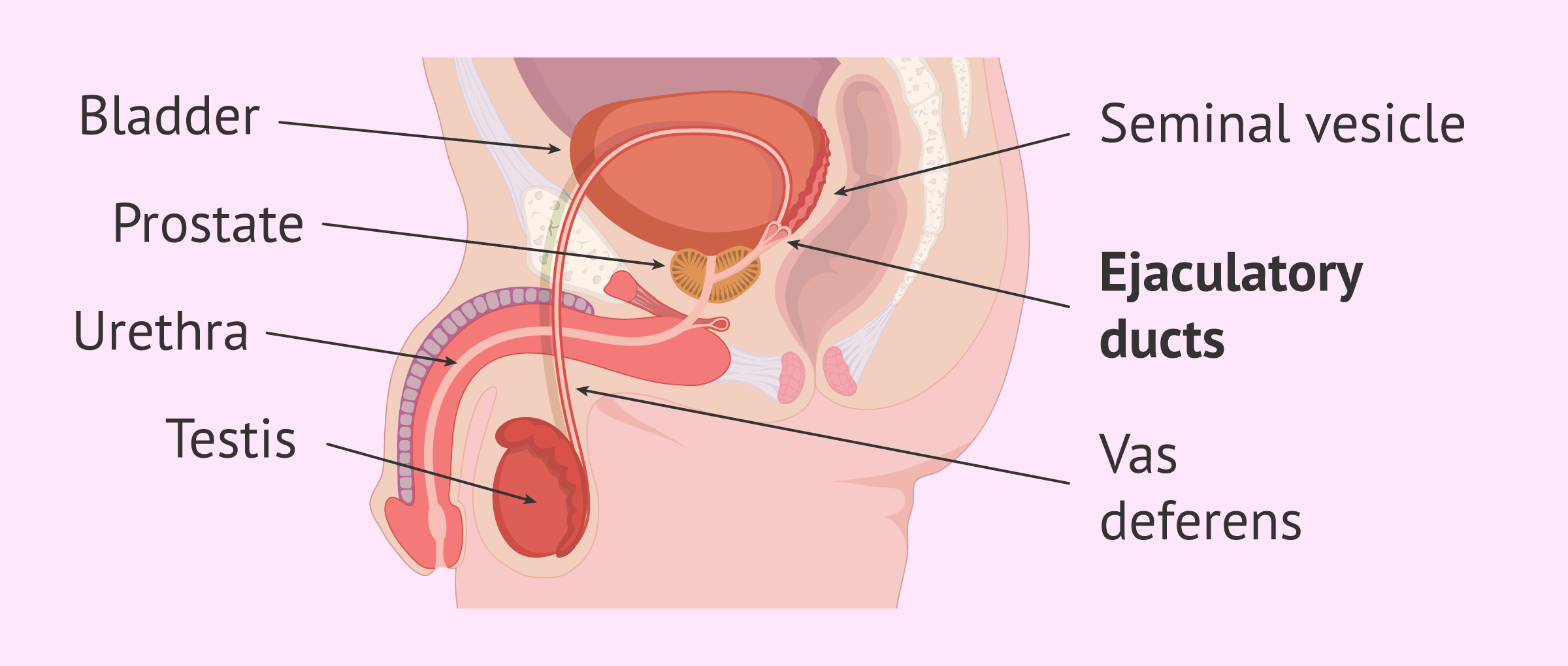
vas deferens
a muscular tube that transports sperm from the epididymis to the ejaculatory duct
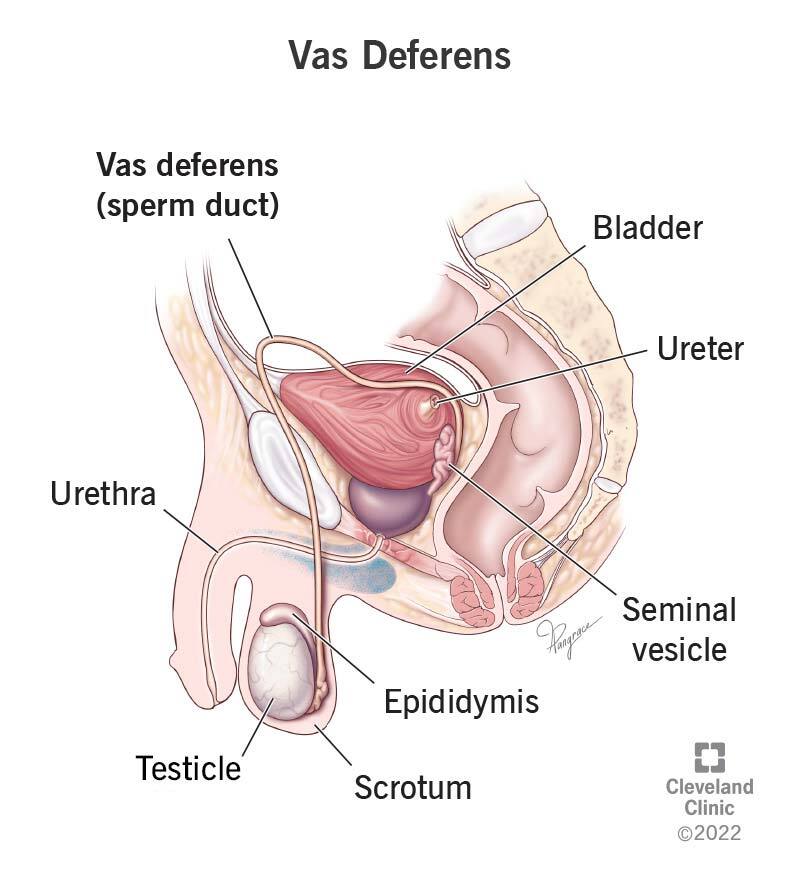
seminal vesicle
a pair of coiled, tubular glands in the male reproductive system located behind the bladder and above the prostate gland; the duct joins the duct from the vas deferens to form the ejaculatory duct
prostate gland
a walnut-sized gland located below the bladder, surrounding the urethra and consisting of three main zones
ejaculatory duct
paired tubes that are formed by the union of the vas deferens and the duct of the seminal vesicle; passes through the prostate gland, where sperm is mixed with fluid from seminal vesicles and prostatic fluids, then empties into the prostatic urethra at the verumontanum
bulbourethral gland
two small glands in the male reproductive system that produce pre-ejaculate to lubricate the urethra and neutralize acidic urine
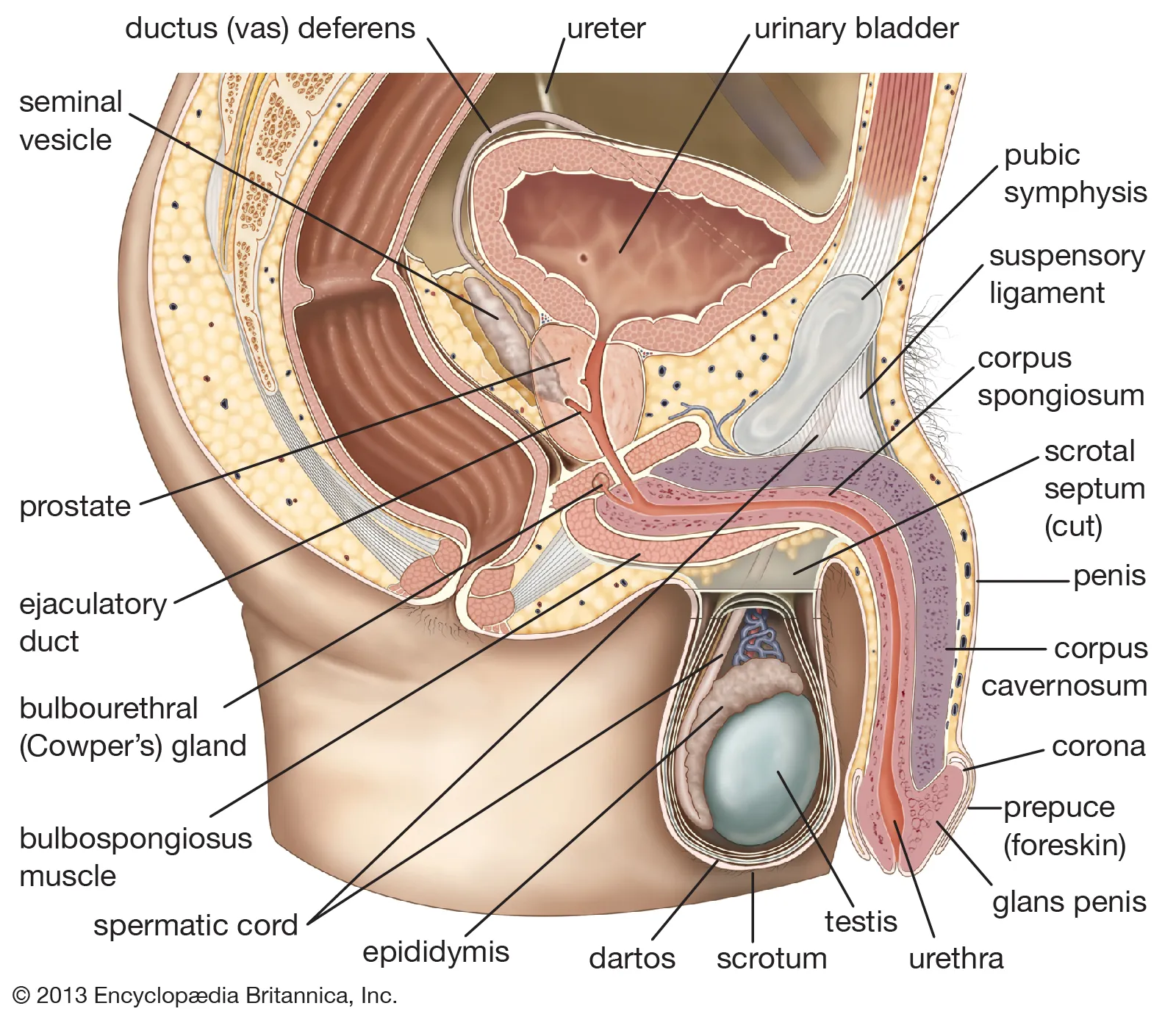
penis
made of three major parts (root, body & glans) and internal structure contains erectile tissue
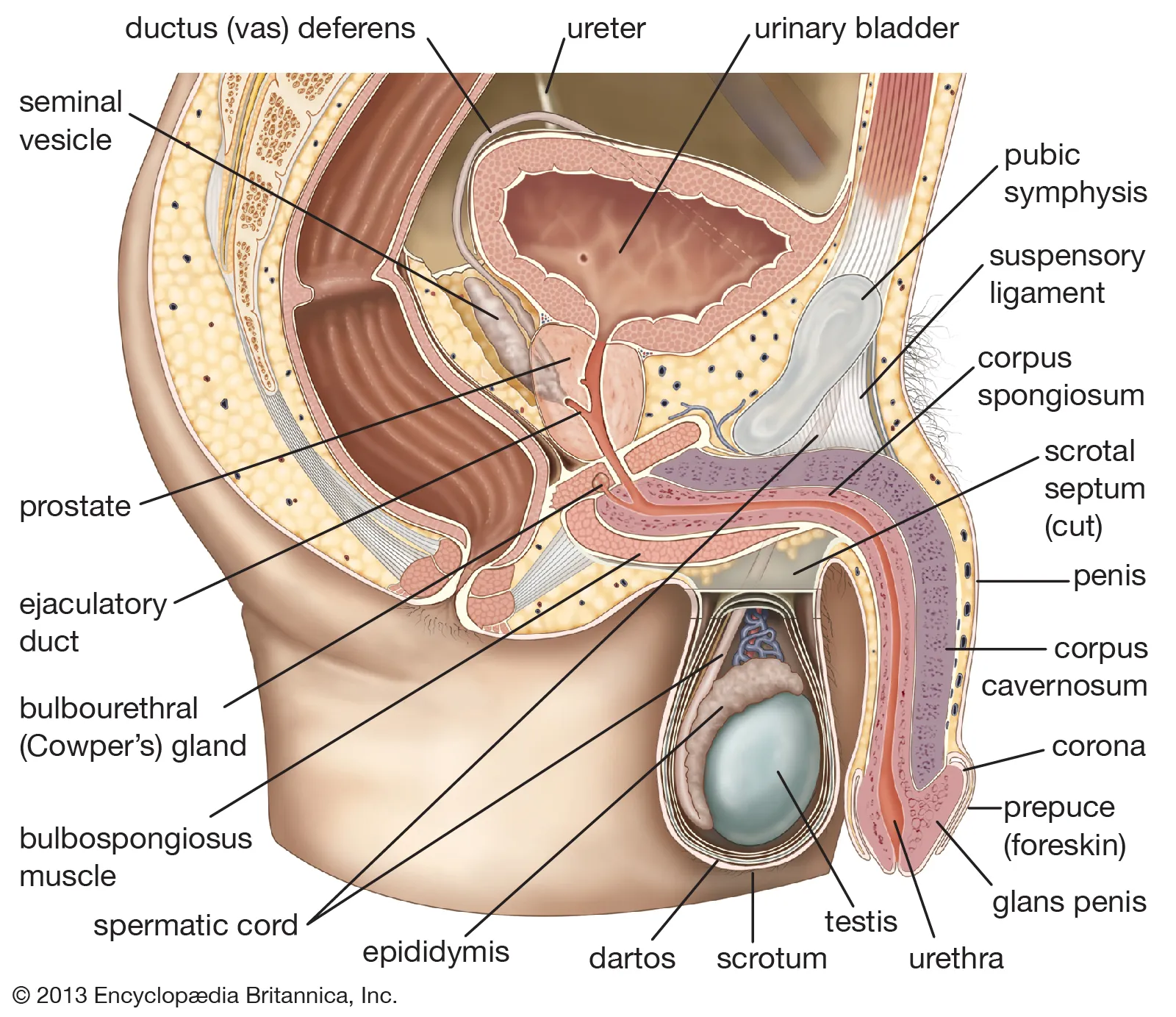
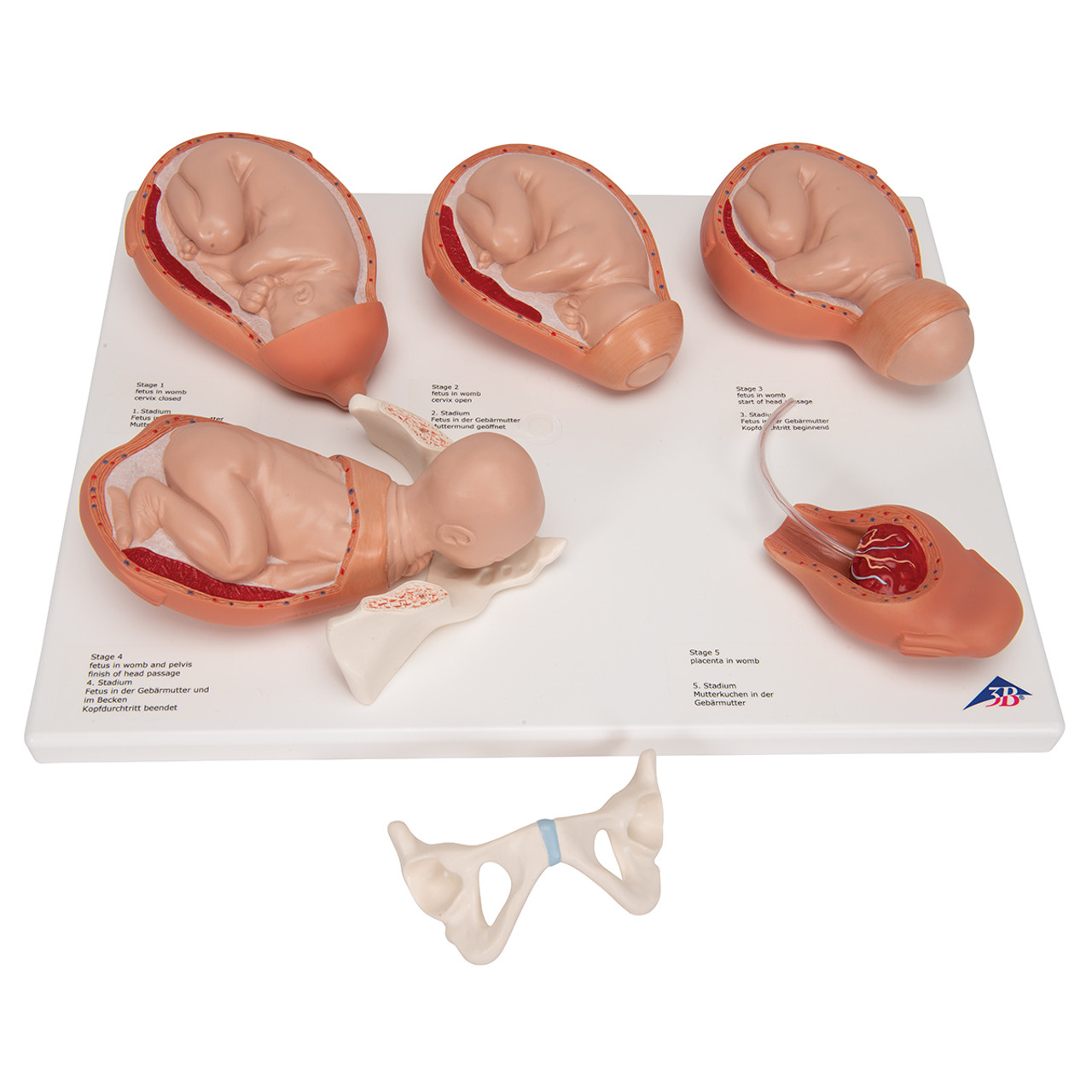
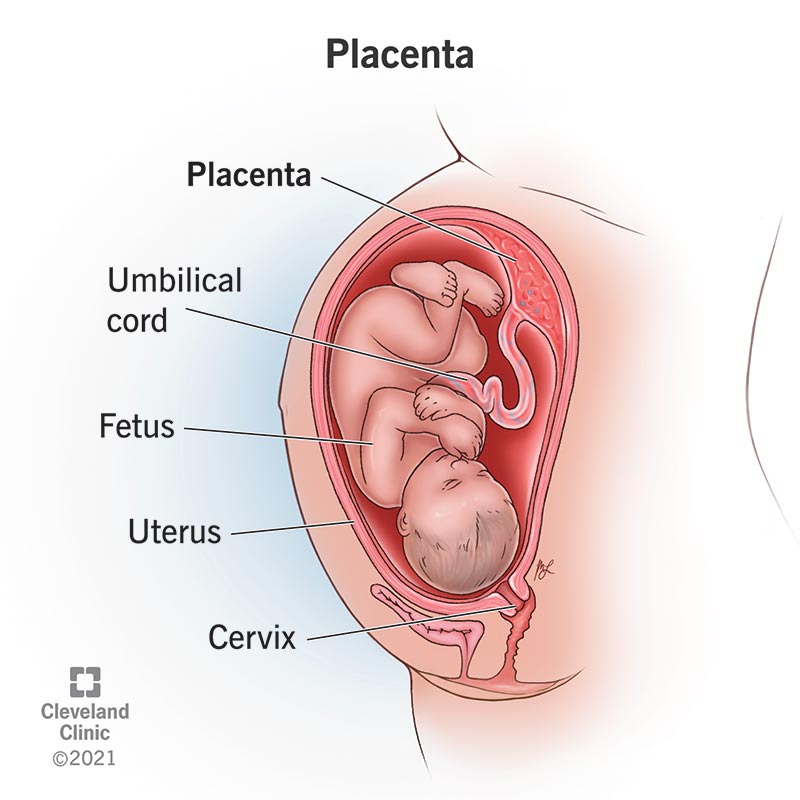
pregnant uterus
a normal uterus that is enlarged as the fetus grows
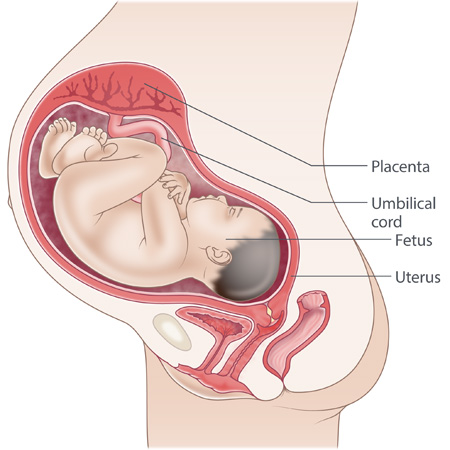
placenta
a temporary organ that develops during pregnancy to support the fetus; material and fetal side that is connected to the fetus via the umbilical cord; facilitates the transfer of oxygen, nutrients and waste between mother and fetus
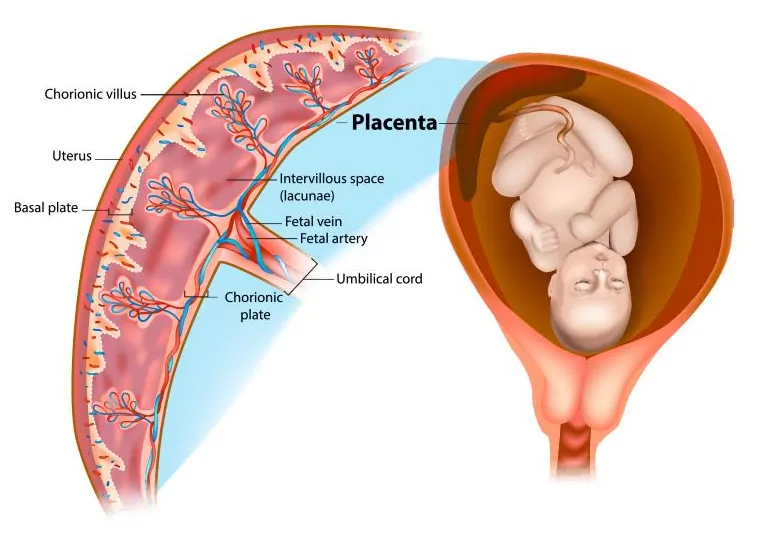
umbilical cord
connects the fetus to the placenta and contains two umbilical arteries, which carry deoxygenated blood from the fetus to the placenta, and one umbilical vein, which carries oxygenated blood from the placenta to the fetus
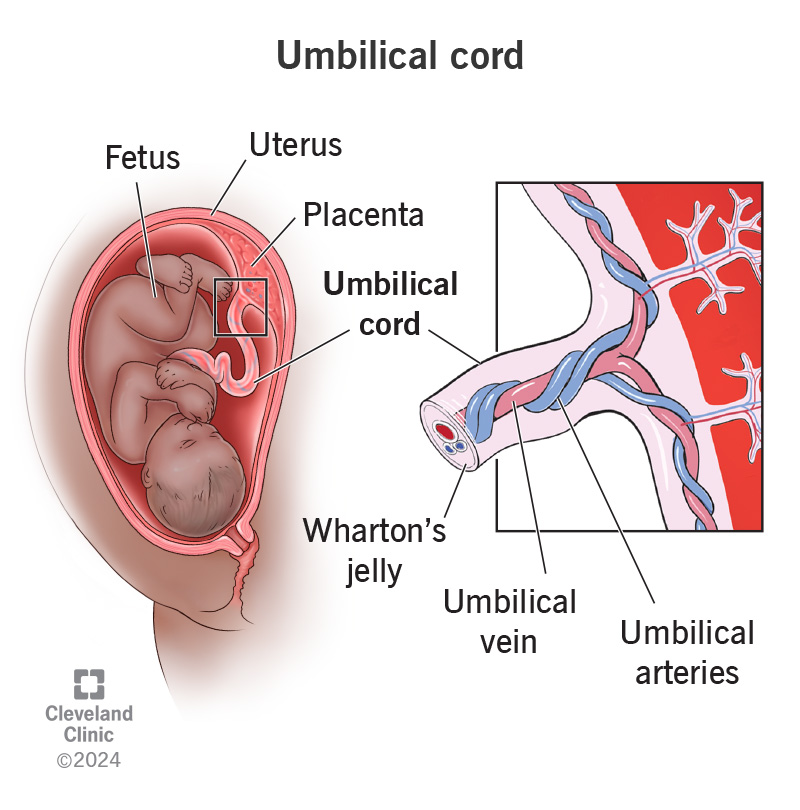
fetus
an unborn baby from the 8th week after fertilization until birth; surrounded by amniotic sac and connected to the placenta via the umbilical cord
stages of birth
full term, dilation, expulsion 1, expulsion 2, placental
full term pregnancy
upper left corner
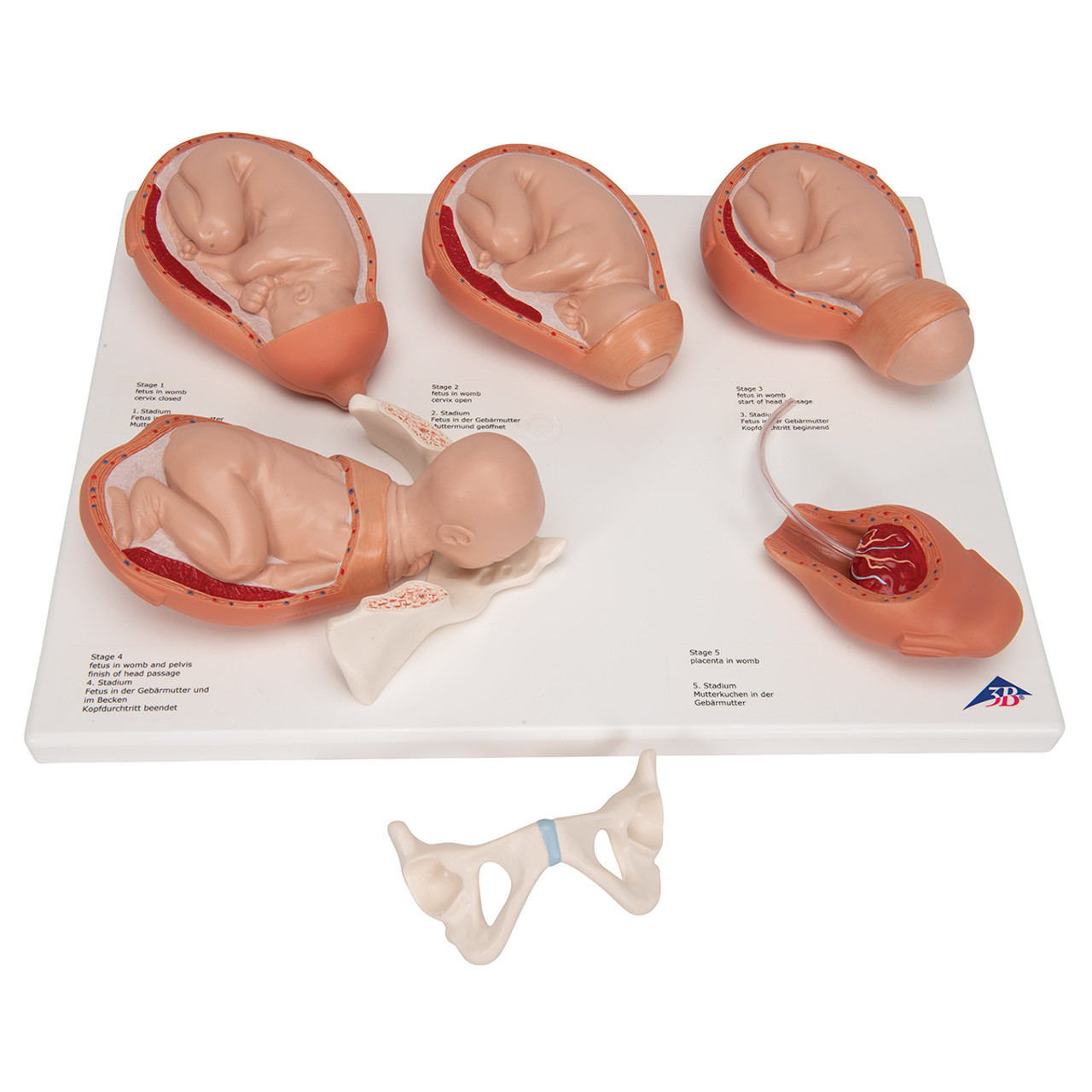
dilation
top middle
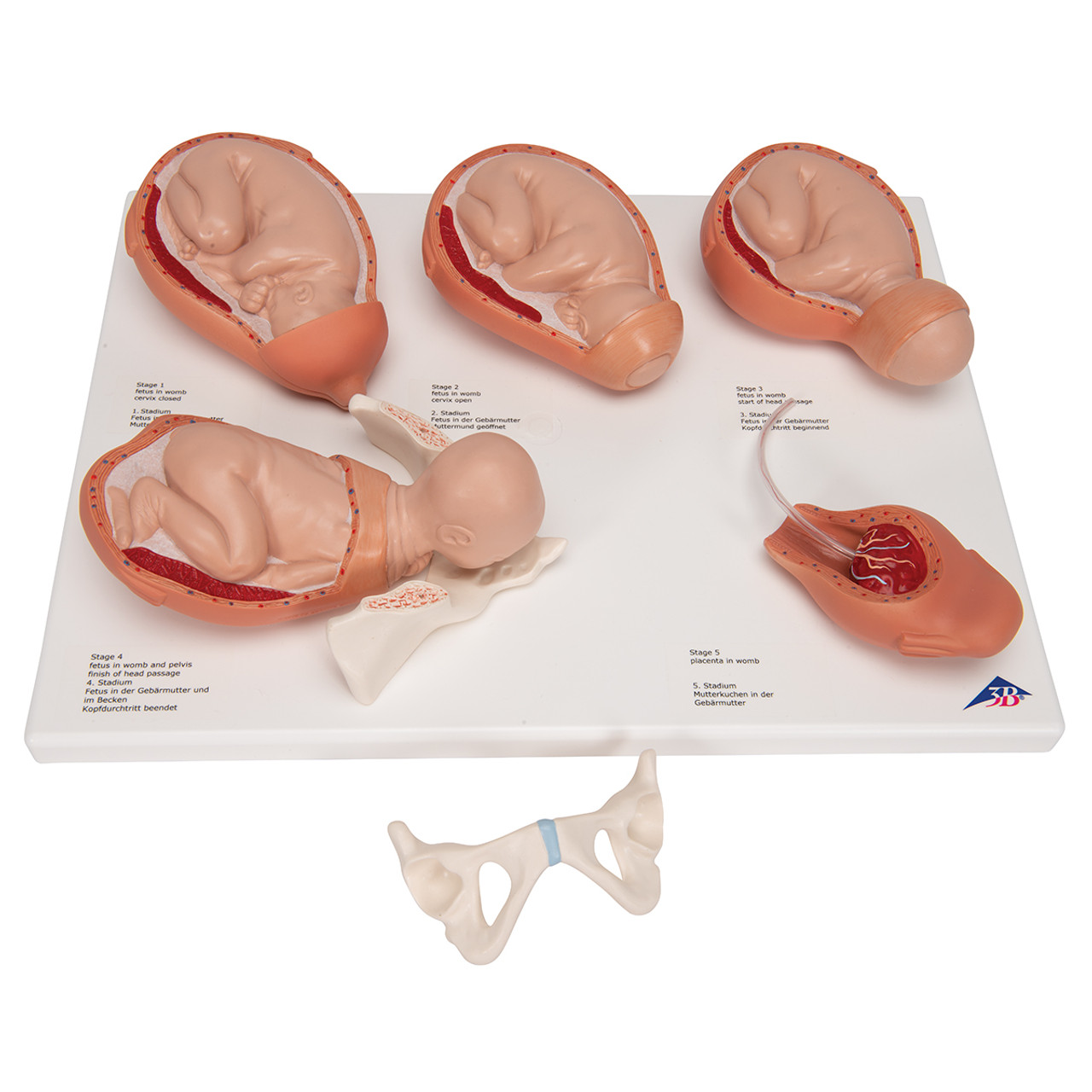
expulsion 1
top right
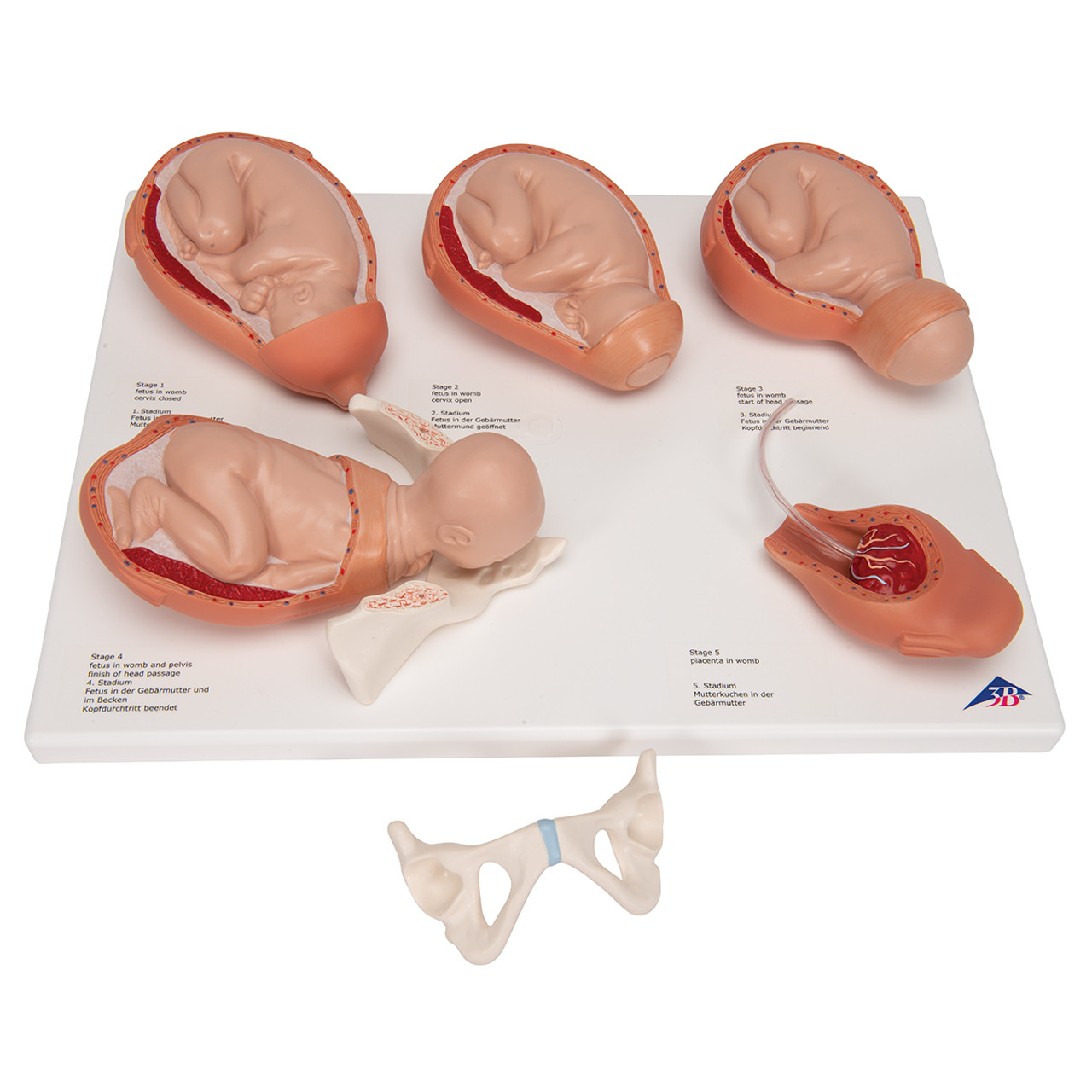
expulsion 2
bottom left
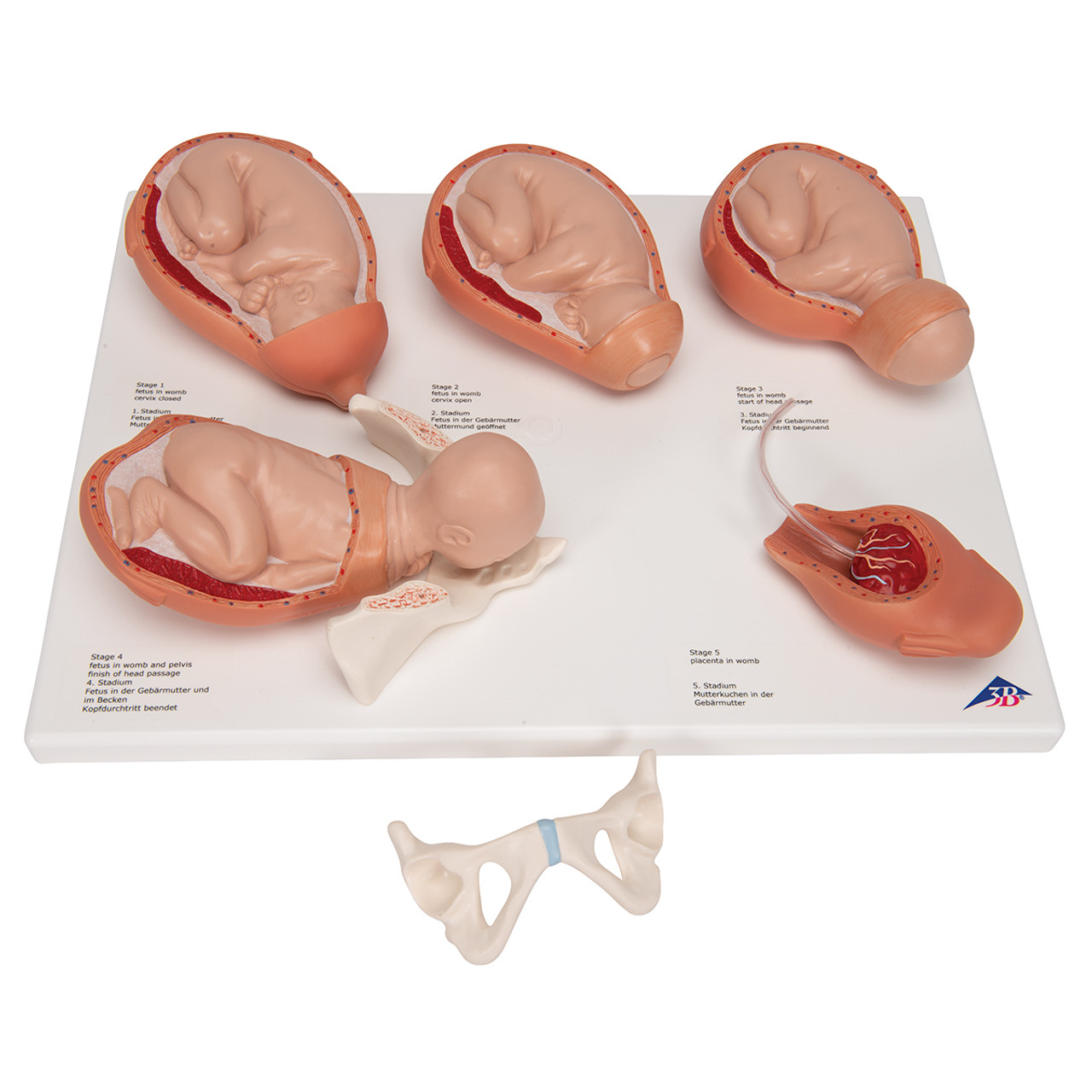
placental
bottom right