MGMT 3000 Guhde Test 3
1/250
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
251 Terms
Organizing
the deployment of organizational resources to achieve strategic goals
Organizational Chart
The visual representation of an organization's structure
Organization Structure includes three things...
- (TASKS) the set of formal tasks assigned to individuals and departments
- (RELATIONSHIPS) formal reporting relationships
- (STRUCTURE) the design of systems to ensure effective coordination of employees across department
Division of Labor
the degree to which organizational tasks are subdivided into separate jobs
Chain of Command
an unbroken line of authority that links all employees in an organization and shows who reports to whom
Authority
the formal and legitimate right of a manager to make decisions, issue orders, and allocate resources to achieve outcomes/goals
Responsibility
the duty to perform the task or activity assigned
Accountability
willingness or obligation to accept responsibility
Delegation
the process that managers use to transfer authority and responsibility down the hierarchy
Line Authority
managers have formal authority to direct and control immediate subordinates - connected via a line in the organizational chart
Line Departments
perform tasks that reflect the organization's mission- generate revenue
Staff authority
authority that includes the right to advise, recommend, and counsel in the staff specialists' area of expertise.
Staff departments
support line departments- cost center
Span of Management
the number of employees reporting to a supervisor
Tall Structure
span of management is narrow and therefore has many hierarchical levels, many layers of management
Flat Structure
span of management is wide and therefore has few hierarchical levels, fewer layers of management
Centralization
decision authority is located near the top of the organization
Decentralization
decision authority is pushed downward to lower organization levels
Departmentalization
basis for grouping positions into departments in the total organization
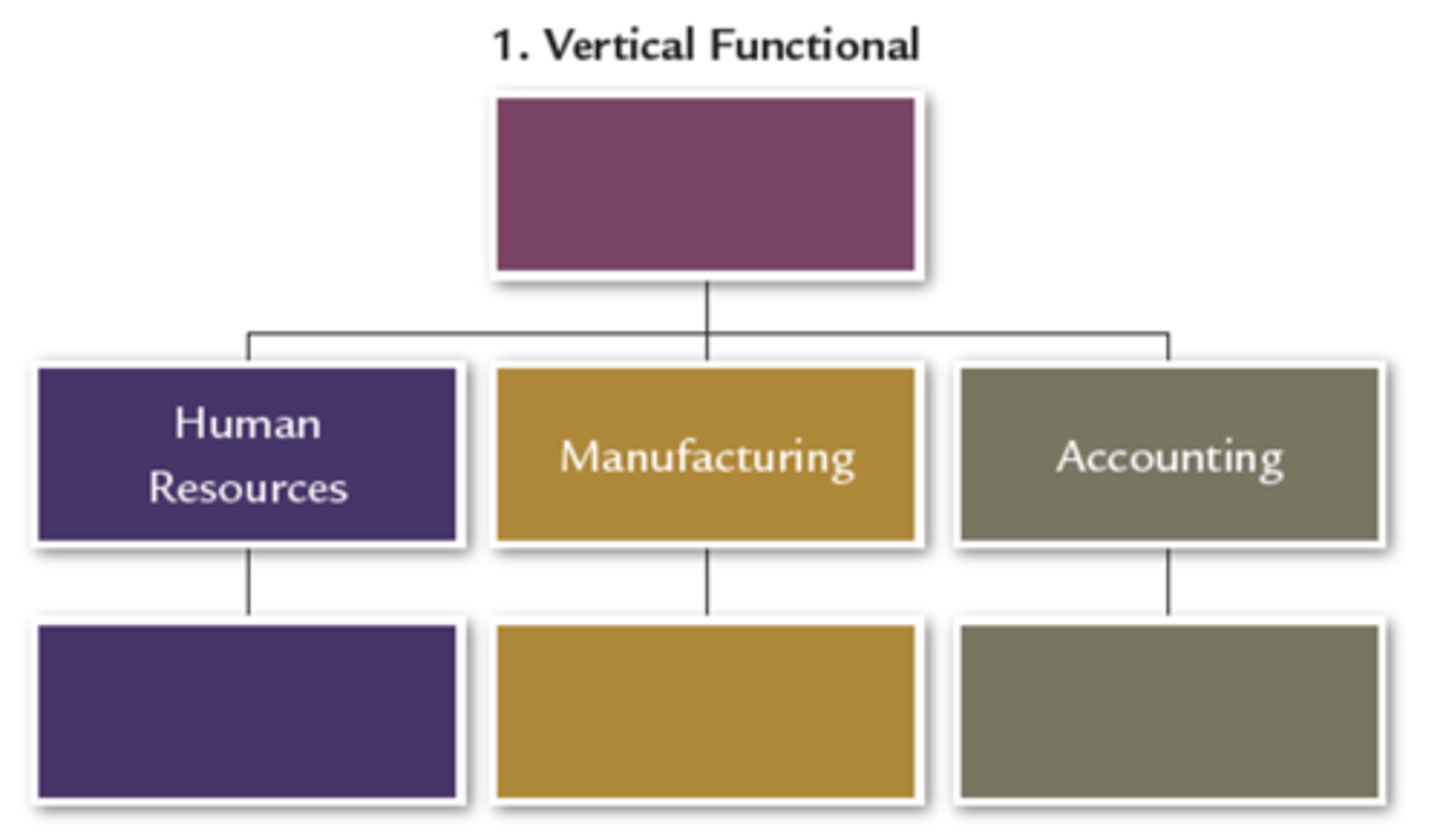
Vertical Functional Structure
the grouping of activities by common function
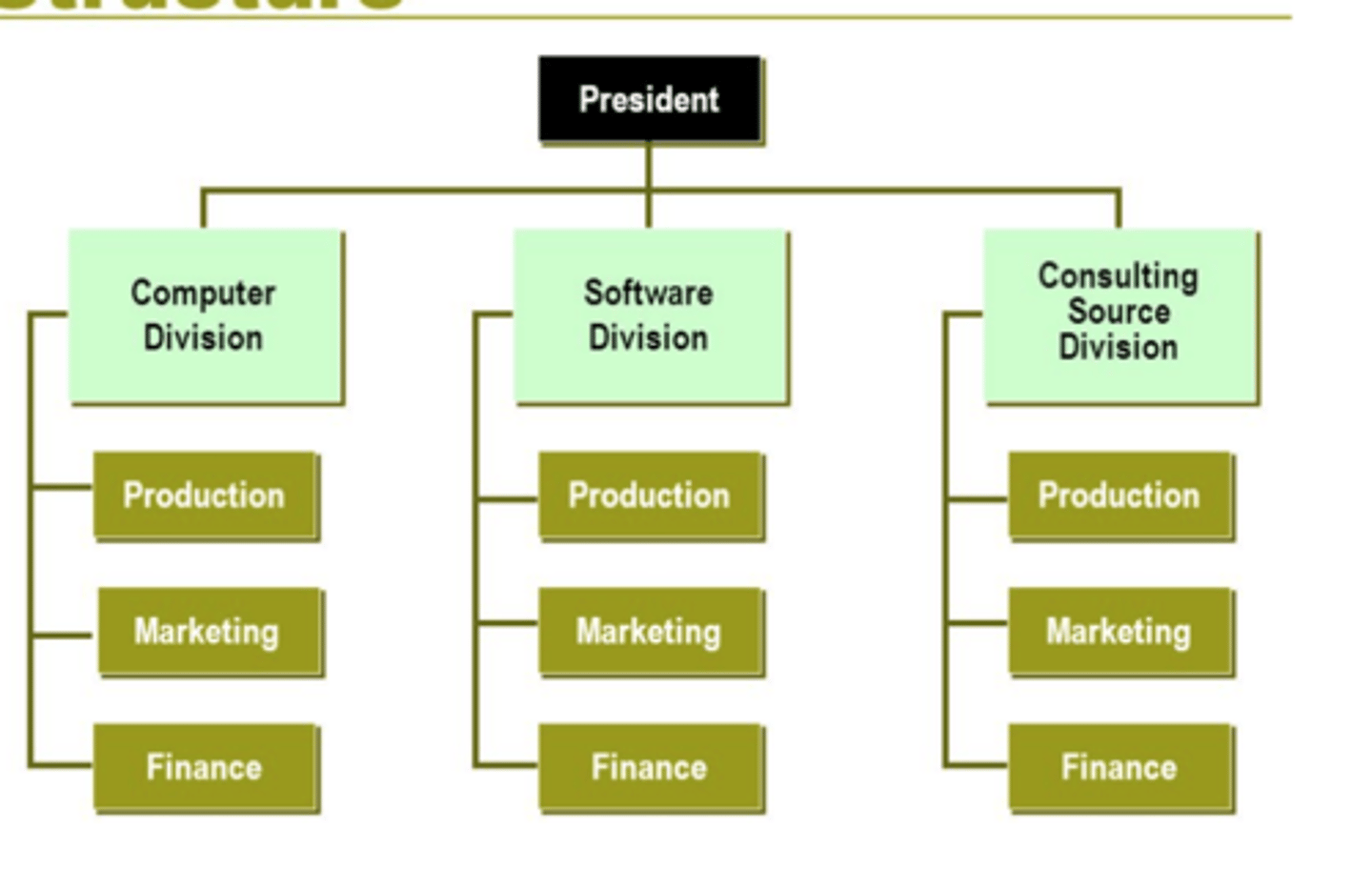
Divisional Structure
departments are grouped together based on similar organizational outputs such as product/service OR geographic
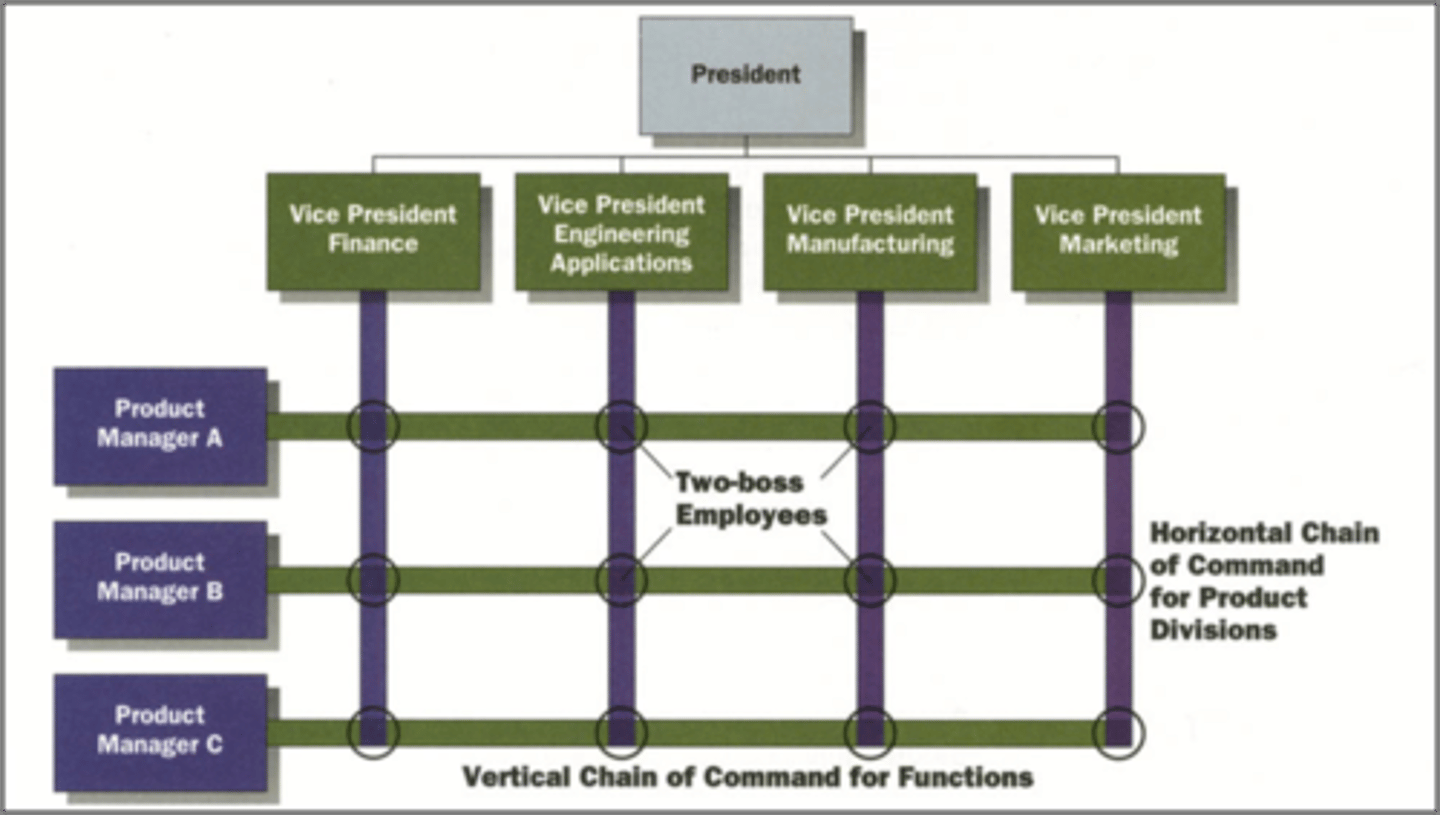
Matrix Approach
combines both functional and divisional approaches simultaneously, in the same part of the organization
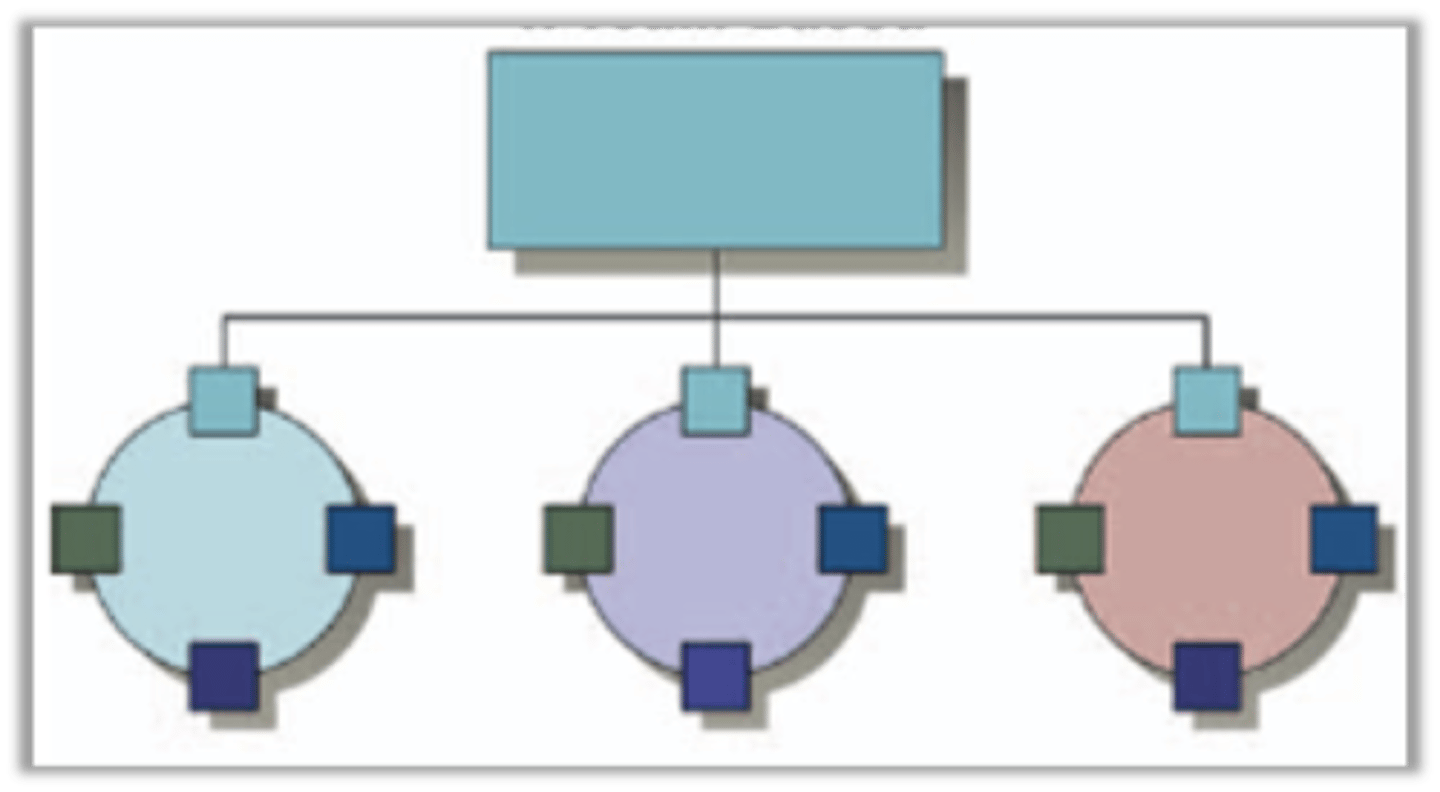
Team Approach
consist of employees from various functional departments who are responsible to meet as a team and resolve mutual problems
Coordination
the managerial task of collaborating across departments
Collaboration
joint effort between people from two or more departments to produce outcomes that meet a common goal or shared purpose and that are typically greater than what could be achieved working alone to achieve synergy
Blind Hiring
managers focus on an applicant's job skills and performance rather than educational credentials, appearance, or prior experience
Artificial Intelligence
Algorithms used to reduce bias in hiring decisions
Employer Brand
promoting an organization as a highly desirable place to work
Matching Model
match between what the organization has to offer and the needs of the individual
Human Resource Planning
the forecasting of HR needs and the projected matching of individuals with expected job vacancies
recruiting
activities or practices that define the characteristics of applicants to whom selection procedures are ultimately applied
Job Analysis
systematic process of gathering and interpreting information about the essential duties, tasks, responsibilities, and context of a job
Job description
summary of the tasks, duties, and responsibilities of a job
Realistic Job Preview
gives applicants all pertinent and realistic information about the job and the organization
Internship
arrangement whereby an intern exchanges free or low-cost labor for the opportunity to explore a career or gain valuable work experience in a particular field
one-way video interview platforms
receive questions on the screen and then record answers
Structured Interview
set of standardized questions that are asked of every applicant so comparisons can easily be made
Behavioral Questions
ask people to describe how they have performed a certain task or handled a specific problem
Employment Test
such as cognitive ability tests, physical ability tests, personality inventories, and other assessments
background check
search a candidates' criminal record, credit history, and other indications of honesty, integrity, and stability as well as view candidate's presence on social media
Training
teaching employee the skills, abilities, knowledge, to perform current job
Development
developing employees for future promotions
Self-Awareness
being aware of the internal aspects of yourself, including personality traits, beliefs, emotions, and perceptions, and appreciating how your patterns affect other people
What are two keys to Self-Awareness
1. Soliciting Feedback
2. Using Self-Assessment
Blind Spots
attributes of ourselves that we aren't aware of or don't recognize as problems--which limit our effectiveness and hinder our success.
Self-Confidence
general assurance in one's own ideas, judgement, and capabilities
Self-Efficacy
an individual's strong belief that he or she can accomplish a specific task or outcome successfully
Job Satisfaction
the degree to which a person finds fulfillment in his or her job
The highest job satisfaction rate ever was recorded in 2019. What was it?
54%
Organizational Commitment
refers to an employee's loyalty to and engagement with the organization
What percent of people say that they strongly trust their top management?
20%
Perception
the cognitive process that people use to make sense out of the environment by selecting, organizing, and interpreting information from that environment.
What are the three steps to the Perception Process?
1. Observe
2. Screen
3. Organize
Perception Process: Observe
Observing information via the senses
Perception Process: Screen
screening the information and selecting what to process
Perception Process: Organize
organizing the selected data into patterns for interpretation and response
Perceptual Distortions
errors in perceptual judgement that arise from inaccuracies in any part of the perception process
Stereotyping
the tendency to assign an individual to a group or broad category and then attribute widely held generalizations about the group to the individual
The Halo Effect
occurs when the perceiver develops an overall impression of a person or situation based on one characteristic, either favorable or unfavorable
Attributions
judgements about what caused a person's behavior--something about the person or something about the situation.
Internal Attribution
says that characteristics of the person led to the behavior
External Attribution
says that something about the situation caused the person's behavior
fundamental attribution error
we tend to underestimate the influence of external factors and overestimate the influence of internal factors when evaluating the mistakes of others, BUT we typically overestimate the influence of external factors and underestimate the influence of internal factors when evaluating our own mistakes.
Self-Serving Bias
people give themselves too much credit when they do well, and give external forces too much blame when they fail.
personality
the set of characteristics that underlie a relatively stable pattern of behavior in response to ideas, objects, or people in the environment.
Big Five Personality Factors
1. Extroversion
2. Agreeableness
3. Conscientiousness
4. Emotional Stability
5. Openness to Experience
The Four Key Personality Areas for Managers
1. Grit
2. Authoritarianism
3. Machiavellianism
4. Problem-Solving Styles
The Four Key Personality Areas for Managers: Grit
an individual's passion and persistence for achieving a long-term goal
The Four Key Personality Areas for Managers: Authoritarianism
the belief that power and status differences should exist within the organization
The Four Key Personality Areas for Managers: Machiavellianism
the acquisition of power and the manipulation of other people for purely personal gain
2 Ways people gather information
1. Sensation
2. Intuition
2 Ways people make judgements about information
1. Thinking
2. Feeling
Sensation-Thinking
Emphasizes details, is decisive, focuses on short term goals, and develops rules and regulations for judging performance
Intuitive-Thinking
Prefers dealing with theoretical problems, is creative and progressive, focuses on possibilities, is able to consider a number of options simultaneously
Sensation-Feeling
Shows concern for real-life human problems, is pragmatic and analytical, emphasizes detailed facts, and focuses on structuring organizations for the benefit of people
Intuitive-Feeling
Avoids specifics, is charismatic, people-oriented, broad themed, and decentralizes decision making, developing few rules and regulations
2 ways people prefer to conclude information
1. Judging
2. Perceiving
Judging
preferring closure and completion in making decisions
Perceiving
preferring to explore many alternatives with flexibility and spontaneity, dislike deadlines, and may change their minds several times
Myers-Briggs Type Indicator
a personality test that taps four characteristics and classifies people into 1 of 16 personality types
2 Most prominent Myers-Briggs qualities in effective managers
1. Thinking
2. Judging
emotion
a mental state that arises spontaneously within a person based on interaction with the environment rather than through conscious effort and is often accompanied by physiological changes
Emotional Contagion
the tendency of people to absorb and express the emotions, moods, and attitudes of those around them.
Negativity Bias
the term used in psychology to describe how the human mind reacts more quickly and strongly to perceived bad things than it does to good things.
4 Components of Emotional Intelligence
1. Self-Awareness
2. Self-Management
3. Social Awareness
4. Relationship Management
Self-Management
the ability to control disruptive or harmful emotions and balance your moods so that worry, anxiety, fear, and anger do not cloud your thinking and get in the way of what needs to be done.
Social Awareness
the ability to understand others and practice empathy, which means being able to put yourself in someone else's shoes, to recognize what others are feeling without them needing to tell you.
Relationship Management
the ability to connect to others, build positive relationships, respond to the emotions of others, and influence others.
3 Basic Principles of Self-Management
1. Clarity of Mind
2. Clarity of Objectives
3. An Organized System
Clarity of Mind
Anything you consider unfinished needs to be placed in some kind of trusted system outside your head.
Clarity of Objectives
be clear about exactly what you need to do and decide the steps to take toward accomplishing it.
An Organized System
keep reminders in a well-organized system
5 Steps to Getting Organized
1. Empty your head
2. Decide the next action
3. Get Organized
4. Perform a weekly review
5. Now do it.
5 Steps to Getting Organized: Empty your head
to clear your mind, you first have to see all the many things weighing on it.
5 Steps to Getting Organized: Decide the Next Action
for each item in your buckets, decide the real, specific, physical action that you need to take next.
3 steps to Deciding the Next Action
1. Do it - if something can be done in less than two minutes, do it.
2. Delegate it - if someone else can do this, delegate it to them.
3. Defer it - if something will take longer than two minutes, defer it to a to-do list.
5 Steps to Getting Organized: Get Organized.
organize all items that you've deferred
5 Steps to Getting Organized: Perform a weekly review.
review your complete "next actions" list and your calendar for the coming week to prepare yourself.
4 actions to take during a personal weekly review.
1. Collect and process all the new stuff
2. Review your entire system
3. Revise your lists
4. Get clear, up to date, and complete about what needs to be done next.
5 Steps to Getting Organized: Now do it.
Actually do what you say you're going to do.