OChem Test 1
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
What is organic chemistry
the study of carbon containing molecules
What happens during a reaction?
Molecules collide and bonds are formed and or broken
_____ and _______ reside in the nucleus
Protons (+1) and neutrons (neutral) reside in the nucleus
______ reside in the orbitals outside the nuceus
Electrons (-1)
how can one determine the number of valence electrons?
by looking at the periodic table
_____ are pairs of electrons that are shared between atoms
covalent bonds
As energy increases, stability ______
decreases
As energy decreases, stability _______
increases
what are the atoms that are most commonly bonded with carbon?
hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, halogens
Cabon’s bonding is _________
tetravalent
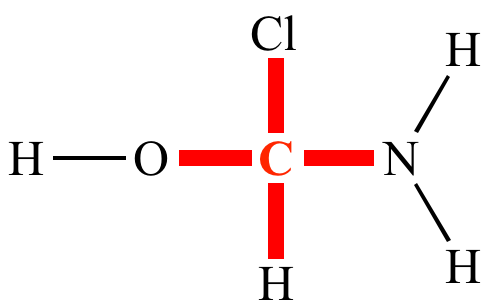
Nitrogen’s bonding is _______

Oxygen’s bonding is
divalent
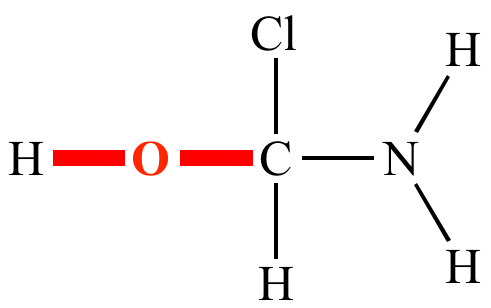
Halogen’s bonding is ______
monovalent
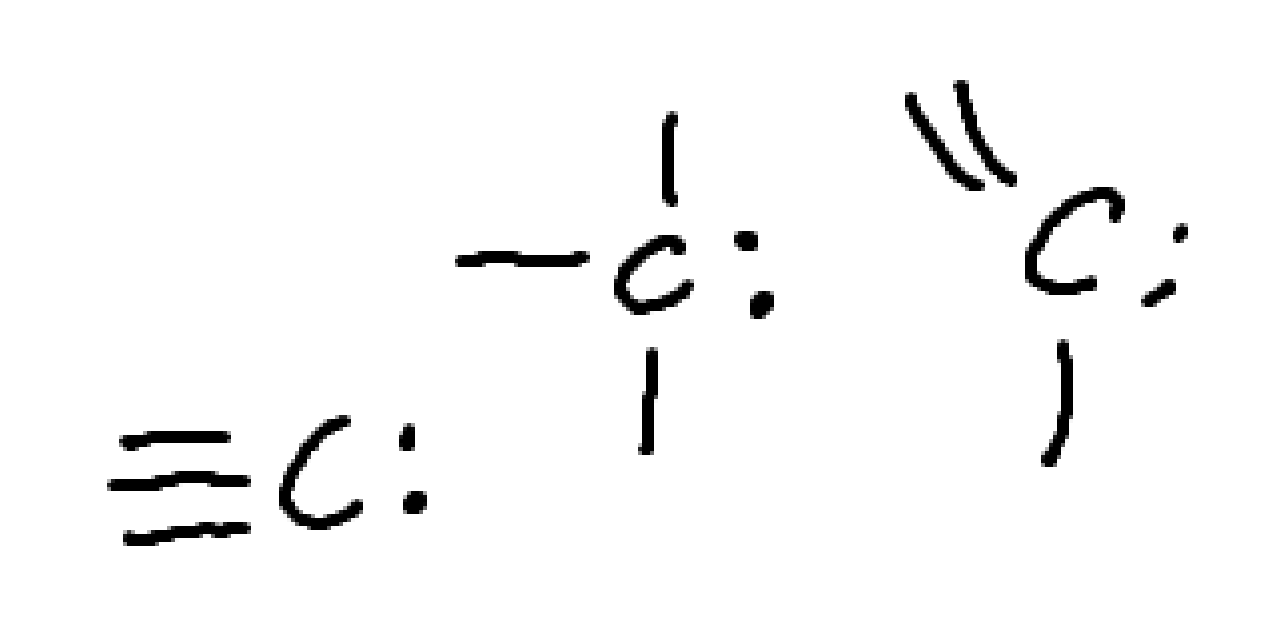
What charge is this?
negative carbon
carboanion
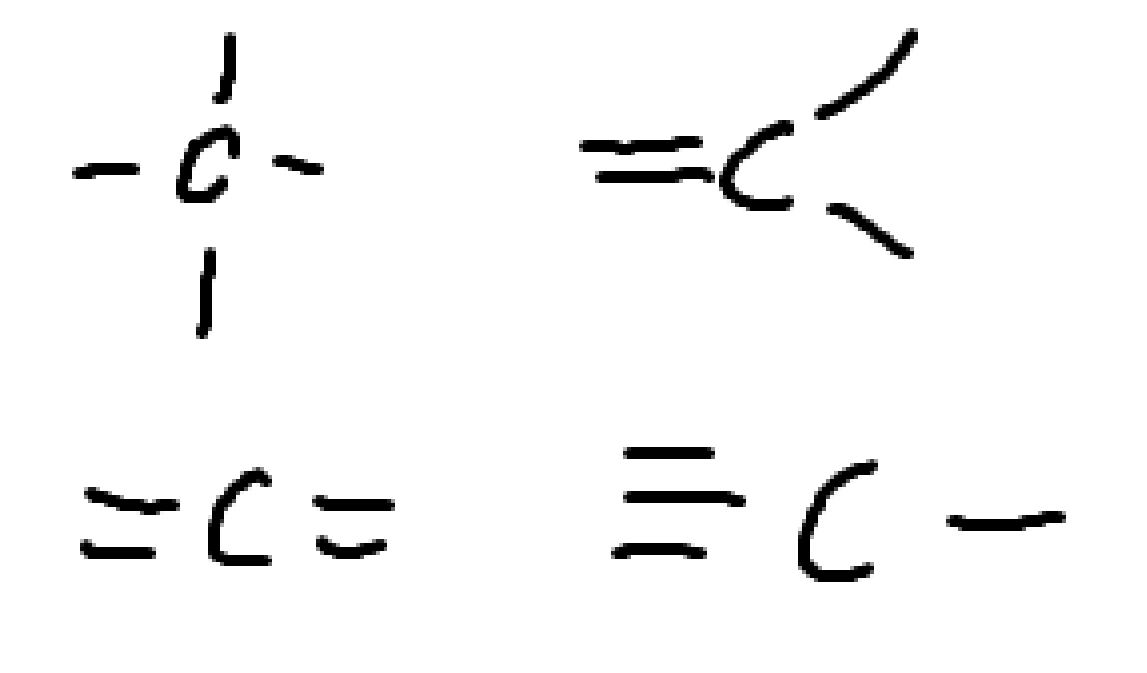
what charge is this?
no charge. neutral carbon.
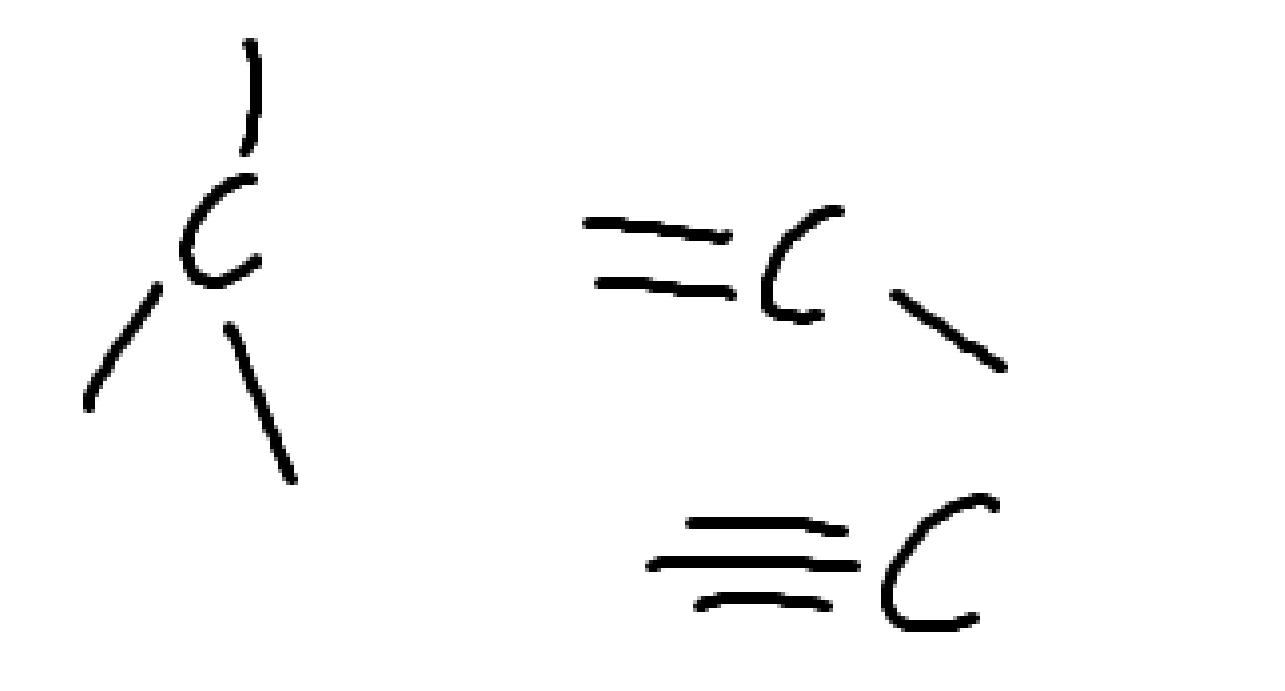
what charge is this
positive
carbocation
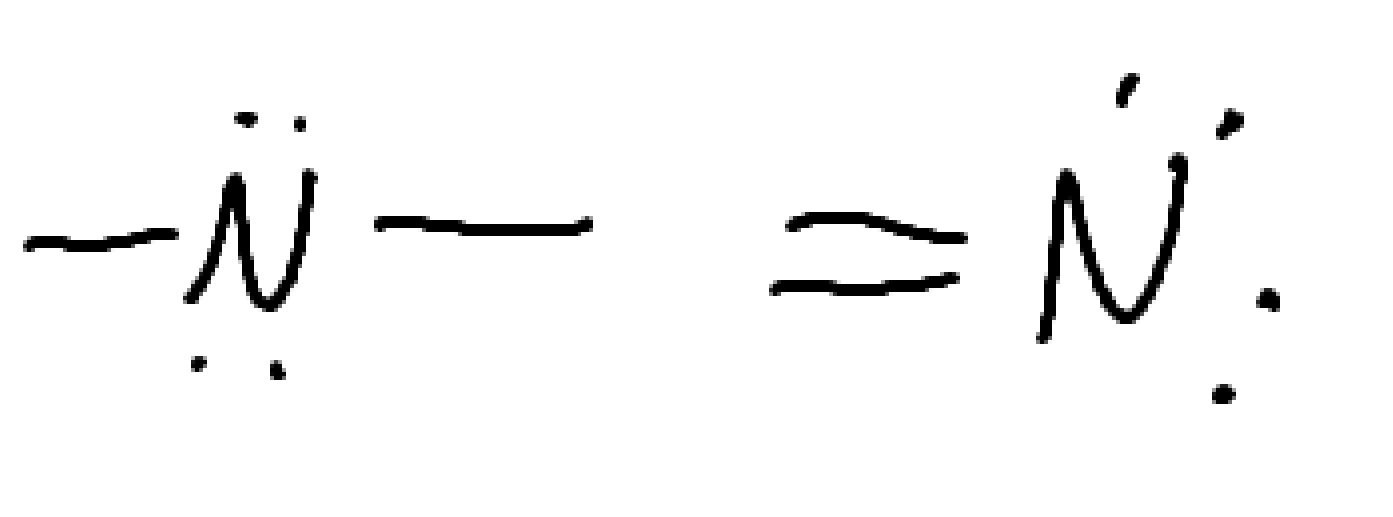
what charge is this?
negative
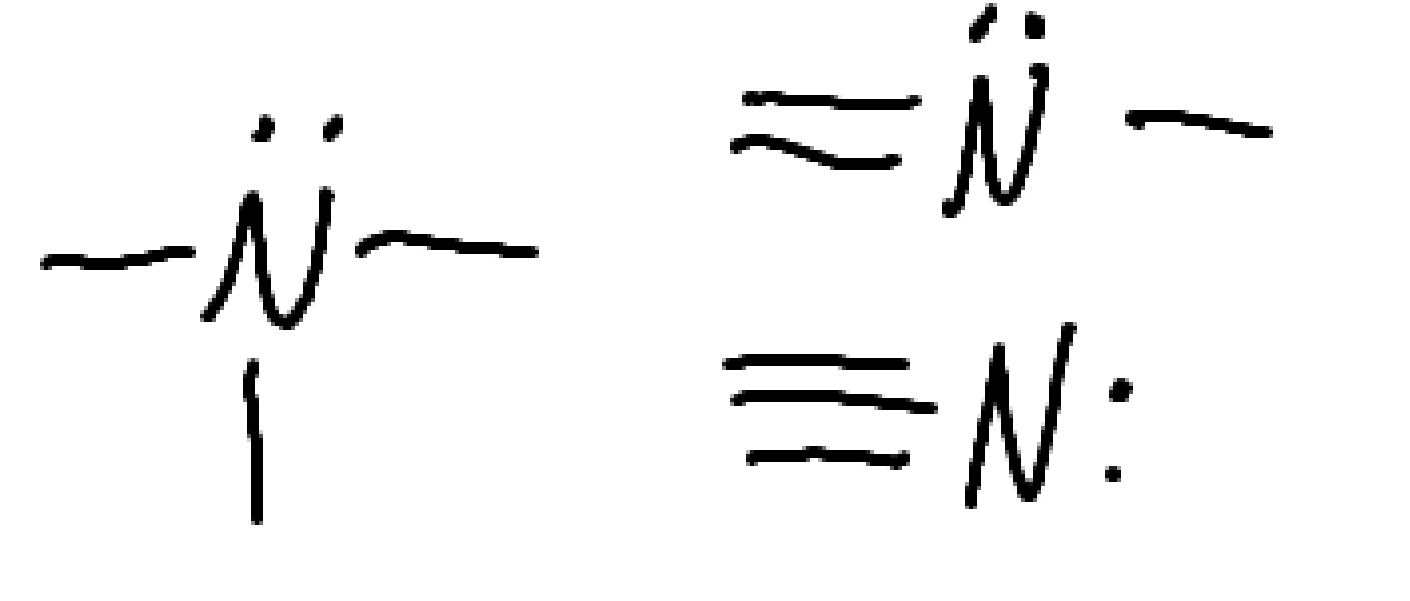
what charge is this?
none.
this is neutral nitrogen
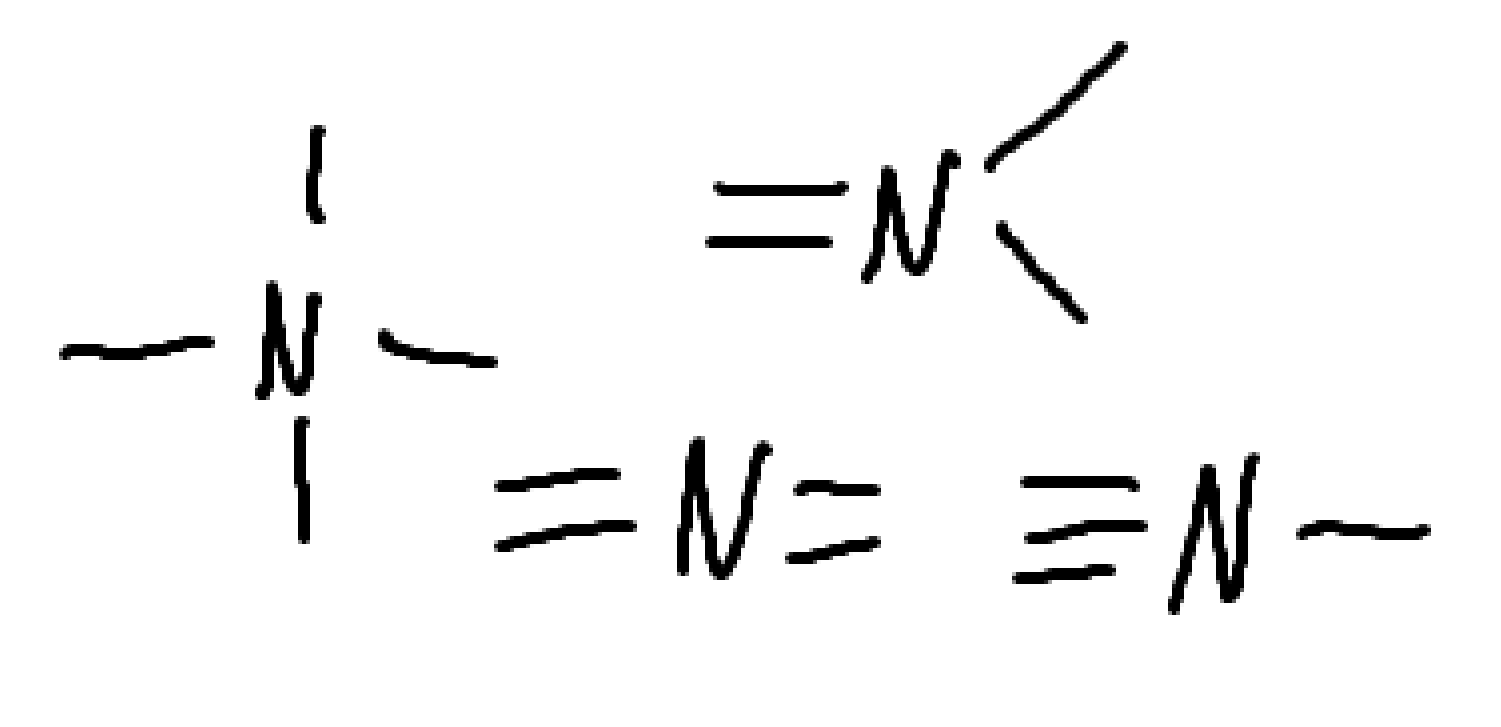
What charge is this?
positive

what charge is this?
negative
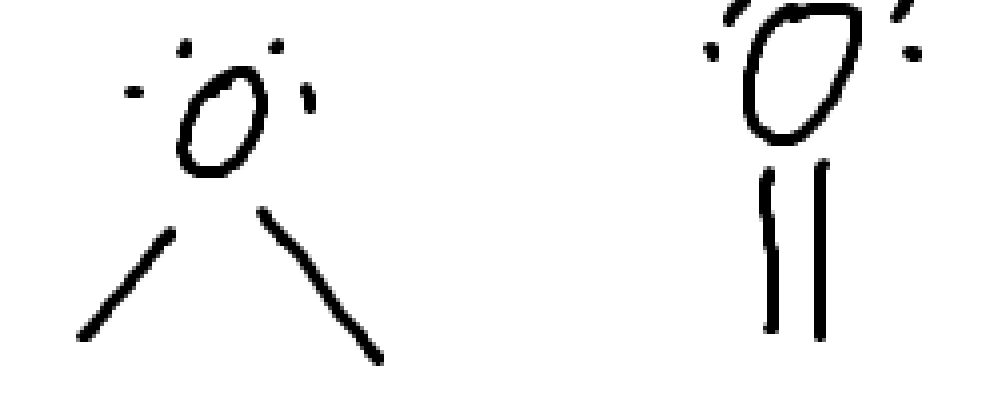
what charge is this
neutral oxygen
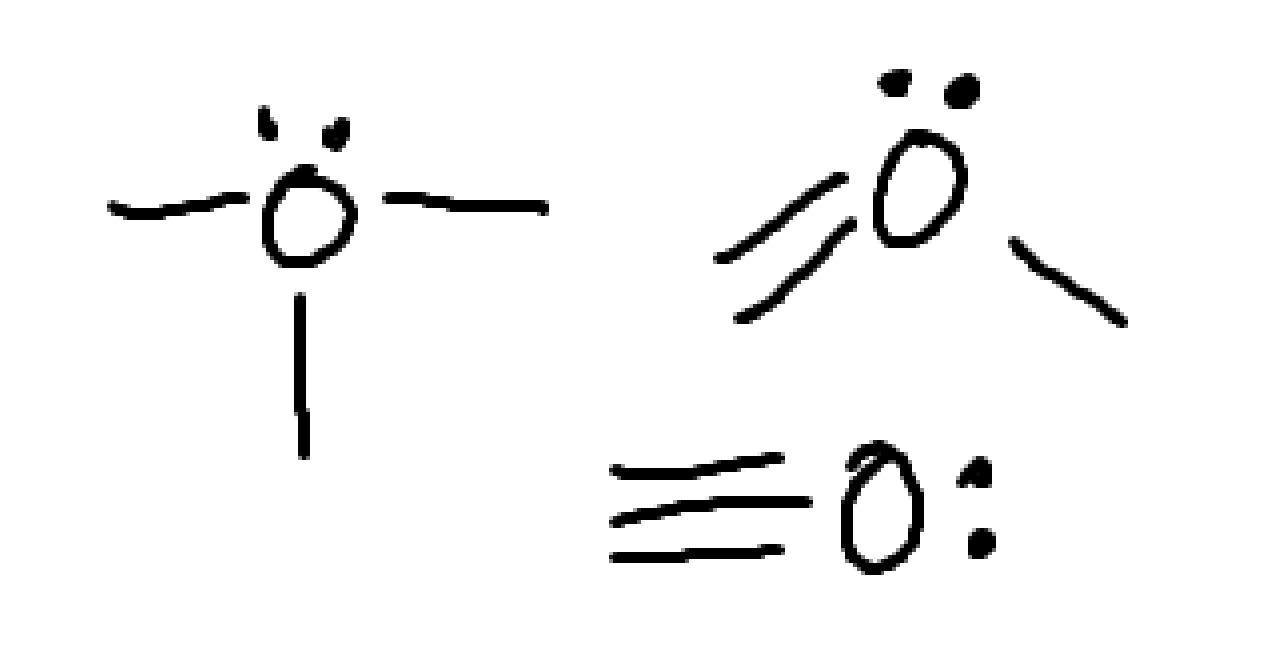
what is the charge
positive
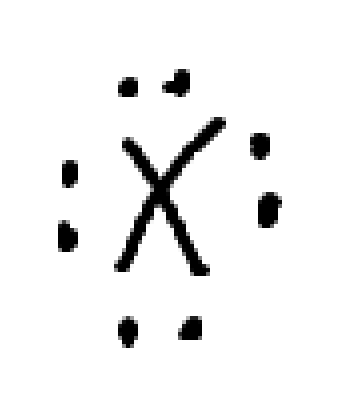
what is the charge
negative
what charge is this
neutral halogen
What is the formula that we can use to calculate formal charge?
Formal charge= # of VE - #LP+#B
or the way i used to remember it it was
VE-NB+CE (venice)
What is electronegativity?
How strongly an atom attracts shared electrons
electronegativity increases moving toward fluorine
What are the three types of bonds?
Covalent, Polar Covalent, Ionic
What type of bond shares electrons between two atoms? Electronegativity is less than 1
Covalent bond
What type of bond shares electrons between two atoms with electronegativity above one?
polar covalent bond
What type of bond is where electrons are not shard and the two atoms have electronegativity difference of more than 1.7? The more electronegative atom owns the electrons
Ionic bond
What happens to polarity of the bond as electronegativity increases?
it is more polar
Electrons behave as both _____ and _____
waves and particles
We should think of an atomic orbital of a cloud of ________. _____ increases with electronegativity
electron density
A covalent bond occurs when atomic orbitals ____
overlap
Wjhat are the two theories for describing atomic orbital overlap?
valence bond theory and molecular orbital theory
only _____________ results in a bond
constructive interference
The more s character in the orbital, the ____ and the _____ the bond
stronger and shorter
What is the steric number?
number of hybrid orbitals= number of bonds + number of lone pairs
if the steric number is 4, then it is ….
sp3
The steric number is 2 and the hybridization is sp. What is the Electron Domain Geometry? What is the bond angle?
linear
180 degrees
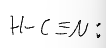
the steric number is 3 and the hybridization is sp2. What is the electron domain geometry? What is the bond angle?
trigonal planar.
120 degrees

The steric number is 4 and the hybridization is sp3. What is the electon domain geometry? What is the bond angle?
tetrahedral
~109.5 degrees
lone pairs lead to a slightly ___ bond angle which changes ______
smaller
molecular geometry (not electron geometry)
If you have polar bonds, does that mean the molecule is polar
NO
What are three types of intermolecular forces?
dispersion forces (london dispersion forces)
dipole-dipole
hydrogen bonding
What intermolecular force is present in everything?
dispersion forces (london dispersion forces)
What intermolecular force involves polar moelcules?
dipole-dipole
what intermolecular force is the strongest but still weaker than a covalent bond
hydrogen bond
Dipole-dipole forces result when polar molecules line up their _____ charges
opposite
compared to weaker IMFs, molecules exhbititing ______ attractions will have a higher melting and boiling point
dipole-dipole
Hydrogen bonding is the attractive force between a H bonded to an ______ and a _____
electronegative atom (N,O,F) and a lone pair of electrons
The greater the _______ of a molecule, the more temporary dipole attractions are possible
surface area
what is true of branching as it pertains to surface area and boiling pt
more branching leads to less surface area and lower boiling point
like dissolves ____
like
How does soap work?
oil molecules are nonpolar.
soap molecules organize into micelles in water, which form a nonpolar interior and carry dirt away.
What is true of the postitioning of solid and hatched lines in 3D drawings?
they must be near each other and not seperate
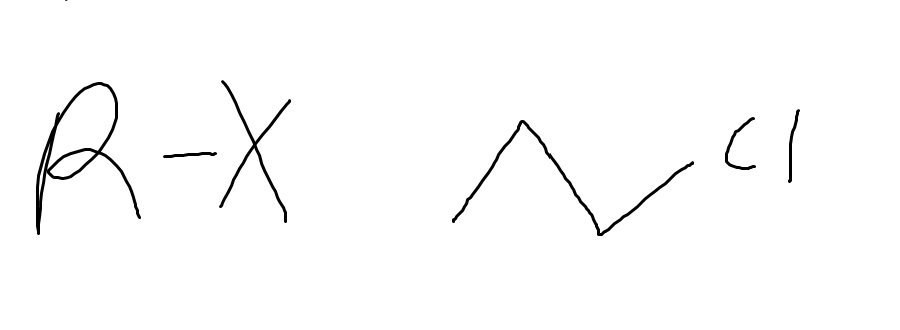
name the functional group and why
alkyl halide
carbon bonded with a halogen (Cl, Br, I , F)
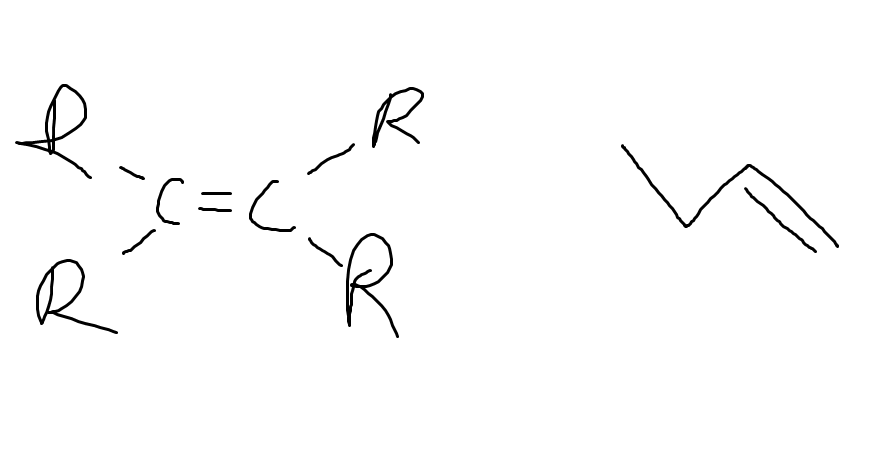
What functional group and why
Alkene
carbon to carbon double bond
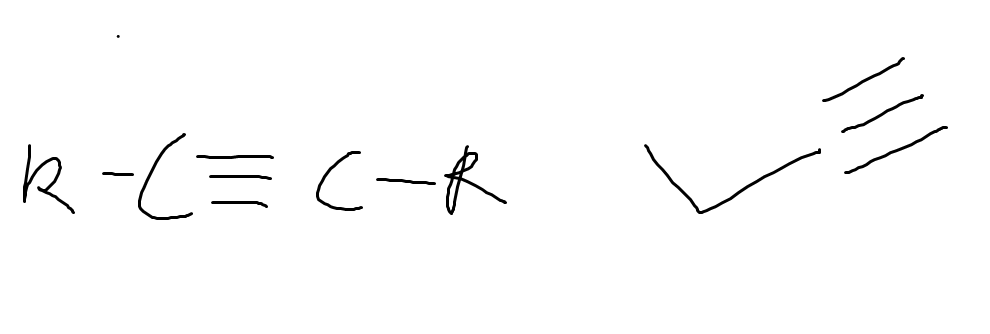
what functional group is this and why
alkyne
triple bond between carbons
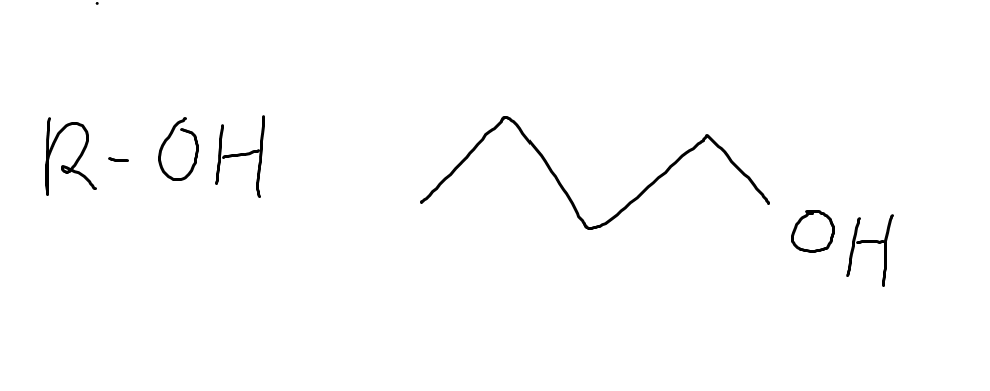
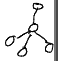
What functional group is this and why
alcohol
because of the OH group
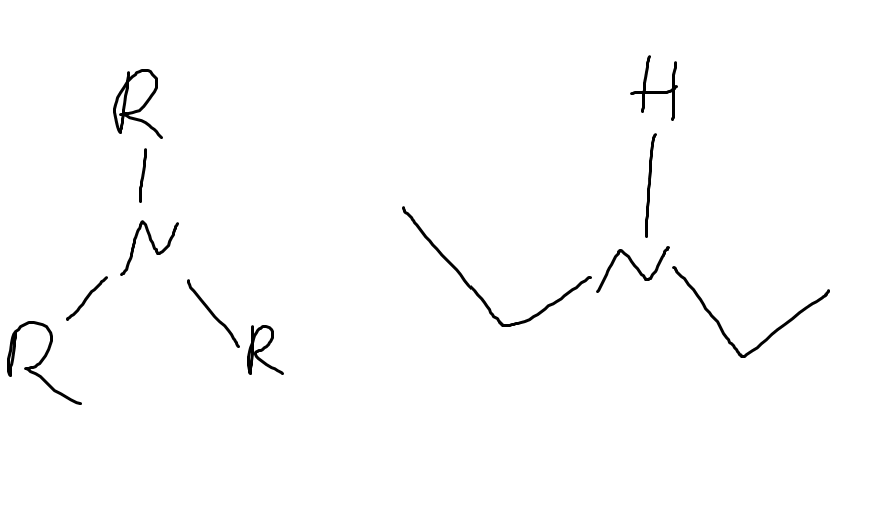
What functional group is this
Amine
nitrogen containing
The spreading of electrons called ______ is a stabilizing factor. it is often referred to as _________
delocalization
resonance stabilization
Should you ever break a single bond when making a resonance structure
FUCK NOOOO
define allylic lone pairs.
when a compound contains a carbon-carbon double bond.
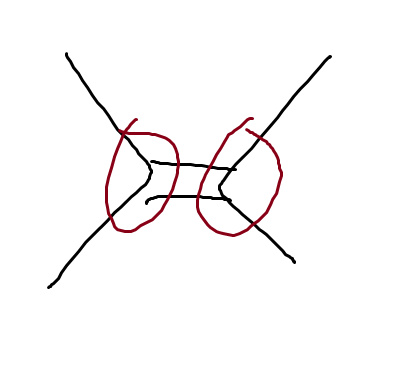
what is this
vinylic positions
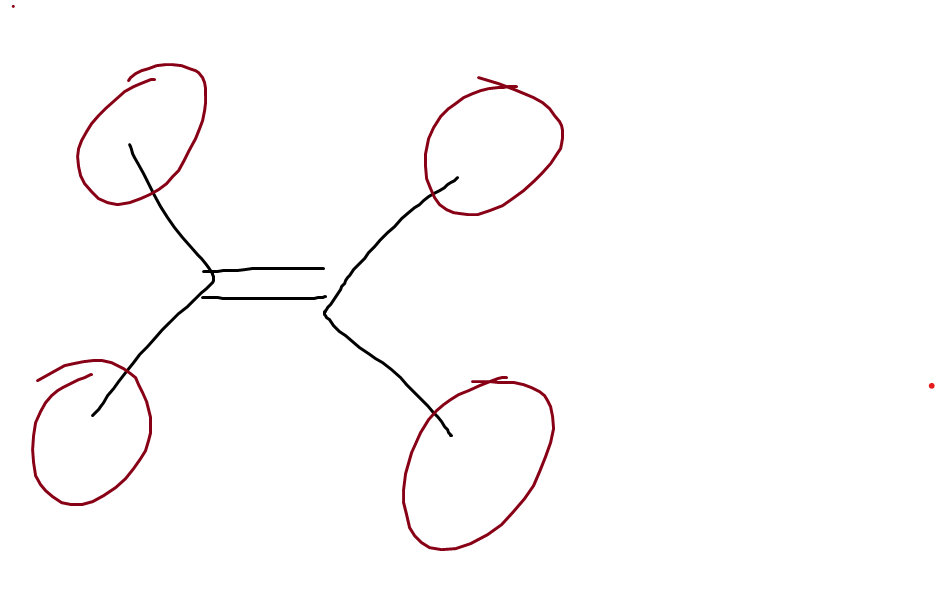
What is this
allylic positions
What are the five general bonding patterns in which resonance occurs?
1) an allylic lone pair
2) an allylic carbocation
3) a lone pair adjacent to C+
4) A pi bond between two atoms of differing electronegativity
5) conjugated pi bonds in a ring
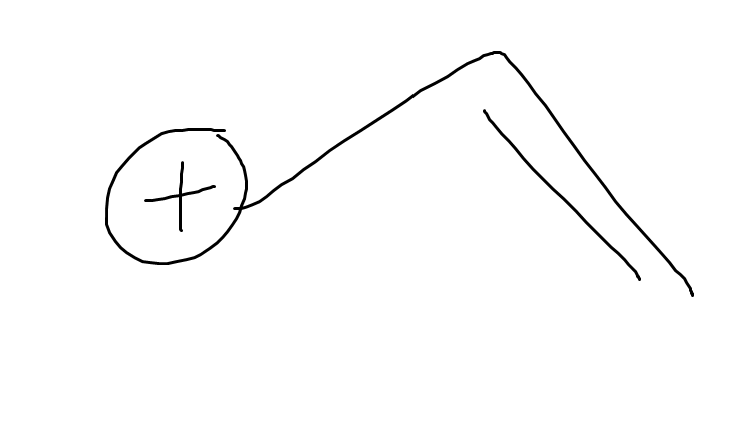
What is this
allylic carbocation
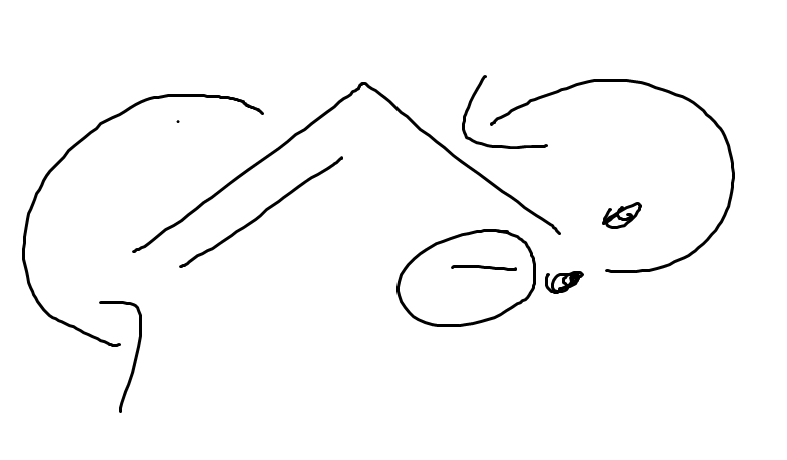

what is this
allylic lone pairs
What are the rules for importance in resonence structures
-the most significant contributors have the greatest number of filled octets
-the fewer the formal, the more significant
-a structure with a few negative charge on a more electronegative atom will be more significant (and vice versa)
-When both have stable “good” Lewis structures, they contribute equally
A structure with a negative charge on the more electronegative atom will be _____ significant
more
(negative charge on the carbon will be bad news)
A structure with a positive charge on the less electronegative atom will be ____ signfiicant
more
positive charge on oxygen is bad
What happens when a lone pair participates in resonence?
it will occupy a p orbital rather from a hybridized orbital
When an atom possesses a pi bond and a lone pair, what will happen pertaining to resonance?
they will generally not participate in resonance
_____ donate a proton (acids or bases)
acids
_____ accept a proton (acids or bases)
bases
A _______ results when a base accepts a protein
conjugate acid
A ____ results when an acid gives up a protein
conjugate base
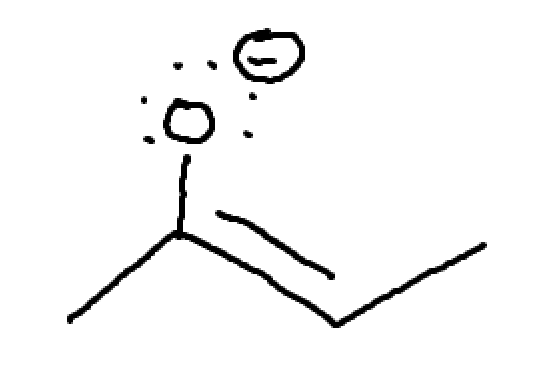
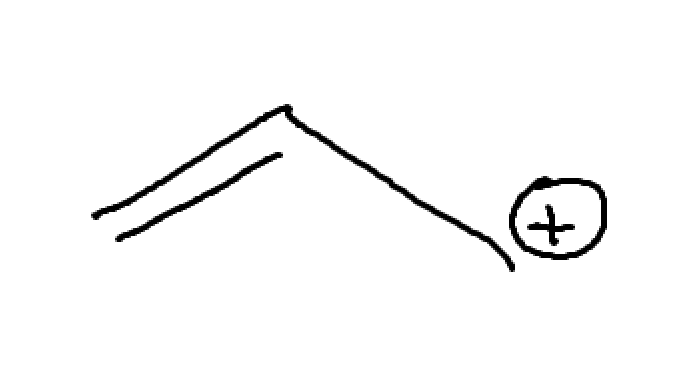
what is this? how will we move things?
allylic lone pair
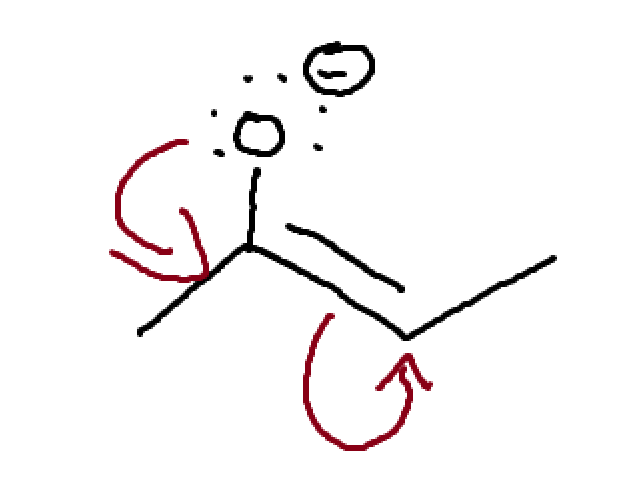
What is this? How can we move things?
Allylic carbocation
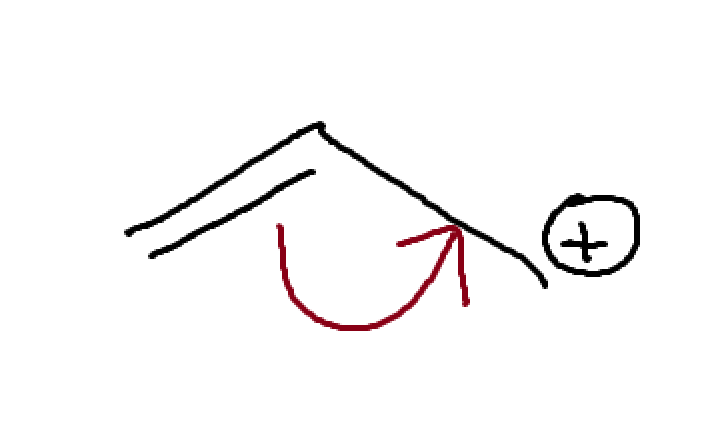

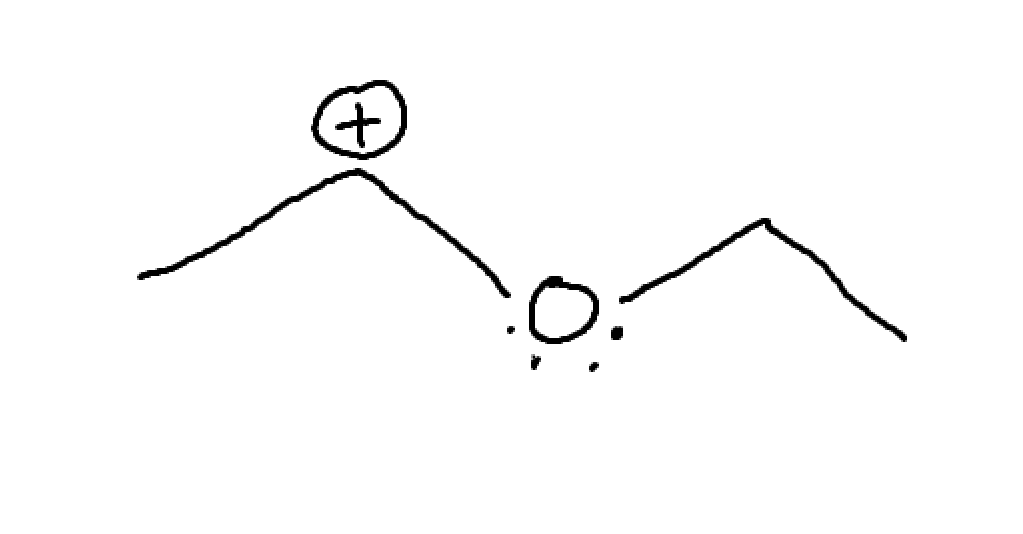
What is this? How can we expect it to act?
Lone pair adjacent to C+
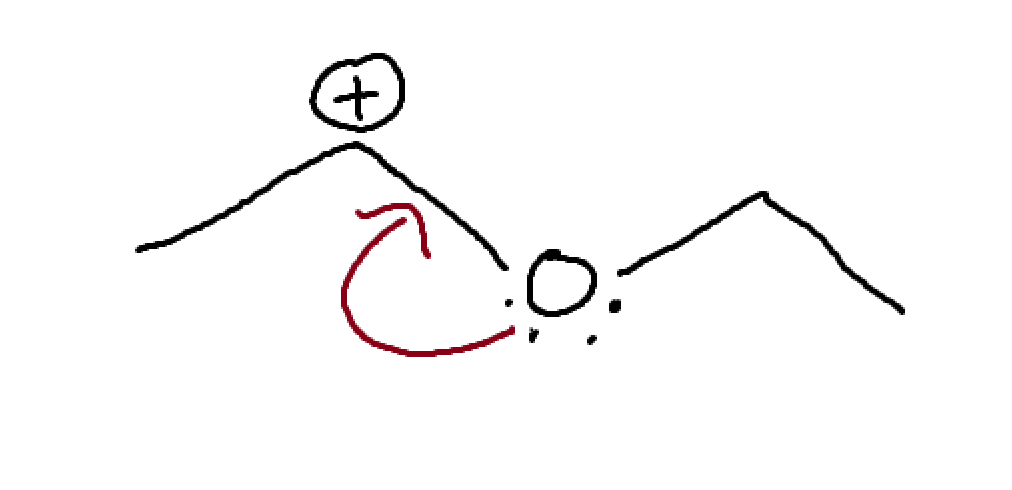
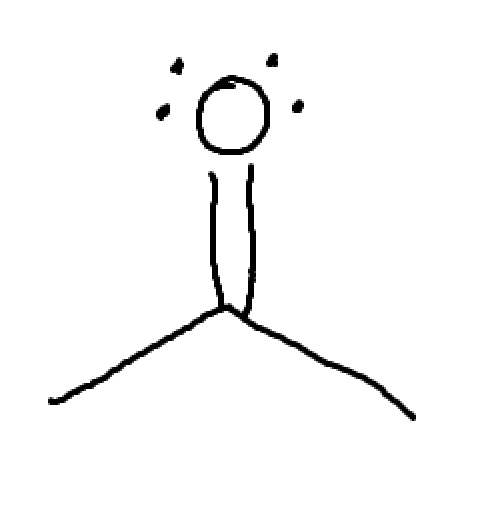
what is this? How might we move things?
pi bond between two atoms of differing electronegativity.
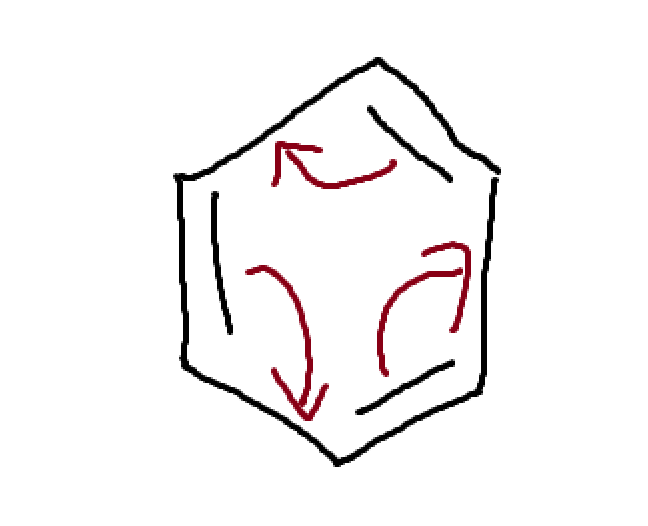
what type of structure is this and how do you solve it?
Conjugated pi bonds enclosed in a ring
What is the pka of HBr and HCl?
<0
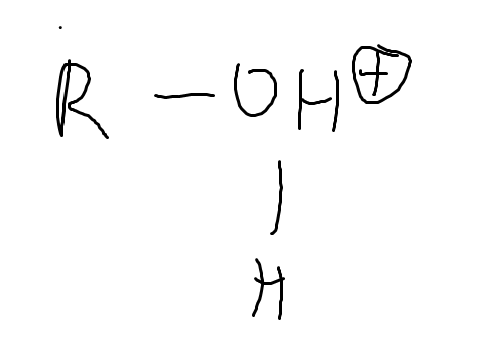
What is the pka of H3O+ or
~0
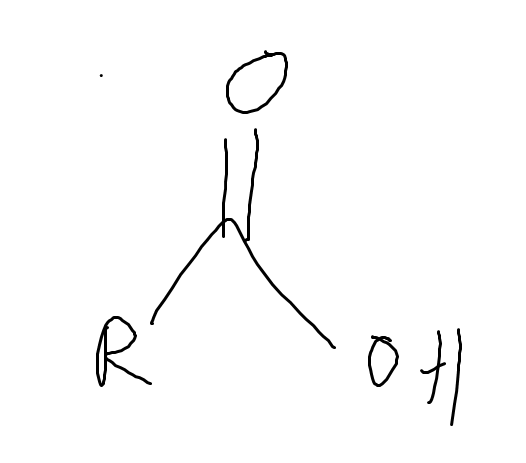
What is the pka of (carboxylic)
~3-5

What is the pka of
(protonated amine)
~10
what is the general pka of water
~14
what is the general pka of alcohol?
~15
what is the general pka of an alkyne?
~25
what is the general pka of an amine?
~40
What does equilibrium favor?
the weaker acid and the weaker base
What uses numerical data to compare how strong acids are?
Quantitative strength analysis
if Ka <1 the reaction is _____ favored
reactant favored and strong acid
if ka > 1 the reaction is _____ favored and a ____ acid
product favored and weak acid
the ____ the acid the more stable the conjugate base
STRONGER
conjugate base is whatever is remaining after we lose a hydrogen
What are the factors that stabilize a negative charge?
ARIO (A really interesting occasion) (i had a rather interesting day today)
-the type of atom that carries the charge
-resonance
-inductive effects
-the type of orbital where the charge resides
When moving down a column, the ____ is the most important factor. What does this aspect tell us?
size tells us that the larger the atom, the more stable a negative charge will be. Size increases as you move down the periodic table
When moving across rows (periods), ______ is the most important factor. What is true here?
electronegativity
the more electronegative atom will better stabilize the negative charge.
_____ stabilizes a negative charge by spreading it out across multiple atoms
resonance