plant cell walls
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
purpose of the cell wall
maintaining/ determining cell shape
support and mechanical strength
prevents the cell membrane from bursting in a hypotonic medium (resists water pressure)
controls the rate and direction of cell growth and regulates cell volume
physical barrier to pathogens & water in suberized (root) cells
carbohydrate storage
signaling
economic products
biofuels
carbohydrate storage in the cell wall
components of the cell wall can be reused in other metabolic process (especially seeds
signaling in the cell wall
fragments of the wall, oligasaccharins, act as hormones
stimulate ethylene synthesis
induce phytoalexin (defense chemicals produced in response to a fungal/ bacterial infection)
induce chitinase
increase cytoplasmic calcium levels
cause an “oxidative burst”
biofuels from the cell wall
via fermentation
cellulosic ethanol
produced from wood, grasses, or the inedible parts of plants
produced from lignocellulose
structural material that comprises much of the mass of plants
comprised of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin
what is the main ingredient in cell walls?
polysaccharides
carbohydrates
lipids (fats)
proteins
components of the cell wall
cellulose
cross-linking glycans
pectic polysaccharides
protein
lignin
suberin, wax, cutin
water
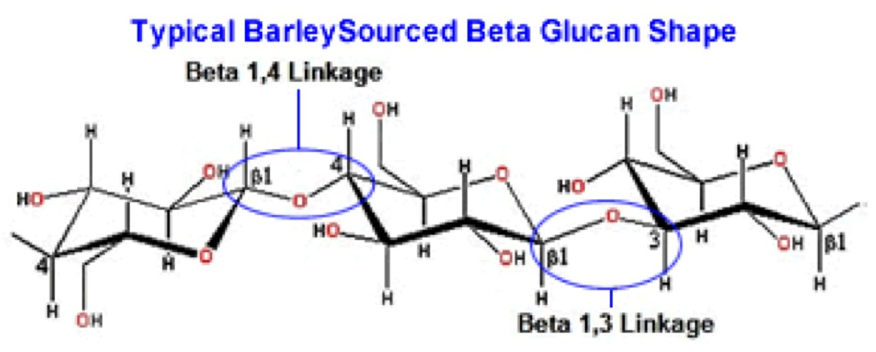
cellulose in the cell wall
1→4 beta linkage (alternating)
cross linking glycans in the cell wall
it’s short length & branches allows it to link microfibrils
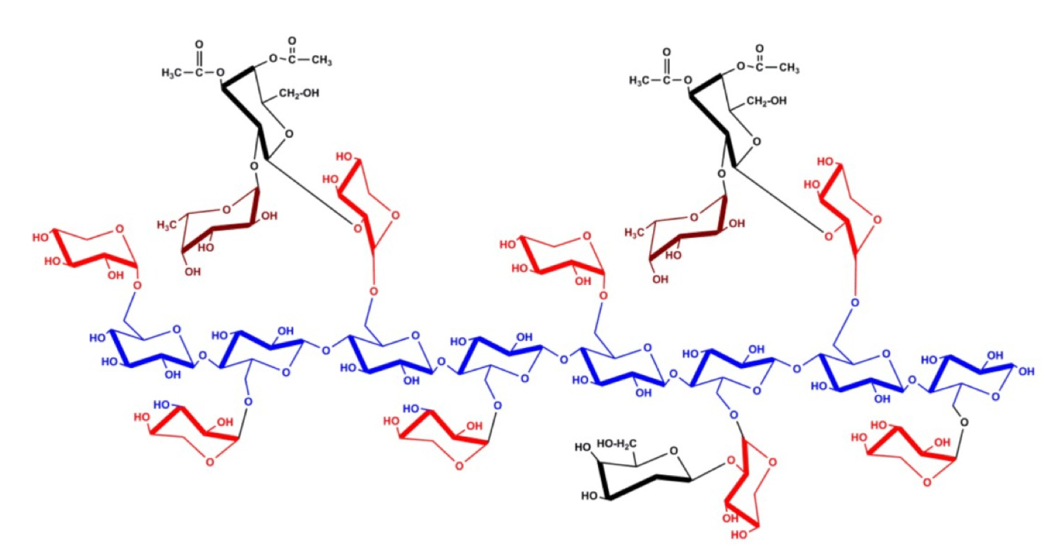
pectic polysaccharides in the cell wall
thickening agent in jams & jellies
pectin 2 is a polysaccharide
monomer is glucose (alpha 1→ 4 linkage)
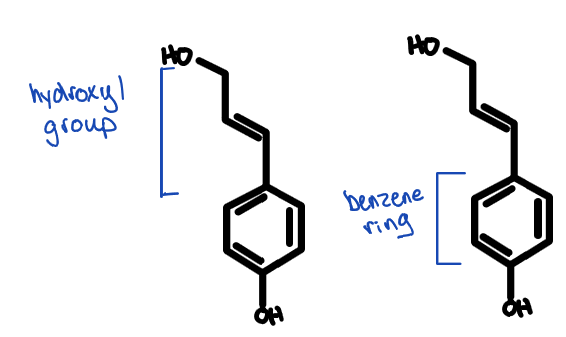
lignin in the cell wall
only found in the secondary cell well
comprised of a hydroxyl group & benzene ring
primary meristem
refers to the three fundamental tissue types (protoderm, ground meristem, procambium) that the apical meristem produces, which then from the plant’s primary tissues (epidermis, ground tissue, vascular tissue) and contribute to growth in length
apical meristem
the specific location (tips of roots & shoots) that are the source of primary growth
phragmoplast
the dynamic cellular machinery (microtubules, actin, vesicles) that builds the cell plate
the construction crew & the tools
cell plate is the actual wall being built between the two new daughter cells
where is cellulose made?
cell surface
catalyzed by cellulose synthase
made in ER by ribosomes
ER → vesicles → golgi → cell membrane
two catalytic sites that transfer two glucoses at a time
cellulose synthase
large protein complex embedded in the plasma membrane of plants
synthesizes cellulose
does so by linking glucose units from UDP-glucose into long chains
forms microfibrils for structural support
UDP- glucose
a vital, activated sugar molecule used by all living cells as a building block and donor for synthesizing complex carbohydrates like glycogen (energy storage), sucrose (plant sugar), and lipopolysaccharides (bacterial cell walls)
acid growth hypothesis
explains how the plant hormone auxin promotes cell expansion by acidifying the cell wall (apoplast), causing it to loosen and stretchy under turgor pressure
extansins
patch holes in the cell wall
expansins
appear to be the primary wall-loosening enzymes