Building Utilities 3: Lighting and Illumination
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Illumination
defined as the act of illuminating, or supplying light
Lighting
The equipment or fixture used to provide illumination
Intensity
Referred to as luminous intensity described as quantity of visible light that is emitted in unit time per unit solid angle
Luminous flux
Measure of the total perceived power of light
Color of light is measured in [BLANK]
Kelvin (K)
Lower K
warm colored lighting
Higher K
cool colored lighting
Color Rendering Index (CRI)
measurement showing effect of a light source on the color of objects based on a 0 to 100 scale
Correlated Color Temperature (CCT)
A measure of the coolness (red, orange) to warmness (blue-white) appearance of a light; measured in kelvins (K).
Illuminance
Total luminous flux on a surface per unit area; SI Unit is Lux
Glare
A phenomenon caused by extremely bright light sources or by strong brightness contrasts in the visual field
Light
Defined as an artificial source of illumination
Inverse Square Law
the intensity of radiation is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source of radiation
Luminescence
light emitted by means other than burning, such as chemical or biochemical action or radiation
Fluorescence
A means of producing light from gaseous discharge
Light travels at what speed?
3.0 x 10^8 m/s (186,000 miles per second)
Absorption
When a composite light such as white, falls on a surface other than black, selective absorption occurs.
Absorptance
The ratio of light absorbed by a material to the light falling upon it
Reflection
the bouncing back of a ray of light, sound, or heat when the ray hits a surface that it does not go through
Laws of reflection
1) The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection.
2) The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal all lie in the same plane.
specular reflection
a reflection produced by a smooth surface in which the light at an angle equal to the angle of incidence
diffuse reflection
Reflection that occurs when parallel rays of light hit a rough surface and all reflect at different angles
spread reflection
polished surface that is hammered, deeply etched, or engraved, and spreads out any rays it reflects.
Compound reflection
Reflector materials that exhibits all three types of reflection components to varying degree
Transmission
the passage of light through an object. Refracted as it enters the material, but emerges at the same angle that it entered.
Diffusion
When reflected light rays are distributed in all directions with maximum intensity normal to the surface.
Refraction
There is a change in speed of light as it travels from one medium to another and there is a bending of the ray of light.
Polarization
the phenomenon in which waves of light or other radiation are restricted in direction of vibration
Interference
The phenomenon of modification in the intensity of light due to redistribution of light energy in the region of superposition of two or more light waves.
diffraction of light waves
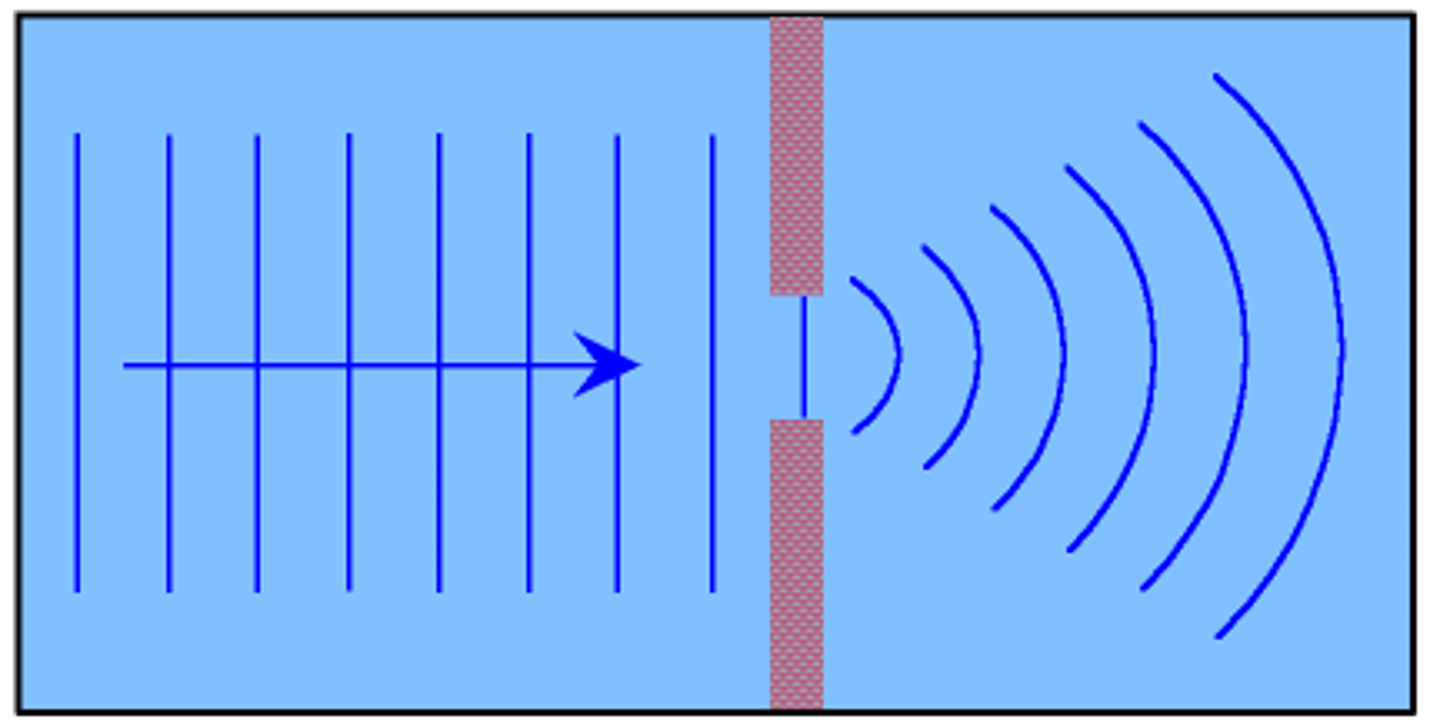
Occurs when an object causes a wave to change direction and bend around it
Produces bluish white color; contains mercury vapor use for industrial and outdoor purposes.
Mercury lamp
Contains mercury vapor and other halides to improve efficacy and their color-rendering characteristics. These are lamps used for indoor purposes
Metal Halide (MH) lamp
Lamp that is constructed with two envelopes: an inner envelope (arc tube) made with material that has electric resistance to sodium and an outer envelope to protect the arc tube.
High Pressure Sodium (HPS) lamp
The initial lumens of luminaires will drop by certain percentage after a period of use.
Light Loss Factor
When luminaire collects dirt on its surface the light output is reduced to a certain degree.
Lamp Dirt Depreciation (LDD)
The ratio between the lumen generated from the luminaire and the lumen reaching the work of plane
Coefficient of Utilization (CU)
1 lumen per sq. ft.
Footcandle
Lumen
unit of luminous flux
Lux
1 lumen per sq. m.
Luminosity
the true brightness of an object; lumens per watt
Luminance
The luminous intensity of any surface in a given direction per unit of projected area of the surface, as viewed from the direction.